Protein-Stuffed Bell Peppers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hot, tasty, meaty, and vegan! You can have it all. And with this recipe, you’ll want to err on the side of overcatering, because everyone will want some. As for healthiness, we’ve got lycopene, lutein and a stack of other carotenoids, a plethora of other polyphenols, and a veritable garden party of miscellaneous phytochemicals otherwise categorized. It’s full of protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, relatively low-fat but the fats present are healthy. It’s antidiabetic, anti-CVD, anticancer, antineurodegeneration, and basically does everything short of making you sing well too.
You will need
- 4 large bell peppers, tops sliced open and innards removed (keep the tops; we will put them back on later)
- 1 cup quinoa, rinsed
- 1 can black beans, drained and rinsed
- 1 small zucchini (diced)
- 1 small eggplant (diced)
- 1 small red onion (finely chopped)
- ½ bulb garlic, minced*
- 1 tbsp tomato paste
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tsp dried basil
- 2 tsp dried thyme
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 2 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp smoked paprika
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
*we always try to give general guidelines with regard to garlic, but the reality is it depends on the size and strength of your local garlic, which we cannot account for, as well as your personal taste. Same situation with hot peppers of various kinds. This writer (it’s me, hi) would generally use about 2x the garlic and pepper advised in our recipes. All we can say is: follow your heart!
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the quinoa with the chia seeds, and cook as per normal cooking of quinoa (i.e. bring to a boil and then simmer for about 15 minutes until cooked and fluffy). Drain and rinse (carefully, without losing the chia seeds; use a sieve).
2) Heat your grill to a high heat. Combine the zucchini, eggplant, onion, garlic, and olive oil in a big bowl and mix well, ensuring an even distribution of the oil. Now also add the herbs and spices (including the MSG or salt) and mix well again. Put them all to grill for about 5 minutes, turning as necessary.
3) Heat your oven to a high heat. Take the grilled vegetables and combine them in a bowl with the quinoa-and-chia, and the black beans, as well as the tomato paste. Mix everything well. Spoon the mixture generously into the bell peppers, replacing the tops (it can be loosely), and bake for about 5–10 minutes, keeping an eye on them; you want them to be lightly charred, but not a burnt offering.
4) Serve! This dish works well as a light lunch or as part of a larger spread.
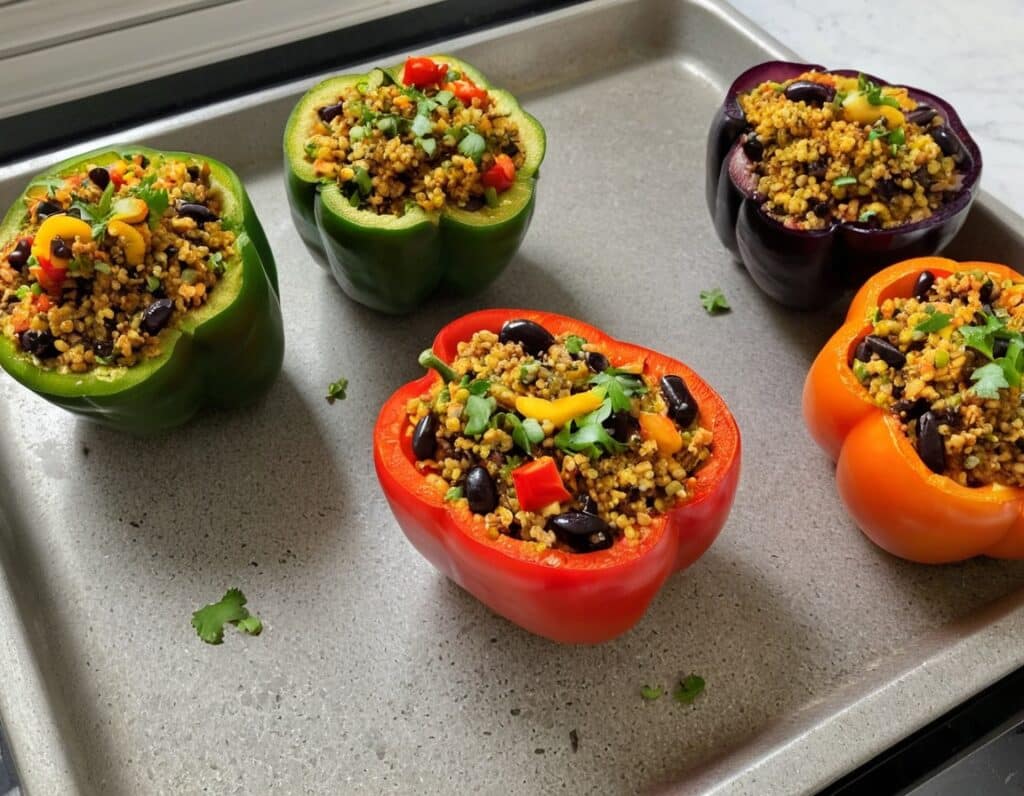

(before going in the oven with lids replaced to keep moisture in)
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- A Spectrum Of Specialties: Which Color Bell Peppers To Pick?
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value: If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Chickpeas vs Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Their First Baby Came With Medical Debt. These Illinois Parents Won’t Have Another.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
JACKSONVILLE, Ill. — Heather Crivilare was a month from her due date when she was rushed to an operating room for an emergency cesarean section.
The first-time mother, a high school teacher in rural Illinois, had developed high blood pressure, a sometimes life-threatening condition in pregnancy that prompted doctors to hospitalize her. Then Crivilare’s blood pressure spiked, and the baby’s heart rate dropped. “It was terrifying,” Crivilare said.
She gave birth to a healthy daughter. What followed, though, was another ordeal: thousands of dollars in medical debt that sent Crivilare and her husband scrambling for nearly a year to keep collectors at bay.
The Crivilares would eventually get on nine payment plans as they juggled close to $5,000 in bills.
“It really felt like a full-time job some days,” Crivilare recalled. “Getting the baby down to sleep and then getting on the phone. I’d set up one payment plan, and then a new bill would come that afternoon. And I’d have to set up another one.”
Crivilare’s pregnancy may have been more dramatic than most. But for millions of new parents, medical debt is now as much a hallmark of having children as long nights and dirty diapers.
About 12% of the 100 million U.S. adults with health care debt attribute at least some of it to pregnancy or childbirth, according to a KFF poll.
These people are more likely to report they’ve had to take on extra work, change their living situation, or make other sacrifices.
Overall, women between 18 and 35 who have had a baby in the past year and a half are twice as likely to have medical debt as women of the same age who haven’t given birth recently, other KFF research conducted for this project found.
“You feel bad for the patient because you know that they want the best for their pregnancy,” said Eilean Attwood, a Rhode Island OB-GYN who said she routinely sees pregnant women anxious about going into debt.
“So often, they may be coming to the office or the hospital with preexisting debt from school, from other financial pressures of starting adult life,” Attwood said. “They are having to make real choices, and what those real choices may entail can include the choice to not get certain services or medications or what may be needed for the care of themselves or their fetus.”
Best-Laid Plans
Crivilare and her husband, Andrew, also a teacher, anticipated some of the costs.
The young couple settled in Jacksonville, in part because the farming community less than two hours north of St. Louis was the kind of place two public school teachers could afford a house. They saved aggressively. They bought life insurance.
And before Crivilare got pregnant in 2021, they enrolled in the most robust health insurance plan they could, paying higher premiums to minimize their deductible and out-of-pocket costs.
Then, two months before their baby was due, Crivilare learned she had developed preeclampsia. Her pregnancy would no longer be routine. Crivilare was put on blood pressure medication, and doctors at the local hospital recommended bed rest at a larger medical center in Springfield, about 35 miles away.
“I remember thinking when they insisted that I ride an ambulance from Jacksonville to Springfield … ‘I’m never going to financially recover from this,’” she said. “‘But I want my baby to be OK.’”
For weeks, Crivilare remained in the hospital alone as covid protocols limited visitors. Meanwhile, doctors steadily upped her medications while monitoring the fetus. It was, she said, “the scariest month of my life.”
Fear turned to relief after her daughter, Rita, was born. The baby was small and had to spend nearly two weeks in the neonatal intensive care unit. But there were no complications. “We were incredibly lucky,” Crivilare said.
When she and Rita finally came home, a stack of medical bills awaited. One was already past due.
Crivilare rushed to set up payment plans with the hospitals in Jacksonville and Springfield, as well as the anesthesiologist, the surgeon, and the labs. Some providers demanded hundreds of dollars a month. Some settled for monthly payments of $20 or $25. Some pushed Crivilare to apply for new credit cards to pay the bills.
“It was a blur of just being on the phone constantly with all the different people collecting money,” she recalled. “That was a nightmare.”
Big Bills, Big Consequences
The Crivilares’ bills weren’t unusual. Parents with private health coverage now face on average more than $3,000 in medical bills related to a pregnancy and childbirth that aren’t covered by insurance, researchers at the University of Michigan found.
Out-of-pocket costs are even higher for families with a newborn who needs to stay in a neonatal ICU, averaging $5,000. And for 1 in 11 of these families, medical bills related to pregnancy and childbirth exceed $10,000, the researchers found.
“This forces very difficult trade-offs for families,” said Michelle Moniz, a University of Michigan OB-GYN who worked on the study. “Even though they have insurance, they still have these very high bills.”
Nationwide polls suggest millions of these families end up in debt, with sometimes devastating consequences.
About three-quarters of U.S. adults with debt related to pregnancy or childbirth have cut spending on food, clothing, or other essentials, KFF polling found.
About half have put off buying a home or delayed their own or their children’s education.
These burdens have spurred calls to limit what families must pay out-of-pocket for medical care related to pregnancy and childbirth.
In Massachusetts, state Sen. Cindy Friedman has proposed legislation to exempt all these bills from copays, deductibles, and other cost sharing. This would parallel federal rules that require health plans to cover recommended preventive services like annual physicals without cost sharing for patients. “We want … healthy children, and that starts with healthy mothers,” Friedman said. Massachusetts health insurers have warned the proposal will raise costs, but an independent state analysis estimated the bill would add only $1.24 to monthly insurance premiums.
Tough Lessons
For her part, Crivilare said she wishes new parents could catch their breath before paying down medical debt.
“No one is in the right frame of mind to deal with that when they have a new baby,” she said, noting that college graduates get such a break. “When I graduated with my college degree, it was like: ‘Hey, new adult, it’s going to take you six months to kind of figure out your life, so we’ll give you this six-month grace period before your student loans kick in and you can get a job.’”
Rita is now 2. The family scraped by on their payment plans, retiring the medical debt within a year, with help from Crivilare’s side job selling resources for teachers online.
But they are now back in debt, after Rita’s recurrent ear infections required surgery last year, leaving the family with thousands of dollars in new medical bills.
Crivilare said the stress has made her think twice about seeing a doctor, even for Rita. And, she added, she and her husband have decided their family is complete.
“It’s not for us to have another child,” she said. “I just hope that we can put some of these big bills behind us and give [Rita] the life that we want to give her.”
About This Project
“Diagnosis: Debt” is a reporting partnership between KFF Health News and NPR exploring the scale, impact, and causes of medical debt in America.
The series draws on original polling by KFF, court records, federal data on hospital finances, contracts obtained through public records requests, data on international health systems, and a yearlong investigation into the financial assistance and collection policies of more than 500 hospitals across the country.
Additional research was conducted by the Urban Institute, which analyzed credit bureau and other demographic data on poverty, race, and health status for KFF Health News to explore where medical debt is concentrated in the U.S. and what factors are associated with high debt levels.
The JPMorgan Chase Institute analyzed records from a sampling of Chase credit card holders to look at how customers’ balances may be affected by major medical expenses. And the CED Project, a Denver nonprofit, worked with KFF Health News on a survey of its clients to explore links between medical debt and housing instability.
KFF Health News journalists worked with KFF public opinion researchers to design and analyze the “KFF Health Care Debt Survey.” The survey was conducted Feb. 25 through March 20, 2022, online and via telephone, in English and Spanish, among a nationally representative sample of 2,375 U.S. adults, including 1,292 adults with current health care debt and 382 adults who had health care debt in the past five years. The margin of sampling error is plus or minus 3 percentage points for the full sample and 3 percentage points for those with current debt. For results based on subgroups, the margin of sampling error may be higher.
Reporters from KFF Health News and NPR also conducted hundreds of interviews with patients across the country; spoke with physicians, health industry leaders, consumer advocates, debt lawyers, and researchers; and reviewed scores of studies and surveys about medical debt.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
Infections, Heart Failure, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some health news to round off the week:
The Infection That Leads To Heart Failure
It’s long been held that, for example, flossing reduces heart disease risk, with the hypothesis being that if plaque bacteria enter the blood stream, well, that’s an even worse place for plaque bacteria to be. Now, with much more data, attention has turned to
- actual infections, and
- actual heart failure
Way to up the ante! And, it holds true regardless of what kind of infection. So, you might think that a UTI, for example, is surely “downstream” and should not affect the heart, but it does. Because of this, researchers currently believe that it is not the infection itself, so much as the body’s inflammation response to infection, that leads to the heart failure. Which is reasonable, because, for example, atherosclerosis is made mostly not of cholesterol itself, but rather mostly of dead immune cells that got stuck in the cholesterol.
Moreover, it’s not so much about the acute inflammatory response (which is almost always a good thing, circumstantially), but rather that after cases where an infection managed to take hold, the immune system can then often stay on high alert for many years alter. Long COVID is an obvious recent example of this, but it’s hardly a new phenomenon; see for example post-polio syndrome, and consider how many more such post-infection maladies are likely to exist that never got a name because they flew under the radar or got diagnosed as fibromyalgia or something (fibromyalgia is a common diagnosis doctors give when they acknowledge something’s wrong, and it causes pain and exhaustion, but they don’t know what, and it appears to be stable—so while it can be helpful to put a name to the collection of symptoms, it’s a non-diagnosis diagnosis on the doctors’ part. It’s saying “I diagnose you with hurty tiredness”).
The take-away from all this? Avoid infections, for your heart’s sake, and if you do get an infection, take it seriously even if it’s minor. The safe amount of infection is “no infection”.
Read in full: Study uncovers new link between infections and heart failure
Cold Water Immersion: Hot Or Not?
The evidence is clear for some benefits; for others, not so much:
- It’s great (if you’re already in fair health, and definitely not if you have a heart condition) to improve circulation and stress response
- There may be some benefits to immune function, but however reasonable the hypothesis, actual evidence is thin on the ground
- The oft-hyped mood benefits are a) marginal b) short-lived, with benefits fading after 3 months of regular cold baths/showers/etc
Read in full: The big chill: Is cold-water immersion good for our health?
Related: Ice Baths: To Dip Or Not To Dip?
The Unspoken Trials Of Going To The Gym (While Being A Woman)
Public health decision-makers often think that getting people to go to the gym more is a matter of public information, or perhaps branding. Some who have their thinking heads on might even realize that there may be economic factors for many. But for women, there’s an additional factor—or rather, an additionally prominent factor. The study we’ll link started with this observation (please read it in the voice of your favorite nature documentary narrator):
❝Despite an increase in gym memberships, women are less active than men and little is known about the barriers women face when navigating gym spaces.❞
What then, of these shy, elusive creatures that make up a mere 51% of the world’s population?
A medium-sized (n=279) study of women, of whom 84% being current gym-goers, reported often feeling “judged for their appearance or performance, as well as having to fight for space in the gym and to be taken seriously, while navigating harassment and unsolicited comments from men”
Even gym attire becomes an issue:
❝Aligning with previous literature, women often chose attire based on comfort and functionality. However, their choices were also influenced by comparisons with others or fear of judgement for wearing non-branded attire or looking too put together. Many women also chose gym attire to hide perceived problem areas or avoid appearance concerns, including visible sweat stains.❞
…which main seem silly; you’re at the gym, of course you’re going to sweat, but if you’re the only one with visible sweat stains, then there can be social consequences (bad ones).
Similarly, there’s a “damned if you do; damned if you don’t” when it comes to working out while fat—on the one hand, society conflates fatness with laziness; on the other, it can be extra intimidating to be the only fat person in a gym full of people who look like they’re going to audition for a superhero movie.
❝In the gym, just like in other areas of life, women often feel stuck between being seen as ‘too much’ and ‘not enough’, dealing with judgement about how they look, how they perform, and even how much space they take up. Even though the pressure to be super thin is decreasing, the growing focus on being muscular and athletic is creating new challenges. It is pushing unrealistic standards that can negatively affect women’s body image and overall well-being.❞
Writer’s note: I live a few minutes walk from my nearest gym, and I work out at home instead. This way, if I want to do yoga in my pajamas, I can. If I want to use my treadmill naked and watch my T+A bounce in the mirror, I can. If I want to lift weights in the dress I happened to be wearing, I can. Alas that I can’t swim at home!
Read in full: Women face multiple barriers while exercising in gyms
Related: Body Image Dissatisfaction/Appreciation Across The Ages
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Ideal Blood Pressure Numbers Explained
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Maybe I missed it but the study on blood pressure did it say what the 2 numbers should read ideally?❞
We linked it at the top of the article rather than including it inline, as we were short on space (and there was a chart rather than a “these two numbers” quick answer), but we have a little more space today, so:
Category Systolic (mm Hg) Diastolic (mm Hg) Normal < 120 AND < 80 Elevated 120 – 129 AND < 80 Stage 1 – High Blood Pressure 130 – 139 OR 80 – 89 Stage 2 – High Blood Pressure 140 or higher OR 90 or higher Hypertensive Crisis Above 180 AND/OR Above 120 To oversimplify for a “these two numbers” answer, under 120/80 is generally considered good, unless it is under 90/60, in which case that becomes hypotension.
Hypotension, the blood pressure being too low, means your organs may not get enough oxygen and if they don’t, they will start shutting down.
To give you an idea how serious this, this is the closed-circuit equivalent of the hypovolemic shock that occurs when someone is bleeding out onto the floor. Technically, bleeding to death also results in low blood pressure, of course, hence the similarity.
So: just a little under 120/80 is great.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Food for Life – by Dr. Tim Spector
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is, as the author puts it, “an eater’s guide to food and nutrition”. Rather than telling us what to eat or not eat, he provides an overview of what the latest science has to say about various foods, and leaves us to make our own informed decisions.
He also stands firmly by the “personalized nutrition” idea that he introduced in his previous book which we reviewed the other day, and gives advice on what tests we might like to perform.
The writing style is accessible, without shying away from reference to hard science. Dr. Spector provides lots of information about key chemicals, genes, gut bacteria, and more—as well as simply providing a very enjoyable read along the way.
Bottom line: if you’d like a much better idea of what food is (and isn’t) doing what, this book is an invaluable resource.
Click here to check out Food for Life, and make the best decisions for you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Are “Adaptogens” Anyway? (And Other Questions Answered)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I tried to use your calculator for heart health, and was unable to enter in my height or weight. Is there another way to calculate? Why will that field not populate?❞
(this is in reference to yesterday’s main feature “How Are You, Really? And How Old Is Your Heart?“)
How strange! We tested it in several desktop browsers and several mobile browsers, and were unable to find any version that didn’t work. That includes switching between metric and imperial units, per preference; both appear to work fine. Do be aware that it’ll only take numerical imput, though.
Did anyone else have this problem? Let us know! (You can reply to this email, or use the handy feedback widget at the bototm)
❝I may have missed it, but how much black pepper provides benefits?❞
So, for any new subscribers joining us today, this is about two recent main features:
As for a daily dosage of black pepper, it varies depending on the benefit you’re looking for, but:
- 5–20mg of piperine is the dosage range used in most scientific studies we looked at
- 10mg is a very common dosage found in many popular supplements
- That’s the mass of piperine though, so if taking it as actual black pepper rather than as an extract, ½ teaspoon is considered sufficient to enjoy benefits.
❝I loved the health benefits of pepper. I do not like pepper. Where can I get it as a supplement?❞
You can simply buy whole black peppercorns and take a few with water as though they were tablets. Your stomach acid will do the rest. Black pepper is also good for digestion, so taking it with a meal is best.
You can buy piperine (black pepper extract) by itself as a supplement in powder form, but if you don’t like black pepper, you will probably not like this powder either. We couldn’t find it readily in capsule form.
You can buy piperine (black pepper extract) as an adjunct to other supplements, with perhaps the most common/popular being turmeric capsules that also contain 10mg (or more) piperine per capsule. Shop around if you like, but here’s one that has 15mg piperine* per capsule, for example.
*They call it “Bioperine®” but that is literally just piperine. Same goes if you see “Absorbagen™”, it’s still just piperine.
❝What do you mean when you say that something is adaptogenic?❞
Simple version: it means it helps the body adapt to stress, by adjusting the body’s natural responses. Thus, adaptogenic supplements can be contrasted with tranquilizing drugs that mask stress by brute force, for example.
Technical version: adaptogenic activity refers to improving physiological stress resilience, such as by moderating and modulating hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis signaling, and/or by regulating levels of endogenic compounds involved in the cellular stress response.
Read more (technical version):
Read more (simple version):
European Medicines Agency’s Reflection Paper On The Adaptogenic Concept
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
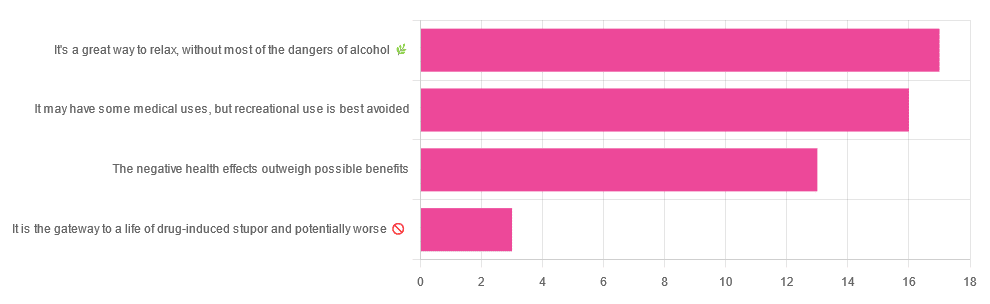
We asked you for your (health-related) opinion on cannabis use—specifically, the kind with psychoactive THC, not just CBD. We got the above-pictured, below-described, spread of responses:
- A little over a third of you voted for “It’s a great way to relax, without most of the dangers of alcohol”.
- A little under a third of you voted for “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”.
- About a quarter of you voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits”
- Three of you voted for “It is the gateway to a life of drug-induced stupor and potentially worse”
So, what does the science say?
A quick legal note first: we’re a health science publication, and are writing from that perspective. We do not know your location, much less your local laws and regulations, and so cannot comment on such. Please check your own local laws and regulations in that regard.
Cannabis use can cause serious health problems: True or False?
True. Whether the risks outweigh the benefits is a personal and subjective matter (for example, a person using it to mitigate the pain of late stage cancer is probably unconcerned with many other potential risks), but what’s objectively true is that it can cause serious health problems.
One subscriber who voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits” wrote:
❝At a bare minimum, you are ingesting SMOKE into your lungs!! Everyone SEEMS TO BE against smoking cigarettes, but cannabis smoking is OK?? Lung cancer comes in many forms.❞
Of course, that is assuming smoking cannabis, and not consuming it as an edible. But, what does the science say on smoking it, and lung cancer?
There’s a lot less research about this when it comes to cannabis, compared to tobacco. But, there is some:
❝Results from our pooled analyses provide little evidence for an increased risk of lung cancer among habitual or long-term cannabis smokers, although the possibility of potential adverse effect for heavy consumption cannot be excluded.❞
Read: Cannabis smoking and lung cancer risk: Pooled analysis in the International Lung Cancer Consortium
Another study agreed there appears to be no association with lung cancer, but that there are other lung diseases to consider, such as bronchitis and COPD:
❝Smoking cannabis is associated with symptoms of chronic bronchitis, and there may be a modest association with the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Current evidence does not suggest an association with lung cancer.❞
Read: Cannabis Use, Lung Cancer, and Related Issues
Cannabis edibles are much safer than smoking cannabis: True or False?
Broadly True, with an important caveat.
One subscriber who selected “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”, wrote:
❝I’ve been taking cannabis gummies for fibromyalgia. I don’t know if they’re helping but they’re not doing any harm. You cannot overdose you don’t become addicted.❞
Firstly, of course consuming edibles (rather than inhaling cannabis) eliminates the smoke-related risk factors we discussed above. However, other risks remain, including the much greater ease of accidentally overdosing.
❝Visits attributable to inhaled cannabis are more frequent than those attributable to edible cannabis, although the latter is associated with more acute psychiatric visits and more ED visits than expected.❞
Note: that “more frequent” for inhaled cannabis, is because more people inhale it than eat it. If we adjust the numbers to control for how much less often people eat it, suddenly we see that the numbers of hospital admissions are disproportionately high for edibles, compared to inhaled cannabis.
Or, as the study author put it:
❝There are more adverse drug events associated on a milligram per milligram basis of THC when it comes in form of edibles versus an inhaled cannabis. If 1,000 people smoked pot and 1,000 people at the same dose in an edible, then more people would have more adverse drug events from edible cannabis.❞
See the numbers: Acute Illness Associated With Cannabis Use, by Route of Exposure
Why does this happen?
- It’s often because edibles take longer to take effect, so someone thinks “this isn’t very strong” and has more.
- It’s also sometimes because someone errantly eats someone else’s edibles, not realising what they are.
- It’s sometimes a combination of the above problems: a person who is now high, may simply forget and/or make a bad decision when it comes to eating more.
On the other hand, that doesn’t mean inhaling it is necessarily safer. As well as the pulmonary issues we discussed previously, inhaling cannabis has a higher risk of cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (and the resultant cyclic vomiting that’s difficult to treat).
You can read about this fascinating condition that’s sometimes informally called “scromiting”, a portmanteau of screaming and vomiting:
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome
You can’t get addicted to cannabis: True or False?
False. However, it is fair to say that the likelihood of developing a substance abuse disorder is lower than for alcohol, and much lower than for nicotine.
See: Prevalence of Marijuana Use Disorders in the United States Between 2001–2002 and 2012–2013
If you prefer just the stats without the science, here’s the CDC’s rendering of that:
Addiction (Marijuana or Cannabis Use Disorder)
However, there is an interesting complicating factor, which is age. One is 4–7 times more likely to develop a substance abuse disorder, if one starts use as an adolescent, rather than later in life:
Cannabis is the gateway to use of more dangerous drugs: True or False?
False, generally speaking. Of course, for any population there will be some outliers, but there appears to be no meaningful causal relation between cannabis use and other substance use:
Interestingly, the strongest association (where any existed at all) was between cannabis use and opioid use. However, rather than this being a matter of cannabis use being a gateway to opioid use, it seems more likely that this is a matter of people looking to both for the same purpose: pain relief.
As a result, growing accessibility of cannabis may actually reduce opioid problems:
- Cannabis as a Gateway Drug for Opioid Use Disorder
- Association between medical cannabis laws and opioid overdose mortality has reversed over time
Some final words…
Cannabis is a complex drug with complex mechanisms and complex health considerations, and research is mostly quite young, due to its historic illegality seriously cramping science by reducing sample sizes to negligible. Simply put, there’s a lot we still don’t know.
Also, we covered some important topics today, but there were others we didn’t have time to cover, such as the other potential psychological benefits—and risks. Likely we’ll revisit those another day.
Lastly, while we’ve covered a bunch of risks today, those of you who said it has fewer and lesser risks than alcohol are quite right—the only reason we couldn’t focus on that more, is because to talk about all the risks of alcohol would make this feature many times longer!
Meanwhile, whether you partake or not, stay safe and stay well.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: