Ozempic vs Five Natural Supplements
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Semaglutide (GLP-1 agonist) drugs Ozempic and Wegovy really do work for losing weight, provided one then remains on these expensive drugs for life. Dr. Jin Sung recommends a supplements-based approach, instead.
Natural Alternatives
Dr. Sung recommends:
- Berberine, which increases production and secretion of GLP-1.
- Probiotics, which increase GLP-1 secretion. In particular he recommends Akkermansia municiphila which secretes P9, and this protein stimulates GLP-1 production and secretion.
- Psyllium, a soluble dietary fiber which will increase short-chain fatty acids which then help with increasing GLP-1.
- Curcumin, which enhances L-cell numbers, in turn promoting and increasing GLP-1 secretion. Also, curcumin may prolong gastric emptying, and increase insulin sensitivity.
- Ginseng, of which the bioactive compound stimulates secretion of GLP-1, and also has anti-diabetic effects.
Dr. Sung explains more about each of these in his video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to know more?
You might enjoy our previous main feature looking at some of the pros and cons:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Which Vitamin Brands Are Effective?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝As far as specific brands of vitamin…some are good some not. I don’t like being told what buy but I guess I want to know which are effective. Could there be some brands recognized as good given to us?❞
The most reliable brands are generally those with the most transparency:
- They tell you what is in the supplement; not just the active ingredient(s), with doses, but also any buffers etc.
- They tell you, in the case of ingredients that can have various different sources, what the source is.
- They are, ideally, well-certified and independently tested.
Our previous sponsor Ora is a good example of a company that does this.
Additionally, in terms of bioavailability, generally speaking the order of preference goes liquid > capsule/softgel > tablet, so that’s something to look out for, too.
Note: “liquid” includes powders that are ingested when dissolved/suspended in water, and also includes tablets that become a liquid when dissolved/dispersed in water and ingested that way.
Share This Post
-
The Non-Alcoholic Drinker – by James Ellison
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A mere few decades ago, it was often considered antisocial not to smoke. These days, it’s antisocial if you do. The same social change is starting to happen now with alcohol—Millennials are drinking much less than they did in decades past, and Gen Z are hardly drinking at all.
The author, himself a Baby Boomer, champions the cause of mindful, and/but joyful, abstemiousness. Which latter two words don’t often go together, but in this case, he really has put in a lot of work to make non-alcoholic drinking as exciting, fun, and sophisticated as alcoholic drinking always marketed itself to be.
The mocktail recipes in this book are an order of magnitude better than any others this reviewer has encountered before, and did you know they have non-alcoholic bitters now? As in, the cocktail ingredient. Nor is it the only non-alcoholic botanical used, and the ingredients in general are as varied and flavorful, if not sometimes more so, than many that get used in alcoholic mixes.
This book is a very far cry from “rum and coke without the rum”, and instead will have you excited to go ingredient-shopping, and even more excited when you find out how great non-alcoholic things can taste if given the right attention.
As a convenient extra touch, all the ingredients he mentions are available from Amazon, which takes away the fear of “ok, but where do I get…” when it comes to getting things in.
The book does cover things besides just the recipes themselves though, and also talks the reader through navigating non-alcoholism when friends of your own age (unless you’re one of our younger readers) are probably mostly still partying with alcohol.
Really, the biggest value of this book is the recipes, though.
Bottom line: if you’d like to entertain with sophistication and grace and/but not with alcohol, or even just take up a fun new healthy hobby, this book is by far the best book on non-alcoholic mixology that this reviewer has seen to date.
Click here to check out The Non-Alcoholic Drinker, and get mixing non-alcoholically!
Share This Post
-
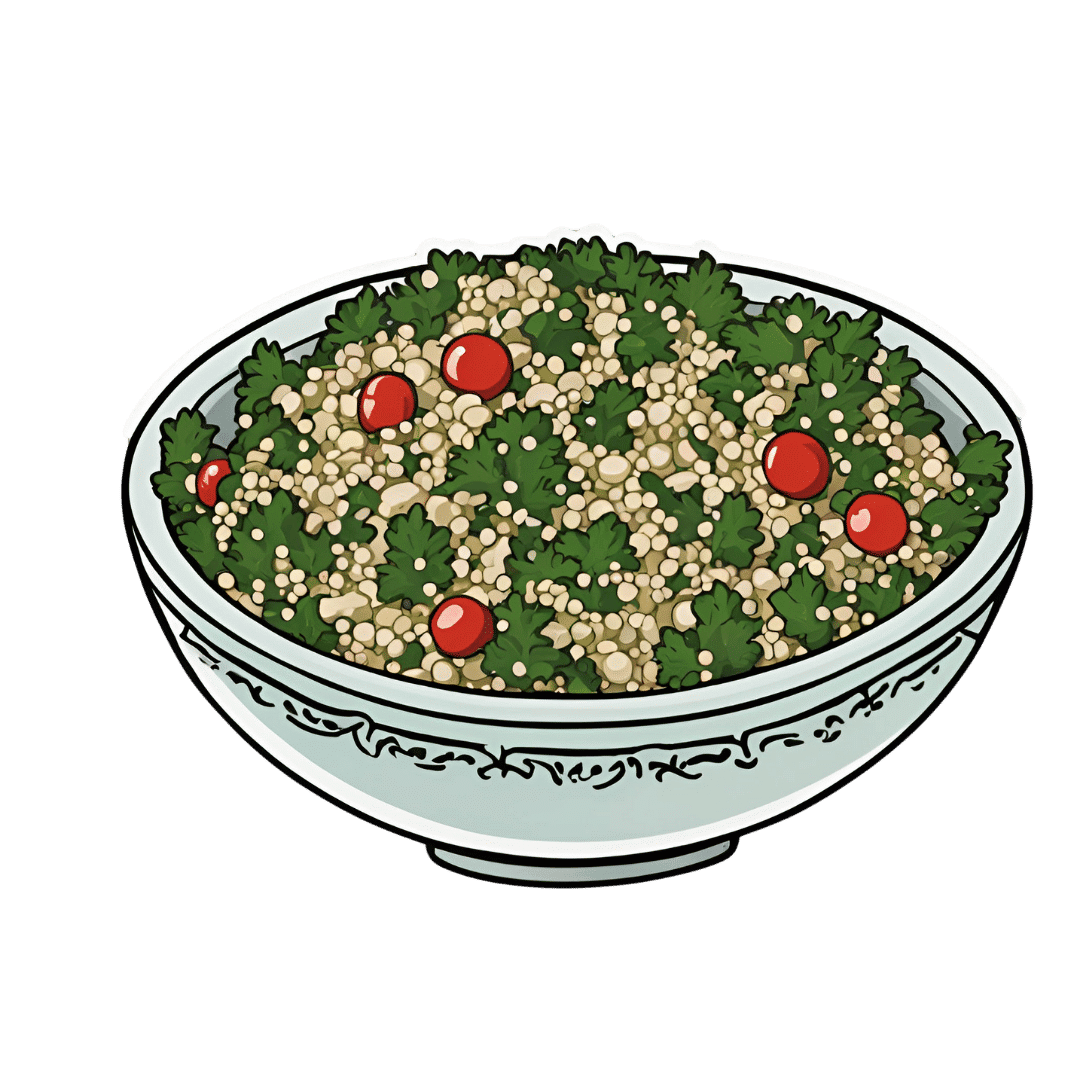
Quercetin Quinoa Probiotic Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This quercetin-rich salad is a bit like a tabbouleh in feel, with half of the ingredients switched out to maximize phenolic and gut-healthy benefits.
You will need
- ½ cup quinoa
- ½ cup kale, finely chopped
- ½ cup flat leaf parsley, finely chopped
- ½ cup green olives, thinly sliced
- ½ cup sun-dried tomatoes, roughly chopped
- 1 pomegranate, peel and pith removed
- 1 preserved lemon, finely chopped
- 1 oz feta cheese or plant-based equivalent, crumbled
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tbsp capers
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
Note: you shouldn’t need salt or similar here, because of the diverse gut-healthy fermented products bringing their own salt with them
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Rinse the quinoa, add the tbsp of chia seeds, cook as normal for quinoa (i.e. add hot water, bring to boil, simmer for 15 minutes or so until pearly and tender), carefully (don’t lose the chia seeds; use a sieve) drain and rinse with cold water to cool. Shake off excess water and/or pat dry on kitchen paper if necessary.
2) Mix everything gently but thoroughly.
3) Serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tasty Tabbouleh with Tahini ← in case you want an actual tabbouleh
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Fight Inflammation & Protect Your Brain, With Quercetin
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
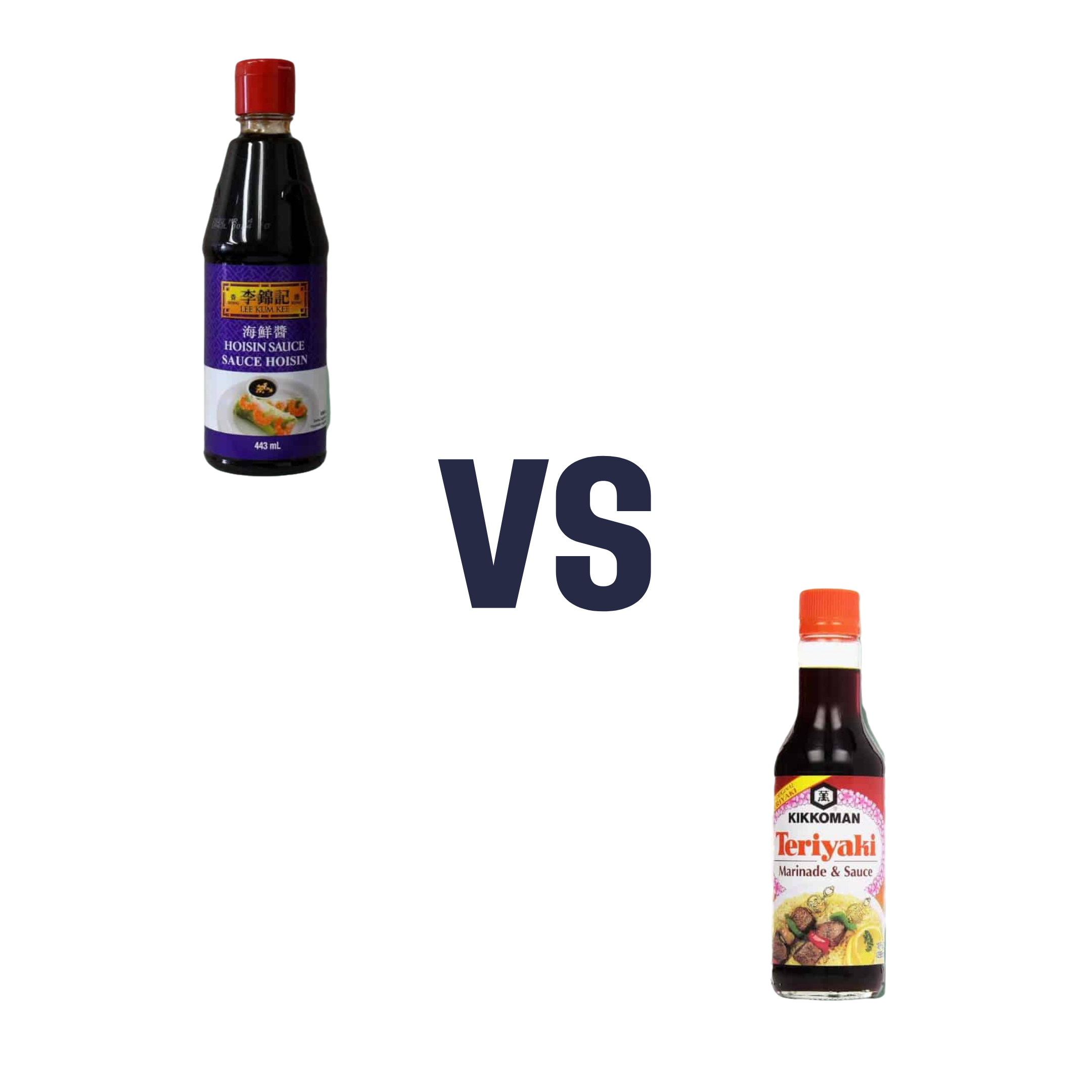
Hoisin Sauce vs Teriyaki Sauce – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing hoisin sauce to teriyaki sauce, we picked the teriyaki sauce.
Why?
Neither are great! But spoonful for spoonful, the hoisin sauce has about 5x as much sugar.
Of course, exact amounts will vary by brand, but the hoisin will invariably be much more sugary than the teriyaki.
On the flipside, the teriyaki sauce may sometimes have slightly more salt, but they are usually in approximately the same ballpark of saltiness, so this is not a big deciding factor.
As a general rule of thumb, the first few ingredients will look like this for each, respectively:
Hoisin:
- Sugar
- Water
- Soybeans
Teriyaki:
- Soy sauce (water, soybeans, salt)
- Rice wine
- Sugar
In essence: hoisin is a soy-flavored syrup, while teriyaki is a sweetened soy sauce
Wondering about that rice wine? The alcohol content is negligible, sufficiently so that teriyaki sauce is not considered alcoholic. For health purposes, it is well under the 0.05% required to be considered alcohol-free.
For religious purposes, we are not your rabbi or imam, but to our best understanding, teriyaki sauce is generally considered kosher* (the rice wine being made from rice) and halal (the rice wine being de-alcoholized by the processing, making the sauce non-intoxicating).
Want to try some?
You can compare these examples side-by-side yourself:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Bird Flu: Children At High Risk; Older Adults Not So Much
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In this week’s news roundup…
Children at highest risk for bird flu
When a new infectious disease comes out, we get used to hearing the usual refrain, “children, the elderly, those with compromised immune systems” are those considered at greatest risk, and therefore first in line for vaccines.
In this case, however, it seems that older adults appear to be rather more resilient to bird flu than children, and it’s noted that early childhood influenza exposure can elicit immune responses that last a lifetime. For those whose lifetime was not curtailed by the initial infection, that means they may enjoy extra defenses now.
You may be wondering whether this headline statement is just a hypothesis based on that, and no, it’s not. It’s a (albeit tentative, like most things in any emerging science, as responses to a novel infection will always be) conclusion based on blood samples from a little over 150 people born between 1927 and 2026 (so, quite a range), and examining the antibodies found therein; adults born prior to 1968 are the ones who are most likely to have been exposed to H1N1 or H2N2 in childhood, resulting in them now having antibodies that work against the H5N1 virus (but still, by all means please do take all sensible precautions anyway!):
Read in full: Older adults might be more resistant to bird flu infections than children, research finds
Related: What you need to know about H5N1 bird flu
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists? They work, but at what cost?
We’re not talking about the side effects this time! Nor even the “what happens if you stop taking it” problems.
Rather, the “cost” in this case is the literal financial cost; out of a selection of weight loss drugs examined, semaglutide (such as Ozempic and Wegovy) and tirzepatide (such as Zepbound and Eli Lilly) were the only ones deemed to not be cost-effective for patients:
Read in full: Semaglutide, tirzepatide not deemed cost-effective obesity therapies despite benefits
Related: Most People Who Start GLP-1 RAs Quit Them Within A Year (Here’s Why)
Inflammation now, brittle bones later
Chronic inflammation is a root cause of many diseases (due in part to how it weakens the immune system, but also because of how the body functions so badly in general when it’s constantly at war with itself, as is the case in chronic inflammation), and it worsens many diseases that it doesn’t outright cause.
In this case, the new science is that chronic inflammation also makes changes to bone density over time.
Spoiler: the changes are not good changes
Furthermore, this holds true for young people also, not just people in the usual demographic that one would expect for brittle bones (especially: older women with untreated menopause, but also just anyone older than middle-aged in general, as most people start losing about 1% of bone density per year after their mid-30s).
Read in full: Inflammation proteins linked to bone density changes over time
Related: The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How anti-vaccine figures abuse data to trick you
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The anti-vaccine movement is nearly as old as vaccines themselves. For as long as humans have sought to harness our immune system’s incredible ability to recognize and fight infectious invaders, critics and conspiracy theorists have opposed these efforts.
Anti-vaccine tactics have advanced since the early days of protesting “unnatural” smallpox inoculation, and the rampant abuse of scientific data may be the most effective strategy yet.
Here’s how vaccine opponents misuse data to deceive people, plus how you can avoid being manipulated.
Misappropriating raw and unverified safety data
Perhaps the oldest and most well-established anti-vaccine tactic is the abuse of data from the federal Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, or VAERS. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration maintain VAERS as a tool for researchers to detect early warning signs of potential vaccine side effects.
Anyone can submit a VAERS report about any symptom experienced at any point after vaccination. That does not mean that these symptoms are vaccine side effects.
VAERS was not designed to determine if a specific vaccine caused a specific adverse event. But for decades, vaccine opponents have misinterpreted, misrepresented, and manipulated VAERS data to convince people that vaccines are dangerous.
Anyone relying on VAERS to draw conclusions about vaccine safety is probably trying to trick you. It isn’t possible to determine from VAERS data alone if a vaccine caused a specific health condition.
VAERS isn’t the only federal data that vaccine opponents abuse. Originally created for COVID-19 vaccines, V-safe is a vaccine safety monitoring system that allows users to report—via text message surveys—how they feel and any health issues they experience up to a year after vaccination. Anti-vaccine groups have misrepresented data in the system, which tracks all health experiences, whether or not they are vaccine-related.
The U.S. Department of Defense’s Defense Medical Epidemiology Database (DMED) has also become a target of anti-vaccine misinformation. Vaccine opponents have falsely claimed that DMED data reveals massive spikes in strokes, heart attacks, HIV, cancer, and blood clots among military service members since the COVID-19 vaccine rollout. The spike was due to an updated policy that corrected underreporting in the previous years
Misrepresenting legitimate studies
A common tactic vaccine opponents use is misrepresenting data from legitimate sources such as national health databases and peer-reviewed studies. For example, COVID-19 vaccines have repeatedly been blamed for rising cancer and heart attack rates, based on data that predates the pandemic by decades.
A prime example of this strategy is a preliminary FDA study that detected a slight increase in stroke risk in older adults after a high-dose flu vaccine alone or in combination with the bivalent COVID-19 vaccine. The study found no “increased risk of stroke following administration of the COVID-19 bivalent vaccines.”
Yet vaccine opponents used the study to falsely claim that COVID-19 vaccines were uniquely harmful, despite the data indicating that the increased risk was almost certainly driven by the high-dose flu vaccine. The final peer-reviewed study confirmed that there was no elevated stroke risk following COVID-19 vaccination. But the false narrative that COVID-19 vaccines cause strokes persists.
Similarly, the largest COVID-19 vaccine safety study to date confirmed the extreme rarity of a few previously identified risks. For weeks, vaccine opponents overstated these rare risks and falsely claimed that the study proves that COVID-19 vaccines are unsafe.
Citing preprint and retracted studies
When a study has been retracted, it is no longer considered a credible source. A study’s retraction doesn’t deter vaccine opponents from promoting it—it may even be an incentive because retracted papers can be held up as examples of the medical establishment censoring so-called “truthtellers.” For example, anti-vaccine groups still herald Andrew Wakefield nearly 15 years after his study falsely linking the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine to autism was retracted for data fraud.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought the lasting impact of retracted studies into sharp focus. The rush to understand a novel disease that was infecting millions brought a wave of scientific publications, some more legitimate than others.
Over time, the weaker studies were reassessed and retracted, but their damage lingers. A 2023 study found that retracted and withdrawn COVID-19 studies were cited significantly more frequently than valid published COVID-19 studies in the same journals.
In one example, a widely cited abstract that found that ivermectin—an antiparasitic drug proven to not treat COVID-19—dramatically reduced mortality in COVID-19 patients exemplifies this phenomenon. The abstract, which was never peer reviewed, was retracted at the request of its authors, who felt the study’s evidence was weak and was being misrepresented.
Despite this, the study—along with the many other retracted ivermectin studies—remains a touchstone for proponents of the drug that has shown no effectiveness against COVID-19.
In a more recent example, a group of COVID-19 vaccine opponents uploaded a paper to The Lancet’s preprint server, a repository for papers that have not yet been peer reviewed or published by the prestigious journal. The paper claimed to have analyzed 325 deaths after COVID-19 vaccination, finding COVID-19 vaccines were linked to 74 percent of the deaths.
The paper was promptly removed because its conclusions were unsupported, leading vaccine opponents to cry censorship.
Applying animal research to humans
Animals are vital to medical research, allowing scientists to better understand diseases that affect humans and develop and screen potential treatments before they are tested in humans. Animal research is a starting point that should never be generalized to humans, but vaccine opponents do just that.
Several animal studies are frequently cited to support the claim that mRNA COVID-19 vaccines are dangerous during pregnancy. These studies found that pregnant rats had adverse reactions to the COVID-19 vaccines. The results are unsurprising given that they were injected with doses equal to or many times larger than the dose given to humans rather than a dose that is proportional to the animal’s size.
Similarly, a German study on rat heart cells found abnormalities after exposure to mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. Vaccine opponents falsely insinuated that this study proves COVID-19 vaccines cause heart damage in humans and was so universally misrepresented that the study’s author felt compelled to dispute the claims.
The author noted that the study used vaccine doses significantly higher than those administered to humans and was conducted in cultured rat cells, a dramatically different environment than a functioning human heart.
How to avoid being misled
The internet has empowered vaccine opponents to spread false information with an efficiency and expediency that was previously impossible. Anti-vaccine narratives have advanced rapidly due to the rampant exploitation of valid sources and the promotion of unvetted, non-credible sources.
You can avoid being tricked by using multiple trusted sources to verify claims that you encounter online. Some examples of credible sources are reputable public health entities like the CDC and World Health Organization, personal health care providers, and peer-reviewed research from experts in fields relevant to COVID-19 and the pandemic.
Read more about anti-vaccine tactics:
- How vaccine opponents spread misinformation
- How misinformation tricks our brains
- How vaccine opponents use kids to spread misinformation
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: