What you need to know about H5N1 bird flu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
On May 30, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that a Michigan dairy worker tested positive for H5N1 bird flu. It was the fourth person to test positive for H5N1 in the United States, following another recent case in Michigan, an April case in Texas, and an initial case in Colorado in 2022.
H5N1 bird flu has been spreading among bird species in the U.S. since 2021, killing millions of wild birds and poultry. In late March 2024, H5N1 bird flu was found in cows for the first time, causing an outbreak in dairy cows across several states.
U.S. public health officials and researchers are particularly concerned about this outbreak because the virus has infected cows and other mammals and has spread from a cow to a human for the first time.
This bird flu strain has shown to not only make wild mammals, including marine mammals and bears, very sick but to also cause high rates of death among species, says Jane Sykes, professor of small animal medicine at the University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine.
“And now that it has been found in cattle, [it] raises particular concern for spread to all the animal species, including people,” adds Sykes.
Even though the risk for human infection is low and there has never been human-to-human transmission of H5N1, there are several actions you can take to stay protected. Read on to learn more about H5N1 bird flu and the current outbreak.
What is H5N1?
H5N1 is a type of influenza virus that most commonly affects birds, causing them severe respiratory illness and death.
The H5N1 strain first emerged in China in the 1990s, and it has continued to spread around the world since then. In 1997, the virus spread from animals to humans in Hong Kong for the first time, infecting 18 people, six of whom died.
Since 2020, the H5N1 strain has caused “an unprecedented number of deaths in wild birds and poultry in many countries,” according to the World Health Organization.
Even though bird flu is rare in humans, an H5N1 infection can cause mild to severe illness and can be fatal in some cases. It can cause eye infection, upper respiratory symptoms, and pneumonia.
What do we know about the 2024 human cases of H5N1 in the U.S.?
The Michigan worker who tested positive for H5N1 in late May is a dairy worker who was exposed to infected livestock. They were the first to experience respiratory symptoms—including a cough without a fever—during the current outbreak. They were given an antiviral and the CDC says their symptoms are resolving.
The Michigan farm worker who tested positive earlier in May only experienced eye-related symptoms and has already recovered. And the dairy worker who tested positive for the virus in Texas in April only experienced eye redness as well, was treated with an antiviral medication for the flu, and is recovering.
Is H5N1 bird flu in the milk we consume?
The Food and Drug Administration has found traces of H5N1 bird flu virus in raw or unpasteurized milk. However, pasteurized milk is safe to drink.
Pasteurization, the process of heating milk to high temperatures to kill harmful bacteria (which the majority of commercially sold milk goes through), deactivates the virus. In 20 percent of pasteurized milk samples, the FDA found small, inactive (not live nor infectious) traces of the virus, but these fragments do not make pasteurized milk dangerous.
In a recent Infectious Diseases Society of America briefing, Dr. Maximo Brito, a professor at the University of Illinois College of Medicine, said that it’s important for people to avoid “drinking unpasteurized or raw milk [because] there are other diseases, not only influenza, that could be transmitted by drinking unpasteurized milk.”
What can I do to prevent bird flu?
While the risk of H5N1 infection in humans is low, people with exposure to infected animals (like farmworkers) are most at risk. But there are several actions you can take to stay protected.
One of the most important things, according to Sykes, is taking the usual precautions we’ve taken with COVID-19 and other respiratory viruses, including frequent handwashing, especially before eating.
“Handwashing and mask-wearing [are important], just as we learned from the pandemic,” Sykes adds. “And it’s not wearing a mask at all times, but thinking about high-risk situations, like when you’re indoors in a crowded environment, where transmission of respiratory viruses is much more likely to occur.”
There are other steps you can take to prevent H5N1, according to the CDC:
- Avoid direct contact with sick or dead animals, including wild birds and poultry.
- Don’t touch surfaces that may have been contaminated with animal poop, saliva, or mucus.
- Cook poultry and eggs to an internal temperature of 165 degrees Fahrenheit to kill any bacteria or virus, including H5N1. Generally, avoid eating undercooked food.
- Avoid consuming unpasteurized or raw milk or products like cheeses made with raw milk.
- Avoid eating uncooked or undercooked food.
- Poultry and livestock farmers and workers and bird flock owners should wear masks and other personal protective equipment “when in direct or close physical contact with sick birds, livestock, or other animals; carcasses; feces; litter; raw milk; or surfaces and water that might be contaminated with animal excretions from potentially or confirmed infected birds, livestock, or other animals.” (The CDC has more recommendations for this population here.)
Is there a vaccine for H5N1?
The CDC said there are two candidate H5N1 vaccines ready to be made and distributed in case the virus starts to spread from person to person, and the country is now moving forward with plans to produce millions of vaccine doses.
The FDA has approved several bird flu vaccines since 2007. The U.S. has flu vaccines in stockpile through the National Pre-Pandemic Influenza Vaccine Stockpile program, which allows for quick response as strains of the flu virus evolve.
Could this outbreak become a pandemic?
Scientists and researchers are concerned about the possibility of H5N1 spreading among people and causing a pandemic. “Right now, the risk is low, but as time goes on, the potential for mutation to cause widespread human infection increases,” says Sykes.
“I think this virus jumping into cows has shown the urgency to keep tracking [H5N1] a lot more closely now,” Peter Halfmann, research associate professor at the University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Influenza Research Institute tells PGN. “We have our eyes on surveillance now. … We’re keeping a much closer eye, so it’s not going to take us by surprise.”
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Common Sense Labs: Blood Labs Demystified – by Dr. Ken Berry & Kim Howerton
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most people, if given their test results as a set of numbers, will have no idea what they mean.
And a doctor or nurse saying “this is good”, “this is a bit low”, “this is very high” etc isn’t that much more informative, as it doesn’t really give a true feel for the information.
Dr. Berry produced this book to bridge that knowledge gap, and in his words, “put the power of health back in the hands of the people”. The book also covers what blood tests to recommend annually (finding common recommendations insufficient), and how to go about asking for those if your doctor might be keen to brush you off.
This is a short book (weighing in at a lithe 78 pages), but the information contained therein is very dense, and very convenient to have it all in one place.
As one Amazon reviewer wrote,
❝Someone said you can find the information on the Internet, but I would say good luck with that. It will be many many many hours compiling the gold that is in this book.❞
Writer’s anecdote: indeed, I recently had 14 blood tests done as part of a regular checkup (I’m pleased to report I could not be in better health), and while interpreting the results, I had to look up a lot of things (which were often in the wrong units*), and if I’d had this book already, it would have been a breeze, as it covers everything I had done!
*On which note, this book does provide results in US and International units, so you won’t be left wondering how to convert mmol/mol into mmol/L or mg/dL or such.
Bottom line: if you are a person who has blood, this book will at some point be of immense value to you, if not immediately!
Click here to check out Common Sense Labs, and understand what your blood is saying!
Share This Post
-
Gut – by Dr. Giulia Enders
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
On account of being an organ (or rather, a system of organs) whose functions are almost entirely autonomic, most of us don’t think about our gut much. We usually know there’s acid in the stomach, and we usually know there are “good and bad” gut bacteria. But what of the rest of what goes on?
For anyone who has a hazy half-remembered knowledge from school, this will serve as not only a reminder, but a distinct upgrade in knowledge.
Dr. Giuliua Enders talks us through not just the processes of what goes on, but, as a medical doctor, also many instances of what can go wrong, for example:
- Why do some people’s bodies mistake nuts for a deadly threat (and consequently, accidentally elevate them to the status of actually becoming a deadly threat)?
- Why are some people lactose-intolerant, and why do food intolerances often pop up later with age?
- Why do constipation and diarrhoea happen?
- Why is it that stress can cause stomach ulcers?
The style of writing is light and easy-reading, and the illustrations are clear too. This is a very accessible book that doesn’t assume prior knowledge, and also doesn’t skimp on the scientific explanations—there’s no dumbing down here.
Bottom line: knowing what goes on in our gut as akin to knowing what goes on under the hood of a car. A lot of the time we don’t need to know, but knowing can make a big difference from time to time, and that’s when you’ll wish you’d learned!
Share This Post
-
America Worries About Health Costs — And Voters Want to Hear From Biden and Republicans
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
President Joe Biden is counting on outrage over abortion restrictions to help drive turnout for his reelection. Former President Donald Trump is promising to take another swing at repealing Obamacare.
But around America’s kitchen tables, those are hardly the only health topics voters want to hear about in the 2024 campaigns. A new KFF tracking poll shows that health care tops the list of basic expenses Americans worry about — more than gas, food, and rent. Nearly 3 in 4 adults — and majorities of both parties — say they’re concerned about paying for unexpected medical bills and other health costs.
“Absolutely health care is something on my mind,” Rob Werner, 64, of Concord, New Hampshire, said in an interview at a local coffee shop in January. He’s a Biden supporter and said he wants to make sure the Affordable Care Act, also known as Obamacare, is retained and that there’s more of an effort to control health care costs.
The presidential election is likely to turn on the simple question of whether Americans want Trump back in the White House. (Nikki Haley, the former South Carolina governor and U.S. ambassador to the United Nations, remained in the race for the Republican nomination ahead of Super Tuesday, though she had lost the first four primary contests.) And neither major party is basing their campaigns on health care promises.
But in the KFF poll, 80% of adults said they think it’s “very important” to hear presidential candidates talk about what they’d do to address health care costs — a subject congressional and state-level candidates can also expect to address.
“People are most concerned about out-of-pocket expenses for health care, and rightly so,” said Andrea Ducas, vice president of health policy at the Center for American Progress, a Washington, D.C.-based progressive think tank.
Here’s a look at the major health care issues that could help determine who wins in November.
Abortion
Less than two years after the Supreme Court overturned the constitutional right to an abortion, it is shaping up to be the biggest health issue in this election.
That was also the case in the 2022 midterm elections, when many voters rallied behind candidates who supported abortion rights and bolstered Democrats to an unexpectedly strong showing. Since the Supreme Court’s decision, voters in six states — including Kansas, Kentucky, and Ohio, where Republicans control the legislatures — have approved state constitutional amendments protecting abortion access.
Polls show that abortion is a key issue to some voters, said Robert Blendon, a public opinion researcher and professor emeritus at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. He said up to 30% across the board see it as a “personal” issue, rather than policy — and most of those support abortion rights.
“That’s a lot of voters, if they show up and vote,” Blendon said.
Proposals to further protect — or restrict — abortion access could drive voter turnout. Advocates are working to put abortion-related measures on the ballot in such states as Arizona, Florida, Missouri, and South Dakota this November. A push in Washington toward a nationwide abortion policy could also draw more voters to the polls, Blendon said.
A surprise ruling by the Alabama Supreme Court in February that frozen embryos are children could also shake up the election. It’s an issue that divides even the anti-abortion community, with some who believe that a fertilized egg is a unique new person deserving of full legal rights and protections, and others believing that discarding unused embryos as part of the in vitro fertilization process is a morally acceptable way for couples to have children.
Pricey Prescriptions
Drug costs regularly rank high among voters’ concerns.
In the latest tracking poll, more than half — 55% — said they were very worried about being able to afford prescription drugs.
Biden has tried to address the price of drugs, though his efforts haven’t registered with many voters. While its name doesn’t suggest landmark health policy, the Inflation Reduction Act, or IRA, which the president signed in August 2022, included a provision allowing Medicare to negotiate prices for some of the most expensive drugs. It also capped total out-of-pocket spending for prescription drugs for all Medicare patients, while capping the price of insulin for those with diabetes at $35 a month — a limit some drugmakers have extended to patients with other kinds of insurance.
Drugmakers are fighting the Medicare price negotiation provision in court. Republicans have promised to repeal the IRA, arguing that forcing drugmakers to negotiate lower prices on drugs for Medicare beneficiaries would amount to price controls and stifle innovation. The party has offered no specific alternative, with the GOP-led House focused primarily on targeting pharmacy benefit managers, the arbitrators who control most Americans’ insurance coverage for medicines.
Costs of Coverage
Health care costs continue to rise for many Americans. The cost of employer-sponsored health plans have hit new highs in the past few months, raising costs for employers and workers alike. Experts have attributed the increase to high demand and expensive prices for certain drugs and treatments, notably weight loss drugs, as well as to medical inflation.
Meanwhile, the ACA is popular. The KFF poll found that more adults want to see the program expanded than scaled back. And a record 21.3 million people signed up for coverage in 2024, about 5 million of them new customers.
Enrollment in Republican-dominated states has grown fastest, with year-over-year increases of 80% in West Virginia, nearly 76% in Louisiana, and 62% in Ohio, according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
Public support for Obamacare and record enrollment in its coverage have made it politically perilous for Republicans to pursue the law’s repeal, especially without a robust alternative. That hasn’t stopped Trump from raising that prospect on the campaign trail, though it’s hard to find any other Republican candidate willing to step out on the same limb.
“The more he talks about it, the more other candidates have to start answering for it,” said Jarrett Lewis, a partner at Public Opinion Strategies, a GOP polling firm.
“Will a conversation about repeal-and-replace resonate with suburban women in Maricopa County?” he said, referring to the populous county in Arizona known for being a political bellwether. “I would steer clear of that if I was a candidate.”
Biden and his campaign have pounced on Trump’s talk of repeal. The president has said he wants to make permanent the enhanced premium subsidies he signed into law during the pandemic that are credited with helping to increase enrollment.
Republican advisers generally recommend that their candidates promote “a market-based system that has the consumer much more engaged,” said Lewis, citing short-term insurance plans as an example. “In the minds of Republicans, there is a pool of people that this would benefit. It may not be beneficial for everyone, but attractive to some.”
Biden and his allies have criticized short-term insurance plans — which Trump made more widely available — as “junk insurance” that doesn’t cover care for serious conditions or illnesses.
Entitlements Are Off-Limits
Both Medicaid and Medicare, the government health insurance programs that cover tens of millions of low-income, disabled, and older people, remain broadly popular with voters, said the Democratic pollster Celinda Lake. That makes it unlikely either party would pursue a platform that includes outright cuts to entitlements. But accusing an opponent of wanting to slash Medicare is a common, and often effective, campaign move.
Although Trump has said he wouldn’t cut Medicare spending, Democrats will likely seek to associate him with other Republicans who support constraining the program’s costs. Polls show that most voters oppose reducing any Medicare benefits, including by raising Medicare’s eligibility age from 65. However, raising taxes on people making more than $400,000 a year to shore up Medicare’s finances is one idea that won strong backing in a recent poll by The Associated Press and NORC Center for Public Affairs Research.
Brian Blase, a former Trump health adviser and the president of Paragon Health Institute, said Republicans, if they win more control of the federal government, should seek to lower spending on Medicare Advantage — through which commercial insurers provide benefits — to build on the program’s efficiencies and ensure it costs taxpayers less than the traditional program.
So far, though, Republicans, including Trump, have expressed little interest in such a plan. Some of them are clear-eyed about the perils of running on changing Medicare, which cost $829 billion in 2021 and is projected to consume nearly 18% of the federal budget by 2032.
“It’s difficult to have a frank conversation with voters about the future of the Medicare program,” said Lewis, the GOP pollster. “More often than not, it backfires. That conversation will have to happen right after a major election.”
Addiction Crisis
Many Americans have been touched by the growing opioid epidemic, which killed more than 112,000 people in the United States in 2023 — more than gun deaths and road fatalities combined. Rural residents and white adults are among the hardest hit.
Federal health officials have cited drug overdose deaths as a primary cause of the recent drop in U.S. life expectancy.
Republicans cast addiction as largely a criminal matter, associating it closely with the migration crisis at the U.S. southern border that they blame on Biden. Democrats have sought more funding for treatment and prevention of substance use disorders.
“This affects the family, the neighborhood,” said Blendon, the public opinion researcher.
Billions of dollars have begun to flow to states and local governments from legal settlements with opioid manufacturers and retailers, raising questions about how to best spend that money. But it isn’t clear that the crisis, outside the context of immigration, will emerge as a campaign issue.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
More Than One Way To Kill Pain
This is Dr. Deepak Ravindran (MD, FRCA. FFPMRCA, EDRA. FIPP, DMSMed). He has decades of experience and is a specialist in acute and chronic pain management, anesthesia, musculoskeletal medicine, and lifestyle medicine.
A quick catch-up, first:
We’ve written about chronic pain management before:
Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
As well as:
Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief
Dr. Ravindran’s approach
Dr. Ravindran takes a “trauma-informed care” approach to his professional practice, and recommends the same for others.
In a nutshell, this means starting from a position of not “what’s wrong with you?”, but rather “what happened to you?”.
This seemingly subtle shift is important, because it means actually dealing with a person’s issues, instead of “take one of these and call my secretary next month”. Read more:
Pain itself can be something of a many-headed hydra. Dr. Ravindran’s approach is equally many-headed; specifically, he has a 7-point plan:
Medications
Dr. Ravindran sees painkillers (and a collection of other drugs, like antidepressants and muscle relaxants) as a potential means to an end worth exploring, but he doesn’t expect them to be the best choice for everyone, and nor does he expect them to be a cure-all. Neither should we. He also advises being mindful of the drawbacks and potential complications of these drugs, too.
Interventions
Sometimes, surgery is the right choice. Sometimes it isn’t. Often, it will change a life—one way or the other. Similar to with medications, Dr. Ravindran is very averse to a “one size fits all” approach here. See also:
The Insider’s Guide To Making Hospital As Comfortable As Possible
Neuroscience and stress management
Often a lot of the distress of pain is not just the pain itself, but the fear associated with it. Will it get worse if I move wrong or eat the wrong thing? How long will it last? Will it ever get better? Will it get worse if I do nothing?. Dr. Ravindran advises tackling this, with the same level of importance as the pain itself. Here’s a good start:
Stress, And Building Psychological Resilience
Diet and the microbiome
Many chronic illnesses are heavily influenced by this, and Dr. Ravindran’s respect for lifestyle medicine comes into play here. While diet might not fix all our ills, it certainly can stop things from being a lot worse. Beyond the obvious “eat healthily” (Mediterranean diet being a good starting point for most people), he also advises doing elimination tests where appropriate, to screen out potential flare-up triggers. You also might consider:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet
Sleep
“Get good sleep” is easy advice for those who are not in agonizing pain that sometimes gets worse from staying in the same position for too long. Nevertheless, it is important, and foundational to good health. So it’s important to explore—whatever limitations one might realistically have—what can be done to improve it.
If you can only sleep for a short while at a time, you may get benefit from this previous main feature of ours:
How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
Exercise and movement
The trick here is to move little and often; without overdoing it, but without permitting loss of mobility either. See also:
The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, And Move More
Therapies of the mind and body
This is about taking a holistic approach to one’s wellness. In Dr. Ravindran’s words:
❝Mind-body therapies are often an extremely sensitive topic about which people hold very strong opinions and sometimes irrational beliefs.
Some, like reiki and spiritual therapy and homeopathy, have hardly any scientific evidence to back them up, while others like yoga, hypnosis, and meditation/mindfulness are mainstream techniques with many studies showing the benefits, but they all work for certain patients.❞
In other words: evidence-based is surely the best starting point, but if you feel inclined to try something else and it works for you, then it works for you. And that’s a win.
Want to know more?
You might like his book…
The Pain-Free Mindset: 7 Steps to Taking Control and Overcoming Chronic Pain
He also has a blog and a podcast.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Chickpeas vs Pinto Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing chickpeas to pinto beans, we picked the pinto beans.
Why?
Both are great! And an argument could be made for either…
In terms of macros, pinto beans have slightly more fiber and slightly more protein, while chickpeas have slightly more carbs, and thus predictably higher net carbs. In the category of those proteins, they both have a comparable spread of amino acods, with pinto beans having very slightly more of each amino acid. All this adds up to a clear, but moderate, win for pinto beans.
When it comes to vitamins, technically chickpeas have more of vitamins A, B3, B5, C, K, and choline, but the margins are so small as to be almost meaningless. Meanwhile, pinto beans have more of vitamins B1, B6, and E, and/but the only one where the margin is enough to really care about is vitamin E (a little over 2x what chickpeas have). So, an argument could be made either way, but we’re going to call this category a tie.
The story with minerals is similar; chickpeas have more copper, iron, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc, all with small margins, while pinto beans have more potassium and selenium, and/but also less sodium. We’d call this either a tie, or a very slight win for chickpeas.
Adding up the sections gives for a very modest win for pinto beans, but as we say, an argument could be made for either.
Certainly, enjoy both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Chickpeas vs Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
- Kidney Beans vs Fava Beans – Which is Healthier?
- What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Saturated Fat: What’s The Truth?
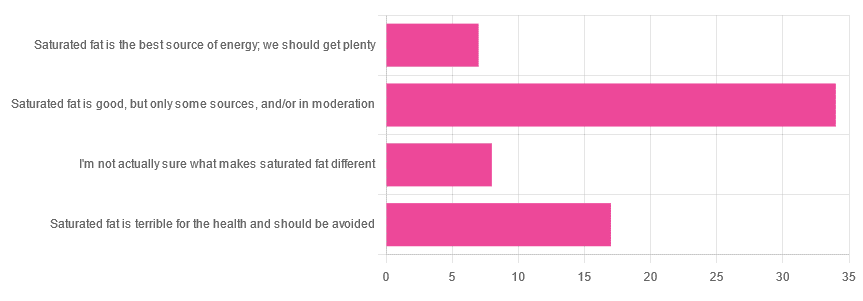
We asked you for your health-related opinion of saturated fat, and got the above-pictured, below-described, set of results.
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”
- This is an easy one to vote for, because of the “and/or in moderation” part, which tends to be a “safe bet” for most things.
- Next most popular was “Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided”
- About half as many recorded votes were for “I’m not actually sure what makes saturated fat different”, which is a very laudable option to click. Admitting when we don’t know things (and none of us know everything) is a very good first step to learning about them!
- Fewest recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty”.
So, what does the science say?
First, a bit of physics, chemistry, and biology
You may be wondering what, exactly, saturated fats are “saturated” with. That’s a fair question, so…
All fats have a molecular structure made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Saturated fats are saturated with hydrogen, and thus have only single bonds between carbon atoms (unsaturated fats have at least one double-bond between carbon atoms).
The observable effect this has on them, is that fats that are saturated with hydrogen are solid at room temperature, whereas unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature. Their different properties also make for different interactions inside the human body, including how likely or not they are to (for example) clog arteries.
See also: Could fat in your bloodstream cause blood clots?
Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty: True or False?
False, in any reasonable interpretation, anyway. That is to say, if your idea of “plenty” is under 13g (e.g: two tablespoons of butter, and no saturated fat from other sources, e.g. meat) per day, then yes, by all means feel free to eat plenty. More than that, though, and you might want to consider trimming it down a bit.
The American Heart Association has this to say:
❝When you hear about the latest “diet of the day” or a new or odd-sounding theory about food, consider the source.
The American Heart Association recommends limiting saturated fats, which are found in butter, cheese, red meat and other animal-based foods, and tropical oils.
Decades of sound science has proven it can raise your “bad” cholesterol and put you at higher risk for heart disease.❞
Source: The American Heart Association Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations on Saturated Fat
The British Heart Foundation has a similar statement:
❝Despite what you read in the media, our advice is clear: replace saturated fats with unsaturated fats and avoid trans fats. Saturated fat is the kind of fat found in butter, lard, ghee, fatty meats and cheese. This is linked to an increased risk of heart and circulatory disease❞
Source: British Heart Foundation: What does fat do and what is saturated fat?
As for the World Health Organization:
❝1. WHO strongly recommends that adults and children reduce saturated fatty acid intake to 10% of total energy intake
2. WHO suggests further reducing saturated fatty acid intake to less than 10% of total energy intake
3. WHO strongly recommends replacing saturated fatty acids in the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids; monounsaturated fatty acids from plant sources; or carbohydrates from foods containing naturally occurring dietary fibre, such as whole grains, vegetables, fruits and pulses.❞
Source: Saturated fatty acid and trans-fatty acid intake for adults and children: WHO guideline
Please note, organizations such as the AHA, the BHF, and the WHO are not trying to sell us anything, and just would like us to not die of heart disease, the world’s #1 killer.
As for “the best source of energy”…
We evolved to eat (much like our nearest primate cousins) a diet consisting mostly of fruits and other edible plants, with a small supplementary amount of animal-source protein and fats.
That’s not to say that because we evolved that way we have to eat that way—we are versatile omnivores. But for example, we are certainly not complete carnivores, and would quickly sicken and die if we tried to live on only meat and animal fat (we need more fiber, more carbohydrates, and many micronutrients that we usually get from plants)
The closest that humans tend to come to doing such is the ketogenic diet, which focuses on a high fat, low carbohydrate imbalance, to promote ketosis, in which the body burns fat for energy.
The ketogenic diet does work, and/but can cause a lot of health problems if a lot of care is not taken to avoid them.
See for example: 7 Keto Risks To Keep In Mind
Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided: True or False?
False, if we are talking about “completely”.
Firstly, it’s practically impossible to cut out all saturated fats, given that most dietary sources of fat are a mix of saturated, unsaturated (mono- and poly-), and trans fats (which are by far the worst, but beyond the scope of today’s main feature).
Secondly, a lot of research has been conducted and found insignificant or inconclusive results, in cases where saturated fat intake was already within acceptable levels (per the recommendations we mentioned earlier), and then cut down further.
Rather than fill up the newsletter with individual studies of this kind here’s a high-quality research review, looking at 19 meta-analyses, each of those meta-analyses having looked at many studies:
Dietary saturated fat and heart disease: a narrative review
Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation: True or False?
True! The moderation part is easy to guess, so let’s take a look at the “but only some sources”.
We were not able to find any convincing science to argue for health-based reasons to favor plant- or animal-sourced saturated fat. However…
Not all saturated fats are created equal (there are many kinds), and also many of the foods containing them have additional nutrients, or harmful compounds, that make a big difference to overall health, when compared gram-for-gram in terms of containing the same amount of saturated fat.
For example:
- Palm oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of palmitic acid, which raises LDL (“bad” cholesterol) without affecting HDL (“good” cholesterol), thus having an overall heart-harmful effect.
- Most animal fats contain a disproportionate amount of stearic acid, which has statistically insignificant effects on LDL and HDL levels, and thus is broadly considered “heart neutral” (in moderation!)
- Coconut oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of lauric acid, which raises total cholesterol, but mostly HDL without affecting LDL, thus having an overall heart-beneficial effect (in moderation!)
Do you know what’s in the food you eat?
Test your knowledge with the BHF’s saturated fat quiz!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”