How To Keep Warm (Without Sweat Patches!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I saw an advert on the subway for a pillow spray that guarantees a perfect night’s sleep. What does the science say about smells/sleep?❞
That is certainly a bold claim! Unless it’s contingent, e.g. “…or your money back”. Because otherwise, it absolutely cannot guarantee that.
There is some merit:
❝Odors can modulate the latency to sleep onset, as well as the quality and duration of sleep. Olfactory modulation of sleep may be mediated by direct synaptic interaction between the olfactory system and sleep control nuclei, and/or indirectly through odor modulation of arousal and respiration.
Such modulation appears most heavily influenced by past associations and expectations about the odor, beyond any potential direct physicochemical effect❞
Source: Reciprocal relationships between sleep and smell
Translating that from sciencese:
Sometimes we find pleasant smells relaxing, and placebo effect also helps.
That “any potential direct physiochemical effect”, though, when it does occur, is things like this…
Read: Odor blocking of stress hormone responses
…but that’s a mouse study, and those odors may only work to block three specific mouse stress responses to three specific stressors: physical restraint, predator odor, and male–male confrontation.
In other words: if, perchance, those three things are not what’s stressing you in bed at night (we won’t make assumptions), and/or you are not a mouse, it may not help.
(and this, dear readers, is why we must read articles, and not just headlines!)
But! If you are going to go for a pillow fragrance, something well-associated with being relaxing and soporific, such as lavender, is the way to go:
- Effects of aromatherapy on sleep quality and anxiety of patients
- Effects of Aromatherapy on the Anxiety, Vital Signs, and Sleep Quality of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Patients in Intensive Care Units
- Effect of lavender aromatherapy on vital signs and perceived quality of sleep in the intermediate care unit: a pilot study
tl;dr = patients found lavender fragrances relaxing, experienced less anxiety, got better sleep (significantly or insignificantly, depending on the study) and enjoyed lower blood pressure (significantly or insignificantly, depending on the study).
PS: this writer uses a pillow spray like this one
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Counterclockwise – by Dr. Ellen Langer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written previously about Dr. Langer’s famous “Counterclockwise” study that saw reversals in biological markers of aging after a one-week intervention that consisted only of a (albeit rather intensive) mental reframe with regard to their age.
This book, as you might expect from the title, refers to that experiment a lot—but it doesn’t stop there. While the Counterclockwise experiment remains Dr. Langer’s most well-known, it’s not her most recent, and she draws from a wealth of research (her own and that of her colleagues in the field) to show the extent and limit of psychosomatic effect on aging.
Note:
- psychosomatic effect does not mean: “imagining it”
- psychosomatic effect means: “your brain regulates almost everything else in your body, directly or indirectly, including your autonomic functions, which includes immune function, tissue replacement, and more”
And as for when it comes to aging? Aging, like cancer, is in large part a problem of immune dysfunction; in both cases cells (be they senescent or cancerous, respectively) are not being killed when they are supposed to be, and in both cases, better instructions will improve the matter.
Many larger-scale markers of aging, such as mobility, are a case of the body only being able to do what the tissues allow, and the tissues are being constantly rebuilt (for better or for worse) according to autonomically-implemented specifications, and cells’ ability to carry out those orders.
Beyond the cellular physiology, this book discusses (a lot) the brain-down mechanisms by which the most powerful organ in our body can tell the rest of the body how old to be.
Dr. Langer also discusses the matter of “priming”, that is to say, how external factors prime us to believe certain things about our age and, with it, our health. These things can include popular media, conversations with friends and family, and healthcare providers’ framing of certain issues.
For example, a person just under a certain age and a person just over a certain age could both go to the doctor with the same complaint—a pain in a certain joint, let’s say. The doctor may refer the slightly younger patient for an x-ray because “let’s see what’s going on here”, and prescribe the slightly older patient some painkillers because “this is perfectly normal at your age”. One resultant problem is obvious: a difference in the standard of care. But the other resultant problem is less obvious: the older patient has now been primed to believe, by a confident authority figure, “it is natural for my body to be in a state of decline now, and this is what to expect”.
Thus, Dr. Langer prescribes mindfulness, not in the mindfulness meditation sense (though sure, do that too), but rather in the sense of consciously interacting with the world and making our own decisions about our own health and, yes, our own age. Because after all, our body neither knows nor cares how many times it has flown around the sun, and merely responds to physiological stimuli—including those we can influence with psychological reframing.
The book is not, per se, a “how-to” guide, rather it is an explanatory treatise, but it contains more than enough information to put it into practice, and indeed, she does also provide some exercises to do along the way.
The style is… Vivacious, without being especially upbeat. Dr. Langer is enthused about her work, yes, but she’s also angry at how many people are having their health sabotaged on the daily, and calls for a more health-first approach (as opposed to illness-first).
Bottom line: this is the book on our brain’s power over aging, so if that topic interests you, this book absolutely belongs on your bookshelf. Well, in your hands, and then on the bookshelf, and then back in your hands from time to time.
Click here to check out Counterclockwise, and age counterclockwise as her experimental subjects did!
Share This Post
-
From Lupus To Arthritis: New Developments
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This week’s health news round-up highlights some things that are getting better, and some things that are getting worse, and how to be on the right side of both:
New hope for lupus sufferers
Lupus is currently treated mostly with lifelong medications to suppress the immune system, which is not only inconvenient, but also can leave people more open to infectious diseases. The latest development uses CAR T-cell technology (as has been used in cancer treatment for a while) to genetically modify cells to enable the body’s own immune system to behave properly:
Read in full: Exciting new lupus treatment could end need for lifelong medication
Related: How to Prevent (Or Reduce The Severity Of) Inflammatory Diseases
It’s in the hips
There are a lot of different kinds of hip replacements, and those with either delta ceramic or oxidised zirconium head with a highly cross-linked polyethylene liner/cup have the lowest risk of need for revision in the 15 years after surgery. This is important, because obviously, once it’s in there, you want it to be able to stay in there and not have to be touched again any time soon:
Read in full: Study identifies hip implant materials with the lowest risk of needing revision
Related: Nobody Likes Surgery, But Here’s How To Make It Much Less Bad
Sooner is better than later
Often, people won’t know about an unwanted pregnancy in the first six weeks, but for those who are able to catch it early, Very Early Medical Abortion (VEMA) offers a safe an effective way of doing so, with success rate being linked to earliness of intervention:
Read in full: Very early medication abortion is effective and safe, study finds
Related: What Might A Second Trump Presidency Look Like for Health Care?
Increased infectious disease risks from cattle farms
Many serious-to-humans infectious diseases enter the human population via the animal food chain, and in this case, bird flu becoming more rampant amongst cows is starting to pose a clear threat to humans, so this is definitely something to be aware of:
Read in full: Bird flu infects 1 in 14 dairy workers exposed; CDC urges better protections
Related: With Only Gloves To Protect Them, Farmworkers Say They Tend Sick Cows Amid Bird Flu
Herald of woe
Gut health affects most of the rest of health, and there are a lot of links between gut and bone health. In this case, an association has been found between certain changes in the gut microbiome, and subsequent onset of rheumatoid arthritis:
Read in full: Changes in gut microbiome could signal onset of rheumatoid arthritis
Related: Stop Sabotaging Your Gut
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Sun Exposure Dilemma
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Sun Exposure Dilemma
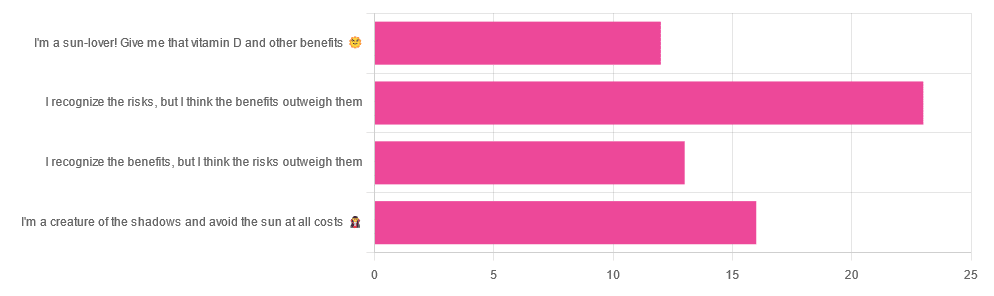
Yesterday, we asked you about your policy on sun exposure, and got the above-pictured, below-described, set of answers:
- A little over a third of respondents chose “I recognize the risks, but I think the benefits outweigh them”
- A quarter of respondents chose “I am a creature of the shadows and I avoid the sun at all costs”
- A little over a fifth of respondents chose “I recognize the benefits, but I think the risks outweigh them”
- A little under a fifth of respondents chose “I’m a sun-lover! Give me that vitamin D and other benefits!”
All in all, this is perhaps the most even spread of answers we’ve had for Friday mythbuster polls—though the sample size was smaller than it often is.
Of those who added comments, common themes were to mention your local climate, and the importance of sunscreen and/or taking vitamin D supplements.
One subscriber mentioned having lupus and living in Florida, which is a particularly unfortunate combination:
Lupus Foundation | Lupus & UV exposure: What you need to know
Another subscriber wrote:
❝Use a very good sunscreen with a high SPF all the time. Reapply after swimming or as needed! I also wear polarized sunglasses anytime I’m outside.❞
…which are important things to note too, and a lot of people forget!
See also: Who Screens The Sunscreens? (on fearing chemical dangers, vs the protection given)
But, onto today’s science for the topic at hand…
We need to get plenty of sun to get plenty of vitamin D: True or False?
True or False, depending on so many factors—to the point that many people get it wildly wrong in either direction.
Whether we are getting enough vitamin D depends on many circumstances, including:
- The climate (and depending on latitude, time of year) where we live
- Our genes, and especially (but not only) our skintone
- The clothes we wear (or don’t)
- Our diet (and not just “how much vitamin D do we consume”)
- Chronic diseases that affect vitamin D metabolism and/or requirements and/or sensitivity to the sun
For a rundown on these factors and more, check out:
Should I be getting my vitamin D levels checked?
Notably, on the topic of whether you should stay in the sun for longer to get more vitamin D…
❝The body can only produce a certain amount of vitamin D at the time, so staying in the sun any longer than needed (which could be just a few minutes, in a sunny climate) is not going to help increase your vitamin D levels, while it will increase your risk of skin cancer.❞
In contrast, she does also note:
❝During winter, catching enough sun can be difficult, especially if you spend your days confined indoors. Typically, the required exposure increases to two to three hours per week in winter. This is because sunlight exposure can only help produce vitamin D if the UVB rays reach us at the correct angle. So in winter we should regularly spend time outside in the middle of the day to get our dose of vitamin D.❞
See also: Vitamin D & Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
We can skip the sun and get our vitamin D from diet/supplements: True or False?
True! However, vitamin D is not the only health benefit of sun exposure.
Not only is sunlight-induced serotonin production important for many things ranging from mood to circadian rhythm (which in turn affects many other aspects of health), but also…
While too much sun can cause skin cancer, too little sun could cause other kinds of cancer:
Benefits of Sunlight: A Bright Spot for Human Health
Additionally, according to new research, the circadian rhythm benefits we mentioned above may also have an impact on type 2 diabetes:
Can catching some rays help you fight off type 2 diabetes?
Which way to jump?
A lot of it depends on who you are, ranging from the factors we mentioned earlier, to even such things as “having many moles” or “having blonde hair”.
This latter item, blonde hair, is a dual thing: it’s a matter of genetic factors that align with being prone to being more sensitive to the sun, as well as being a lesser physical barrier to the sun’s rays than dark hair (that can block some UV rays).
So for example, if two people have comparably gray hair now, but one of them used to have dark hair and the other blonde, there will still be a difference in how they suffer damage, or don’t—and yes, even if their skin is visually of the same approximate skintone.
You probably already know for yourself whether you are more likely to burn or tan in the sun, and the former group are less resistant to the sun’s damage… But the latter group are more likely to spend longer in the sun, and accumulate more damage that way.
If you’d like a very comprehensive downloadable, here are the guidelines issued by the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence:
NICE Guidelines | Sunlight exposure: risks and benefits
…and skip to “At risk groups”, if you don’t want to read the whole thing; “Skin type” is also an important subsection, which also uses your hair and eye color as indicators.
Writer’s note: genetics are complicated and not everyone will fall neatly into categories, which is why it’s important to know the individual factors.
For example, I am quite light-skinned with slightly graying dark hair and gray-blue eyes, and/but also have an obscure Sámi gene that means my skin makes vitamin D easily, while simultaneously being unusually resistant to burning (I just tan). Basically: built for the midnight sun of the Arctic circle.
And yet! My hobbies include not getting skin cancer, so I tend to still be quite mindful of UV levels in different weathers and times of day, and make choices (schedule, clothing, sunscreen or not) accordingly.
Bottom line:
That big self-perpetuating nuclear explosion in the sky is responsible for many things, good and bad for our health, so be aware of your own risk factors, especially for vitamin D deficiency, and skin cancer.
- If you have a predisposition to both, that’s unfortunate, but diet and supplementation at least can help with the vitamin D while getting modest amounts of sun at most.
- Remember that you can only make so much vitamin D at once, so sunbathing for health benefits need only take a few minutes
- Remember that sunlight is important for our circadian rhythm, which is important for many things.
- That’s governed by specific photoreceptor cells, though, so we don’t need our skin to be exposed for that; we just need to be able to see sunlight.
- If you’re going to be out in the sun, and not covered up, sunscreen is your friend, and yes, that goes for clear cold days under the winter sun too.
- Most phone weather apps these days have a UV index score as part of the data they give. Get used to checking it as often as you’d check for rain.
Stay safe, both ways around!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Burn – by Dr. Herman Pontzer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all have reasons to want to focus on our metabolism. Speed it up to burn more fat; slow it down to live longer. Tweak it for more energy in the day. But what actually is it, and how does it work?
Dr. Herman Pontzer presents a very useful overview of not just what our metabolism is and how it works, but also why.
The style of the book is casual, but doesn’t skimp on the science. Whether we are getting campfire stories of Hadza hunter-gatherers, or an explanation of the use of hydrogen isotopes in metabolic research, Dr. Pontzer keeps things easy-reading.
One of the main premises of the book is that our caloric expenditure is not easy to change—if we exercise more, our bodies will cut back somewhere else. After all, the body uses energy for a lot more than just moving. With this in mind, Dr. Pontzer makes the science-based case for focusing more on diet than exercise if weight management is our goal.
In short, if you’d like your metabolism to be a lot less mysterious, this book can help render a lot of science a lot more comprehensible!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Health Fix – by Dr. Ayan Panja
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The book is divided into three main sections:
- The foundations
- The aspirations
- The fixes
The foundations are an overview of the things you’re going to need to know, about biology, behaviors, and being human.
The aspirations are research-generated common hopes, desires, dreams and goals of patients who have come to Dr. Panja for help.
The fixes are exactly what you’d hope them to be. They’re strategies, tools, hacks, tips, tricks, to get you from where you are now to where you want to be, health-wise.
The book is well-structured, with deep-dives, summaries, and practical advice of how to make sure everything you’re doing works together as part of the big picture that you’re building for your health.
All in all, a fantastic catch-all book, whatever your health goals.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
“Why Does It Hurt When I Have Sex?” (And What To Do About It)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is one that affects mostly women, with 43% of American women reporting such issues at some point. There’s a distribution curve to this, with higher incidence in younger and older women; younger while first figuring things out, and older with menopause-related body changes. But, it can happen at any time (and often not for obvious reasons!), so here’s what OB/GYN Dr. Jennifer Lincoln advises:
Many possibilities, but easily narrowed down
Common causes include:
- vaginal dryness, which itself can have many causes (half of which are “low estrogen levels” for various different reasons)
- muscular issues, which can be in response to anxiety, pain, and occur as a result of pelvic floor muscle tightening
- vulvar issues, ranging from skin disorders (e.g. lichen sclerosis or lichen planus) to nerve disorders (e.g. vestibulitis or vestibulodynia)
- uterine issues, including endometriosis, fibroids, or scar tissue if you had a surgery
- infections, of the STI variety, but bear in mind that some STIs such as herpes do not necessarily require direct sexual contact per se, and yeast infections definitely don’t. Some STIs are more serious than others, so getting things checked out is a good idea (don’t worry, clinics are discreet about this sort of thing)
- bowel issues, notwithstanding that we have been talking about vaginal sex here, it can’t be happy if its anatomical neighbors aren’t happy—so things like IBS, Crohn’s, or even just constipation, aren’t irrelevant
- trauma, of various kinds, affecting sexual experiences
That’s a lot of possibilities, so if there’s not something standing out as “yes, now that you mention it, it’s obviously that”, Dr. Lincoln recommends a full health evaluation and examination of medical history, as well as a targeted physical exam. That may not be fun, but at least, once it’s done, it’s done.
Treatments vary depending on the cause, of course, and there are many kinds of physical and psychological therapies, as well as surgeries for the uterine issues we mentioned.
Happily, many of the above things can be addressed with simpler and less invasive methods, including learning more about the relevant anatomy and physiology and how to use it (be not ashamed; most people never got meaningful education about this!)*, vulvar skin care (“gentle” is the watchword here), the difference a good lube can make, and estrogen supplementation—which if you’re not up for general HRT, can be a topical estrogen cream that alleviates sexual function issues without raising blood serum estradiol levels.
*10almonds tip: check out the recommended book “Come As You Are” in our links below; it has 400 pages of stuff most people never knew about anatomy and physiology down there; you can thank us later!
Meanwhile, for more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Water-based Lubricant vs Silicon-based Lubricant – Which is Healthier? (counterintuitively, it’s the silicon! But do give it a quick read, because here be science)
- How To Avoid Urinary Tract Infections (may be relevant; always good to know)
- Come As You Are – by Dr. Emily Nagoski (book; if we could only recommend one book on responsible vagina ownership, this would be the one)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: