Who Screens The Sunscreens?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We Screen The Sunscreens!
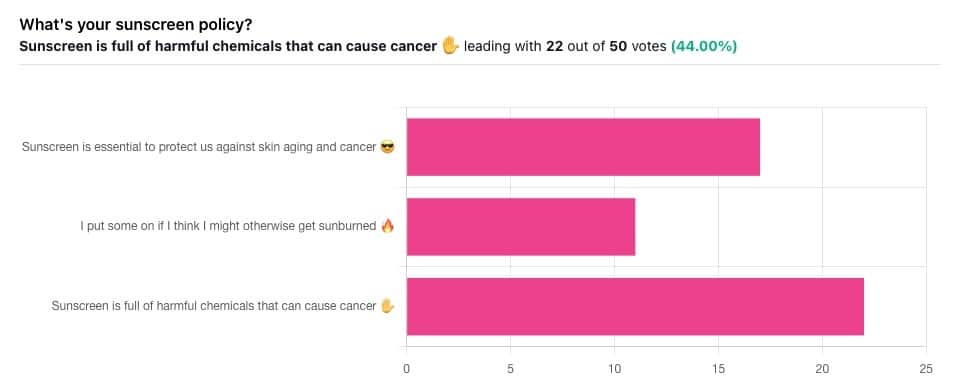
Yesterday, we asked you what your sunscreen policy was, and got a spread of answers. Apparently this one was quite polarizing!
One subscriber who voted for “Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer” wrote:
❝My mom died of complications from melanoma, so we are vigilant about sun and sunscreen. We are a family of campers and hikers and gardeners—outdoors in all seasons—and we never burn❞
Our condolences with regard to your mom! Life is so precious, and when something like that happens, it tends to stick with us. We’re glad you and your family are taking care of yourselves.
Of the subscribers who voted for “I put some on if I think I might otherwise get sunburned”, about half wrote to express uncertainties:
- uncertainty about how safe it is, and
- uncertainty about how helpful it is
…so we’re going to tackle those questions in a moment. But what of those who voted for “Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer”?
Of those, only one wrote a message, which was to say one has to be very careful of what is in the formula.
Let’s take a look, then…
Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer: True or False?
False—according to current best science. Research is ongoing!
There are four main chemicals (found in most sunscreens) that people tend to worry about:
- Abobenzone
- Oxybenzone
- Octocrylene
- Ecamsule
Now, these two sound like four brands of rocket fuel, but then, dihydrogen monoxide (DHMO), which is also found in most sunscreens, sounds like a deadly toxin too. That’s water, by the way.
But what of these four chemicals? Well, as we say, research is ongoing, but we found a study that measured all four, to see how much got into the blood, and what adverse effects, if any, this caused.
We’ll skip to their conclusion:
❝In this preliminary study involving healthy volunteers, application of 4 commercially available sunscreens under maximal use conditions resulted in plasma concentrations that exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens. The systemic absorption of sunscreen ingredients supports the need for further studies to determine the clinical significance of these findings. These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen.❞
Now, “exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens” sounds alarming, so why did they close with the words “These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen”?
Let’s skip back up to a line from the results:
❝The most common adverse event was rash, which developed in 1 participant with each sunscreen.❞
This was most probably due to the oxybenzone, which can cause allergic skin reactions in some people.
Let us take a moment to remember the most common adverse event that occurs from not wearing sunscreen: sunburn!
You can read the full study here:
None of those ingredients have been found to be carcinogenic, even at the maximal blood plasma concentrations studied, from applications 4x/day to 75% of the body.
UVA rays, on the other hand, are absolutely very much known to cause cancer, and the effect is cumulative.
Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer: True or False?
True, unequivocally, unless we live indoors and/or otherwise never go about under sunlight.
“But our ancestors—” lived under the same sun we do, and either used sunscreen or got advanced skin aging and cancer.
Sunscreen of times past ranged from mud to mineral lotions, but it’s pretty much always existed. Even non-human animals that have skin and don’t have fur or feathers, tend to take mud-baths in sunny parts of the world.
If you’d like to avoid oxybenzone and other chemicals, though, you might have your reasons. Maybe you’re allergic, or maybe you read that it’s a potential endocrine disruptor with estrogen-like and anti-androgenic properties that you don’t want.
There are other options, to include physical blockers containing zinc and titanium dioxide, which are generally recognized as safe and effective ingredients.
If you’re interested, you can even make your own sunscreen that blocks both UVA and UVB rays (UVA is what causes skin cancer; UVB is “milder” and is what causes sunburn):
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
As the U.S. Struggles With a Stillbirth Crisis, Australia Offers a Model for How to Do Better
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ProPublica is a Pulitzer Prize-winning investigative newsroom. Sign up for The Big Story newsletter to receive stories like this one in your inbox.
Series: Stillbirths:When Babies Die Before Taking Their First Breath
The U.S. has not prioritized stillbirth prevention, and American parents are losing babies even as other countries make larger strides to reduce deaths late in pregnancy.
The stillbirth of her daughter in 1999 cleaved Kristina Keneally’s life into a before and an after. It later became a catalyst for transforming how an entire country approaches stillbirths.
In a world where preventing stillbirths is typically far down the list of health care priorities, Australia — where Keneally was elected as a senator — has emerged as a global leader in the effort to lower the number of babies that die before taking their first breaths. Stillbirth prevention is embedded in the nation’s health care system, supported by its doctors, midwives and nurses, and touted by its politicians.
In 2017, funding from the Australian government established a groundbreaking center for research into stillbirths. The next year, its Senate established a committee on stillbirth research and education. By 2020, the country had adopted a national stillbirth plan, which combines the efforts of health care providers and researchers, bereaved families and advocacy groups, and lawmakers and government officials, all in the name of reducing stillbirths and supporting families. As part of that plan, researchers and advocates teamed up to launch a public awareness campaign. All told, the government has invested more than $40 million.
Meanwhile, the United States, which has a far larger population, has no national stillbirth plan, no public awareness campaign and no government-funded stillbirth research center. Indeed, the U.S. has long lagged behind Australia and other wealthy countries in a crucial measure: how fast the stillbirth rate drops each year.
According to the latest UNICEF report, the U.S. was worse than 151 countries in reducing its stillbirth rate between 2000 and 2021, cutting it by just 0.9%. That figure lands the U.S. in the company of South Sudan in Africa and doing slightly better than Turkmenistan in central Asia. During that period, Australia’s reduction rate was more than double that.
Definitions of stillbirth vary by country, and though both Australia and the U.S. mark stillbirths as the death of a fetus at 20 weeks or more of pregnancy, to fairly compare countries globally, international standards call for the use of the World Health Organization definition that defines stillbirth as a loss after 28 weeks. That puts the U.S. stillbirth rate in 2021 at 2.7 per 1,000 total births, compared with 2.4 in Australia the same year.
Every year in the United States, more than 20,000 pregnancies end in a stillbirth. Each day, roughly 60 babies are stillborn. Australia experiences six stillbirths a day.
Over the past two years, ProPublica has revealed systemic failures at the federal and local levels, including not prioritizing research, awareness and data collection, conducting too few autopsies after stillbirths and doing little to combat stark racial disparities. And while efforts are starting to surface in the U.S. — including two stillbirth-prevention bills that are pending in Congress — they lack the scope and urgency seen in Australia.
“If you ask which parts of the work in Australia can be done in or should be done in the U.S., the answer is all of it,” said Susannah Hopkins Leisher, a stillbirth parent, epidemiologist and assistant professor in the stillbirth research program at the University of Utah Health. “There’s no physical reason why we cannot do exactly what Australia has done.”
Australia’s goal, which has been complicated by the pandemic, is to, by 2025, reduce the country’s rate of stillbirths after 28 weeks by 20% from its 2020 rate. The national plan laid out the target, and it is up to each jurisdiction to determine how to implement it based on their local needs.
The most significant development came in 2019, when the Stillbirth Centre of Research Excellence — the headquarters for Australia’s stillbirth-prevention efforts — launched the core of its strategy, a checklist of five evidence-based priorities known as the Safer Baby Bundle. They include supporting pregnant patients to stop smoking; regular monitoring for signs that the fetus is not growing as expected, which is known as fetal growth restriction; explaining the importance of acting quickly if fetal movement changes or decreases; advising pregnant patients to go to sleep on their side after 28 weeks; and encouraging patients to talk to their doctors about when to deliver because in some cases that may be before their due date.
Officials estimate that at least half of all births in the country are covered by maternity services that have adopted the bundle, which focuses on preventing stillbirths after 28 weeks.
“These are babies whose lives you would expect to save because they would survive if they were born alive,” said Dr. David Ellwood, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Griffith University, director of maternal-fetal medicine at Gold Coast University Hospital and a co-director of the Stillbirth Centre of Research Excellence.
Australia wasn’t always a leader in stillbirth prevention.
In 2000, when the stillbirth rate in the U.S. was 3.3 per 1,000 total births, Australia’s was 3.7. A group of doctors, midwives and parents recognized the need to do more and began working on improving their data classification and collection to better understand the problem areas. By 2014, Australia published its first in-depth national report on stillbirth. Two years later, the medical journal The Lancet published the second report in a landmark series on stillbirths, and Australian researchers applied for the first grant from the government to create the stillbirth research center.
But full federal buy-in remained elusive.
As parent advocates, researchers, doctors and midwives worked to gain national support, they didn’t yet know they would find a champion in Keneally.
Keneally’s improbable journey began when she was born in Nevada to an American father and Australian mother. She grew up in Ohio, graduating from the University of Dayton before meeting the man who would become her husband and moving to Australia.
When she learned that her daughter, who she named Caroline, would be stillborn, she remembers thinking, “I’m smart. I’m educated. How did I let this happen? And why did nobody tell me this was a possible outcome?”
A few years later, in 2003, Keneally decided to enter politics. She was elected to the lower house of state parliament in New South Wales, of which Sydney is the capital. In Australia, newly elected members are expected to give a “first speech.” She was able to get through just one sentence about Caroline before starting to tear up.
As a legislator, Keneally didn’t think of tackling stillbirth as part of her job. There wasn’t any public discourse about preventing stillbirths or supporting families who’d had one. When Caroline was born still, all Keneally got was a book titled “When a Baby Dies.”
In 2009, Keneally became New South Wales’ first woman premier, a role similar to that of an American governor. Another woman who had suffered her own stillbirth and was starting a stillbirth foundation learned of Keneally’s experience. She wrote to Keneally and asked the premier to be the foundation’s patron.
What’s the point of being the first female premier, Keneally thought, if I can’t support this group?
Like the U.S., Australia had previously launched an awareness campaign that contributed to a staggering reduction in sudden infant death syndrome, or SIDS. But there was no similar push for stillbirths.
“If we can figure out ways to reduce SIDS,” Keneally said, “surely it’s not beyond us to figure out ways to reduce stillbirth.”
She lost her seat after two years and took a break from politics, only to return six years later. In 2018, she was selected to serve as a senator at Australia’s federal level.
Keneally saw this as her second chance to fight for stillbirth prevention. In the short period between her election and her inaugural speech, she had put everything in place for a Senate inquiry into stillbirth.
In her address, Keneally declared stillbirth a national public health crisis. This time, she spoke at length about Caroline.
“When it comes to stillbirth prevention,” she said, “there are things that we know that we’re not telling parents, and there are things we don’t know, but we could, if we changed how we collected data and how we funded research.”
The day of her speech, March 27, 2018, she and her fellow senators established the Select Committee on Stillbirth Research and Education.
Things moved quickly over the next nine months. Keneally and other lawmakers traveled the country holding hearings, listening to testimony from grieving parents and writing up their findings in a report released that December.
“The culture of silence around stillbirth means that parents and families who experience it are less likely to be prepared to deal with the personal, social and financial consequences,” the report said. “This failure to regard stillbirth as a public health issue also has significant consequences for the level of funding available for research and education, and for public awareness of the social and economic costs to the community as a whole.”
It would be easy to swap the U.S. for Australia in many places throughout the report. Women of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander backgrounds experienced double the rate of stillbirth of other Australian women; Black women in America are more than twice as likely as white women to have a stillbirth. Both countries faced a lack of coordinated research and corresponding funding, low autopsy rates following a stillbirth and poor public awareness of the problem.
The day after the report’s release, the Australian government announced that it would develop a national plan and pledged $7.2 million in funding for prevention. Nearly half was to go to education and awareness programs for women and their health care providers.
In the following months, government officials rolled out the Safer Baby Bundle and pledged another $26 million to support parents’ mental health after a loss.
Many in Australia see Keneally’s first speech as senator, in 2018, as the turning point for the country’s fight for stillbirth prevention. Her words forced the federal government to acknowledge the stillbirth crisis and launch the national action plan with bipartisan support.
Australia’s assistant minister for health and aged care, Ged Kearney, cited Keneally’s speech in an email to ProPublica where she noted that Australia has become a world leader in stillbirth awareness, prevention and supporting families after a loss.
“Kristina highlighted the power of women telling their story for positive change,” Kearney said, adding, “As a Labor Senator Kristina Keneally bravely shared her deeply personal story of her daughter Caroline who was stillborn in 1999. Like so many mothers, she helped pave the way for creating a more compassionate and inclusive society.”
Keneally, who is now CEO of Sydney Children’s Hospitals Foundation, said the number of stillbirths a day in Australia spurred the movement for change.
“Six babies a day,” Keneally said. “Once you hear that fact, you can’t unhear it.”
Australia’s leading stillbirth experts watched closely as the country moved closer to a unified effort. This was the moment for which they had been waiting.
“We had all the information needed, but that’s really what made it happen.” said Vicki Flenady, a perinatal epidemiologist, co-director of the Stillbirth Centre of Research Excellence based at the Mater Research Institute at the University of Queensland, and a lead author on The Lancet’s stillbirth series. “I don’t think there’s a person who could dispute that.”
Flenady and her co-director Ellwood had spent more than two decades focused on stillbirths. After establishing the center in 2017, they were now able to expand their team. As part of their work with the International Stillbirth Alliance, they reached out to other countries with a track record of innovation and evidence-based research: the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Ireland. They modeled the Safer Baby Bundle after a similar one in the U.K., though they added some elements.
In 2019, the state of Victoria, home to Melbourne, was the first to implement the Safer Baby Bundle. But 10 months into the program, the effort had to be paused for several months because of the pandemic, which forced other states to cancel their launches altogether.
“COVID was a major disruption. We stopped and started,” Flenady said.
Still, between 2019 and 2021, participating hospitals across Victoria were able to reduce their stillbirth rate by 21%. That improvement has yet to be seen at the national level.
A number of areas are still working on implementing the bundle. Westmead Hospital, one of Australia’s largest hospitals, planned to wrap that phase up last month. Like many hospitals, Westmead prominently displays the bundle’s key messages in the colorful posters and flyers hanging in patient rooms and in the hallways. They include easy-to-understand slogans such as, “Big or small. Your baby’s growth matters,” and, “Sleep on your side when baby’s inside.”
As patients at Westmead wait for their names to be called, a TV in the waiting room plays a video on stillbirth prevention, highlighting the importance of fetal movement. If a patient is concerned their baby’s movements have slowed down, they are instructed to come in to be seen within two hours. The patient’s chart gets a colorful sticker with a 16-point checklist of stillbirth risk factors.
Susan Heath, a senior clinical midwife at Westmead, came up with the idea for the stickers. Her office is tucked inside the hospital’s maternity wing, down a maze of hallways. As she makes the familiar walk to her desk, with her faded hospital badge bouncing against her navy blue scrubs, it’s clear she is a woman on a mission. The bundle gives doctors and midwives structure and uniform guidance, she said, and takes stillbirth out of the shadows. She reminds her staff of how making the practices a routine part of their job has the power to change their patients’ lives.
“You’re trying,” she said, “to help them prevent having the worst day of their life.”
Christine Andrews, a senior researcher at the Stillbirth Centre who is leading an evaluation of the program’s effectiveness, said the national stillbirth rate beyond 28 weeks has continued to slowly improve.
“It is going to take a while until we see the stillbirth rate across the whole entire country go down,” Andrews said. “We are anticipating that we’re going to start to see a shift in that rate soon.”
As officials wait to receive and standardize the data from hospitals and states, they are encouraged by a number of indicators.
For example, several states are reporting increases in the detection of babies that aren’t growing as they should, a major factor in many late-gestation stillbirths. Many also have seen an increase in the number of pregnant patients who stopped smoking. Health care providers also are more consistently offering post-stillbirth investigations, such as autopsies.
In addition to the Safer Baby Bundle, the national plan also calls for raising awareness and reducing racial disparities. The improvements it recommends for bereavement care are already gaining global attention.
To fulfill those directives, Australia has launched a “Still Six Lives” public awareness campaign, has implemented a national stillbirth clinical care standard and has spent two years developing a culturally inclusive version of the Safer Baby Bundle for First Nations, migrant and refugee communities. Those resources, which were recently released, incorporated cultural traditions and used terms like Stronger Bubba Born for the bundle and “sorry business babies,” which is how some Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander women refer to stillbirth. There are also audio versions for those who can’t or prefer not to read the information.
In May, nearly 50 people from the state of Queensland met in a large hotel conference room. Midwives, doctors and nurses sat at round tables with government officials, hospital administrators and maternal and infant health advocates. Some even wore their bright blue Safer Baby T-shirts.
One by one, they discussed their experiences implementing the Safer Baby Bundle. One midwifery group was able to get more than a third of its patients to stop smoking between their first visit and giving birth.
Officials from a hospital in one of the fastest-growing areas in the state discussed how they carefully monitored for fetal growth restriction.
And staff from another hospital, which serves many low-income and immigrant patients, described how 97% of pregnant patients who said their baby’s movements had decreased were seen for additional monitoring within two hours of voicing their concern.
As the midwives, nurses and doctors ticked off the progress they were seeing, they also discussed the fear of unintended consequences: higher rates of premature births or increased admissions to neonatal intensive care units. But neither, they said, has materialized.
“The bundle isn’t causing any harm and may be improving other outcomes, like reducing early-term birth,” Flenady said. “I think it really shows a lot of positive impact.”
As far behind as the U.S. is in prioritizing stillbirth prevention, there is still hope.
Dr. Bob Silver, who co-authored a study that estimated that nearly 1 in 4 stillbirths are potentially preventable, has looked to the international community as a model. Now, he and Leisher — the University of Utah epidemiologist and stillbirth parent — are working to create one of the first stillbirth research and prevention centers in the U.S. in partnership with stillbirth leaders from Australia and other countries. They hope to launch next year.
“There’s no question that Australia has done a better job than we have,” said Silver, who is also chair of the University of Utah Health obstetrics and gynecology department. “Part of it is just highlighting it and paying attention to it.”
It’s hard to know what parts of Australia’s strategy are making a difference — the bundle as a whole, just certain elements of it, the increased stillbirth awareness across the country, or some combination of those things. Not every component has been proven to decrease stillbirth.
The lack of U.S. research on the issue has made some cautious to adopt the bundle, Silver said, but it is clear the U.S. can and should do more.
There comes a point when an issue is so critical, Silver said, that people have to do the best they can with the information that they have. The U.S. has done that with other problems, such as maternal mortality, he said, though many of the tactics used to combat that problem have not been proven scientifically.
“But we’ve decided this problem is so bad, we’re going to try the things that we think are most likely to be helpful,” Silver said.
After more than 30 years of working on stillbirth prevention, Silver said the U.S. may be at a turning point. Parents’ voices are getting louder and starting to reach lawmakers. More doctors are affirming that stillbirths are not inevitable. And pressure is mounting on federal institutions to do more.
Of the two stillbirth prevention bills in Congress, one already sailed through the Senate. The second bill, the Stillbirth Health Improvement and Education for Autumn Act, includes features that also appeared in Australia’s plan, such as improving data, increasing awareness and providing support for autopsies.
And after many years, the National Institutes of Health has turned its focus back to stillbirths. In March, it released a report with a series of recommendations to reduce the nation’s stillbirth rate that mirror ProPublica’s reporting about some of the causes of the crisis. Since then, it has launched additional groups to begin to tackle three critical angles: prevention, data and bereavement. Silver co-chairs the prevention group.
In November, more than 100 doctors, parents and advocates gathered for a symposium in New York City to discuss everything from improving bereavement care in the U.S to tackling racial disparities in stillbirth. In 2022, after taking a page out of the U.K.’s book, the city’s Mount Sinai Hospital opened the first Rainbow Clinic in the U.S., which employs specific protocols to care for people who have had a stillbirth.
But given the financial resources in the U.S. and the academic capacity at American universities and research institutions, Leisher and others said federal and state governments aren’t doing nearly enough.
“The U.S. is not pulling its weight in relation either to our burden or to the resources that we have at our disposal,” she said. “We’ve got a lot of babies dying, and we’ve got a really bad imbalance of who those babies are as well. And yet we look at a country with a much smaller number of stillbirths who is leading the world.”
“We can do more. Much more. We’re just not,” she added. “It’s unacceptable.”
Share This Post
-
From straight to curly, thick to thin: here’s how hormones and chemotherapy can change your hair
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Head hair comes in many colours, shapes and sizes, and hairstyles are often an expression of personal style or cultural identity.
Many different genes determine our hair texture, thickness and colour. But some people’s hair changes around the time of puberty, pregnancy or after chemotherapy.
So, what can cause hair to become curlier, thicker, thinner or grey?
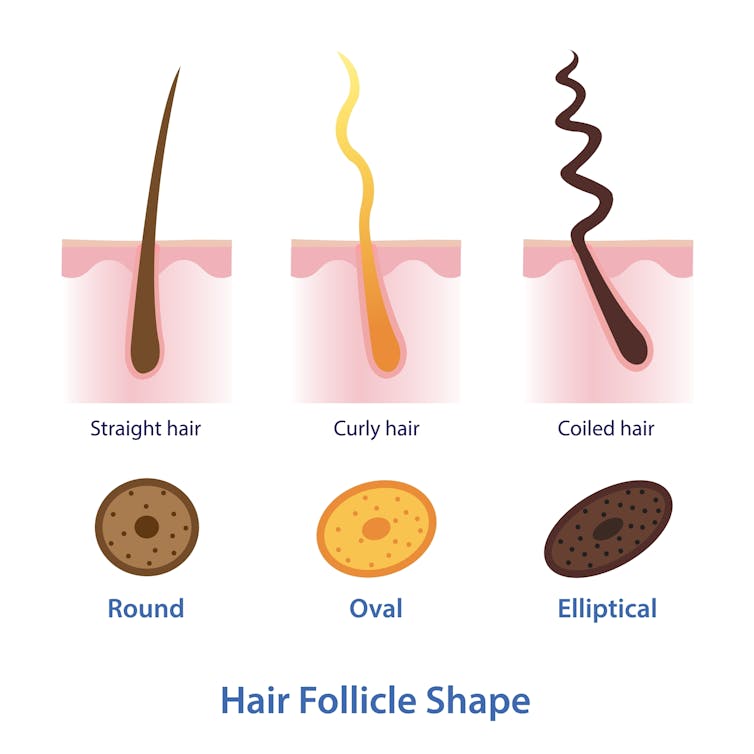
Curly or straight? How hair follicle shape plays a role
Hair is made of keratin, a strong and insoluble protein. Each hair strand grows from its own hair follicle that extends deep into the skin.
Curly hair forms due to asymmetry of both the hair follicle and the keratin in the hair.
Follicles that produce curly hair are asymmetrical and curved and lie at an angle to the surface of the skin. This kinks the hair as it first grows.
The asymmetry of the hair follicle also causes the keratin to bunch up on one side of the hair strand. This pulls parts of the hair strand closer together into a curl, which maintains the curl as the hair continues to grow.
Follicles that are symmetrical, round and perpendicular to the skin surface produce straight hair.
Each hair strand grows from its own hair follicle.
Mosterpiece/ShutterstockLife changes, hair changes
Our hair undergoes repeated cycles throughout life, with different stages of growth and loss.
Each hair follicle contains stem cells, which multiply and grow into a hair strand.
Head hairs spend most of their time in the growth phase, which can last for several years. This is why head hair can grow so long.
Let’s look at the life of a single hair strand. After the growth phase is a transitional phase of about two weeks, where the hair strand stops growing. This is followed by a resting phase where the hair remains in the follicle for a few months before it naturally falls out.
The hair follicle remains in the skin and the stems cells grow a new hair to repeat the cycle.
Each hair on the scalp is replaced every three to five years.
Each hair on the scalp is replaced every three to five years.
Just Life/ShutterstockHormone changes during and after pregnancy alter the usual hair cycle
Many women notice their hair is thicker during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, high levels of oestrogen, progesterone and prolactin prolong the resting phase of the hair cycle. This means the hair stays in the hair follicle for longer, with less hair loss.
A drop in hormones a few months after delivery causes increased hair loss. This is due to all the hairs that remained in the resting phase during pregnancy falling out in a fairly synchronised way.
Hair can change around puberty, pregnancy or after chemotherapy
This is related to the genetics of hair shape, which is an example of incomplete dominance.
Incomplete dominance is when there is a middle version of a trait. For hair, we have curly hair and straight hair genes. But when someone has one curly hair gene and one straight hair gene, they can have wavy hair.
Hormonal changes that occur around puberty and pregnancy can affect the function of genes. This can cause the curly hair gene of someone with wavy hair to become more active. This can change their hair from wavy to curly.
Researchers have identified that activating specific genes can change hair in pigs from straight to curly.
Chemotherapy has very visible effects on hair. Chemotherapy kills rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles, which causes hair loss. Chemotherapy can also have genetic effects that influence hair follicle shape. This can cause hair to regrow with a different shape for the first few cycles of hair regrowth.
Your hair can change at different stages of your life.
Igor Ivakhno/ShutterstockHormonal changes as we age also affect our hair
Throughout life, thyroid hormones are essential for production of keratin. Low levels of thyroid hormones can cause dry and brittle hair.
Oestrogen and androgens also regulate hair growth and loss, particularly as we age.
Balding in males is due to higher levels of androgens. In particular, high dihydrotestosterone (sometimes shortened to DHT), which is produced in the body from testosterone, has a role in male pattern baldness.
Some women experience female pattern hair loss. This is caused by a combination of genetic factors plus lower levels of oestrogen and higher androgens after menopause. The hair follicles become smaller and smaller until they no longer produce hairs.
Reduced function of the cells that produce melanin (the pigment that gives our hair colour) is what causes greying.
Theresa Larkin, Associate professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
True Age – by Dr. Morgan Levine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Yesterday’s book review (Counterclockwise) was about psychological factors affecting physical aging (progression or reversal thereof); today we have a book about the physiological factors affecting physical aging (progression or reversal thereof).
Dr. Levine is first and foremost a gerontological epigeneticist, and a lot of this book touches on her research in that field and that of her colleagues.
She does also discuss direct environmental factors also though, and—as you might well expect—lifestyle factors.
Regular readers of 10almonds are unlikely to gain anything new in the category of lifestyle matters, but a lot of the other material will be enlightening, especially with regard to the things that might at first glance seem set in stone, but we can in fact modify, and thus “choose our own adventure” when it comes to how the rest of our life plays out, healthwise (so: choose wisely!).
The book is mostly an overview on the (at time of writing: 2022) current state of affairs in the world of longevity research, and although it’s not a “how to” manual, there is plenty in the category of practical takeaways to be gleaned too.
The style is is mostly light pop science, but with a lot of hard science woven in—she is a good explainer, and has clearly made a notable effort to explain complex concepts in simple ways, while still delivering the complex concepts too (i.e. not overly “dumbing down”).
Bottom line: if you’d like to know about what can be done to increase your healthspan and general longevity, this book has a lot of answers!
Click here to check out True Age, and shift yours in the direction you prefer!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Plant-Based Diet Revolution – by Dr. Alan Desomond
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is this just another gut-healthy cooking guide? Not entirely…
For a start, it’s not just about giving you a healthy gut; it also covers a healthy heart and a healthy brain. There’s lots of science in here!
It’s also aimed as a transitional guide to eating more plants and fewer animal products, if you so choose. And if you don’t so choose, at least having the flexibility to cook both ways.
The recipes themselves (organized into basics, breakfasts, lunches, mains, desserts) are clear and easy while also being calculated to please readers (and their families) who are used to eating more meat. There are, for instance, plenty of healthy proteins, healthy fats, and comfort foods.
The “28 days” of the title refers to a meal plan using the recipes from the book; it’s not a big feature of the book though, so use it or don’t, but the cooking advice itself is more than worth the price of the book and the recipes are certainly great.
Bottom line: if you’re thinking of taking a “Meatless Mondays” approach to making your diet healthier, this book can help you do that in style!
Click here to check out The Plant-Based Diet Revolution, and upgrade your culinary repertoire!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Complete Guide To Fasting – By Dr. Jason Fung
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to intermittent fasting, the plethora of options can be daunting at first, as can such questions as what fluids are ok to take vs what will break the fast, what to expect in terms of your first fasting experience, and how not to accidentally self-sabotage.
Practised well, intermittent fasting can be a very freeing experience, and not at all uncomfortable. Practised badly, it can be absolutely miserable, and this is one of those things where knowledge makes the difference.
Dr. Fung (yes, the same Dr. Fung we’ve featured before as an expert on metabolic health) shares this knowledge over the course of 304 pages, with lots of scientific information and insider tips. He covers the different kinds of fasting, how each of them work and what they do for the body and brain, hunger/satiety hacks, lots of “frequently asked questions”, and even a range of recipes to help smooth your journey along its way.
The style is very well-written pop-science; it’s engaging and straightforward without skimping on science at all.
Bottom line: if you’re thinking of trying intermittent fasting but aren’t sure where/how to best get started, this book can set you off on the right foot and keep you on the right track thereafter.
Click here to check out The Complete Guide to Fasting, and enjoy the process as well as the results!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dreams: Relevance, Meanings, Interpretations
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I have a question or a suggestion for coverage in your “Psychology Sunday”. Dreams: their relevance, meanings ( if any) interpretations? I just wondered what the modern psychological opinions are about dreams in general.❞
We’ll indeed do that one of these Psychology Sundays! Thanks for suggesting it.
What we can say in advance is that there’s certainly not a single unified scientific consensus yet, but there are two or three prevailing views definitely worth covering, e.g. randomly generated, a by-product of reorganizing information in the brain, or expressions of subconscious thoughts/feelings.
There are also differences between a top-down/bottom-up approach to understanding dreaming, and efforts to tie those two together.
Watch this space!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: