Can Ginkgo Tea Be Made Safe? (And Other Questions)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I’d be interested in OTC prostrate medication safety and effectiveness.❞
Great idea! Sounds like a topic for a main feature one day soon, but while you’re waiting, you might like this previous main feature we did, about a supplement that performs equally to some prescription BPH meds:
❝Was very interested in the article on ginko bilboa as i moved into a home that has the tree growing in the backyard. Is there any way i can process the leaves to make a tea out of it.❞
Glad you enjoyed! First, for any who missed it, here was the article on Ginkgo biloba:
Ginkgo Biloba, For Memory And, Uh, What Else Again?
Now, as that article noted, Ginkgo biloba seeds and leaves are poisonous. However, there are differences:
The seeds, raw or roasted, contain dangerous levels of a variety of toxins, though roasting takes away some toxins and other methods of processing (boiling etc) take away more. However, the general consensus on the seeds is “do not consume; it will poison your liver, poison your kidneys, and possibly give you cancer”:
Ginkgo biloba L. seed; A comprehensive review of bioactives, toxicants, and processing effects
The leaves, meanwhile, are much less poisonous with their ginkgolic acids, and their other relevant poison is very closely related to that of poison ivy, involving long-chain alkylphenols that can be broken down by thermolysis, in other words, heat:
However, this very thorough examination of the potential health benefits and risks of ginkgo tea, comes to the general conclusion “this is not a good idea, and is especially worrying in elders, and/or if taking various medications”:
In summary:
- Be careful
- Avoid completely if you have a stronger-than-usual reaction to poison ivy
- If you do make tea from it, green leaves appear to be safer than yellow ones
- If you do make tea from it, boil and stew to excess to minimize toxins
- If you do make tea from it, doing a poison test is sensible (i.e. start with checking for a skin reaction to a topical application on the inside of the wrist, then repeat at least 6 hours later on the lips, then at least 6 hours later do a mouth swill, then at least 12 hours later drink a small amount, etc, and gradually build up to “this is safe to consume”)
For safety (and legal) purposes, let us be absolutely clear that we are not advising you that it is safe to consume a known poisonous plant, and nor are we advising you to do so.
But the hopefully only-ever theoretical knowledge of how to do a poison test is a good life skill, just in case
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Rushing Woman’s Syndrome – by Dr. Libby Weaver
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s well-known that very many women suffer from “the triple burden” of professional work, housework, and childcare. And it’s not even necessarily that we resent any of those things or feel like they’re a burden; we (hopefully) love our professions, homes, children. But, here’s the thing: no amount of love will add extra hours to the day!
On the psychological level, a lot is about making more conscious decisions and fewer automatic reactions. For example, everyone wants everything from us right now, if not by yesterday, but when do they need it? And, is it even our responsibility? Not everything is, and many of us take on more than we should in our effort to be “enough”.
On the physical level, she covers hormones, including the menstrual/menopausal and the metabolic, as well as liver health, digestive issues, and sleep.
The style is direct and friendly, making frequent references to science but not getting deep into it.
It’s worth noting that while she acknowledges other demographics exist, she’s writing mainly for an audience of otherwise healthy straight white women with children and at least moderate financial resources, so if you fall outside of those things, there may be things that society will penalize you for and expect more from you in return for less, so that is a limitation of the book.
Bottom line: if the above describes you, you will probably get value out of this book.
Click here to check out Rushing Woman’s Syndrome, and take care of yourself too!
Share This Post
-
Asparagus vs Edamame – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing asparagus to edamame, we picked the edamame.
Why?
Perhaps it’s a little unfair comparing a legume to a vegetable that’s not leguminous (given legumes’ high protein content), but these two vegetables often serve a similar culinary role, and there is more to nutrition than protein. That said…
In terms of macros, edamame has a lot more protein and fiber; it also has more carbs, but the ratio is such that edamame still has the lower glycemic index. Thus, the macros category is a win for edamame in all relevant aspects.
When it comes to vitamins, things are a little closer; asparagus has more of vitamins A, B3, and C, while edamame has more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, and B9. All in all, a moderate win for edamame, unless we want to consider the much higher vitamin C content of asparagus as particularly more relevant.
In the category of minerals, asparagus boasts only more selenium (and more sodium, not that that’s a good thing for most people in industrialized countries), while edamame has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. An easy win for edamame.
In short, enjoy both (unless you have a soy allergy, because edamame is young soy beans), but edamame is the more nutritionally dense by far.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
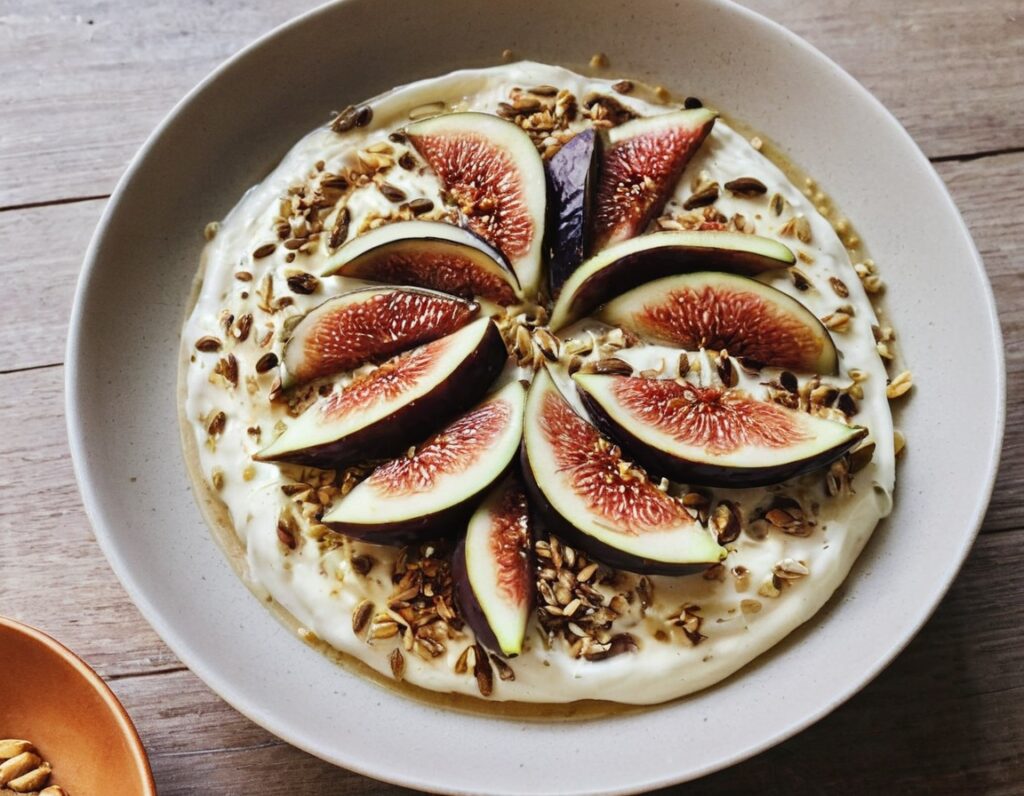
The Gut-Healthiest Yogurt
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Not only is this yogurt, so it’s winning from the start with its probiotic goodness, but also it’s full of several kinds of fiber, and gut-healthy polyphenols too. Plus, it’s delicious. The perfect breakfast, but don’t let us stop you from enjoying it at any time of day!
You will need
- 1 cup yogurt with minimal additives. Live Greek yogurt is a top-tier choice, and plant-based varieties are fine too (just watch out, again, for needless additives)
- 7 dried figs, roughly chopped
- 6 fresh figs, thinly sliced
- 5 oz chopped pitted dates
- 4 tbsp mixed seeds (pumpkin, sunflower, and chia are a great combination)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Soak the dried figs, the dates, and half the seeds in hot water for at least 5 minutes. Drain (be careful not to lose the chia seeds) and put in a blender with ¼ cup cold water.
2) Blend the ingredients from the last step into a purée (you can add a little more cold water if it needs it).
3) Mix this purée into the yogurt in a bowl, and add in the remaining seeds, mixing them in thoroughly.
4) Top with the sliced figs, and serve (or refrigerate, up to a few days, until needed).
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Dates vs Figs – Which is Healthier?
- The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The surprising ways ‘swimming off’ a hangover can be risky, even if alcohol has left your system
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s the morning after a big night and you’re feeling the effects of too much alcohol.
So it can be tempting to “refresh” and take the edge off a hangover with a swim at the beach, or a dip in the cool waters of your local river or pool.
But you might want to think twice.
The day after heavy drinking can affect your body, energy levels and perception of risk in many ways. This means you’re more likely to drown or make careless decisions – even without high levels of alcohol in your blood.
Wanderlust Media/Shutterstock Alcohol + water + summer = drowning
Alcohol is one of the main reasons why someone’s more likely to die due to drowning. And Australians consume a lot of it, including around the water.
The risk of drowning, and injury, including incidents involving alcohol, dramatically increases over the summer festive period – in particular on public holidays and long weekends.
Among people aged 18 and over who drowned in rivers where alcohol was involved, we found some 40% had a blood alcohol concentration of at least 0.20%. That’s four times the upper legal limit of 0.05% when driving a car on a full licence.
When we breathalysed people at four Australian rivers, we found higher levels of blood alcohol with higher temperatures, and particularly on public holidays.
At the beach, intoxication due to alcohol and/or drugs is involved in 23% of drowning deaths with an average blood alcohol concentration of 0.19%.
How about if you’re hungover?
Getting alcohol out of your body is a relatively slow process. On average, alcohol is metabolised at a rate of 0.015% per hour. So if someone stops drinking at 2am with a blood alcohol concentration of 0.20%, their alcohol levels don’t drop to zero until 4pm the next day.
Although hangovers can vary from person to person, typical symptoms include headache, muscle aches, fatigue, weakness, thirst, nausea, stomach pain, vertigo, irritability, sensitivity to light and sound, anxiety, sweating and increased blood pressure.
As well as feeling a bit dusty, the day after an evening of heavy drinking, you’re not so good at identifying risks and reacting to them.
In a pool, this might mean not noticing it’s too shallow to dive safely. In natural waterways, this might mean not noticing a strong river current or a rip current at the beach. Or someone might notice these hazards but swim or dive in anyway.
You don’t have to have alcohol in your blood to be affected. Fatigue can set in, leading you to make careless decisions. tismaja/Shutterstock In one study, we found that after a four-day Australian music festival where people drank heavily, even people who were sober (no longer had alcohol in their blood) were still affected.
Compared to baseline tests in the lab we ran three weeks before the festival, people who were sober the day after the festival had faster reaction times in a test to gauge their attention. But they made more mistakes. This suggests hangovers coupled with fatigue lead to quicker but more careless behaviour.
In and around water this could be the difference between life and death.
Positive blood alcohol readings, including of alcohol from the night before, are commonly implicated in drowning deaths as a result of risky behaviours such as jumping into the water, both at a river and along the coast. Jumping can cause physical injury or render you unconscious, leading to drowning.
Alcohol, including the day after drinking, can also make drowning more likely for a number of other reasons. It also reduces people’s coordination and reaction times.
What else is going on?
Alcohol makes the blood vessels near your skin open up (dilate). So more blood flows into them, making you feel hot. This means you may stay in colder water for longer, increasing your risk of hypothermia.
Alcohol can even make CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) less effective, should you need to be resuscitated.
Normally, your body controls levels of certain minerals (or electrolytes) in the blood. But electrolyte imbalance is common after heavy drinking, including the day after. It’s the reason why hangover symptoms such as muscle pain can lead to cramps in your arms or legs. This can become dangerous when being in or on the water.
Low blood sugar levels the day after drinking is also common. This can lead to people becoming exhausted more quickly when doing physical activities, including swimming.
Other hazards include cold water, high waves and deep water, all of which your body may not be capable of dealing with if you’re feeling the effects of a big night.
What can we do about it?
Authorities regularly warn about the dangers of alcohol intoxication and being near the water. Young people and men are often targeted because these are the groups more likely to drown where alcohol is involved.
Beaches may have alcohol-free zones. Rivers rarely have the same rules, despite similar dangers. https://www.youtube.com/embed/5Salt-kkGUo?wmode=transparent&start=0 Royal Life Saving urges men to ‘make the right call’ and avoid alcohol around the water.
How to stay safe around water if you’re drinking
So take care this summer and stay out of the water if you’re not feeling your best:
- do your swimming before your drinking
- look out for your mates, especially ones who may have had a few too many or are hungover
- avoid getting back into the water after you’ve drunk alcohol or if you’re not feeling your best the next day.
Amy Peden, NHMRC Research Fellow, School of Population Health & co-founder UNSW Beach Safety Research Group, UNSW Sydney; Emmanuel Kuntsche, Director of the Centre for Alcohol Policy Research, La Trobe University, and Jasmin C. Lawes, Adjunct Senior Lecturer, UNSW Beach Safety Research Group, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Correct An Upper Spine Hump (Simple Stretch & Exercise)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Generally called a neck hump in this video, it can be in the cervical (neck) vertebrae or it can be in the thoracic (upper back) vertebrae. It’s also known as a dowager’s hump, buffalo hump, or kyphosis.
However, it can be fixed:
What to do
First understand the cause: it generally comes from poor posture, especially from prolonged desk work or phone use.
With that in mind…
- Posture adjustments: lean back in a chair to counter gravity’s pull on your head. Avoid slumping; keep your head aligned with your spine.
- Stretching: lie flat on the floor without pillows to restore spinal alignment. Gradually reduce pillow height during sleep to decrease neck hyperflexion.
- Neck retraction: pull chin straight back while keeping your eyes looking forwards. Hold for 15 seconds, gradually increasing to 60 seconds. Perform 10 repetitions, resting between sets.
- Strengthening: lean forward and pull the chin back against gravity. Hold, or repeat for 10 repetitions. Over time, increase duration to a minute.
For more on all of this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Pains That Good Posture Now Can Help You Avoid Later
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Women’s Strength Training Anatomy Workouts – by Frédéric Delavier
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed another book of Delavier’s, “Women’s Strength Training Anatomy“, which itself is great. This book adds a lot of practical advice to that one’s more informational format, but to gain full benefit of this one does not require having read that one.
A common reason that many women avoid strength-training is because they do not want to look muscular. Largely this is based on a faulty assumption, since you will never look like a bodybuilder unless you also eat like a bodybuilder, for example.
However, for those for whom the concern remains, today’s book is an excellent guide to strength-training with aesthetics in mind as well as functionality.
The exercises are divided into sections, thus: round your glutes / tone your quadriceps / shape your hamstrings / trim your calves / flatten your abs / curve your shoulders / develop a pain-free upper back / protect your lower back / enhance your chest / firm up your arms.
As you can see, a lot of these are mindful of aesthetics, but there’s nothing here that’s antithetical to function, and some (especially for example “develop a pain-free upper back” and “protect your lower back“) are very functional indeed.
Bottom line: Delavier’s anatomy and exercise books are top-tier, and this one is no exception. If you are a woman and would like to strength-train (or perhaps you already do, and would like to refine your training), then this book is an excellent choice.
Click here to check out Women’s Strength Training Anatomy Workouts, and have the body you want!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: