The Dopamine Precursor And More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Is This Supplement “NALT”?
N-Acetyl L-Tyrosine (NALT) is a form of tyrosine, an amino acid that the body uses to build other things. What other things, you ask?
Well, like most amino acids, it can be used to make proteins. But most importantly and excitingly, the body uses it to make a collection of neurotransmitters—including dopamine and norepinephrine!
- Dopamine you’ll probably remember as “the reward chemical” or perhaps “the motivation molecule”
- Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is what powers us up when we need a burst of energy.
Both of these things tend to get depleted under stressful conditions, and sometimes the body can need a bit of help replenishing them.
What does the science say?
This is Research Review Monday, after all, so let’s review some research! We’re going to dive into what we think is a very illustrative study:
A 2015 team of researchers wanted to know whether tyrosine (in the form of NALT) could be used as a cognitive enhancer to give a boost in adverse situations (times of stress, for example).
They noted:
❝The potential of using tyrosine supplementation to treat clinical disorders seems limited and its benefits are likely determined by the presence and extent of impaired neurotransmitter function and synthesis.❞
More on this later, but first, the positive that they also found:
❝In contrast, tyrosine does seem to effectively enhance cognitive performance, particularly in short-term stressful and/or cognitively demanding situations. We conclude that tyrosine is an effective enhancer of cognition, but only when neurotransmitter function is intact and dopamine and/or norepinephrine is temporarily depleted❞
That “but only”, is actually good too, by the way!
You do not want too much dopamine (that could cause addiction and/or psychosis) or too much norepinephrine (that could cause hypertension and/or heart attacks). You want just the right amount!
So it’s good that NALT says “hey, if you need some more, it’s here, if not, no worries, I’m not going to overload you with this”.
Read the study: Effect of tyrosine supplementation on clinical and healthy populations under stress or cognitive demands
About that limitation…
Remember they said that it seemed unlikely to help in treating clinical disorders with impaired neurotransmitter function and/or synthesis?
Imagine that you employ a chef in a restaurant, and they can’t keep up with the demand, and consequently some of the diners aren’t getting fed. Can you fix this by supplying the chef with more ingredients?
Well, yes, if and only if the problem is “the chef wasn’t given enough ingredients”. If the problem is that the oven (or the chef’s wrist) is broken, more ingredients aren’t going to help at all—something different is needed in those cases.
So it is with, for example, many cases of depression.
See for example: Tyrosine for depression: a double-blind trial
About blood pressure…
You may be wondering, “if NALT is a precursor of norepinephrine, a vasoconstrictor, will this increase my blood pressure adversely?”
Well, check with your doctor as your own situation may vary, but under normal circumstances, no. The effect of NALT is adaptogenic, meaning that it can help keep its relevant neurotransmitters at healthy levels—not too low or high.
See what we mean, for example in this study where it actually helped keep blood pressure down while improving cognitive performance under stress:
Effect of tyrosine on cognitive function and blood pressure under stress
Bottom line:
For most people, NALT is a safe and helpful way to help keep healthy levels of dopamine and norepinephrine during times of stress, giving cognitive benefits along the way.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Finding Geriatric Doctors for Seniors
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝[Can you write about] the availability of geriatric doctors Sometimes I feel my primary isn’t really up on my 70 year old health issues. I would love to find a doctor that understands my issues and is able to explain them to me. Ie; my worsening arthritis in regards to food I eat; in regards to meds vs homeopathic solutions.! Thanks!❞
That’s a great topic, worthy of a main feature! Because in many cases, it’s not just about specialization of skills, but also about empathy, and the gap between studying a condition and living with a condition.
About arthritis, we’re going to do a main feature specifically on that quite soon, but meanwhile, you might like our previous article:
Keep Inflammation At Bay (arthritis being an inflammatory condition)
Share This Post
-
Rehab Science – by Dr. Tom Walters
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many books of this kind deal with the injury but not the pain; some source talk about pain but not the injury; this one does both, and more.
Dr. Walters discusses in detail the nature of pain, various different kinds of pain, the factors that influence pain, and, of course, how to overcome pain.
He also takes us on a tour of various different categories of injury, because some require very different treatment than others, and while there are some catch-all “this is good/bad for healing” advices, sometimes what will help with one injury with hinder healing another. So, this information alone would make the book a worthwhile read already.
After this two-part theory-heavy introduction, the largest part of the book is given over to rehab itself, in a practical fashion.
We learn about how to make an appropriate rehab plan, get the material things we need for it (if indeed we need material things), and specific protocols to follow for various different body parts and injuries.
The style is very much that of a textbook, well-formatted and with plenty of illustrations throughout (color is sometimes relevant, so we recommend a print edition over Kindle for this one).
Bottom line: if you have an injury to heal, or even just believe in being prepared, this book is an excellent guide.
Click here to check out Rehab Science, to overcome pain and heal from injury!
Share This Post
-
Are Brain Chips Safe?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ready For Cyborgization?
In yesterday’s newsletter, we asked you for your views on Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs), such as the Utah Array and Neuralink’s chips on/in brains that allow direct communication between brains and computers, so that (for example) a paralysed person can use a device to communicate, or manipulate a prosthetic limb or two.
We didn’t get as many votes as usual; it’s possible that yesterday’s newsletter ended up in a lot of spam filters due to repeated use of a word in “extra ______ olive oil” in its main feature!
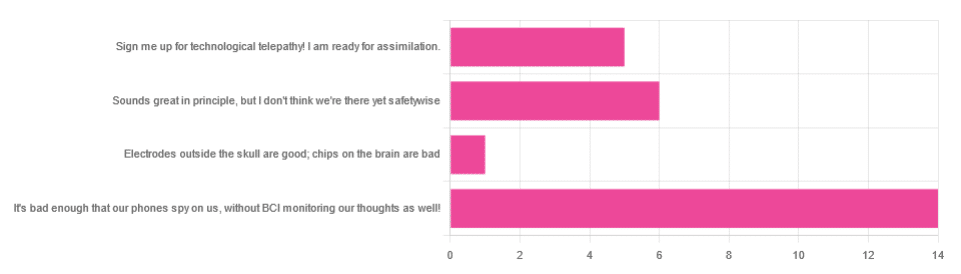
However, of the answers we did get…
- About 54% said “It’s bad enough that our phones spy on us, without BCI monitoring our thoughts as well!”
- About 23% said “Sounds great in principle, but I don’t think we’re there yet safetywise”
- About 19% said “Sign me up for technological telepathy! I am ready for assimilation”
- One (1) person said “Electrode outside the skull are good; chips on the brain are bad”
But what does the science say?
We’re not there yet safetywise: True or False?
True, in our opinion, when it comes to the latest implants, anyway. While it’s very difficult to prove a negative (it could be that everything goes perfectly in human trials), “extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence”, and so far this seems to be lacking.
The stage before human trials is usually animal trials, starting with small creatures and working up to non-human primates if appropriate, before finally humans.
- Good news: the latest hot-topic BCI device (Neuralink) was tested on animals!
- Bad news: to say it did not go well would be an understatement
The Gruesome Story of How Neuralink’s Monkeys Actually Died
The above is a Wired article, and we tend to go for more objective sources, however we chose this one because it links to very many objective sources, including an open letter from the Physicians’ Committee for Responsible Medicine, which basically confirms everything in the Wired article. There are lots of links to primary (medical and legal) sources, too.
Electrodes outside the skull are good; chips on/in the brain are bad: True or False?
True or False depending on how they’re done. The Utah Array (an older BCI implant, now 20 years old, though it’s been updated many times since) has had a good safety record, after being used by a few dozen people with paralysis to control devices:
How the Utah Array is advancing BCI science
The Utah Array works on the same general principle as Neuralink, but the mechanics of its implementation are very different:
- The Utah Array involves a tiny bundle of microelectrodes (held together by a rigid structure that looks a bit like a nanoscale hairbrush) put in place by a brain surgeon, and that’s that.
- The Neuralink has a dynamic web of electrodes, implanted by a little robot that acts like a tiny sewing machine to implant many polymer threads, each containing its own a bunch of electrodes.
In theory, the latter is much more advanced. In practice, so far, the former has a much better safety record.
I am right to be a little worried about giving companies access to my brain: True or False?
True or False, depending on the nature of your concern.
For privacy: current BCI devices have quite simple switches operated consciously by the user. So while technically any such device that then runs its data through Bluetooth or WiFi could be hacked, this risk is no greater than using a wireless mouse and/or keyboard, because it has access to about the same amount of information.
For safety: yes, probably there is cause to be worried. Likely the first waves of commercial users of any given BCI device will be severely disabled people who are more likely to waive their rights in the hope of a life-changing assistance device, and likely some of those will suffer if things go wrong.
Which on the one hand, is their gamble to make. And on the other hand, makes rushing to human trials, for companies that do that, a little more predatory.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Dealing With Waking Up In The Night
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I’m now in my sixties and find that I invariably wake up at least once during the night. Is this normal? Even if it is, I would still like, once in a while, to sleep right through like a teenager. How might this be achieved, without pills?❞
Most people wake up briefly between sleep cycles, and forget doing so. But waking up for more than a brief moment is indeed best avoided. In men of your age, if you’re waking to pee (especially if it’s then not actually that easy to pee), it can be a sign of an enlarged prostate. Which is again a) normal b) not optimal.
By “without pills” we’ll assume you mean “without sleeping pills”. There are options to treat an enlarged prostate, including well-established supplements. We did a main feature on this:
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
If the cause of waking up is something else, then again this is common for everyone as we get older, and again it’s not optimal. But since there are so many possible causes (and thus solutions), it’s more than we can cover in less than a main feature, so we’ll have to revisit this later.
Meanwhile, take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Lucid Dreaming: How To Do It, & Why
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Lucid Dreaming: Methods & Uses
We’ve written about dreaming more generally before:
Today we’re going to be talking more about a subject we’ve only touched on previously: lucid dreaming
What it is: lucid dreaming is the practice of being mentally awake while dreaming, with awareness that it is a dream, and control over the dream.
Why is it useful? Beyond simply being fun, it can banish nightmares, it can improve one’s relationship with sleep (always something to look forward to, and sleep doesn’t feel like a waste of time at all!), and it can allow for exploring a lot of things that can’t easily be explored otherwise—which can be quite therapeutic.
How to do it
There are various ways to induce lucid dreaming, but the most common and “entry-level” method is called Mnemonic-Induced Lucid Dreaming (MILD).
MILD involves having some means of remembering what one has forgotten, i.e., that one is dreaming. To break it down further, first we’ll need to learn how to perform a reality check. Again, there are many of these, but one of the simplest is to ask yourself:
How did I get here?
- If you can retrace your steps with relative ease and the story of how you got here does not sound too much like a dream sequence, you are probably not dreaming.
- If you are dreaming, however, chances are that nothing actually led to where you are now; you just appeared here.
Other reality checks include checking whether books, clocks, and/or lightswitches work as they should—all are notorious for often being broken in dreams; books have gibberish or missing or repeated text; clocks do not tell the correct time and often do not even tell a time that could be real (e.g: 07:72), and lightswitches may turn a light on/off without actually changing the level of illumination in the room.
Now, a reality check is only useful if you actually perform it, so this is where MILD comes in.
You need to make a habit of doing a reality check frequently. Whenever you remember, it’s a good time to do a reality check, but you should also try tying it to something. Many people use a red light, because then they can also use a timed red light during the night to subconsciously cue them that they are dreaming. But it could be as simple as “whenever I go to the bathroom, I do a reality check”.
With this in mind, a fun method that has extra benefits is to try to use a magical power, such as psychokinesis. If (while fully awake) whenever you go to pick up some object you imagine it just wooshing magically to meet your hand halfway, then at some point you’ll instinctively do that while dreaming, and it’ll stand a good chance of working—and thus cluing you in that you are dreaming.
How to stay lucid
When you awaken within a dream (i.e. become lucid), there’s a good chance of one of two things happening quickly:
- you forget again
- you wake up
So when you realize you are dreaming, do two things at once:
- verbally repeat to yourself “I am dreaming now”. This will help stretch your awareness from one second to the next.
- look at your hands, and touch things, especially the floor and/or walls. This will help to ground you within the dream.
Things to do while lucid
Flying is a good fun entry-level activity; it’s very common to initially find it difficult though, and only be able to lift up very slightly before gently falling down, or things like that. A good tip is: instead of trying to move yourself, you stay still and move the dream around you, as though you are rotating a 3D model (because guess what: you are).
Confronting your nightmares and/or general fears is a good thing for many. Think, while you’re still awake during the day, about what you would do about the source/trigger of your fear if you had magical powers. Whatever you choose, keep it consistent for now, because this is about habit-forming.
Example: let’s say there’s a person from your past who appears in your nightmares. Let’s say your chosen magic would be “I would cause the ground to open up, swallow them, and close again behind them”. Vividly imagine that whenever they come to mind while you are awake, and when you encounter them next in a nightmare, you’ll remember to do exactly that, and it’ll work.
Learning about your own subconscious is a more advanced activity, but once you’re used to lucid dreaming, you can remember that everything in there is an internal projection of your own mind, so you can literally talk to parts of your subconscious, including past versions of yourself, or singular parts of your greater-whole personality, as per IFS:
Take Care Of Your “Unwanted” Parts Too!
Want to know more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Signs Of Low Estrogen In Women: What Your Skin, Hair, & Nails Are Trying To Tell You
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Skin, hair, and nails are often thought of purely as a beauty thing, but in fact they can be indicative of a lot of other aspects of health. Dr. Andrea Suarez takes us through some of them in this video about the systemic (i.e., whole-body, not just related to sex things) effects of estrogen, and/or a deficiency thereof.
Beyond the cosmetic
Low estrogen levels are usual in women during and after untreated menopause, resulting in various changes in the skin, hair, and nails, that reflect deeper issues, down to bone health, heart health, brain health, and more. Since we can’t see our bones or hearts or brains without scans (or a serious accident/incident), we’re going to focus on the outward signs of estrogen deficiency.
Estrogen helps maintain healthy collagen production, skin elasticity, wound healing, and moisture retention, making it essential for youthful and resilient skin. Declining estrogen levels with menopause lead to a thinner epidermis, decreased collagen production, and more pronounced wrinkles. Skin elasticity also diminishes, which slows the skin’s ability to recover from stretching or deformation. Wound healing also becomes slower, increasing the risk of infections and extended recovery periods after injuries or surgeries—bearing in mind that collagen is needed in everything from our skin to our internal connective tissue (fascia) and joints and bones. So all those things are going to struggle to recover from injury (and surgery is also an injury) without it.
Other visible changes associated with declining estrogen include significant dryness as a result of reduced hyaluronic acid and glycosaminoglycan production, which are essential for moisture retention. The skin becomes more prone to irritation and increased water loss. Additionally, estrogen deficiency results in less resistance to oxidative stress, making the skin more susceptible to damage from environmental factors such as UV radiation and pollution, as well as any from-the-inside pollution that some may have depending on diet and lifestyle.
Acne and enlarged pores are associated with increased testosterone, but testosterone and estrogen are antagonistic in most ways, and in this case a decrease in estrogen will do the same, due increased unopposed androgen signaling affecting the oil glands. The loss of supportive collagen also causes the skin around pores to lose structure, making them appear larger. The reduction in skin hydration further exacerbates the visibility of pores and can contribute to the development of blackheads due to abnormal cell turnover.
Blood vessel issues tend to arise as estrogen levels drop, leading to a reduction in angiogenesis, i.e. the formation and integrity of blood vessels. This results in more fragile and leaky blood vessels, making the skin more prone to bruising, especially on areas frequently exposed to the sun, such as the backs of the hands. This weakened vasculature also further contributes to the slower wound healing that we talked about, due to less efficient delivery of growth factors.
Hair and nail changes often accompany estrogen deficiency. Women may notice hair thinning, increased breakage, and a greater likelihood of androgenic alopecia. The texture of the hair can change, becoming more brittle. Similarly, nails can develop ridges, split more easily, and become more fragile due to reduced collagen and keratin production, which also affects the skin around the nails.
As for what to do about it? Management options for estrogen-deficient skin include:
- Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (HRT), which can improve skin elasticity, boost collagen production, and reduce dryness and fragility, as well as addressing the many more serious internal things that are caused by the same deficiency as these outward signs.
- Low-dose topical estrogen cream, which can help alleviate skin dryness and increase skin strength, won’t give the systemic benefits (incl. to bones, heart, brain, etc) that only systemic HRT can yield.
- Plant-based phytoestrogens, which are not well-evidenced, but may be better than nothing if nothing is your only other option. However, if you are taking anything other form of estrogen, don’t use phytoestrogens as well, or they will compete for estrogen receptors, and do the job not nearly so well while impeding the bioidentical estrogen from doing its much better job.
And for all at any age, sunscreen continues to be one of the best things to put on one’s skin for general skin health, and this is even more true if running low on estrogen.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
These Signs Often Mean These Nutrient Deficiencies (Do You Have Any?)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: