Mango vs Papaya – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing mango to papaya, we picked the mango.
Why?
Both are great! But there are some things to set them apart:
In terms of macros, this one’s not so big of a difference. They are equal in fiber, while mango has more protein and slightly more carbs. They are both low glycemic index, so we’ll call this one a tie, or the slenderest nominal win for papaya.
When it comes to vitamins, mango has more of vitamins A, B1, B3, B5, B7, B9, E, K, and choline, while papaya has more vitamin C. However, a cup of mango already gives the RDA of vitamin C, so at this point, it’s not even really much of a bonus that papaya has more. In any case, a clear and overwhelming win in the vitamins category for mango.
As for minerals, this one’s closer; mango has more copper, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc, while papaya has more calcium, iron, and magnesium. Still, a 4:3 win for mango.
Adding these up makes for a clear win for mango. However, one extra thing to bear in mind about both:
Both of these fruits interact with warfarin and many other anticoagulants. So if you’re taking those, you might want to skip these, or at least consult with your doctor/pharmacist for input on your personal situation.
Aside from that; enjoy both; diversity is good! But mango is the more nutritionally dense, and thus the winner here.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
5 Ways To Make Your Smoothie Blood Sugar Friendly (Avoid the Spike!)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
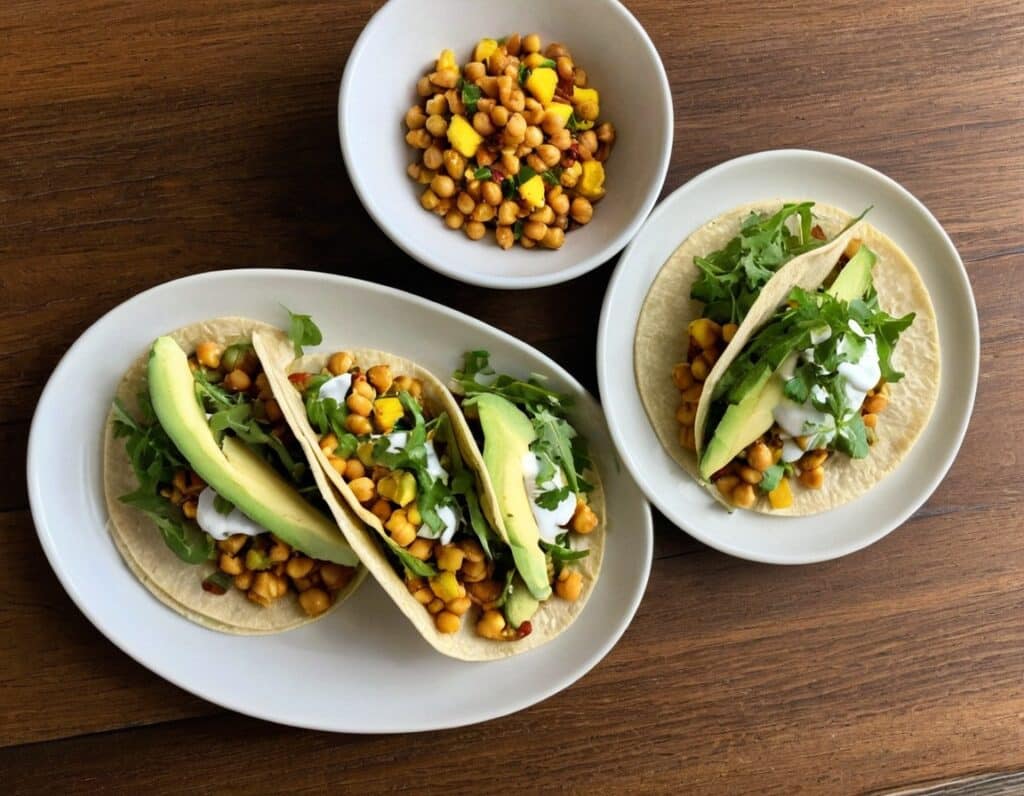
Toasted Chick’n Mango Tacos
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tacos aren’t generally held up as the world’s healthiest food, but they can be! There’s so much going on in this dish today, healthwise, in a good way, that it’s hard to know where to start. But suffice it to say, these tacos are great for your gut, heart, blood sugars, and more.
You will need
For the chickpeas:
- 1 can chickpeas, drained
- 1 tbsp ras el-hanout*
- 1 tsp red pepper flakes
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
*You can easily make this yourself; following our recipe (linked above in the ingredients list) will be better than buying it ready-made, and if you have strong feelings about any of the ingredients, you can adjust per your preference.
For the tahini sauce:
- ⅓ cup tahini
- 2 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- 2 tbsp finely chopped fresh dill
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced
- 1 tsp red pepper flakes
- ½ tsp black pepper, coarse ground
It may seem like salt is conspicuous by its absence, but there is already enough in the chickpeas component; you do not want to overwhelm the dish. Trust us that enjoying these things together will be well-balanced and delicious as written.
For the mango relish:
- ½ mango, pitted, peeled, and cubed
- 2 tsp apple cider vinegar
- 2 tsp cilantro, finely chopped (substitute with parsley if you have the “cilantro tastes like soap” gene)
- 1 tsp red pepper flakes
For building the taco:
- Soft corn tortillas
- Handful of arugula
- 1 avocado, pitted, peeled, and sliced
- ½ red onion, sliced
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat a sauté pan with a little olive oil in; add the chickpeas and then the rest of the ingredients from the chickpea section; cook for about 5 minutes, stirring frequently, and set aside.
2) Combine the tahini sauce ingredients in a small bowl, stirring in ¼ cup water, and set aside.
3) Combine the mango relish ingredients in a separate small bowl, and set aside. You can eat the other half of the mango if you like.
4) Lightly toast the tortillas in a dry skillet, or using a grill.
5) Assemble the tacos; we recommend the order: tortillas, arugula, avocado slices, chickpeas, mango relish, red onion slices, tahini sauce.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we hit all five today! Yay!
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- Coconut vs Avocado – Which is Healthier?
- Lettuce vs Arugula – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Diabetes Code – by Dr. Jason Fung
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cure this serious disease with diet!” is often a bold-claim that overreaches scientific rigor, but in this case, it’s well-established as scientifically valid.
Caveat up-front: the only known circumstance in which this won’t work is if you have comorbidities that prevent you from following the advice.
You may be wondering: is this just the Mediterranean diet again? The answer is that the Mediterreanean diet (or similar) is part of it. But there’s a lot more to this book than that.
Dr. Fung explains to us a lot of the physiology of type 2 diabetes; how insulin resistance occurs, how it becomes a vicious cycle that we get locked into, and how to escape it.
- We learn about the role of fructose, and why fruit is very healthful whereas high-fructose corn syrup and similars are very much not.
- We learn about the role of the liver in glycogen metabolism, and how to un-fatty a fatty liver. Good news: the liver has famously strong self-regenerative abilities, if we give it a break to allow it to do so!
- We learn why portion control doesn’t work, and why intermittent fasting does (here be science).
Dr. Fung’s very readable explanations are free from needless jargon while not dumbing down. The writing style is clear and direct: “this happens this way”, “do this, not that”, etc.
Bottom line: if you have type 2 diabetes and would like to not have that (or if you are pre-diabetic and would like to avoid diabetes) this is a book for you. If you are in great metabolic health and would like to stay that way as you get older, then this is a book for you too.
Click here to check out The Diabetes Code, and get/keep your metabolic health in order!
Share This Post
-
A person in Texas caught bird flu after mixing with dairy cattle. Should we be worried?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The United States’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has issued a health alert after the first case of H5N1 avian influenza, or bird flu, seemingly spread from a cow to a human.
A farm worker in Texas contracted the virus amid an outbreak in dairy cattle. This is the second human case in the US; a poultry worker tested positive in Colorado in 2022.
The virus strain identified in the Texan farm worker is not readily transmissible between humans and therefore not a pandemic threat. But it’s a significant development nonetheless.
Some background on bird flu
There are two types of avian influenza: highly pathogenic or low pathogenic, based on the level of disease the strain causes in birds. H5N1 is a highly pathogenic avian influenza.
H5N1 first emerged in 1997 in Hong Kong and then China in 2003, spreading through wild bird migration and poultry trading. It has caused periodic epidemics in poultry farms, with occasional human cases.
Influenza A viruses such as H5N1 are further divided into variants, called clades. The unique variant causing the current epidemic is H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b, which emerged in late 2020 and is now widespread globally, especially in the Americas.
In the past, outbreaks could be controlled by culling of infected birds, and H5N1 would die down for a while. But this has become increasingly difficult due to escalating outbreaks since 2021.
Wild animals are now in the mix
Waterfowl (ducks, swans and geese) are the main global spreaders of avian flu, as they migrate across the world via specific routes that bypass Australia. The main hub for waterfowl to migrate around the world is Quinghai lake in China.
But there’s been an increasing number of infected non-waterfowl birds, such as true thrushes and raptors, which use different flyways. Worryingly, the infection has spread to Antarctica too, which means Australia is now at risk from different bird species which fly here.
H5N1 has escalated in an unprecedented fashion since 2021, and an increasing number of mammals including sea lions, goats, red foxes, coyotes, even domestic dogs and cats have become infected around the world.
Wild animals like red foxes which live in peri-urban areas are a possible new route of spread to farms, domestic pets and humans.
Dairy cows and goats have now become infected with H5N1 in at least 17 farms across seven US states.
What are the symptoms?
Globally, there have been 14 cases of H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b virus in humans, and 889 H5N1 human cases overall since 2003.
Previous human cases have presented with a severe respiratory illness, but H5N1 2.3.4.4b is causing illness affecting other organs too, like the brain, eyes and liver.
For example, more recent cases have developed neurological complications including seizures, organ failure and stroke. It’s been estimated that around half of people infected with H5N1 will die.
The case in the Texan farm worker appears to be mild. This person presented with conjunctivitis, which is unusual.
Food safety
Contact with sick poultry is a key risk factor for human infection. Likewise, the farm worker in Texas was likely in close contact with the infected cattle.
The CDC advises pasteurised milk and well cooked eggs are safe. However, handling of infected meat or eggs in the process of cooking, or drinking unpasteurised milk, may pose a risk.
Although there’s no H5N1 in Australian poultry or cattle, hygienic food practices are always a good idea, as raw milk or poorly cooked meat, eggs or poultry can be contaminated with microbes such as salmonella and E Coli.
If it’s not a pandemic, why are we worried?
Scientists have feared avian influenza may cause a pandemic since about 2005. Avian flu viruses don’t easily spread in humans. But if an avian virus mutates to spread in humans, it can cause a pandemic.
One concern is if birds were to infect an animal like a pig, this acts as a genetic mixing vessel. In areas where humans and livestock exist in close proximity, for example farms, markets or even in homes with backyard poultry, the probability of bird and human flu strains mixing and mutating to cause a new pandemic strain is higher.
There are a number of potential pathways to a pandemic caused by influenza. Author provided The cows infected in Texas were tested because farmers noticed they were producing less milk. If beef cattle are similarly affected, it may not be as easily identified, and the economic loss to farmers may be a disincentive to test or report infections.
How can we prevent a pandemic?
For now there is no spread of H5N1 between humans, so there’s no immediate risk of a pandemic.
However, we now have unprecedented and persistent infection with H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b in farms, wild animals and a wider range of wild birds than ever before, creating more chances for H5N1 to mutate and cause a pandemic.
Unlike the previous epidemiology of avian flu, where hot spots were in Asia, the new hot spots (and likely sites of emergence of a pandemic) are in the Americas, Europe or in Africa.
Pandemics grow exponentially, so early warnings for animal and human outbreaks are crucial. We can monitor infections using surveillance tools such as our EPIWATCH platform.
The earlier epidemics can be detected, the better the chance of stamping them out and rapidly developing vaccines.
Although there is a vaccine for birds, it has been largely avoided until recently because it’s only partially effective and can mask outbreaks. But it’s no longer feasible to control an outbreak by culling infected birds, so some countries like France began vaccinating poultry in 2023.
For humans, seasonal flu vaccines may provide a small amount of cross-protection, but for the best protection, vaccines need to be matched exactly to the pandemic strain, and this takes time. The 2009 flu pandemic started in May in Australia, but the vaccines were available in September, after the pandemic peak.
To reduce the risk of a pandemic, we must identify how H5N1 is spreading to so many mammalian species, what new wild bird pathways pose a risk, and monitor for early signs of outbreaks and illness in animals, birds and humans. Economic compensation for farmers is also crucial to ensure we detect all outbreaks and avoid compromising the food supply.
C Raina MacIntyre, Professor of Global Biosecurity, NHMRC L3 Research Fellow, Head, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW Sydney; Ashley Quigley, Senior Research Associate, Global Biosecurity, UNSW Sydney; Haley Stone, PhD Candidate, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW Sydney; Matthew Scotch, Associate Dean of Research and Professor of Biomedical Informatics, College of Health Solutions, Arizona State University, and Rebecca Dawson, Research Associate, The Kirby Institute, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
In Plain English…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Time!
This is the bit whereby each week, we respond to subscriber questions/requests/etc
Have something you’d like to ask us, or ask us to look into? Hit reply to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom, and a Real Human™ will be glad to read it!
Q: Love to have someone research all the additives in our medicines, (risk of birth control and breast cancer) and what goes in all of our food and beverages. So much info out there, but there are so many variations, you never know who to believe.
That’s a great idea! There are a lot of medicines and food and beverages out there, so that’s quite a broad brief, but! We could well do a breakdown of very common additives, and demystify them, sorting them into good/bad/neutral, e.g:
- Ascorbic acid—Good! This is Vitamin C
- Acetic acid—Neutral! This is vinegar
- Acetylsalicylic acid—Good or Bad! This is aspirin (a painkiller and blood-thinning agent, can be good for you or can cause more problems than it solves, depending on your personal medical situation. If in doubt, check with your doctor)
- Acesulfame K—Generally Neutral! This is a sweetener that the body can’t metabolize, so it’s also not a source of potassium (despite containing potassium) and will generally do nothing. Unless you have an allergy to it, which is rare but is a thing.
- Sucralose—Neutral! This is technically a sugar (as is anything ending in -ose), but the body can’t metabolize it and processes it as a dietary fiber instead. We’d list it as good for that reason, but honestly, we doubt you’re eating enough sucralose to make a noticeable difference to your daily fiber intake.
- Sucrose—Bad! This is just plain sugar
Sometimes words that sound the same can ring alarm bells when they need not, for example there’s a big difference between:
- Potassium iodide (a good source of potassium and iodine)
- Potassium cyanide (the famous poison; 300mg will kill you; half that dose will probably kill you)
- Cyanocobalamine (Vitamin B12)
Let us know if there are particular additives (or particular medications) you’d like us to look at!
While for legal reasons we cannot give medical advice, talking about common contraindications (e.g., it’s generally advised to not take this with that, as one will stop the other from working, etc) is definitely something we could do.
For example! St. John’s Wort, very popular as a herbal mood-brightener, is on the list of contraindications for so many medications, including:
- Antidepressants
- Birth control pills
- Cyclosporine, which prevents the body from rejecting transplanted organs
- Some heart medications, including digoxin and ivabradine
- Some HIV drugs, including indinavir and nevirapine
- Some cancer medications, including irinotecan and imatinib
- Warfarin, an anticoagulant (blood thinner)
- Certain statins, including simvastatin
Q: As I am a retired nurse, I am always interested in new medical technology and new ways of diagnosing. I have recently heard of using the eyes to diagnose Alzheimer’s. When I did some research I didn’t find too much. I am thinking the information may be too new or I wasn’t on the right sites.
(this is in response to last week’s piece on lutein, eyes, and brain health)
We’d readily bet that the diagnostic criteria has to do with recording low levels of lutein in the eye (discernible by a visual examination of macular pigment optical density), and relying on the correlation between this and incidence of Alzheimer’s, but we’ve not seen it as a hard diagnostic tool as yet either—we’ll do some digging and let you know what we find! In the meantime, we note that the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease (which may be of interest to you, if you’re not already subscribed) is onto this:
See also:
- Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease (mixture of free and paid content)
- Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports (open access—all content is free)
Q: As to specific health topics, I would love to see someone address all these Instagram ads targeted to women that claim “You only need to ‘balance your hormones’ to lose weight, get ripped, etc.” What does this mean? Which hormones are they all talking about? They all seem to be selling a workout program and/or supplements or something similar, as they are ads, after all. Is there any science behind this stuff or is it mostly hot air, as I suspect?
Thank you for asking this, as your question prompted yesterday’s main feature, What Does “Balancing Your Hormones” Even Mean?
That’s a great suggestion also about addressing ads (and goes for health-related things in general, not just hormonal stuff) and examining their claims, what they mean, how they work (if they work!), and what’s “technically true but may
be misleading* cause confusion”*We don’t want companies to sue us, of course.
Only, we’re going to need your help for this one, subscribers!
See, here at 10almonds we practice what we preach. We limit screen time, we focus on our work when working, and simply put, we don’t see as many ads as our thousands of subscribers do. Also, ads tend to be targeted to the individual, and often vary from country to country, so chances are good that we’re not seeing the same ads that you’re seeing.
So, how about we pull together as a bit of a 10almonds community project?
- Step 1: add our email address to your contacts list, if you haven’t already
- Step 2: When you see an ad you’re curious about, select “share” (there is usually an option to share ads, but if not, feel free to screenshot or such)
- Step 3: Send the ad to us by email
We’ll do the rest! Whenever we have enough ads to review, we’ll do a special on the topic.
We will categorically not be able to do this without you, so please do join in—Many thanks in advance!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Yoga Safety: Simple Guidelines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I was wondering whether there were very simple, clear bullet points or instructions on things to be wary of in Yoga.❞
That’s quite a large topic, and not one that lends itself well to being conveyed in bullet points, but first we’ll share the article you sent us when sending this question:
Tips for Avoiding Yoga Injuries
…and next we’ll recommend the YouTube channel @livinleggings, whose videos we feature here from time to time. She (Liv) has a lot of good videos on problems/mistakes/injuries to avoid.
Here’s a great one to get you started:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
When And Why Do We Pick Up Our Phones?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The School of Life’s Alain de Botton makes the argument that—if we pay attention, if we keep track—there’s an understory to why we pick up our phones:
It’s not about information
Yes, our phones (or rather, the apps therein) are designed to addict us, to draw us back, to keep us scrolling and never let us go. We indeed seek out information like our ancestors once sought out berries; searching, encouraged by a small discovery, looking for more. The neurochemistry is similar.
But when we look at the “when” of picking up our phones, de Botton says, it tells a different story:
We pick them up not to find out what’s going on with the world, but rather specifically to not find out what’s going with ourselves. We pick them up to white out some anxiety we don’t want to examine, a line of thought we don’t want to go down, memories we don’t want to consider, futures we do not want to have to worry about.
And of course, phones do have a great educational potential, are an immensely powerful tool for accessing knowledge of many kinds—if only we can remain truly conscious while using them, and not take them as the new “opiate of the masses”.
De Botton bids us, when next we pick up our phone. ask a brave question:
“If I weren’t allowed to consult my phone right now, what might I need to think about?”
As for where from there? There’s more in the video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Further reading
Making Social Media Work For Your Mental Health
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: