How To *Really* Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Healthiest Habit-Building
Why was that book “Atomic Habits” called that? It wasn’t just because it’s a catchy title…
Habits are—much like atoms—things that are almost imperceptibly small, yet when stacked, they make up the substance of many much larger and more obvious things, and also contain an immense amount of potential power.
About that power…
Habits are the “compound interest” of natural human life. Every action we take, every decision we make, makes our life (often imperceptibly) better or worse. But getting even just 1% better or 1% worse at something every day? That’s going to not just add up over time… It’ll actively compound over time.
Habits will snowball one way or the other, good or bad. So, we want to control that snowball so that it works for us rather than against us.
Thus, we need to choose habits that are helpful to us, rather than those that are harmful to us. Top examples include:
- Making healthy food choices rather than unhealthy ones
- Moving our body regularly rather than being sedentary
- Having a good bedtime/morning routine rather than a daily chaotic blur
- Learning constantly rather than digging into old beliefs out of habit
- Forging healthy relationships rather than isolating ourselves
We all know that to make a habit stick, we need to practice it regularly, with opinions varying on how long it takes for something to become habit. Some say 21 days; some say 66. The number isn’t the important part!
What is important
You will never get to day 66, much less will you get to day 366, if you don’t first get to day 6 (New Year’s Resolutions, anyone?).
So in the early days especially, when the habit is most likely to get dropped, it’s critical to make the habit as easy as possible to form.
That means:
- The habit should be made as pleasant as possible
- (e.g. by making modifications to it if it’s not already intrinsically pleasant)
- The habit should take under 2 minutes to do at first
- (no matter if it takes longer than 2 minutes to be useful; it’ll never be useful if you don’t first get it to stick, so make your initial commitment only 2 minutes, just to get in the habit)
- The habit should have cues to remind you
- (as it’s not habit yet, you will need to either set a reminder on your phone, or leave a visual reminder, such as your workout clothes laid out ready for you in the morning, or a bowl of fruit in plain view where you spend a lot of time)
What gets measured, gets done
Streaks are a great way to do this. Habit-tracking apps help. Marks on a calendar or in a journal are also totally fine.
What can help especially, and that a lot of people don’t do, is to have a system of regular personal reviews—like a work “performance review”, but for oneself and one’s own life.
Set a reminder or write on the calendar / in your diary, to review monthly, or weekly if you prefer, such things as:
- How am I doing in the areas of life that are important to me?
- Have a list of the areas of life that are important to you, by the way, and genuinely reflect on each of them, e.g:
- Health
- Finances
- Relationships
- Learning
- Sleep
- Etc
- Have a list of the areas of life that are important to you, by the way, and genuinely reflect on each of them, e.g:
- What is working for me, and what isn’t working for me?
- What will I do better in this next month/week?
…and then do it!
Good luck, and may it all stack up in your favor!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Quit Like a Woman – by Holly Whitaker
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed “quit drinking” books before, so what makes this one different?
While others focus on the science of addiction and the tips and tricks of habit breaking/forming, this one is more about environmental factors, and that because of society being as it is, we as women often face different challenges when it comes to drinking (or not). Not necessarily easier or harder than men’s in this case, but different. And that sometimes calls for different methods to deal with them. This book explores those.
She also looks at such matters as how to quit alcohol when you’ve never stuck to a diet, and other such very down-to-earth topics, in a well-researched and non-preachy fashion.
Bottom line: if you’ve sometimes tried to quit drinking or even just to cut back, but found the deck stacked against you and things conspire to undermine your efforts, this book will give you a clearer path forward.
Click here to check out Quite Like A Woman, And Take Care Of Yourself!
Share This Post
-
The Immunostimulant Superfood
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eat These Greens!
Chlorella vulgaris, henceforth “chlorella”, is a simple green algae that has a lot of health benefits.
Note: most of the studies here are for Chlorella vulgaris specifically. However, some are for other species of the Chlorella genus, of which Chlorella vulgaris is by far the most common, hence the name (vulgaris = common). The relevant phytochemical properties appear to be the same regardless.
Superfood
While people generally take it as a supplement rather than a food item in any kind of bulk, it is more than 50% protein and contains all 9 essential amino acids.
As you might expect of a green superfood, it’s also full of many antioxidants, most of them carotenoids, and these pack a punch, for example against cancer:
It also has a lot of vitamins and minerals, and even omega-3.
Which latter also means it helps improve lipids and is thus particularly…
Heart healthy
❝Daily consumption of Chlorella supplements provided the potential of health benefits reducing serum lipid risk factors, mainly triglycerides and total cholesterol❞
Its heart-healthy benefits don’t stop at lipids though, and include blood pressure management, as in this study that found…
❝GABA-rich Chlorella significantly decreased high-normal blood pressure and borderline hypertension, and is a beneficial dietary supplement for prevention of the development of hypertension. ❞
About that GABA, if you’re curious about that, check out:
GABA Against Stress, Anxiety, & More
May remove heavy metals
We’re going with “may” for this one as we could only find animal studies so far (probably because most humans don’t have megadoses of heavy metals in them, which makes testing harder).
Here’s an example animal study, though:
Enhanced elimination of tissue methyl mercury in [Chlorella]-fed mice
Immunostimulant
This one’s clearer, for example in this 8-week study (with humans) that found…
❝Serum concentrations of interferon-γ (p<0.05) and interleukin-1β (p<0.001) significantly increased and that of interleukin-12 (p<0.1) tended to increase in the Chlorella group.
The increments of these cytokines after the intervention were significantly bigger in the Chlorella group than those in the placebo group. In addition, NK cell activities (%) were significantly increased in Chlorella group, but not in Placebo group.
The increments of NK cell activities (%) were also significantly bigger in the Chlorella group than the placebo group.
Additionally, changed levels of NK cell activity were positively correlated with those of serum interleukin-1β (r=0.280, p=0.047) and interferon-γ (r=0.271, p<0.005).❞
tl;dr = it boosts numerous different kinds of immune cells
PS, if you click though to the study, you may be momentarily alarmed by the first paragraph of the abstract that says “However, there were no direct evidences for the effect of Chlorella supplementation on immune/inflammation response in healthy humans“
this is from the “Background” section of the abstract, so what they are saying is “before we did this study, nobody had done this yet”.
So, be assured that the results are worthwhile and compelling.
Is it safe?
Based on the studies, it has a good safety profile. However, as it boosts the immune system, you may want to check with your doctor if you have an autoimmune disorder, and/or you are on immunosuppressants.
And in general, of course always check with your doctor/pharmacist if unsure about any potential drug interactions.
Want some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Health Tips for Males Too
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Articles are very informative and helpful. Maybe it’s me but things seem to lean more toward females. That being said don’t forget us males❞
Rest assured, we could never forget you! We try to make as much as possible of our content applicable to as many as possible of our readers, but of course not everything can be relevant for everyone.
This is, presumably, in response to our recent feature on menopausal health, because previous to that, our next-most-recent main feature that centred women’s health was a month ago—that was about breast cancer, and did have a section on breast cancer in men too. You might also enjoy the book we reviewed recently about prostate health, or our regular sponsor offering testosterone therapy. Please feel free to check out our articles on saw palmetto against male pattern baldness and BPH, as well as mental health issues that disproportionally affect men.
And of course, if you have specific questions/requests about men’s health (or any other health topic) we’re only ever an email away (or use the handy feedback widget, as you did to make this request)!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What’s the difference between shyness and social anxiety?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
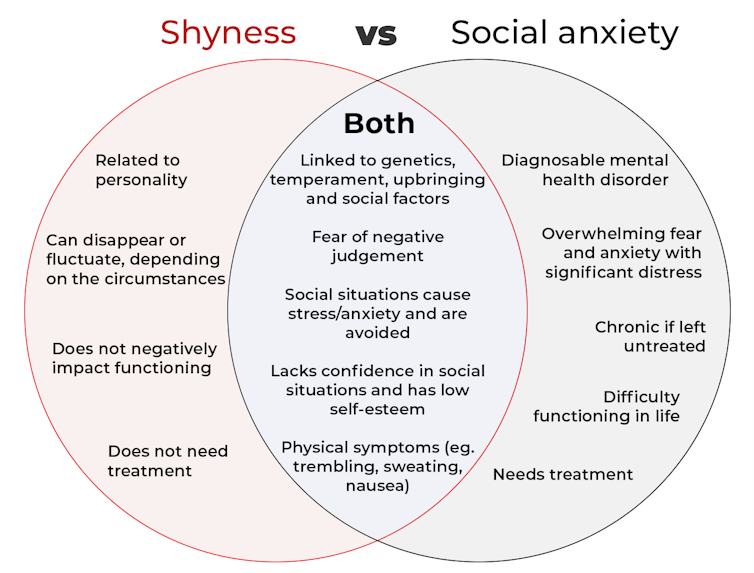
The terms “shyness” and “social anxiety” are often used interchangeably because they both involve feeling uncomfortable in social situations.
However, feeling shy, or having a shy personality, is not the same as experiencing social anxiety (short for “social anxiety disorder”).
Here are some of the similarities and differences, and what the distinction means.
pathdoc/Shutterstock How are they similar?
It can be normal to feel nervous or even stressed in new social situations or when interacting with new people. And everyone differs in how comfortable they feel when interacting with others.
For people who are shy or socially anxious, social situations can be very uncomfortable, stressful or even threatening. There can be a strong desire to avoid these situations.
People who are shy or socially anxious may respond with “flight” (by withdrawing from the situation or avoiding it entirely), “freeze” (by detaching themselves or feeling disconnected from their body), or “fawn” (by trying to appease or placate others).
A complex interaction of biological and environmental factors is also thought to influence the development of shyness and social anxiety.
For example, both shy children and adults with social anxiety have neural circuits that respond strongly to stressful social situations, such as being excluded or left out.
People who are shy or socially anxious commonly report physical symptoms of stress in certain situations, or even when anticipating them. These include sweating, blushing, trembling, an increased heart rate or hyperventilation.
How are they different?
Social anxiety is a diagnosable mental health condition and is an example of an anxiety disorder.
For people who struggle with social anxiety, social situations – including social interactions, being observed and performing in front of others – trigger intense fear or anxiety about being judged, criticised or rejected.
To be diagnosed with social anxiety disorder, social anxiety needs to be persistent (lasting more than six months) and have a significant negative impact on important areas of life such as work, school, relationships, and identity or sense of self.
Many adults with social anxiety report feeling shy, timid and lacking in confidence when they were a child. However, not all shy children go on to develop social anxiety. Also, feeling shy does not necessarily mean a person meets the criteria for social anxiety disorder.
People vary in how shy or outgoing they are, depending on where they are, who they are with and how comfortable they feel in the situation. This is particularly true for children, who sometimes appear reserved and shy with strangers and peers, and outgoing with known and trusted adults.
Individual differences in temperament, personality traits, early childhood experiences, family upbringing and environment, and parenting style, can also influence the extent to which people feel shy across social situations.
Not all shy children go on to develop social anxiety. 249 Anurak/Shutterstock However, people with social anxiety have overwhelming fears about embarrassing themselves or being negatively judged by others; they experience these fears consistently and across multiple social situations.
The intensity of this fear or anxiety often leads people to avoid situations. If avoiding a situation is not possible, they may engage in safety behaviours, such as looking at their phone, wearing sunglasses or rehearsing conversation topics.
The effect social anxiety can have on a person’s life can be far-reaching. It may include low self-esteem, breakdown of friendships or romantic relationships, difficulties pursuing and progressing in a career, and dropping out of study.
The impact this has on a person’s ability to lead a meaningful and fulfilling life, and the distress this causes, differentiates social anxiety from shyness.
Children can show similar signs or symptoms of social anxiety to adults. But they may also feel upset and teary, irritable, have temper tantrums, cling to their parents, or refuse to speak in certain situations.
If left untreated, social anxiety can set children and young people up for a future of missed opportunities, so early intervention is key. With professional and parental support, patience and guidance, children can be taught strategies to overcome social anxiety.
Why does the distinction matter?
Social anxiety disorder is a mental health condition that persists for people who do not receive adequate support or treatment.
Without treatment, it can lead to difficulties in education and at work, and in developing meaningful relationships.
Receiving a diagnosis of social anxiety disorder can be validating for some people as it recognises the level of distress and that its impact is more intense than shyness.
A diagnosis can also be an important first step in accessing appropriate, evidence-based treatment.
Different people have different support needs. However, clinical practice guidelines recommend cognitive-behavioural therapy (a kind of psychological therapy that teaches people practical coping skills). This is often used with exposure therapy (a kind of psychological therapy that helps people face their fears by breaking them down into a series of step-by-step activities). This combination is effective in-person, online and in brief treatments.
Treatment is available online as well as in-person. ImYanis/Shutterstock For more support or further reading
Online resources about social anxiety include:
- This Way Up’s online program for managing excessive shyness and fear of social situations
- Beyond Blue’s resources on social anxiety
- a guide to looking after yourself if you have social anxiety, from the Western Australian health department
- social anxiety online program for children and teens from the University of Queensland
- inroads, a self-guided online program for young adults who drink alcohol to manage their anxiety.
We thank the Black Dog Institute Lived Experience Advisory Network members for providing feedback and input for this article and our research.
Kayla Steele, Postdoctoral research fellow and clinical psychologist, UNSW Sydney and Jill Newby, Professor, NHMRC Emerging Leader & Clinical Psychologist, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dates vs Banana – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dates to banana, we picked the dates.
Why?
It was close, and bananas do have some strengths too! We pitted these two against each other as they’re both sweet fruits often used as a sweetening and consistency-altering ingredient in desserts and sweet snacks, so if you’re making a choice between them, here are the things to consider:
In terms of macros, dates have more than 3x the fiber, more than 2x the protein, and a little over 3x the carbs. You may be wondering how this adds up in terms of glycemic index: dates have the lower GI. So, we pick dates, here, for that reason and overall nutritional density too.
When it comes to vitamins, bananas have their moment, albeit barely: dates have more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, and K, while bananas have more of vitamins A, B6, C, E, and choline, making for a marginal victory for bananas in this category.
Looking at minerals next, however, it’s quite a different story: dates have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while bananas are not higher in any mineral. No, not even potassium, for which they are famous—dates have nearly 2x more potassium than bananas.
Adding up these sections makes for a clear win for dates in general!
Enjoy either/both, but dates are the more nutritious snack/ingredient.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
As Nuns Disappear, Many Catholic Hospitals Look More Like Megacorporations
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ST. LOUIS — Inside the more than 600 Catholic hospitals across the country, not a single nun can be found occupying a chief executive suite, according to the Catholic Health Association.
Nuns founded and led those hospitals in a mission to treat sick and poor people, but some were also shrewd business leaders. Sister Irene Kraus, a former chief executive of Daughters of Charity National Health System, was famous for coining the phrase “no margin, no mission.” It means hospitals must succeed — generating enough revenue to exceed expenses — to fulfill their original mission.
The Catholic Church still governs the care that can be delivered to millions in those hospitals each year, using religious directives to ban abortions and limit contraceptives, in vitro fertilization, and medical aid in dying.
But over time, that focus on margins led the hospitals to transform into behemoths that operate for-profit subsidiaries and pay their executives millions, according to hospital tax filings. These institutions, some of which are for-profit companies, now look more like other megacorporations than like the charities for the destitute of yesteryear.
The absence of nuns in the top roles raises the question, said M. Therese Lysaught, a Catholic moral theologist and professor at Loyola University Chicago: “What does it mean to be a Catholic hospital when the enterprise has been so deeply commodified?”
The St. Louis area serves as the de facto capital of Catholic hospital systems. Three of the largest are headquartered here, along with the Catholic hospital lobbying arm. Catholicism is deeply rooted in the region’s culture. During Pope John Paul II’s only U.S. stop in 1999, he led Mass downtown in a packed stadium of more than 100,000 people.
For a quarter century, Sister Mary Jean Ryan led SSM Health, one of those giant systems centered on St. Louis. Now retired, the 86-year-old said she was one of the last nuns in the nation to lead a Catholic hospital system.
Ryan grew up Catholic in Wisconsin and joined a convent while in nursing school in the 1960s, surprising her family. She admired the nuns she worked alongside and felt they were living out a higher purpose.
“They were very impressive,” she said. “Not that I necessarily liked all of them.”
Indeed, the nuns running hospitals defied the simplistic image often ascribed to them, wrote John Fialka in his book “Sisters: Catholic Nuns and the Making of America.”
“Their contributions to American culture are not small,” he wrote. “Ambitious women who had the skills and the stamina to build and run large institutions found the convent to be the first and, for a long time, the only outlet for their talents.”
This was certainly true for Ryan, who climbed the ranks, working her way from nurse to chief executive of SSM Health, which today has hospitals in Illinois, Missouri, Oklahoma, and Wisconsin.
The system was founded more than a century ago when five German nuns arrived in St. Louis with $5. Smallpox swept through the city and the Sisters of St. Mary walked the streets offering free care to the sick.
Their early foray grew into one of the largest Catholic health systems in the country, with annual revenue exceeding $10 billion, according to its 2023 audited financial report. SSM Health treats patients in 23 hospitals and co-owns a for-profit pharmacy benefit manager, Navitus, that coordinates prescriptions for 14 million people.
But Ryan, like many nuns in leadership roles in recent decades, found herself confronted with an existential crisis. As fewer women became nuns, she had to ensure the system’s future without them.
When Ron Levy, who is Jewish, started at SSM as an administrator, he declined to lead a prayer in a meeting, Ryan recounted in her book, “On Becoming Exceptional.”
“Ron, I’m not asking you to be Catholic,” she recalled telling him. “And I know you’ve only been here two weeks. So, if you’d like to make it three, I suggest you be prepared to pray the next time you’re asked.”
Levy went on to serve SSM for more than 30 years — praying from then on, Ryan wrote.
In Catholic hospitals, meetings are still likely to start with a prayer. Crucifixes often adorn buildings and patient rooms. Mission statements on the walls of SSM facilities remind patients: “We reveal the healing presence of God.”
Above all else, the Catholic faith calls on its hospitals to treat everyone regardless of race, religion, or ability to pay, said Diarmuid Rooney, a vice president of the Catholic Health Association. No nuns run the trade group’s member hospitals, according to the lobbying group. But the mission that compelled the nuns is “what compels us now,” Rooney said. “It’s not just words on a wall.”
The Catholic Health Association urges its hospitals to evaluate themselves every three years on whether they’re living up to Catholic teachings. It created a tool that weighs seven criteria, including how a hospital acts as an extension of the church and cares for poor and marginalized patients.
“We’re not relying on hearsay that the Catholic identity is alive and well in our facilities and hospitals,” Rooney said. “We can actually see on a scale where they are at.”
The association does not share the results with the public.
At SSM Health, “our Catholic identity is deeply and structurally ingrained” even with no nun at the helm, spokesperson Patrick Kampert said. The system reports to two boards. One functions as a typical business board of directors while the other ensures the system abides by the rules of the Catholic Church. The church requires the majority of that nine-member board to be Catholic. Three nuns currently serve on it; one is the chair.
Separately, SSM also is required to file an annual report with the Vatican detailing the ways, Kampert said, “we deepen our Catholic identity and further the healing ministry of Jesus.” SSM declined to provide copies of those reports.
From a business perspective, though, it’s hard to distinguish a Catholic hospital system like SSM from a secular one, said Ruth Hollenbeck, a former Anthem insurance executive who retired in 2018 after negotiating Missouri hospital contracts. In the contracts, she said, the difference amounted to a single paragraph stating that Catholic hospitals wouldn’t do anything contrary to the church’s directives.
To retain tax-exempt status under Internal Revenue Service rules, all nonprofit hospitals must provide a “benefit” to their communities such as free or reduced-price care for patients with low incomes. But the IRS provides a broad definition of what constitutes a community benefit, which gives hospitals wide latitude to justify not needing to pay taxes.
On average, the nation’s nonprofit hospitals reported that 15.5% of their total annual expenses were for community benefits in 2020, the latest figure available from the American Hospital Association.
SSM Health, including all of its subsidiaries, spent proportionately far less than the association’s average for individual hospitals, allocating roughly the same share of its annual expenses to community efforts over three years: 5.1% in 2020, 4.5% in 2021, and 4.9% in 2022, according to a KFF Health News analysis of its most recent publicly available IRS filings and audited financial statements.
A separate analysis from the Lown Institute think tank placed five Catholic systems — including the St. Louis region’s Ascension — on its list of the 10 health systems with the largest “fair share” deficits, which means receiving more in tax breaks than what they spent on the community. And Lown said three St. Louis-area Catholic health systems — Ascension, SSM Health, and Mercy — had fair share deficits of $614 million, $235 million, and $92 million, respectively, in the 2021 fiscal year.
Ascension, Mercy, and SSM disputed Lown’s methodology, arguing it doesn’t take into account the gap between the payments they receive for Medicaid patients and the cost of delivering their care. The IRS filings do.
But, Kampert said, many of the benefits SSM provides aren’t reflected in its IRS filings either. The forms reflect “very simplistic calculations” and do not accurately represent the health system’s true impact on the community, he said.
Today, SSM Health is led by longtime business executive Laura Kaiser. Her compensation in 2022 totaled $8.4 million, including deferred payments, according to its IRS filing. Kampert defended the amount as necessary “to retain and attract the most qualified” candidate.
By contrast, SSM never paid Ryan a salary, giving instead an annual contribution to her convent of less than $2 million a year, according to some tax filings from her long tenure. “I didn’t join the convent to earn money,” Ryan said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: