Is Your Gut Leading You Into Osteoporosis?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bacterioides Vulgatus & Bone Health
We’ve talked before about the importance of gut health:
And we’ve shared quite some information and resources on osteoporosis:
- The Bare-bones Truth: Osteoporosis Mythbusting
- Osteoporosis Exercises (What To Do, And What To Avoid)
- Vit D + Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
- Collagen For Bones: We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
- Which Osteoporosis Medication, If Any, Is Right For You?
How the two are connected
A recent study looked at Bacterioides vulgatus, a very common gut bacterium, and found that it suppresses the gut’s production of valeric acid, a short-chain fatty acid that enhances bone density:
❝For the study, researchers analyzed the gut bacteria of more than 500 peri- and post-menopausal women in China and further confirmed the link between B. vulgatus and a loss of bone density in a smaller cohort of non-Hispanic White women in the United States.❞
Pop-sci source: Does gut bacteria cause osteoporosis?
The study didn’t stop there, though. They proceeded to test, with a rodent model, the effect of giving them either:
- more B. vulgatus, or
- valeric acid supplements
The results of this were as expected:
- Those who were given more B. vulgatus got worse bone microstructure
- Those who were given valeric acid supplements got stronger bones overall
Study source: Gut microbiota impacts bone via Bacteroides vulgatus-valeric acid-related pathways
Where can I get valeric acid?
We couldn’t find a handy supplement for this, but it is in many foods, including avocados, blueberries, cocoa beans, and an assortment of birds.
Click here to see a more extensive food list (you’ll need to scroll down a little)
Bonus: if you happen to be on HRT in the form of Estradiol valerate (e.g: Progynova), then that “valerate” is an ester of valeric acid, that your body can metabolize and use as such.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can We Drink To Good Health?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Can we drink to good health?
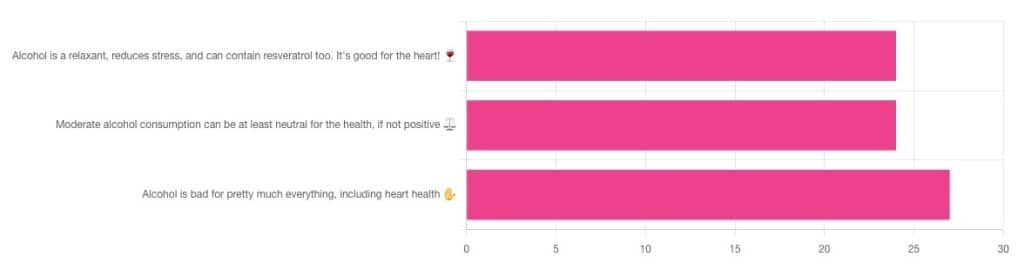
We asked you for your thoughts on alcohol and heart health, and we got quite an even spread of results!
If perchance that’s too tiny to read, the figures were:
- 32% voted for “Alcohol is a relaxant, reduces stress, and can contain resveratrol too. It’s good for the heart!”
- 32% voted for: “Moderate alcohol consumption can be at least neutral for the health, if not positive ⚖️”
- 36% voted for: “Alcohol is bad for pretty much everything, including heart health ✋”
One subscriber who voted for “Alcohol is a relaxant, reduces stress, and can contain resveratrol too. It’s good for the heart!” added the following thoughts:
❝While it isn’t necessary to consume alcohol, moderate amounts can be beneficial and contribute to well-being through social activity, celebrations, etc.❞
That’s an interesting point, and definitely many people do see alcohol that way! Of course, that does not mean that one will find no social activities, celebrations, etc, in parts of the world where alcohol consumption is uncommon. Indeed, in India, wedding parties where no alcohol is consumed can go on for days!
But, “we live in a society” and all that, and while we’re a health newsletter not a social issues newsletter, it’d be remiss of us to not acknowledge the importance of socialization for good mental health—and thus the rest of our health too.
So, if indeed all our friends and family drink alcohol, it can certainly make abstaining more of a challenge.
On that note, let’s take a moment to consider “The French Paradox” (an observation of a low prevalence of ischemic heart disease despite high intakes of saturated fat, a phenomenon accredited to the consumption of red wine).
As it happens, a comprehensive review in “Circulation”, a cardiovascular health journal, has suggested the French Paradox may not be so paradoxical after all.
Research suggests it has more to do with other lifestyle factors (and historic under-reporting of cardiovascular disease by French doctors), which would explain why Japan has lower rates of heart disease, despite drinking little wine, and more beer and spirits.
So, our subscriber’s note may not be completely without reason! It’s just about the party, not the alcohol.
One subscriber who voted for “Moderate alcohol consumption can be at least neutral for the health, if not positive ⚖️” wrote:
❝Keeping in mind, moderate means one glass of wine for women a day and two for men. Hard alcohol doesn’t have the same heart benefits as wine❞
That is indeed the guideline according to some health bodies!
In other places with different guiding advisory bodies, that’s been dropped down to one a day for everyone (the science may be universal, but how government institutions interpret that is not).
About that wine… Specifically, red wine, for its resveratrol content:
While there are polyphenols such as resveratrol in red wine that could boost heart health, there’s so little per glass that you may need 100–1000 glasses to get the dosage that provides benefits in mouse studies. If you’re not a mouse, you might even need more.
To this end, many people prefer resveratrol supplementation. ← link is to an example product, but there are plenty more so feel free to shop around
A subscriber who voted for “Alcohol is bad for pretty much everything, including heart health ✋” says:
❝New guidelines suggest 1 to 2 drinks a week are okay but the less the better.❞
If you haven’t heard these new guidelines, we’ll mention again: every government has its own official bodies and guidelines so perhaps your local guidelines differ, but for example here’s what that World Health Organization has to say (as of January this year):
WHO: No level of alcohol consumption is safe for our health
So, whom to believe? The governments who hopefully consider the welfare of their citizenry more important than the tax dollars from alcohol sales, or the World Health Organization?
It’s a tough one, but we’ll always err on the side of the science.
Share This Post
-
Prevention Is Better Than Cure
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Preventative healthcare is the theme this week:
New year, new risks
The start of a new year is a great time to update adult vaccinations, including the flu shot, any COVID-19 boosters, and vaccines for pneumonia, shingles, and tetanus—when was your last booster, after all? Vaccination recommendations vary by age and health conditions, so do check what’s appropriate in your case. Key vaccines include the pneumonia vaccine for those 65 and older, the shingles vaccine for adults over 50, and the Tdap vaccine every 10 years to protect against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (whooping cough), especially for new parents and grandparents, to protect infants:
Read in full: Why it’s important to update adult vaccinations for a new year
Related: The Truth About Vaccines
The heart-healthiest swap you can do
Based on a large (n=202,863, of which 160,123 women and 42,740 men) dataset, a higher plant-to-animal protein ratio is associated with significantly lower risks of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and coronary artery disease (CAD), with diets lower in meat (especially if lower in red meat) and instead rich in plant-based proteins like legumes, nuts, and whole grains reducing CVD risk by 19% and coronary artery disease risk by 27%. Which is quite considerable.
Substituting even small amounts of animal protein (especially if it’s red meat) with plant protein further enhances heart health:
Read in full: Higher plant-to-animal protein ratio linked to lower risk for CVD, CAD among U.S. adults
Related: Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
Let’s keep pan-resistant superbugs at bay
Researchers want to warn us about the threat of pan-resistant bacteria, which could render all known antibiotics ineffective, leading to a sharp rise in global infection-related deaths.
To be clear, we don’t have anything pan-resistant yet, but antibiotic-resistant superbugs are getting close, and in the long term, are likely to win the evolutionary arms race if we don’t change things to diverge considerably from our current path. Modeling a hypothetical pan-resistant E. coli strain, researchers predicted U.S. sepsis deaths could increase 18- to 46-fold within five years of its emergence.
The study calls for urgent action, including stricter antibiotic stewardship, new drug development, and monitoring technologies, emphasizing that without intervention, the global impact could be catastrophic:
Read in full: A public health emergency is waiting at the bottom of the antibiotic resistance cliff
Related: Stop Sabotaging Your Immune System ← see also (linked therein), 4 ways antibiotics can kill you
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Insights into Osteoporosis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I would like to see some articles on osteoporosis❞
You might enjoy this mythbusting main feature we did a few weeks ago!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Dopa-Bean
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mucuna pruriens, also called the “magic velvet bean”, is an established herbal drug used for the management of male infertility, nervous disorders, and also as an aphrodisiac:
The Magic Velvet Bean of Mucuna pruriens
How it works is more interesting than that, though.
It’s about the dopamine
M. pruriens contains levodopa (L-dopa). That’s right, the same as the dopaminergic medication most often prescribed for Parkinson’s disease. Furthermore, it might even be better than synthetic L-dopa, because:
❝M. pruriens seed extract demonstrated acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity, while synthetic L-dopa enhanced the activity of the enzyme. It can be concluded that the administration of M. pruriens seed might be effective in protecting the brain against neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases.
M. pruriens seed extract containing L-dopa has shown less acetylcholinesterase activity stimulation compared with L-dopa, suggesting that the extract might have a superior benefit for use in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.❞
~ Dr. Narisa Kamkaen et al.
Indeed, it has been tested specifically in (human!) Parkinson’s disease patients, which RCT found:
❝The rapid onset of action and longer on time without concomitant increase in dyskinesias on mucuna seed powder formulation suggest that this natural source of l-dopa might possess advantages over conventional l-dopa preparations in the long term management of Parkinson’s disease❞
~ Dr. Regina Katzenschlager et al.
Read more: Mucuna pruriens in Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind clinical and pharmacological study
Beyond Parkinson’s disease
M. pruriens has also been tested and found beneficial in cases of disease other than Parkinson’s, thus:
Mucuna pruriens in Parkinson’s and in some other diseases: recent advancement and future prospective
…but the science is less well-established for things not generally considered related to dopamine, such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiometabolic disorders.
Note, however, that the science for it being neuroprotective is rather stronger.
Against depression
Depression can have many causes, and (especially on a neurological level) diverse presentations. As such, sometimes what works for one person’s depression won’t touch another person’s, because the disease and treatment are about completely different neurotransmitter dysregulations. So, if a person’s depression is due to a shortage of serotonin, for example, then perking up the dopamine won’t help much, and vice versa. See also:
Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
When it comes to M. pruriens and antidepressant activity, then predictably it will be more likely to help if your depression is due to too little dopamine. Note that this means that even if your depression is dopamine-based, but the problem is with your dopamine receptors and not the actual levels of dopamine, then this may not help so much, depending on what else you have going on in there.
The science for M. pruriens and depression is young, and we only found non-human animal studies so far, for example:
In summary
It’s good against Parkinson’s in particular and is good against neurodegeneration in general.
It may be good against depression, depending on the kind of depression you have.
Is it safe?
That’s a great question! And the answer is: it depends. For most people, in moderation, it should be fine (but, see our usual legal/medical disclaimer). Definitely don’t take it if you have bipolar disorder or any kind of schizoid/psychotic disorder; it is likely to trigger a manic/psychotic episode if you do.
For more on this, we discussed it (pertaining to L-dopa in general, not M. pruriens specifically) at greater length here:
An Accessible New Development Against Alzheimer’s ← scroll down to the heading that reads “Is there a catch?”
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Protein vs Sarcopenia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Protein vs Sarcopenia
This is Dr. Gabrielle Lyon. A medical doctor, she’s board-certified in family medicine, and has also engaged in research and clinical practice in the fields of geriatrics and nutritional sciences.
A quick note…
We’re going to be talking a bit about protein metabolism today, and it’s worth noting that Dr. Lyon personally is vehemently against vegetarianism/veganism, and considers red meat to be healthy.
Scientific consensus on the other hand, holds that vegetarianism and veganism are fine for most people if pursued in an informed and mindful fashion, that white meat and fish are also fine for most people, and red meat is simply not.
If you’d like a recap on the science of any of that:
- Protein: How Much Do We Need, Really?
- Plant vs Animal Protein: Diversity is Key
- Do We Need Animal Products to be Healthy?
Nevertheless, if we look at the science that she provides, the advice is sound when applied to protein in general and without an undue focus on red meat.
How much protein is enough?
In our article linked above, we gave 1–2g/kg/day
Dr. Lyons gives the more specific 1.6g/kg/day for adults older than 40 (this is where sarcopenia often begins!) and laments that many sources offer 0.8g/kg.
To be clear, that “per kilogram” means per kilogram of your bodyweight. For Americans, this means dividing lbs by 2.2 to get the kg figure.
Why so much protein?
Protein is needed to rebuild not just our muscles, but also our bones, joint tissues, and various other parts of us:
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
Additionally, our muscles themselves are important for far more than just moving us (and other things) around.
As Dr. Lyon explains: sarcopenia, the (usually age-related) loss of muscle mass, does more than just make us frail; it also messes up our metabolism, which in turn messes up… Everything else, really. Because everything depends on that.
This is because our muscles themselves use a lot of our energy, and/but also store energy as glycogen, so having less of them means:
- getting a slower metabolism
- the energy that can’t be stored in muscle tissue gets stored somewhere else (like the liver, and/or visceral fat)
So, while for example the correlation between maintaining strong muscles and avoiding non-alcoholic fatty liver disease may not be immediately obvious, it is clear when one follows the metabolic trail to its inevitable conclusion.
Same goes for avoiding diabetes, heart disease, and suchlike, though those things are a little more intuitive.
How can we get so much protein?
It can seem daunting at first to get so much protein if you’re not used to it, especially as protein is an appetite suppressant, so you’ll feel full sooner.
It can especially seem daunting to get so much protein if you’re trying to avoid too many carbs, and here’s where Dr. Lyon’s anti-vegetarianism does have a point: it’s harder to get lean protein without meat/fish.
That said, “harder” does not mean “impossible” and even she acknowledges that lentils are great for this.
If you’re not vegetarian or vegan, collagen supplementation is a good way to make up any shortfall, by the way.
And for everyone, there are protein supplements available if we want them (usually based on whey protein or soy protein)
Anything else we need to do?
Yes! Eating protein means nothing if you don’t do any resistance work to build and maintain muscle. This can take various forms, and Dr. Lyon recommends lifting weights and/or doing bodyweight resistance training (calisthenics, Pilates, etc).
Here are some previous articles of ours, consistent with the above:
- Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
- Overdone It? How To Speed Up Recovery After Exercise
- How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
- Exercises To Do (And Ones To Avoid) If You Have Osteoporosis
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fruit, Fiber, & Leafy Greens… On A Low-FODMAP Diet!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fiber For FODMAP-Avoiders
First, let’s quickly cover: what are FODMAPs?
FODMAPs are fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols.
In plainer English: they’re carbohydrates that are resistant to digestion.
This is, for most people most of the time, a good thing, for example:
When Is A Fiber Not A Fiber? When It’s A Resistant Starch.
Not for everyone…
However, if you have inflammatory bowel syndrome (IBS), including ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, or similar, then suddenly a lot of common dietary advice gets flipped on its head:
While digestion-resistant carbohydrates making it to the end parts of our digestive tract are good for our bacteria there, in the case of people with IBS or similar, it can be a bit too good for our bacteria there.
Which can mean gas (a natural by-product of bacterial respiration) accumulation, discomfort, water retention (as the pseudo-fiber draws water in and keeps it), and other related symptoms, causing discomfort, and potentially disease such as diarrhea.
Again: for most people this is not so (usually: quite the opposite; resistant starches improve things down there), but for those for whom it’s a thing, it’s a Big Bad Thing™.
Hold the veg? Hold your horses.
A common knee-jerk reaction is “I will avoid fruit and veg, then”.
Superficially, this can work, as many fruit & veg are high in FODMAPs (as are fermented dairy products, by the way).
However, a diet free from fruit and veg is not going to be healthy in any sustainable fashion.
There are, however, options for low-FODMAP fruit & veg, such as:
Fruits: bananas (if not overripe), kiwi, grapefruit, lemons, limes, melons, oranges, passionfruit, strawberries
Vegetables: alfalfa, bell peppers, bok choy, carrots, celery, cucumbers, eggplant, green beans, kale, lettuce, olives, parsnips, potatoes (and sweet potatoes, yams etc), radishes, spinach, squash, tomatoes*, turnips, zucchini
*our stance: botanically it’s a fruit, but culinarily it’s a vegetable.
For more on the science of this, check out:
Strategies for Producing Low FODMAPs Foodstuffs: Challenges and Perspectives ← table 2 is particularly informative when it comes to the above examples, and table 3 will advise about…
Bonus
Grains: oats, quinoa, rice, tapioca
…and wheat if the conditions in table 3 (linked above) are satisfied
(worth mentioning since grains also get a bad press when it comes to IBS, but that’s mostly because of wheat)
See also: Gluten: What’s The Truth?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: