Delay Ageing – by Dr. Colin Rose
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Note: the title is spelled that way because it is British English. We generally write in US English here at 10almonds, but we’ll first quote directly from Dr. Rose as written:
❝I have written Delay Ageing because there is some very important recent University research on ageing and age related illness that deserves to be made accessible to a general audience.❞
What is this research? Well, there’s quite a lot over its 300-odd pages (exact number depends on the edition and whether we count end matter), and most of it is tweaks and refinements on things with which you’ll probably be at least brushingly familiar if you’re a regular 10almonds reader.
Dr. Rose addresses the nine hallmarks of aging, of which there are ten, ranging from such things as “telomeres get shorter” and “DNA accumulates damage”, to “stem cells become exhausted” and “cells fail to communicate properly”, and asks the question “what if we were to target all these things simultaneously?”.
Rather than going for drugs on drugs on drugs (half of them to deal with undesired side effects of the previous ones), Dr. Cole leaves no stone unturned to find lifestyle interventions that will improve each of these, even if just a little. Because, all those “little” improvements add up and even compound, and on the flipside, mean that factors of aging aren’t adding up and compounding so much or so quickly anymore.
The rather broad umbrella of “lifestyle interventions” obviously includes food under its auspices, and with it, nutraceuticals. So to give one example, if you’re taking a fisetin supplement (a natural senolytic agent), you’ll find science vindicating that here. And much more.
The style is… Less pop-science and more “textbook written for laypersons”, and you may be thinking “isn’t that the same?” and the difference is that the textbook has a lot less polish and finesse, but often more precise information.
Bottom line: if you’d like to combat aging on 10 different fronts with easily implementable lifestyle interventions, and know exactly what is doing what and how, then this is the book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
This salt alternative could help reduce blood pressure. So why are so few people using it?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One in three Australian adults has high blood pressure (hypertension). Excess salt (sodium) increases the risk of high blood pressure so everyone with hypertension is advised to reduce salt in their diet.
But despite decades of strong recommendations we have failed to get Australians to cut their intake. It’s hard for people to change the way they cook, season their food differently, pick low-salt foods off the supermarket shelves and accept a less salty taste.
Now there is a simple and effective solution: potassium-enriched salt. It can be used just like regular salt and most people don’t notice any important difference in taste.
Switching to potassium-enriched salt is feasible in a way that cutting salt intake is not. Our new research concludes clinical guidelines for hypertension should give patients clear recommendations to switch.
What is potassium-enriched salt?
Potassium-enriched salts replace some of the sodium chloride that makes up regular salt with potassium chloride. They’re also called low-sodium salt, potassium salt, heart salt, mineral salt, or sodium-reduced salt.
Potassium chloride looks the same as sodium chloride and tastes very similar.
Potassium-enriched salt works to lower blood pressure not only because it reduces sodium intake but also because it increases potassium intake. Insufficient potassium, which mostly comes from fruit and vegetables, is another big cause of high blood pressure.
What is the evidence?
We have strong evidence from a randomised trial of 20,995 people that switching to potassium-enriched salt lowers blood pressure and reduces the risks of stroke, heart attacks and early death. The participants had a history of stroke or were 60 years of age or older and had high blood pressure.
An overview of 21 other studies suggests much of the world’s population could benefit from potassium-enriched salt.
The World Health Organisation’s 2023 global report on hypertension highlighted potassium-enriched salt as an “affordable strategy” to reduce blood pressure and prevent cardiovascular events such as strokes.
What should clinical guidelines say?
We teamed up with researchers from the United States, Australia, Japan, South Africa and India to review 32 clinical guidelines for managing high blood pressure across the world. Our findings are published today in the American Heart Association’s journal, Hypertension.
We found current guidelines don’t give clear and consistent advice on using potassium-enriched salt.
While many guidelines recommend increasing dietary potassium intake, and all refer to reducing sodium intake, only two guidelines – the Chinese and European – recommend using potassium-enriched salt.
To help guidelines reflect the latest evidence, we suggested specific wording which could be adopted in Australia and around the world:
Recommended wording for guidance about the use of potassium-enriched salt in clinical management guidelines. Why do so few people use it?
Most people are unaware of how much salt they eat or the health issues it can cause. Few people know a simple switch to potassium-enriched salt can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of a stroke and heart disease.
Limited availability is another challenge. Several Australian retailers stock potassium-enriched salt but there is usually only one brand available, and it is often on the bottom shelf or in a special food aisle.
Potassium-enriched salts also cost more than regular salt, though it’s still low cost compared to most other foods, and not as expensive as many fancy salts now available.
It looks and tastes like normal salt.
Jimmy Dean/UnsplashA 2021 review found potassium-enriched salts were marketed in only 47 countries and those were mostly high-income countries. Prices ranged from the same as regular salt to almost 15 times greater.
Even though generally more expensive, potassium-enriched salt has the potential to be highly cost effective for disease prevention.
Preventing harm
A frequently raised concern about using potassium-enriched salt is the risk of high blood potassium levels (hyperkalemia) in the approximately 2% of the population with serious kidney disease.
People with serious kidney disease are already advised to avoid regular salt and to avoid foods high in potassium.
No harm from potassium-enriched salt has been recorded in any trial done to date, but all studies were done in a clinical setting with specific guidance for people with kidney disease.
Our current priority is to get people being managed for hypertension to use potassium-enriched salt because health-care providers can advise against its use in people at risk of hyperkalemia.
In some countries, potassium-enriched salt is recommended to the entire community because the potential benefits are so large. A modelling study showed almost half a million strokes and heart attacks would be averted every year in China if the population switched to potassium-enriched salt.
What will happen next?
In 2022, the health minister launched the National Hypertension Taskforce, which aims to improve blood pressure control rates from 32% to 70% by 2030 in Australia.
Potassium-enriched salt can play a key role in achieving this. We are working with the taskforce to update Australian hypertension management guidelines, and to promote the new guidelines to health professionals.
In parallel, we need potassium-enriched salt to be more accessible. We are engaging stakeholders to increase the availability of these products nationwide.
The world has already changed its salt supply once: from regular salt to iodised salt. Iodisation efforts began in the 1920s and took the best part of 100 years to achieve traction. Salt iodisation is a key public health achievement of the last century preventing goitre (a condition where your thyroid gland grows larger) and enhancing educational outcomes for millions of the poorest children in the world, as iodine is essential for normal growth and brain development.
The next switch to iodised and potassium-enriched salt offers at least the same potential for global health gains. But we need to make it happen in a fraction of the time.
Xiaoyue Xu (Luna), Scientia Lecturer, UNSW Sydney; Alta Schutte, SHARP Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine, UNSW Sydney, and Bruce Neal, Executive Director, George Institute Australia, George Institute for Global Health
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
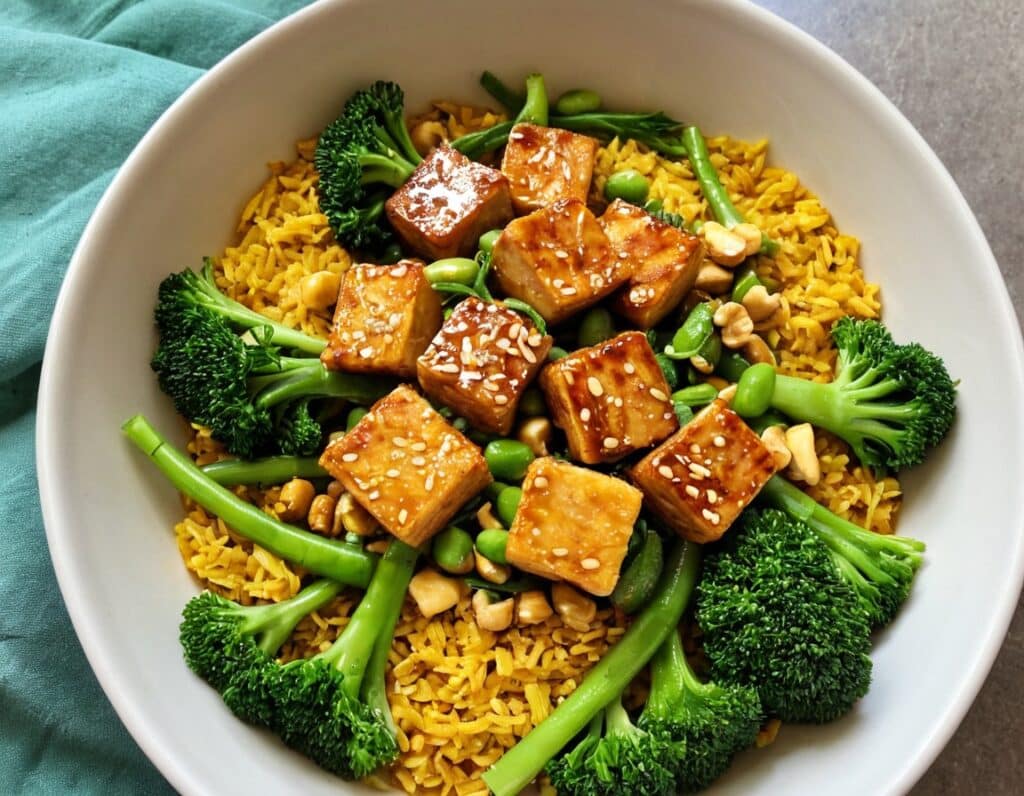
Sesame & Peanut Tofu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Yesterday we learned how to elevate tofu from “nutrition” to “nutritious tasty snack” with our Basic Baked Tofu recipe; today we’re expanding on that, to take it from “nutritious tasty snack” to “very respectable meal”.
You will need
For the tofu:
- The Basic Baked Tofu that we made yesterday (consider making this to be “step zero” of today’s recipe if you don’t already have a portion in the fridge)
For the sauce:
- ⅓ cup peanut butter, ideally with no added sugar or salt (if allergic to peanuts specifically, use almond butter; if allergic to nuts generally, use tahini)
- ¼ bulb garlic, grated or crushed
- 1 tbsp tamarind paste
- 1½ tbsp tamari sauce (or low-sodium soy sauce, if a substitution is necessary)
- 1 tbsp sambal oelek (or sriracha sauce, if a substitution is necessary)
- 1 tsp ground coriander
- 1 tsp ground black pepper
- ½ tsp ground sweet cinnamon
- ½ tsp MSG (or else omit; do not substitute with salt in this case unless you have a particular craving)
- zest of 1 lime
For the vegetables:
- 14 oz broccolini / tenderstem broccoli, thick ends trimmed (failing that, any broccoli)
- 6 oz shelled edamame
- 1½ tsp toasted sesame oil
For serving:
- 4 cups cooked rice (we recommend our Tasty Versatile Rice recipe)
- ½ cup raw cashews, soaked in hot water for at least 5 minutes and then drained (if allergic, substitute cooked chickpeas, rinsed and drained)
- 1 tbsp toasted sesame seeds
- 1 handful chopped cilantro, unless you have the “this tastes like soap” gene, in which case substitute chopped parsley
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the sauce ingredients in a bowl and whisk well (or use a blender if you have one that’s comfortable with this relatively small quantity of ingredients). Taste it, and adjust the ingredient ratios if you’d like more saltiness, sweetness, sourness, spiciness, umami.
2) Prepare a bowl with cold water and some ice. Steam the broccolini and edamame for about 3 minutes; as soon as they become tender, dump them into the ice bathe to halt the cooking process. Let them chill for a few minutes, then drain, dry, and toss in the sesame oil.
3) Reheat the tofu if necessary (an air fryer is great for this), and then combine with half of the sauce in a bowl, tossing gently to coat well.
4) Add a little extra water to the remaining sauce, enough to make it pourable, whisking to an even consistency.
5) Assemble; do it per your preference, but we recommend the order: rice, vegetables, tofu, cashews, sauce, sesame seeds, herbs.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tofu vs Seitan – Which is Healthier?
- Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
- Sweet Cinnamon vs Regular Cinnamon – Which is Healthier?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Finding Peace at the End of Life – by Henry Fersko-Weiss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is not the most cheery book we’ve reviewed, but it is an important one. From its first chapter, with “a tale of two deaths”, one that went as well as can be reasonably expected, and the other one not so much, it presents a lot of choices.
The book is not prescriptive in its advice regarding how to deal with these choices, but rather, investigative. It’s thought-provoking, and asks questions—tacitly and overtly.
While the subtitle says “for families and caregivers”, it’s as much worth when it comes to managing one’s own mortality, too, by the way.
As for the scope of the book, it covers everything from terminal diagnosis, through the last part of life, to the death itself, to all that goes on shortly afterwards.
Stylewise, it’s… We’d call it “easy-reading” for style, but obviously the content is very heavy, so you might want to read it a bit at a time anyway, depending on how sensitive to such topics you are.
Bottom line: this book is not exactly a fun read, but it’s a very worthwhile one, and a good way to avoid regrets later.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
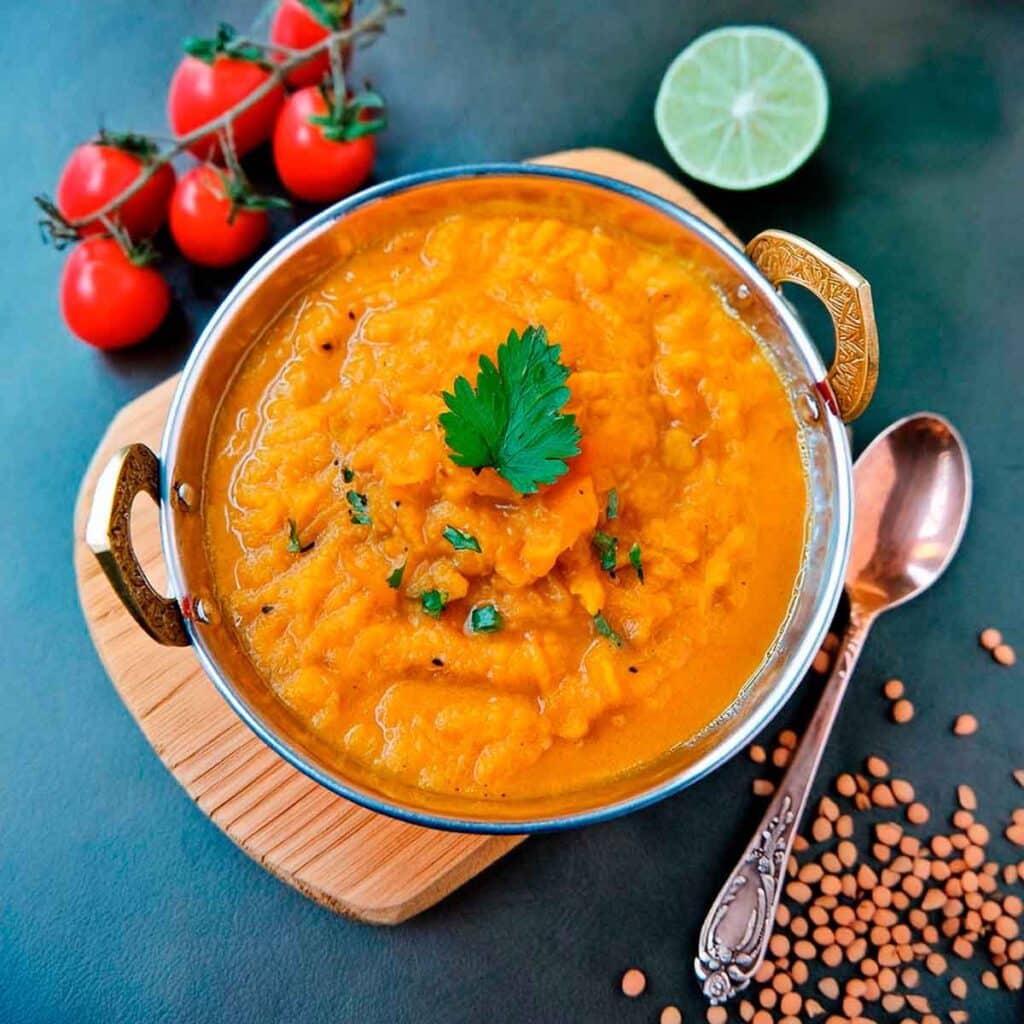
Delicious Daily Daal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You’re not obliged to eat this every day, but you might want to. The reason we called this one this, is because it’s a super simple recipe (don’t be put off by the long ingredients list; it’s mostly spices making it look long) which, after you’ve done it a couple of times, you could practically do it in your sleep quickly and easily.
The name “lentil daal” is a bit like “naan bread”—a redundant tautology repeated more than once unnecessarily, but it helps for international clarity. The dish is usually served with naan, by the way, and rice. We don’t have room for those today, maybe we’ll do them another day; for now, you can just cook rice how you normally do, and buy naan if necessary.
Writer’s note: I love strong flavors; many people don’t. For this reason I’m going to give a “basic” version. Please feel free to multiply the spices if you feel so inclined. Where I give “one teaspoon” of a spice below, I’d use a tablespoon at home. Chili peppers can vary in heat a lot even within the same type, so what I do for any given batch is taste one (raw), judge the heat, and use an appropriate number of peppers accordingly. If you don’t want to do that, I suggest just guessing low (as per the instructions below) and if you find at the end you want more heat, you can always stir in a little hot sauce. I know that sounds heretical, but at the end of the day, the primary goal of cooking is to have the meal you want at the end of it.
You will need
- 1 1/2 cups red lentils
- 1 large onion, chopped
- 1 large bulb garlic, minced
- 1 oz ginger, grated
- 2 hot peppers (e.g. serrano), chopped
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp ground coriander
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- 1 tsp garam masala (this is also ground, but it doesn’t come any other way)
- 1 tsp chili flakes (omit if you’re not a fan of heat)
- 2 tsp cracked black pepper
- 1 tsp salt ← I wouldn’t recommend multiplying this one unless later, to taste. In fact, instead of 1 tsp salt I use 2 tsp MSG, which has less sodium than 1 tsp salt. But “1 tsp salt” is the “easy to find in the store” version.
- 2 large or 3 small tomatoes, chopped (or 1 can chopped tomatoes)
- 2 shallots, thinly sliced
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 tsp mustard seeds
- 1 tsp coriander seeds
- 1 tsp black peppercorns
- 1 lime
- 1/2 cup fresh cilantro, or if you have the “that tastes like soap” gene, parsley, chopped
- Coconut oil for cooking (if you don’t like coconut, consider springing for avocado oil—if you use olive oil, it’ll add an olivey taste which changes the dish a lot; not inherently bad, but it feels a lot less like traditional daal; seed oils are less healthy and we don’t recommend them; ghee is a traditional option and not bad in moderation, but not as healthy as the oils we mentioned first)
- Water for cooking the lentils
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) In a saucepan, boil water and add the lentils; let them simmer while doing the next things.
2) Sauté the onions until translucent. This should only take a few minutes.
3) Add the garlic, ginger, and hot peppers, and keep stirring for another couple of minutes.
4) Add the ground spices (cumin, coriander, turmeric, garam masala) chili flakes, and cracked black pepper, as well as the salt or MSG if using (not both), and stir them in quickly but thoroughly.
For the next step, you may need to transfer to larger pan if your sauté pan isn’t big enough to take the volume; if so, that’s fine, the sauté has done its job and can have a rest now. If your sauté pan is big enough, just carry on in the same pan; this is perfect.
5) Add the lentils with the water you cooked them in (there might not be much water left now, as the lentils will have absorbed a lot of it; this is fine) as well as the chopped tomatoes.
6) Simmer until it has the consistency of a very thick sauce (you can add a splash more water here and there if it seems to need more). In the West it’s common to serve lentils “al dente”, but in the East it’s usual to (for dishes like this) cook them until they start to
7) Add the juice of at least 1/2 of your lime, or the whole lime if you feel so inclined.
8) In a pre-heated skillet, flash-fry the sliced shallots and the seeds (cumin, coriander, mustard, black peppercorns) at the hottest temperature you can muster. Don’t worry if the oil smokes; we’re only going to be at this tadka-making stage for a moment and nothing will stick provided you keep it moving. When the seeds start popping, it’s ready. Add it all to the big pan and stir in.
9) Add the cilantro-or-parsley garnish once you’re ready to serve.
Enjoy!
Learn more
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- How Much Spice Is Right?
- Tasty Polyphenols
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To En-Joy Life (With Long-Term Benefits)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
New Year’s Dissolutions?
We have talked previously about:
The Science Of New Year’s Pre-Resolutions
…and here we are now at the end of the first week of January; how’s it going?
Hopefully, based on that article, it’s been going just great since December! For most people, statistically speaking, it hasn’t.
Around now is typically when many people enter the “bargaining” stage of New Year’s Resolutions, which at this point are often in serious danger of becoming New Year’s Dissolutions.
What’s important, really?
When trying to juggle potentially too many new items, it’s important to be able to decide where to focus one’s efforts in the case of needing to drop a ball or two.
First, the laziest way…
The path of least resistance
This is perhaps most people’s go-to. It, without too much thought, drops whatever feels most onerous, and continues with what seems easiest.
This is not a terrible approach, because what we enjoy, we will be more likely to continue. But it can be improved upon, while still getting that benefit.
Marie Kondo your
resolutionsvaluesInstead of throwing out the new habits that “don’t spark joy”, ask yourself:
“What brings me joy?”
…because often, the answer is something that’s a result of a thing that didn’t “spark joy” directly. Many things in life involve delayed gratification.
Let’s separate the [unwanted action] from the [wanted result] for a moment.
Rather than struggling on with something unpleasant for the hope of joy at the end of the rainbow, though, give yourself permission to improve the middle bit.
For example, if the idea of having lots of energy and good cardiovascular fitness is what prompted you to commit to those 6am runs each morning (but they’re not actually joyous in your experience), what would be more fun and still give you the same benefit?
Now that you know “having lots of energy and good CV fitness” is what sparks joy, not “getting up to run at 6am”, you can change lanes without pulling off the highway entirely.
Maybe a dance class will be more your speed, for example.
The key here is: you’ll have changed your resolution, without breaking it in any way that mattered
Want more ways to keep on track without burning out?
Who doesn’t? So, check out:
How To Keep On Keeping On… Long Term!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Stop Tinnitus, & Improve Your Hearing By 130%
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Caveat: this will depend on the cause of your tinnitus, but there’s a quick diagnostic test first, and it’s for the most common kind 🙂
Step by step
To address noise in the ears (tinnitus) and improve hearing, start by identifying whether the issue is treatable. The diagnostic tests are:
- First, turn your head to the side, tilt it forward and backward, and observe changes in the noise. If the intensity changes, then the noise can be managed.
- Additionally, open and close your mouth, clenching and unclenching your teeth, and note any variations; this is about muscular tension affecting hearing.
- Finally, tilt your head downward—if the noise increases, it may mean it is a venous outflow disorder—there’s a fix for this, too.
Effective exercises focus on releasing tension and improving blood flow:
- Begin with the neck’s scalene muscles, located behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
- Massage these areas by moving your hands up and down and varying head positions slightly forward and backward.
- Repeat on both sides to enhance blood circulation and reduce auditory interference. Next, target the chewing muscles.
- Massage painful areas of the jaw and temporalis muscle in circular motions, working along and across the muscle fibers.
- Divide the temporalis muscle into sections and address each thoroughly to relieve tension and improve hearing.
- Mobilize the outer auditory passage by gently pulling the ear in all directions—starting with the earlobe, middle part, and upper ear.
- Focus on the cartilage above the lobe, moving it up and down to restore mobility and improve blood flow.
These exercises should fix the most common kind of tinnitus, and improve hearing—you’ll know quickly whether it works for you or not. Regular practice is required for sustained results, though.
For more on all this, plus visual demonstrations (e.g. how to find that temporalis muscle, etc), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Tinnitus: Quieting The Unwanted Orchestra In Your Ears ← our main feature on this topic, with more things to try if this didn’t help!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: