Are You A Calorie-Burning Machine?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Burn, Calorie, Burn
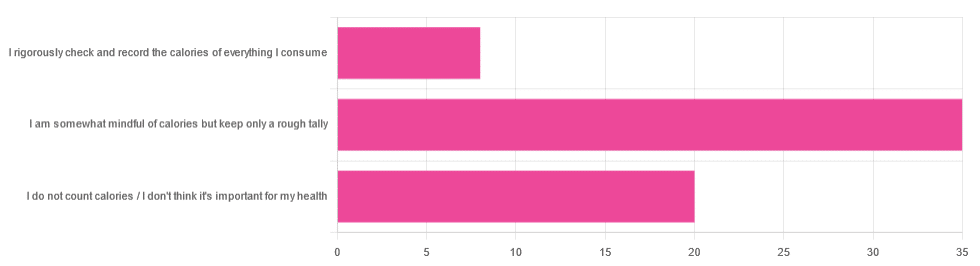
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you whether you count calories, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of answers:
- About 56% said “I am somewhat mindful of calories but keep only a rough tally”
- About 32% said “I do not count calories / I don’t think it’s important for my health”
- About 13% said “I rigorously check and record the calories of everything I consume”
So what does the science say, about the merits of all these positions?
A food’s calorie count is a good measure of how much energy we will, upon consuming the food, have to use or store: True or False?
False, broadly. It can be, at best, a rough guideline. Do you know what a calorie actually is, by the way? Most people don’t.
One thing to know before we get to that: there’s “cal” vs “kcal”. The latter is generally used when it comes to foodstuffs, and it’s what we’ll be meaning whenever we say “calorie” here. 1cal is 1/1000th of a kcal, that’s all.
Now, for what a calorie actually is:
A calorie is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 liter of water by 1℃
Question: so, how to we measure how much food is needed to do that?
Answer: by using a bomb calorimeter! Which is the exciting name for the apparatus used to literally burn food and capture the heat produced to indeed raise the temperature of 1 liter of water by 1℃.
If you’re having trouble imagining such equipment, here it is:
Bomb Calorimeter: Definition, Construction, & Operation (with diagram and FAQs)
The unfortunate implication of the above information
A kilogram of sawdust contains about a 1000 kcal, give or take what wood was used and various other conditions.
However, that does not mean you can usefully eat the sawdust. In other words:
Calorie count tells us only how good something is at raising the temperature of water if physically burned.
Now do you see why oils and sugars have such comparably high calorie counts?
And while we may talk about “burning calories” as a metaphor, we do not, in fact, have a little wood stove inside us burning the food we eat.
A calorie is a calorie: True or False?
Definitely False! Building on from the above… We will get very little energy from sawdust; it’s not just that we can’t use it; we can’t store it either; it’ll mostly pass through as fiber.
(however, please do not use sawdust to get your daily dose of fiber either, as it is not safe for human consumption and may give you diseases, depending on what is lurking in it)
But let’s look at oil and sugar, two very high-calorie categories of food, because they’re really easy to physically burn and they give off a good flame.
A bomb calorimeter may treat them quite equally, but to our body, they are metabolically very different indeed.
For a start, most sugars will get absorbed and processed much more quickly than most oils, and that can overwhelm the liver (responsible for glycogen management), and lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, diabetes, and more. Metabolic syndrome in general, and if you keep it up too much and you may find it’s now a lottery between dying of NAFLD, diabetes, or heart disease (it’ll usually be the heart disease that kills).
See also:
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
- How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
Meanwhile, we know all about the different kinds of nutritional profiles that oils can have, and some can promote having high energy without putting on fat, while others can strain the heart. Not even “a fat is a fat”, so “a calorie is a calorie” doesn’t get much mileage outside of a bomb calorimeter!
See also:
A calorie-controlled / calorie-restricted diet is an effective weight loss strategy: True or False?
True, usually! Surprise!
- On the one hand: calories are a wildly imprecise way to reckon the value of food, and using them as a guide to health can be dangerously misleading
- On the other hand: the very activity of calorie-counting itself promotes mindful eating, which is very good for the health
There is a strong difference between the mind of somebody who is carefully logging their pre-bedtime piece of chocolate and reflecting on its nutritional value, vs someone who isn’t sure whether this is their second or third glass of wine, nor how much the glass contained.
So if you want to get most of the benefits of a calorie-controlled diet without counting calories, you may try taking a “mindful eating” approach to diet.
However! If you want to do this for weight loss, be aware, that you will have to practice it all the time, not just for one meal here and there.
You can read more on how to do “mindful eating” here:
Dr. Rupy Aujla: The Kitchen Doctor | Mindful Eating & Interoception
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Unleashing Your Best Skin – by Jennifer Sun
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author, an aesthetician with a biotech background, explains about the overlap of skin health and skin beauty, making it better from the inside first (diet and other lifestyle factors), and then tweaking things as desired from the outside.
In the broad category of “tweakments” as she puts it, she covers most of the wide array of modern treatments available at many skin care clinics and the options for which at-home do-it-yourself kits are available—and the pros and cons of various approaches.
And yes, those methods do range from microneedling and red light therapy to dermal fillers and thread lifts. Most of them are relatively non-invasive though.
She also covers common ailments of the skin, and how to identify and treat those quickly and easily, without making things worse along the way.
One last thing she also includes is dealing with unwanted hairs—being a very common side-along issue when it comes to aesthetic medicine.
The book is broadly aimed at women, but hormones are not a main component discussed (except in the context of acne), so there’s no pressing reason why this book couldn’t benefit men too. It also addresses considerations when it comes to darker skintones, something that a lot of similar books overlook.
Bottom line: if you find yourself mystified by the world of skin treatment options and wondering what’s really best for you without the bias of someone who’s trying to sell you a particular treatment, then this is the book for you.
Click here to check out Unleashing Your Best Skin, and unleash your best skin!
Share This Post
-
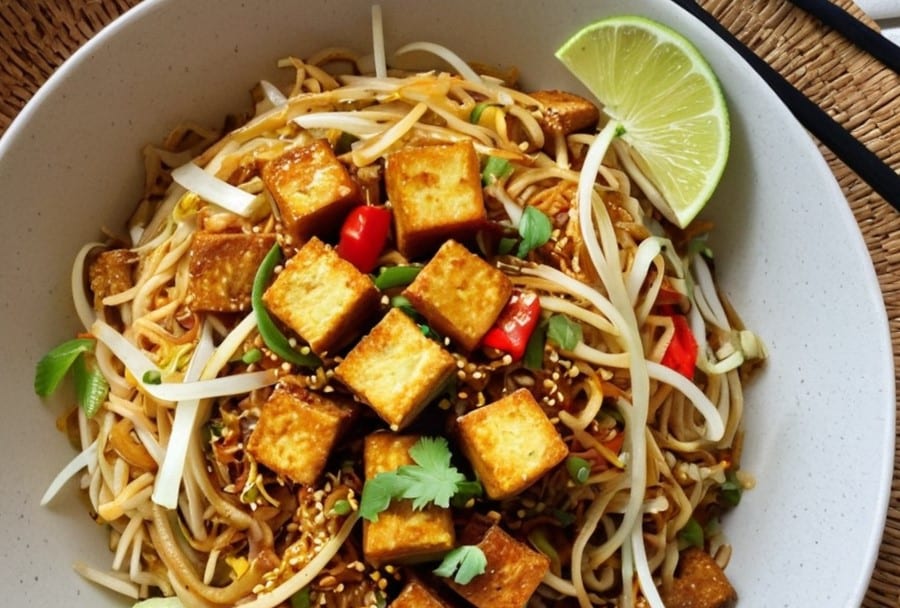
Crispy Tofu Pad Thai
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Easy to make, delicious to enjoy, and packed with phytonutrients, this dish is a great one to add to your repertoire:
You will need
- 10 oz ready-to-wok rice noodles, or 6 oz dry
- 5 oz silken tofu
- 5 oz firm or extra firm tofu, cut into small cubes
- 1 oz arrowroot (or cornstarch if you don’t have arrowroot)
- 4 scallions, sliced
- ¼ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 1″ piece fresh ginger, grated
- 1 red chili, chopped (multiply per your heat preferences)
- 1 red bell pepper, deseeded and thinly sliced
- 4 oz bok choi, thinly sliced
- 4 oz mung bean sprouts
- 1 tbsp tamari (or other, but tamari is traditional) soy sauce
- 1 tbsp sweet chili sauce
- Juice of ½ lime
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Avocado oil, or your preferred oil for stir-frying
- To serve: lime wedges
- Optional garnish: crushed roasted peanuts (if allergic, substitute sesame seeds; peanuts are simply traditional, that’s all)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Scramble the silken tofu. For guidance and also additional seasoning pointers, see our Tasty Tofu Scramble recipe, but omit the thyme.
2) Cook the noodles if necessary (i.e. if they are the dry type and need boiling, as opposed to “ready-to-wok” noodles that don’t), drain, and set aside.
4) Prepare the tofu cubes: if the tofu cubes are dry to the touch, toss them gently in a little oil to coat. If they’re wet to the touch, no need. Dust the tofu cubes with the arrowroot and MSG/salt; you can do this in a bowl, tossing gently to distribute the coating evenly.
4) Heat some oil in a wok over a high heat, and fry the tofu on each side until golden and crispy all over, and set aside.
5) Stir-fry the scallions, garlic, ginger, chili, and bell pepper for about 2 minutes.
6) Add the bean sprouts and bok choi, and keep stir-frying for another 2 minutes.
7) Add everything that’s not already in the pan except the lime wedges and peanuts (i.e., add the things you set aside, plus the remaining as-yet-untouched ingredients) and stir-fry for a further 2 minutes.
8) Serve hot, garnished with the crushed peanuts if using, and with the lime wedges on the side:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc
- Which Bell Peppers To Pick? A Spectrum Of Specialties
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
3 signs your diet is causing too much muscle loss – and what to do about it
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When trying to lose weight, it’s natural to want to see quick results. So when the number on the scales drops rapidly, it seems like we’re on the right track.
But as with many things related to weight loss, there’s a flip side: rapid weight loss can result in a significant loss of muscle mass, as well as fat.
So how you can tell if you’re losing too much muscle and what can you do to prevent it?
EvMedvedeva/Shutterstock Why does muscle mass matter?
Muscle is an important factor in determining our metabolic rate: how much energy we burn at rest. This is determined by how much muscle and fat we have. Muscle is more metabolically active than fat, meaning it burns more calories.
When we diet to lose weight, we create a calorie deficit, where our bodies don’t get enough energy from the food we eat to meet our energy needs. Our bodies start breaking down our fat and muscle tissue for fuel.
A decrease in calorie-burning muscle mass slows our metabolism. This quickly slows the rate at which we lose weight and impacts our ability to maintain our weight long term.
How to tell you’re losing too much muscle
Unfortunately, measuring changes in muscle mass is not easy.
The most accurate tool is an enhanced form of X-ray called a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan. The scan is primarily used in medicine and research to capture data on weight, body fat, muscle mass and bone density.
But while DEXA is becoming more readily available at weight-loss clinics and gyms, it’s not cheap.
There are also many “smart” scales available for at home use that promise to provide an accurate reading of muscle mass percentage.
Some scales promise to tell us our muscle mass. Lee Charlie/Shutterstock However, the accuracy of these scales is questionable. Researchers found the scales tested massively over- or under-estimated fat and muscle mass.
Fortunately, there are three free but scientifically backed signs you may be losing too much muscle mass when you’re dieting.
1. You’re losing much more weight than expected each week
Losing a lot of weight rapidly is one of the early signs that your diet is too extreme and you’re losing too much muscle.
Rapid weight loss (of more than 1 kilogram per week) results in greater muscle mass loss than slow weight loss.
Slow weight loss better preserves muscle mass and often has the added benefit of greater fat mass loss.
One study compared people in the obese weight category who followed either a very low-calorie diet (500 calories per day) for five weeks or a low-calorie diet (1,250 calories per day) for 12 weeks. While both groups lost similar amounts of weight, participants following the very low-calorie diet (500 calories per day) for five weeks lost significantly more muscle mass.
2. You’re feeling tired and things feel more difficult
It sounds obvious, but feeling tired, sluggish and finding it hard to complete physical activities, such as working out or doing jobs around the house, is another strong signal you’re losing muscle.
Research shows a decrease in muscle mass may negatively impact your body’s physical performance.
3. You’re feeling moody
Mood swings and feeling anxious, stressed or depressed may also be signs you’re losing muscle mass.
Research on muscle loss due to ageing suggests low levels of muscle mass can negatively impact mental health and mood. This seems to stem from the relationship between low muscle mass and proteins called neurotrophins, which help regulate mood and feelings of wellbeing.
So how you can do to maintain muscle during weight loss?
Fortunately, there are also three actions you can take to maintain muscle mass when you’re following a calorie-restricted diet to lose weight.
1. Incorporate strength training into your exercise plan
While a broad exercise program is important to support overall weight loss, strength-building exercises are a surefire way to help prevent the loss of muscle mass. A meta-analysis of studies of older people with obesity found resistance training was able to prevent almost 100% of muscle loss from calorie restriction.
Relying on diet alone to lose weight will reduce muscle along with body fat, slowing your metabolism. So it’s essential to make sure you’ve incorporated sufficient and appropriate exercise into your weight-loss plan to hold onto your muscle mass stores.
Strength-building exercises help you retain muscle. BearFotos/Shutterstock But you don’t need to hit the gym. Exercises using body weight – such as push-ups, pull-ups, planks and air squats – are just as effective as lifting weights and using strength-building equipment.
Encouragingly, moderate-volume resistance training (three sets of ten repetitions for eight exercises) can be as effective as high-volume training (five sets of ten repetitions for eight exercises) for maintaining muscle when you’re following a calorie-restricted diet.
2. Eat more protein
Foods high in protein play an essential role in building and maintaining muscle mass, but research also shows these foods help prevent muscle loss when you’re following a calorie-restricted diet.
But this doesn’t mean just eating foods with protein. Meals need to be balanced and include a source of protein, wholegrain carb and healthy fat to meet our dietary needs. For example, eggs on wholegrain toast with avocado.
3. Slow your weight loss plan down
When we change our diet to lose weight, we take our body out of its comfort zone and trigger its survival response. It then counteracts weight loss, triggering several physiological responses to defend our body weight and “survive” starvation.
Our body’s survival mechanisms want us to regain lost weight to ensure we survive the next period of famine (dieting). Research shows that more than half of the weight lost by participants is regained within two years, and more than 80% of lost weight is regained within five years.
However, a slow and steady, stepped approach to weight loss, prevents our bodies from activating defence mechanisms to defend our weight when we try to lose weight.
Ultimately, losing weight long-term comes down to making gradual changes to your lifestyle to ensure you form habits that last a lifetime.
At the Boden Group, Charles Perkins Centre, we are studying the science of obesity and running clinical trials for weight loss. You can register here to express your interest.
Nick Fuller, Charles Perkins Centre Research Program Leader, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Diabetes Drugs That Can Cut Asthma Attacks By 70%
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Asthma, obesity, and type 2 diabetes are closely linked, with the latter two greatly increasing asthma attack risk.
While bronchodilators / corticosteroids can have immediate adverse effects due to sympathetic nervous system activation, and lasting adverse effects due to the damage it does to metabolic health, diabetes drugs, on the other hand, can improve things with (for most people) fewer unwanted side effects.
Great! Which drugs?
Metformin, and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs).
Specifically, researchers have found:
- Metformin is associated with a 30% reduction in asthma attacks
- GLP-1RAs are associated with a 40% reduction in asthma attacks
…and yes, they stack, making for a 70% reduction in the case of people taking both. Furthermore, the results are independent of weight, glycemic control, or asthma phenotype.
In terms of what was counted, the primary outcome was asthma attacks at 12-month follow-up, defined by oral corticosteroid use, emergency visits, hospitalizations, or death.
The effect of metformin on asthma attacks was not affected by BMI, HbA1c levels, eosinophil count, asthma severity, or sex.
Of the various extra antidiabetic drugs trialled in this study, only GLP-1 receptor agonists showed a further and sustained reduction in asthma attacks.
Here’s the study itself, hot off the press, published on Monday:
JAMA Int. Med. | Antidiabetic Medication and Asthma Attacks
“But what if I’m not diabetic?”
Good news:
More than half of all US adults are eligible for semaglutide therapy ← this is because they’ve expanded the things that semaglutide (the widely-used GLP-1 receptor agonist drug) can be prescribed for, now going beyond just diabetes and/or weight loss 😎
And metformin, of course, is more readily available than semaglutide, so by all means speak with your doctor/pharmacist about that, if it’s of interest to you.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Apple Cider Vinegar vs Balsamic Vinegar – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apple cider vinegar to balsamic vinegar, we picked the apple cider vinegar.
Why?
It’s close! And it’s a simple one today and they’re both great. Taking either for blood-sugar-balancing benefits is fine, as it’s the acidity that has this effect. But:
- Of the two, balsamic vinegar is the one more likely to contain more sugars, especially if it’s been treated in any fashion, and not by you, e.g. made into a glaze or even a reduction (the latter has no need to add sugar, but sometimes companies do because it is cheaper—so we recommend making your own balsamic vinegar reduction at home)
- Of the two, apple cider vinegar is the one more likely to contain “the mother”, that is to say, the part with extra probiotic benefits (but if the vinegar has been filtered, it won’t have this—it’s just more common to be able to find unfiltered apple cider vinegar, since it has more popular attention for its health benefits than balsamic vinegar does)
So, two wins for apple cider vinegar there.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- 10 Ways To Balance Your Blood Sugars
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- Apple Cider Vinegar vs Apple Cider Vinegar Gummies – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Castor Oil: All-Purpose Life-Changer, Or Snake Oil?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As “trending” health products go, castor oil is enjoying a lot of popularity presently, lauded as a life-changing miracle-worker, and social media is abuzz with advice to put it everywhere from your eyes to your vagina.
But:
- what things does science actually say it’s good for,
- what things lack evidence, and
- what things go into the category of “wow definitely do not do that”?
We don’t have the space to go into all of its proposed uses (there are simply far too many), but we’ll examine some common ones:
To heal/improve the skin barrier
Like most oils, it’s functional as a moisturizer. In particular, its high (90%!) ricinoleic fatty acid content does indeed make it good at that, and furthermore, has properties that can help reduce skin inflammation and promote wound healing:
Bioactive polymeric formulations for wound healing ← there isn’t a conveniently quotable summary we can just grab here, but you can see the data and results, from which we can conclude:
- formulations with ricinoleic acid (such as with castor oil) performed very well for topical anti-inflammatory purposes
- they avoided the unwanted side effects associated with some other contenders
- they consistently beat other preparations in the category of wound-healing
To support hair growth and scalp health
There is no evidence that it helps. We’d love to provide a citation for this, but it’s simply not there. There’s also no evidence that it doesn’t help. For whatever reason, despite its popularity, peer-reviewed science has simply not been done for this, or if it has, it wasn’t anywhere publicly accessible.
It’s possible that if a person is suffering hair loss specifically as a result of prostaglandin D2 levels, that ricinoleic acid will inhibit the PGD2, reversing the hair loss, but even this is hypothetical so far, as the science is currently only at the step before that:
However, due to some interesting chemistry, the combination of castor oil and warm water can result in acute (and irreversible) hair felting, in other words, the strands of hair suddenly glue together to become one mass which then has to be cut off:
“Castor Oil” – The Culprit of Acute Hair Felting
👆 this is a case study, which is generally considered a low standard of evidence (compared to high-quality Randomized Controlled Trials as the highest standard of evidence), but let’s just say, this writer (hi, it’s me) isn’t risking her butt-length hair on the off-chance, and doesn’t advise you to, either. There are other hair-oils out there; argan oil is great, coconut oil is totally fine too.
As a laxative
This time, there’s a lot of evidence, and it’s even approved for this purpose by the FDA, but it can be a bit too good, insofar as taking too much can result in diarrhea and uncomfortable cramping (the cramps are a feature not a bug; the mechanism of action is stimulatory, i.e. it gets the intestines squeezing, but again, it can result in doing that too much for comfort):
Castor Oil: FDA-Approved Indications
To soothe dry eyes
While putting oil in your eyes may seem dubious, this is another one where it actually works:
❝Castor oil is deemed safe and tolerable, with strong anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive, analgesic, antioxidant, wound healing and vasoconstrictive properties.
These can supplement deficient physiological tear film lipids, enabling enhanced lipid spreading characteristics and reducing aqueous tear evaporation.
Studies reveal that castor oil applied topically to the ocular surface has a prolonged residence time, facilitating increased tear film lipid layer thickness, stability, improved ocular surface staining and symptoms.❞
Source: Therapeutic potential of castor oil in managing blepharitis, meibomian gland dysfunction and dry eye
Against candidiasis (thrush)
We couldn’t find science for (or against) castor oil’s use against vaginal candidiasis, but here’s a study that investigated its use against oral candidiasis:
…in which castor oil was the only preparation that didn’t work against the yeast.
Summary
We left a lot unsaid today (so many proposed uses, it feels like a shame to skip them), but in few words: it’s good for skin (including wound healing) and eyes; but we’d give it a miss for hair, candidiasis, and digestive disorders.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: