3 signs your diet is causing too much muscle loss – and what to do about it
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When trying to lose weight, it’s natural to want to see quick results. So when the number on the scales drops rapidly, it seems like we’re on the right track.
But as with many things related to weight loss, there’s a flip side: rapid weight loss can result in a significant loss of muscle mass, as well as fat.
So how you can tell if you’re losing too much muscle and what can you do to prevent it?
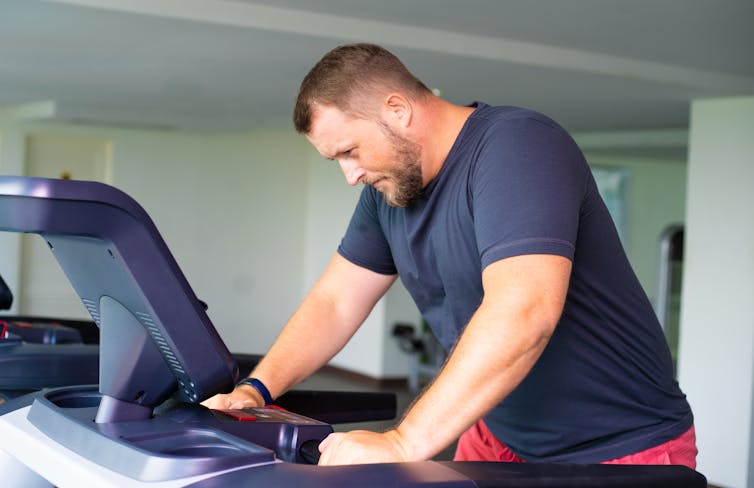

Why does muscle mass matter?
Muscle is an important factor in determining our metabolic rate: how much energy we burn at rest. This is determined by how much muscle and fat we have. Muscle is more metabolically active than fat, meaning it burns more calories.
When we diet to lose weight, we create a calorie deficit, where our bodies don’t get enough energy from the food we eat to meet our energy needs. Our bodies start breaking down our fat and muscle tissue for fuel.
A decrease in calorie-burning muscle mass slows our metabolism. This quickly slows the rate at which we lose weight and impacts our ability to maintain our weight long term.
How to tell you’re losing too much muscle
Unfortunately, measuring changes in muscle mass is not easy.
The most accurate tool is an enhanced form of X-ray called a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan. The scan is primarily used in medicine and research to capture data on weight, body fat, muscle mass and bone density.
But while DEXA is becoming more readily available at weight-loss clinics and gyms, it’s not cheap.
There are also many “smart” scales available for at home use that promise to provide an accurate reading of muscle mass percentage.
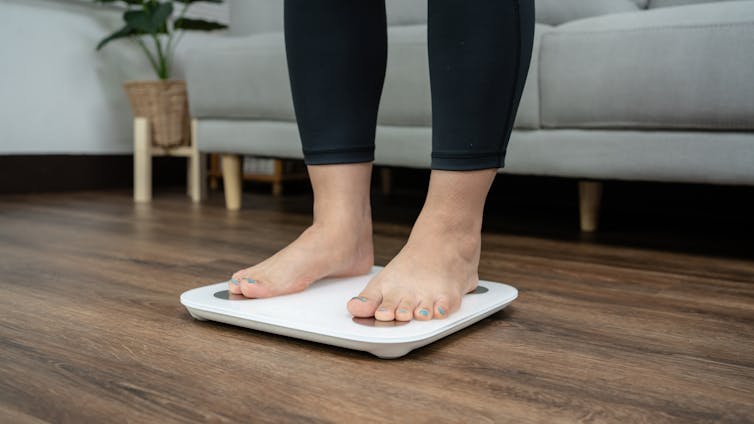

However, the accuracy of these scales is questionable. Researchers found the scales tested massively over- or under-estimated fat and muscle mass.
Fortunately, there are three free but scientifically backed signs you may be losing too much muscle mass when you’re dieting.
1. You’re losing much more weight than expected each week
Losing a lot of weight rapidly is one of the early signs that your diet is too extreme and you’re losing too much muscle.
Rapid weight loss (of more than 1 kilogram per week) results in greater muscle mass loss than slow weight loss.
Slow weight loss better preserves muscle mass and often has the added benefit of greater fat mass loss.
One study compared people in the obese weight category who followed either a very low-calorie diet (500 calories per day) for five weeks or a low-calorie diet (1,250 calories per day) for 12 weeks. While both groups lost similar amounts of weight, participants following the very low-calorie diet (500 calories per day) for five weeks lost significantly more muscle mass.
2. You’re feeling tired and things feel more difficult
It sounds obvious, but feeling tired, sluggish and finding it hard to complete physical activities, such as working out or doing jobs around the house, is another strong signal you’re losing muscle.
Research shows a decrease in muscle mass may negatively impact your body’s physical performance.
3. You’re feeling moody
Mood swings and feeling anxious, stressed or depressed may also be signs you’re losing muscle mass.
Research on muscle loss due to ageing suggests low levels of muscle mass can negatively impact mental health and mood. This seems to stem from the relationship between low muscle mass and proteins called neurotrophins, which help regulate mood and feelings of wellbeing.
So how you can do to maintain muscle during weight loss?
Fortunately, there are also three actions you can take to maintain muscle mass when you’re following a calorie-restricted diet to lose weight.
1. Incorporate strength training into your exercise plan
While a broad exercise program is important to support overall weight loss, strength-building exercises are a surefire way to help prevent the loss of muscle mass. A meta-analysis of studies of older people with obesity found resistance training was able to prevent almost 100% of muscle loss from calorie restriction.
Relying on diet alone to lose weight will reduce muscle along with body fat, slowing your metabolism. So it’s essential to make sure you’ve incorporated sufficient and appropriate exercise into your weight-loss plan to hold onto your muscle mass stores.
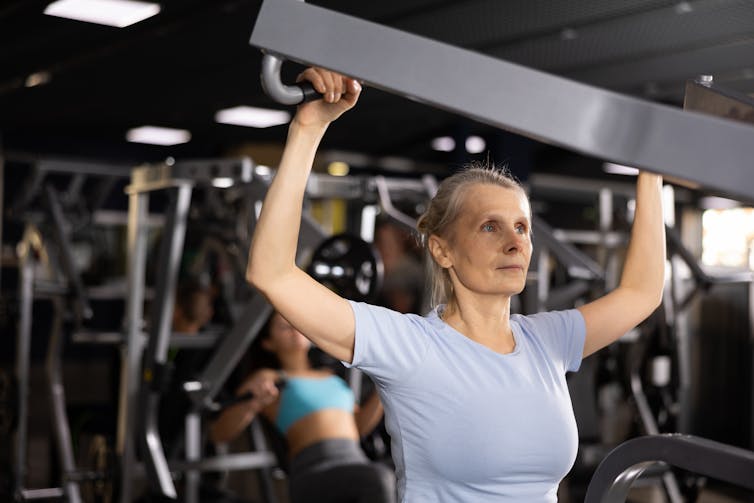

But you don’t need to hit the gym. Exercises using body weight – such as push-ups, pull-ups, planks and air squats – are just as effective as lifting weights and using strength-building equipment.
Encouragingly, moderate-volume resistance training (three sets of ten repetitions for eight exercises) can be as effective as high-volume training (five sets of ten repetitions for eight exercises) for maintaining muscle when you’re following a calorie-restricted diet.
2. Eat more protein
Foods high in protein play an essential role in building and maintaining muscle mass, but research also shows these foods help prevent muscle loss when you’re following a calorie-restricted diet.
But this doesn’t mean just eating foods with protein. Meals need to be balanced and include a source of protein, wholegrain carb and healthy fat to meet our dietary needs. For example, eggs on wholegrain toast with avocado.
3. Slow your weight loss plan down
When we change our diet to lose weight, we take our body out of its comfort zone and trigger its survival response. It then counteracts weight loss, triggering several physiological responses to defend our body weight and “survive” starvation.
Our body’s survival mechanisms want us to regain lost weight to ensure we survive the next period of famine (dieting). Research shows that more than half of the weight lost by participants is regained within two years, and more than 80% of lost weight is regained within five years.
However, a slow and steady, stepped approach to weight loss, prevents our bodies from activating defence mechanisms to defend our weight when we try to lose weight.
Ultimately, losing weight long-term comes down to making gradual changes to your lifestyle to ensure you form habits that last a lifetime.
At the Boden Group, Charles Perkins Centre, we are studying the science of obesity and running clinical trials for weight loss. You can register here to express your interest.
Nick Fuller, Charles Perkins Centre Research Program Leader, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Curiosity Really Kills
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Curiosity Kills The Neurodegeneration
Of the seven things that Leonardo da Vinci considered most important for developing and maintaining the mind, number one on his list was curiosity, and we’re going to be focussing on that today.
In case you are curious about what seven things made Leonardo’s* list, they were:
- Curiosità: an insatiably curious approach to life and an unrelenting quest for continuous learning
- Dimostrazione: a commitment to test knowledge through experience, persistence, and a willingness to learn from mistakes
- Sensazione: the continual refinement of the senses, especially sight, as a means to enliven experience
- Sfumato: (lit: “gone up in smoke”) a willingness to embrace ambiguity, paradox, and uncertainty
- Arte/Scienza: the curated balance of art and science, imagination and logic
- Corporalità: the cultivation of physical grace, ambidexterity, and fitness
- Connessione: a recognition of and appreciation for the interconnectedness of phenomena (systems-based thinking)
*In case you are curious why we wrote “Leonardo” and not “da Vinci” as per our usual convention of shortening names to last names, da Vinci is not technically a name, in much the same way as “of Nazareth” was not a name.
You can read more about all 7 of these in a book that we’ve reviewed previously:
How to Think Like Leonardo da Vinci: Seven Steps to Genius Every Day – by Michael J. Gelb
But for now, let’s take on “curiosity”!
If you need an extra reason to focus on growing and nurturing your curiosity, it was also #1 of Dr. Daniel Levitin’s list of…
The Five Keys Of Aging Healthily
…and that’s from a modern-day neuroscientist whose research focuses on aging, the brain, health, productivity, and creativity.
But how do we foster curiosity in the age of Google?
Curiosity is like a muscle: use it or lose it
While it’s true that many things can be Googled to satisfy one’s curiosity in an instant…
- do you? It’s only useful if you do use it
- is the top result on Google reliable?
- there are many things that aren’t available there
In short: douse “fast
foodinformation” sources, but don’t rely on them! Not just for the sake of having correct information, but also: for the actual brain benefits which is what we are aiming for here with today’s article.If you want the best brain benefits, dive in, and go deep
Here at 10almonds we often present superficial information, with links to deeper information (often: scholarly articles). We do this because a) there’s only so much we can fit in our articles and b) we know you only have so much time available, and/but may choose to dive deeper.
Think of it in layers, e.g:
- Collagen is good for joints and bones
- Collagen is a protein made of these amino acids that also requires these vitamins and minerals to be present in order to formulate it
- Those amino acids are needed in these quantities, of which this particular one is usually the weakest link that might need supplementing, and those vitamins and minerals need to be within this period of time, but not these ones at the exact same time, or else it will disrupt the process of collagen synthesis
(in case you’re curious, we covered this here and here and offered a very good, very in-depth book about it here)
Now, this doesn’t mean that to have a healthy brain you need to have the equivalent knowledge of an anatomy & physiology degree, but it is good to have that level of curiosity in at least some areas of your life—and the more, the better.
Top tips for developing a habit of curiosity
As you probably know, most of our endeavors as humans go best when they are habits:
How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
And as for specifically building a habit of curiosity:
- Make a deal with yourself that when someone is excited to tell you what they know about something (no matter whether it is your grandkid, or the socially awkward nerd at a party, or whoever), listen and learn, no matter the topic.
- Learn at least one language other than your native language (presumably English for most of our readers). Not only does learning a language convey a lot of brain benefits of its own, but also, it is almost impossible to separate language learning from cultural learning, and so you will learn a lot about another culture too, and have whole new worlds opened up to you. Again, more is better, but one second language is already a lot better than none.
- Make a regular habit of going to your local library, and picking out a non-fiction book to take home and read. This has an advantage over a bookshop, by the way (and not just that the library is free): since library books must be returned, you will keep going back, and build a habit of taking out books.
- Pick a skill that you’d like to make into a fully-fledged hobby, and commit to continually learning as much about it as you can. We already covered language-learning above, but others might include: gardening (perhaps a specific kind), cooking (perhaps a specific kind), needlecraft (perhaps a specific kind), dance (perhaps a specific kind). You could learn a musical instrument. Or it could be something very directly useful, like learning to be a first responder in case of emergencies, and committing to continually learning more about it (because there is always more to learn).
And when it comes to the above choices… Pick things that excite you, regardless of how practical or not they are. Because that stimulation that keeps on driving you? That’s what keeps your brain active, healthy, and sharp.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Saunas: Health Benefits (& Caveats)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Heat Is On
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your (health-related) opinion on saunas, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 53% said it is “a healthful activity with many benefits”
- About 25% said it is “best avoided; I feel like I’m dying in there”
- About 12% said “it feels good and therefore can’t be all bad”
So what does the science say?
The heat of saunas carries a health risk: True or False?
False, generally speaking, for any practical purposes. Of course, anything in life comes with a health risk, but statistically speaking, your shower at home is a lot more dangerous than a sauna (risk of slipping with no help at hand).
It took a bit of effort to find a paper on the health risks of saunas, because all the papers on PubMed etc coming up for those keywords were initially papers with “reduces the risk of…”, i.e. ways in which the sauna is healthy.
However, we did find one:
❝Contraindications to sauna bathing include unstable angina pectoris, recent myocardial infarction, and severe aortic stenosis.
Sauna bathing is safe, however, for most people with coronary heart disease with stable angina pectoris or old myocardial infarction.
Very few acute myocardial infarctions and sudden deaths occur in saunas, but alcohol consumption during sauna bathing increases the risk of hypotension, arrhythmia, and sudden death, and should be avoided. ❞
~ Dr. Matti Hannuksela & Dr. Samer Ellahham
Source: Benefits and risks of sauna bathing
So, very safe for most people, safe even for most people with heart disease, but there are exceptions so check with your own doctor of course.
And drinking alcohol anywhere is bad for the health, but in a sauna it’s a truly terrible idea. As an aside, please don’t drink alcohol in the shower, either (risk of slipping with no help at hand, and this time, broken glass too).
On the topic of it being safe for most people’s hearts, see also:
Beneficial effects of sauna bathing for heart failure patients
As an additional note, those who have a particular sensitivity to the heat, may (again please check with your own doctor, as your case may vary) actually benefit from moderate sauna use, to reduce the cardiovascular strain that your body experiences during heatwaves (remember, you can get out of a sauna more easily than you can get out of a heatwave, so for many people it’s a lot easier to do moderation and improve thermoregulatory responses):
Sauna usage can bring many health benefits: True or False?
True! Again, at least for most people. As well as the above-discussed items, here’s one for mortality rates in healthy Finnish men:
Not only that, also…
❝The Finnish saunas have the most consistent and robust evidence regarding health benefits and they have been shown to decrease the risk of health outcomes such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, thromboembolism, dementia, and respiratory conditions; may improve the severity of musculoskeletal disorders, COVID-19, headache and flu, while also improving mental well-being, sleep, and longevity.
Finnish saunas may also augment the beneficial effects of other protective lifestyle factors such as physical activity.
The beneficial effects of passive heat therapies may be linked to their anti-inflammatory, cytoprotective and anti-oxidant properties and synergistic effects on neuroendocrine, circulatory, cardiovascular and immune function.
Passive heat therapies, notably Finnish saunas, are emerging as potentially powerful and holistic strategies to promoting health and extending the healthspan in all populations. ❞
~ Dr. Jari Laukkanen & Dr. Setor Kunutsor
(the repeated clarification of “Finnish sauna” is not a matter of fervent nationalism, by the way, but rather a matter of disambiguating it from Swedish sauna, which has some differences, most notably a lack of steam)
That reminds us: in Scandinavia, it is usual to use a sauna naked, and in Finland in particular, it is a common social activity amongst friends, coworkers, etc. In the US, many people are not so comfortable with nudity, and indeed, many places that provide saunas, may require the wearing of swimwear. But…
Just one problem: if you’re wearing swimwear because you’ve just been swimming in a pool, you now have chlorinated water soaked into your swimwear, which in the sauna, will become steam + chlorine gas. That’s not so good for your health (and is one reason, beyond tradition and simple normalization, for why swimwear is usually not permitted in Finnish saunas).
Want to read more?
You might like our previous main feature,
Turning Up The Heat Against Diabetes & Alzheimer’s ← you guessed it, sauna may be beneficial against these too
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Spice Of Life
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Great newsletter. Am taking turmeric for inflammation of hips and feet. Works like magic. Would like to know how it works, and what tumeric is best combined with – also whether there any risks in longterm use.❞
Glad you’re enjoying! As for turmeric, it sure is great, isn’t it? To answer your questions in a brief fashion:
- How it works: it does a lot of things, but perhaps its most key feature is its autoxidative metabolites that mediate its anti-inflammatory effect. Thus, it slows or inhibits oxidative stress that would otherwise cause inflammation, increase cancer risk, and advance aging.
- Best combined with: black pepper
- Any risks in long-term use: there are no known risks in long-term use ← that’s just one study, but there are lots. Some studies were prompted by reported hepatotoxicity of curcumin supplements, but a) the reports themselves seem to be without evidence b) the reported hepatoxicity was in relation to contaminants in the supplements, not the curcumin itself c) clinical trials were unable to find any hepatotoxicity (or other) risks anyway. Here’s an example of such a study.
You might also like our previous main feature: Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Parenting a perfectionist? Here’s how you can respond
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some children show signs of perfectionism from early on. Young children might become frustrated and rip up their drawing if it’s not quite right. Older children might avoid or refuse to do homework because they’re afraid to make a mistake.
Perfectionism can lead to children feeling overwhelmed, angry and frustrated, or sad and withdrawn.
And yet perfectionism isn’t considered all bad in our society. Being called a “perfectionist” can be a compliment – code for being a great worker or student, someone who strives to do their best and makes sure all jobs are done well.
These seemingly polarised views reflect the complex nature of perfectionism.
Annie Spratt/Unsplash What is perfectionism?
Researchers often separate perfectionism into two parts:
- perfectionistic strivings: being determined to meet goals and achieve highly
- perfectionistic concerns: worry about being able to meet high standards, and self-criticism about performance.
While perfectionistic strivings can be positive and lead to high achievement, perfectionistic concerns can lead to a higher chance of children developing eating disorders or anxiety and depression, and having lower academic achievement.
Perfectionistic concerns can result in lower academic achievement. Jessica Lewis/Unsplash Children and adolescents may experience perfectionism in relation to school work, sport, performance in art or music, or in relation to their own body.
Signs of perfectionistic concerns in children and adolescents may include:
- children being highly critical of themselves
- their reactions to mistakes seeming to be an overreaction
- intense preoccupation and worry over their standards and goals and/or procrastination
- significant change in performance, for example, lower academic results
- irritability and negative emotions, stress and feelings of worthlessness
- social problems with peers and friends, such as bullying and alienating themselves from peers.
A range of genetic, biological and environmental factors influence perfectionism in children. And as a parent, our role is important. While research evidence suggests we can’t successfully increase positive perfectionistic strivings in our children, harsh or controlling parenting can increase negative perfectionistic concerns in children.
Parents who are perfectionistic themselves can also model this to their children.
So, how can we walk the line between supporting our child’s interests and helping them to achieve their potential, without pressuring them and increasing the risk of negative outcomes?
Give them space to grow
A great metaphor is the gardener versus the carpenter described by psychology professor Alison Gopnik.
Instead of trying to build and shape our children by controlling them and their environment (like a carpenter), parents can embrace the spirit of the gardener – providing lots of space for children to grow in their own direction, and nourishing them with love, respect and trust.
Parents don’t need to control their child and their environment. Noah Silliman/Unsplash We can’t control who they become, so it’s better to sit back, enjoy the ride, and look forward to watching the person they grow into.
However, there is still plenty we can do as parents if our child is showing signs of perfectionism. We can role model to our children how to set realistic goals and be flexible when things change or go wrong, help our children manage stress and negative emotions, and create healthy balance in our family daily routine.
Set realistic goals
People with perfectionistic tendencies will often set unattainable goals. We can support the development of flexibility and realistic goal setting by asking curious questions, for example, “what would you need to do to get one small step closer to this goal?” Identifying upper and lower limits for goals is also helpful.
If your child is fixed on a high score at school, for example, set that as the “upper limit” and then support them to identify a “lower limit” they would find acceptable, even if they are less happy with the outcome.
This strategy may take time and practice to widen the gap between the two, but is useful to create flexibility over time.
If a goal is performance-based and the outcome cannot be guaranteed (for example, a sporting competition), encourage your child to set a personal goal they have more control over.
Parents can help children set goals they can achieve. liz99/Unsplash We can also have conversations about perfectionism from early on, and explain that everyone makes mistakes. In fact, it’s great to model this to our children – talking about our own mistakes and feelings, to show them that we ourselves are not perfect.
Talk aloud practices can help children to see that we “walk the walk”. For example, if you burn dinner you could reflect:
I’m disappointed because I put time and effort into that and it didn’t turn out as I expected. But we all make mistakes. I don’t get things right every time.
Manage stress and negative emotions
Some children and adolescents have a natural tendency towards perfectionism. Rather than trying to control their behaviour, we can provide gentle, loving support.
When our child or adolescent becomes frustrated, angry, sad or overwhelmed, we support them best by helping them to name, express and validate all of their emotions.
Parents may fear that acknowledging their child’s negative emotions will make the emotions worse, but the opposite is true.
Creating healthy balance
The building blocks of healthy child development are strong loving family relationships, good nutrition, creative play and plenty of physical activity, sleep and rest.
Perfectionism is associated with rigidity, and thinking that there is only one correct way to succeed. We can instead encourage flexibility and creativity in children.
Children’s brains grow through play. There is strong research evidence showing that creative, child-led play is associated with higher emotion regulation skills, and a range of cognitive skills, including problem-solving, memory, planning, flexibility and decision-making.
Play helps children’s brains grow. Mi Pham/Unsplash Play isn’t just for young children either – there’s evidence that explorative, creative play of any kind also benefits adolescents and adults.
There is also evidence that getting active outdoors in nature can promote children’s coping skills, emotion regulation and cognitive development.
Elizabeth Westrupp, Associate Professor in Psychology, Deakin University; Gabriella King, Associate Research Fellow, Deakin University, and Jade Sheen, Associate Professor, School of Psychology, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Genetic Risk Factors For Long COVID
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some people, after getting COVID, go on to have Long COVID. There are various contributing factors to this, including:
- Lifestyle factors that impact general disease-proneness
- Immune-specific factors such as being immunocompromised already
- Genetic factors
We looked at some modifiable factors to improve one’s disease-resistance, yesterday:
And we’ve taken a more big-picture look previously:
Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
Along with some more systemic issues:
Why Some People Get Sick More (And How To Not Be One Of Them)
But, for when the “don’t get COVID” ship has sailed, one of the big remaining deciding factors with regard to whether one gets Long COVID or not, is genetic
The Long COVID Genes
For those with their 23andMe genetic data to hand…
❝Study findings revealed that three specific genetic loci, HLA-DQA1–HLA-DQB1, ABO, and BPTF–KPAN2–C17orf58, and three phenotypes were at significantly heightened risk, highlighting high-priority populations for interventions against this poorly understood disease.❞
For those who don’t, then first: you might consider getting that! Here’s why:
Genetic Testing: Health Benefits & Methods
But also, all is not lost meanwhile:
The same study also found that individuals with genetic predispositions to chronic fatigue, depression, and fibromyalgia, as well as other phenotypes such as autoimmune conditions and cardiometabolic conditions, are at significantly higher risk of long-COVID than individuals without these conditions.
Good news, bad news
Another finding was that women and non-smokers were more likely to get Long COVID, than men and smokers, respectively.
Does that mean that those things are protective against Long COVID, which would be very counterintuitive in the case of smoking?
Well, yes and no; it depends on whether you count “less likely to get Long COVID because of being more likely to just die” as protective against Long COVID.
(Incidentally, estrogen is moderately immune-enhancing, while testosterone is moderately immune-suppressing, so the sex thing was not too surprising. It’s also at least contributory to why women get more autoimmune disorders, while men get more respiratory infections such as colds and the like)
Want to know more?
You can read the paper itself, here:
*GWAS = Genome-Wide Association Study
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Life Is in the Transitions – by Bruce Feiler
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Change happens. Sometimes, because we choose it. More often, we don’t get a choice.
Our bodies change; with time, with illness, with accident or incident, or even, sometimes, with effort. People in our lives change; they come, they go, they get sick, they die. Our working lives change; we get a job, we lose a job, we change jobs, our jobs change, we retire.
Whether we’re undergoing cancer treatment or a religious conversion, whether our families are growing or down to the last few standing, change is inescapable.
Our author makes the case that on average, we each undergo at least 5 major “lifequakes”; changes that shake our lives to the core. Sometimes one will come along when we’ve barely got back on our feet from the previous—if we have at all.
What, then, to do about this? We can’t stop change from occurring, and some changes aren’t easy to “roll with”. Feiler isn’t prescriptive about this, but rather, descriptive:
By looking at the stories of hundreds of people he interviewed for this book, he looks at how people pivoted on the spot (or picked up the pieces!) and made the best of their situation—or didn’t.
Bottom line: zooming out like this, looking at many people’s lives, can remind us that while we don’t get to choose what winds we get swept by, we at least get to choose how we set the sails. The examples of others, as this book gives, can help us make better decisions.
Click here to check out Life Is In The Transitions, and get conscious about how you handle yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: