Bold Beans – by Amelia Christie-Miller
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know beans are one of the most healthful foods around, but how to include more of them, without getting boring?
This book has the answer, giving 80 exciting recipes, divided into the following sections:
- Speedy beans
- Bean snacks & sharing plates
- Brothy beans
- Bean bowls
- Hearty salads
- Bean feasts
The recipes are obviously all bean-centric, though if you have a particular dietary restriction, watch out for the warning labels on some (e.g. meat, fish, dairy, gluten, etc), and make a substitution if appropriate.
The recipes themselves have a happily short introductory paragraph, followed by all you’d expect from a recipe book (ingredients, measurements, method, picture)
There’s also a reference section, to learn about different kinds of beans and bean-related culinary methods that can be applied per your preferences.
Bottom line: if you’d like to include more beans in your daily diet but are stuck for making them varied and interesting, this is the book for you!
Click here to check out Bold Beans, and get your pulse racing (in a good way!)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Immunostimulant Superfood
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eat These Greens!
Chlorella vulgaris, henceforth “chlorella”, is a simple green algae that has a lot of health benefits.
Note: most of the studies here are for Chlorella vulgaris specifically. However, some are for other species of the Chlorella genus, of which Chlorella vulgaris is by far the most common, hence the name (vulgaris = common). The relevant phytochemical properties appear to be the same regardless.
Superfood
While people generally take it as a supplement rather than a food item in any kind of bulk, it is more than 50% protein and contains all 9 essential amino acids.
As you might expect of a green superfood, it’s also full of many antioxidants, most of them carotenoids, and these pack a punch, for example against cancer:
It also has a lot of vitamins and minerals, and even omega-3.
Which latter also means it helps improve lipids and is thus particularly…
Heart healthy
❝Daily consumption of Chlorella supplements provided the potential of health benefits reducing serum lipid risk factors, mainly triglycerides and total cholesterol❞
Its heart-healthy benefits don’t stop at lipids though, and include blood pressure management, as in this study that found…
❝GABA-rich Chlorella significantly decreased high-normal blood pressure and borderline hypertension, and is a beneficial dietary supplement for prevention of the development of hypertension. ❞
About that GABA, if you’re curious about that, check out:
GABA Against Stress, Anxiety, & More
May remove heavy metals
We’re going with “may” for this one as we could only find animal studies so far (probably because most humans don’t have megadoses of heavy metals in them, which makes testing harder).
Here’s an example animal study, though:
Enhanced elimination of tissue methyl mercury in [Chlorella]-fed mice
Immunostimulant
This one’s clearer, for example in this 8-week study (with humans) that found…
❝Serum concentrations of interferon-γ (p<0.05) and interleukin-1β (p<0.001) significantly increased and that of interleukin-12 (p<0.1) tended to increase in the Chlorella group.
The increments of these cytokines after the intervention were significantly bigger in the Chlorella group than those in the placebo group. In addition, NK cell activities (%) were significantly increased in Chlorella group, but not in Placebo group.
The increments of NK cell activities (%) were also significantly bigger in the Chlorella group than the placebo group.
Additionally, changed levels of NK cell activity were positively correlated with those of serum interleukin-1β (r=0.280, p=0.047) and interferon-γ (r=0.271, p<0.005).❞
tl;dr = it boosts numerous different kinds of immune cells
PS, if you click though to the study, you may be momentarily alarmed by the first paragraph of the abstract that says “However, there were no direct evidences for the effect of Chlorella supplementation on immune/inflammation response in healthy humans“
this is from the “Background” section of the abstract, so what they are saying is “before we did this study, nobody had done this yet”.
So, be assured that the results are worthwhile and compelling.
Is it safe?
Based on the studies, it has a good safety profile. However, as it boosts the immune system, you may want to check with your doctor if you have an autoimmune disorder, and/or you are on immunosuppressants.
And in general, of course always check with your doctor/pharmacist if unsure about any potential drug interactions.
Want some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
The CBT Workbook for Mental Health – by Dr. Simon Rego & Sarah Fader
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We have often reviewed psychology books here with a note saying “and no, it’s not just a book of the standard CBT techniques that you probably already know”.
So today, this one’s for anyone who was ever thinking “but I don’t know the standard CBT techniques and I would like to know them!”.
The authors outline specific solutions to many common quantifiable problems, with simple exercises that are well-explained and easy to implement.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is not a panacea, but for the things it can be used for, it’s very effective and is a very good “first thing to reach for” to see if it works, because its success rate for a lot of problems is very high.
What kinds of things is this book most likely to help with? A lot of common forms of stress, anxiety, self-esteem issues, cravings, shame, and relationship issues. Other things too, but we can’t list everything and that list already covers a lot of very high-incidence stuff.
Bottom line: if CBT isn’t something already in your toolbox, this book will help you add all its best tips and tricks.
Click here to check out The CBT Workbook for Mental Health, and get tooled up!
Share This Post
-
How To Avoid Slipping Into (Bad) Old Habits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Treating Bad Habits Like Addictions
How often have you started a healthy new habit (including if it’s a “quit this previous thing” new habit), only to find that you slip back into your old ways?
We’ve written plenty on habit-forming before, so here’s a quick recap before we continue:
How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
…and even how to give them a boost:
How To Keep On Keeping On… Long Term!
But how to avoid the relapses that are most likely to snowball?
Borrowing from the psychology of addiction recovery
It’s well known that someone recovering from substance addiction should not have even a small amount of the thing they were addicted to. Not one sip of champagne at a wedding, not one drag of a cigarette, and so forth.
This can go for other bad habits too; make one exception, and suddenly you have a whole string of “exceptions”, and before you know it, it’s not the exception anymore; it’s the new rule—again.
Three things that can help guard against this are:
- Absolutely refuse to romanticize the bad habit. Do not fall for its marketing! And yes, everything has marketing even if not advertising; for example, consider the Platonic ideal of a junk-food-eating couch-potato who is humble, unassuming, agreeable, the almost-holy idea of homely comfort, and why shouldn’t we be comfortable after all, haven’t we earned our chosen hedonism, and so on. It’s seductive, and we need to make the choice to not be seduced by it. In this case for example, yes pleasure is great, but being sick tired and destroying our bodies is not, in fact, pleasurable in the long run. Which brings us to…
- Absolutely refuse to forget why you dropped that behavior in the first place. Remember what it did to you, remember you at your worst. Remember what you feared might become of you if you continued like that. This is something where journaling helps, by the way; remembering our low points helps us to avoid finding ourselves in the same situation again.
- Absolutely refuse to let your guard down due to an overabundance of self-confidence in your future self. We all can easily feel that tomorrow is a mystical land in which all productivity is stored, and also where we are strong, energized, iron-willed, and totally able to avoid making the very mistakes that we are right now in the process of making. Instead, be that strong person now, for the benefit of tomorrow’s you. Because after all, if it’s going to be easy tomorrow, it’s easy now, right?
The above is a very simple, hopefully practical, set of rules to follow. If you like hard science more though, Yale’s Dr. Steven Melemis offers five rules (aimed more directly at addiction recovery, so this may be a big “heavy guns” for some milder habits):
- change your life
- be completely honest
- ask for help
- practice self-care
- don’t bend the rules
You can read his full paper and the studies it’s based on, here:
Relapse Prevention and the Five Rules of Recovery
“What if I already screwed up?”
Draw a line under it, now, and move forwards in the direction you actually want to go.
Here’s a good article, that saves us taking up more space here; it’s very well-written so we do recommend it:
The Abstinence Violation Effect and Overcoming It
this article gives specific, practical advices, including CBT tools to use
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
HRT Side Effects & Troubleshooting
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Heather Hirsch. She’s a board-certified internist, and her clinical expertise focuses on women’s health, particularly in midlife and menopause, and its intersection with chronic diseases (ranging from things associated with sexual health, to things like osteoporosis and heart disease).
So, what does she want us to know?
HRT can be life-changingly positive, but it can be a shaky start
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT), and in this context she’s talking specifically about the most common kind, Menopausal Hormone Therapy (MHT), involves taking hormones that our body isn’t producing enough of.
If these are “bioidentical hormones” as used in most of the industrialized world and increasingly also in N. America, then this is by definition a supplement rather than a drug, for what it’s worth, whereas some non-bioidentical hormones (or hormone analogs, which by definition function similarly to hormones but aren’t the same thing) can function more like drugs.
We wrote a little about his previously:
Hormone Replacement Therapy: A Tale Of Two Approaches
For most people most of the time, bioidentical hormones are very much the best way to go, as they are not only more effective, but also have fewer side effects.
That said, even bioidentical hormones can have some undesired effects, so, how to deal with those?
Don’t worry; bleed happy
A reprise of (usually quite light) menstrual bleeding is the most common side effect of menopausal HRT.
This happens because estrogen affects* the uterus, leading to a build-up and shedding of the uterine lining.
*if you do not have a uterus, estrogen can effect uterine tissue. That’s not a typo—here we mean the verb “effect”, as in “cause to be”. It will not grow a new uterus, but it can cause some clumps of uterine tissue to appear; this means that it becomes possible to get endometriosis without having a uterus. This information should not be too shocking, as endometriosis is a matter of uterine tissue growing inconveniently, often in places where it shouldn’t, and sometimes quite far from the uterus (if present, or its usual location, if absent). However, the risk of this happening is far lower than if you actually have a uterus:
What you need to know about endometriosis
Back to “you have a uterus and it’s making you wish you didn’t”:
This bleeding should, however, be light. It’ll probably be oriented around a 28-day cycle even if you are taking your hormones at the same dose every day of the month, and the bleeding will probably taper off after about 6 months of this.
If the bleeding is heavier, all the time, or persists longer than 6 months, then speak to your gynecologist about it. Any of those three; it doesn’t have to be all three!
Bleeding outside of one’s normal cycle can be caused by anything from fibroids to cancer; statistically speaking it’s probably nothing too dire,but when your safety is in question, don’t bet on “probably”, and do get it checked out:
When A Period Is Very Late (i.e., Post-Menopause)
Dr. Hirsch recommends, as possible remedies to try (preferably under your gynecologist’s supervision):
- lowering your estrogen dose
- increasing your progesterone dose
- taking progesterone continuously instead of cyclically
And if you’re not taking progesterone, here’s why you might want to consider taking this important hormone that works with estrogen to do good things, and against estrogen to rein in some of estrogen’s less convenient things:
Progesterone Menopausal HRT: When, Why, And How To Benefit
(the above link contains, as well as textual information, an explanatory video from Dr. Hirsch herself)
Get the best of the breast
Calm your tits. Soothe your boobs. Destress your breasts. Hakuna your tatas. Undo the calamity beleaguering your mammaries.
Ok, more seriously…
Breast tenderness is another very common symptom when starting to take estrogen. It can worry a lot of people (à la “aagh, what is this and is it cancer!?”), but is usually nothing to worry about. But just to be sure, do also check out:
Keeping Abreast Of Your Cancer Risk: How To Triple Your Breast Cancer Survival Chances
Estrogen can cause feelings of breast fullness, soreness, nipple irritation, and sometimes lactation, but this later will be minimal—we’re talking a drop or two now and again, not anything that would feed a baby.
Basically, it happens when your body hasn’t been so accustomed to normal estrogen levels in a while, and suddenly wakes up with a jolt, saying to itself “Wait what are we doing puberty again now? I thought we did menopause? Are we pregnant? What’s going on? Ok, checking all systems!” and then may calm down not too long afterwards when it notes that everything is more or less as it should be already.
If this persists or is more than a minor inconvenience though, Dr. Hirsch recommends looking at the likely remedies of:
- Adjust estrogen (usually the cause)
- Adjust progesterone (less common)
- If it’s progesterone, changing the route of administration can ameliorate things
What if it’s not working? Is it just me?
Dr. Hirsch advises the most common reasons are simply:
- wrong formulation (e.g. animal-derived estrogen or hormone analog, instead of bioidentical)
- wrong dose (e.g. too low)
- wrong route of administration (e.g. oral vs transdermal; usually transdermal estradiol is most effective but many people do fine on oral; progesterone meanwhile is usually best as a pessary/suppository, but many people do fine on oral)
Writer’s example: in 2022 there was an estrogen shortage in my country, and while I had been on transdermal estradiol hemihydrate gel, I had to go onto oral estradiol valerate tablets for a few months, because that’s what was available. And the tablets simply did not work for me at all. I felt terrible and I have a good enough intuitive sense of my hormones to know when “something wrong is not right”, and a good enough knowledge of the pharmacology & physiology to know what’s probably happening (or not happening). And sure enough, when I got my blood test results, it was as though I’d been taking nothing. It was such a relief to get back on the gel once it became available again!
So, if something doesn’t seem to be working for you, speak up and get it fixed if at all possible.
See also: What You Should Have Been Told About Menopause Beforehand
Want to know more from Dr. Hirsch?
You might like this book of hers, which we haven’t reviewed yet, but present here for your interest:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What are house dust mites and how do I know if I’m allergic to them?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
People often believe they are allergic to house dust. But of the 20% of Australians suffereing with allergies, a number are are actually allergic to microscopic house dust mites.
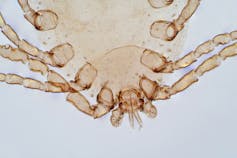
House dust mites belong to the same family as spiders and ticks. They measure just 0.2-0.3 mm, with 50 fitting on a single pinhead. They live for 65–100 days, and females lay 60–100 eggs in their life.
Some 50 house dust mites can fit on one pinhead. Choksawatdikorn/Shutterstock House dust mites love temperate climates and humidity. They feed off the skin cells we and animals shed, as well as mould, which they digest using special enzymes. These enzymes are excreted in their poo about 20 times a day. They also shed fragments of their exoskeletons.
All these fragments trigger allergies in people with this type of allergic rhinitis (which is also known as hay fever)
shuttertock. PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock What are the symptoms?
When people with house dust mite allergy inhale the allergens, they penetrate the mucous membranes of the airways and eyes. Their body recognises the allergens as a threat, releasing chemicals including one called histamine.
This causes symptoms including a runny nose, an itchy nose, eyes and throat, sneezing, coughing and a feeling of mucus at the back of your throat (known as a post-nasal drip).
People with this type of allergy usually mouth breath, snore, rub their nose constantly (creating a nasal crease called the “dust mite salute”) and have dark shadows under their eyes.
House dust mite allergy can also cause poor sleep, constant tiredness, reduced concentration at work or school and lower quality of life.
For people with eczema, their damaged skin barrier can allow house dust mite proteins in. This prompts immune cells in the skin to release chemicals which make already flared skin become redder, sorer and itchier, especially in children.
Symptoms of house dust mite allergy occur year round, and are often worse after going to bed and when waking in the morning. But people with house dust mite allergy and pollen allergies find their year-round symptoms worsen in spring.
How is it diagnosed?
House dust mite allergy symptoms often build up over months, or even years before people seek help. But an accurate diagnosis means you can not only access the right treatment – it’s also vital for minimising exposure.
Your clinician can talk you through treatment options and how to minimise exposure. Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock Doctor and nurse practitioners can order a blood test to check for house dust mite allergy.
Alternatively, health care providers with specialised allergy training can perform skin prick tests. This involves placing drops of the allergens on the arm, along with a positive and negative “control”. After 15 minutes, those who test positive will have developed a mosquito bite-like mark.
How is it treated?
Medication options include one or a combination of:
- daily non-sedating antihistamines
- a steroid nasal spray
- allergy eye drops.
Your health care professional will work with you to develop a rhinitis (hay fever) medical management plan to reduce your symptoms. If you’re using a nasal spray, your health provider will show you how to use it, as people often use it incorrectly.
If you also have asthma or eczema which is worsened by dust mites, your health provider will adapt your asthma action plan or eczema care plan accordingly.
If you experience severe symptoms, a longer-term option is immunotherapy. This aims to gradually turn off your immune system’s ability to recognise house dust mites as a harmful allergen.
Immunotherapy involves taking either a daily sublingual tablet, under the tongue, or a series of injections. Injections require monthly attendances over three years, after the initial weekly build-up phase.
These are effective, but are costly (as well as time-consuming). So it’s important to weigh up the potential benefits and downsides with your health-care provider.
How can you minimise house dust mites?
There are also important allergy minimisation measures you can take to reduce allergens in your home.
Each week, wash your bedding and pyjamas in hot water (over 60°C). This removes house dust mite eggs and debris.
Opt for doonas, covers or quilts that can be washed in hot water above 60°C. Alternatively, low-cost waterproof or leak proof covers can keep house dust mites out.
If you can, favour blinds and wood floors over curtains and carpet. Dust blinds and surfaces with a damp cloth each week and vacuum while wearing a mask, or have someone else do it, as house dust mites can become airborne during cleaning.
But beware of costly products with big marketing budgets and little evidence to support their use. A new mattress, for example, will always be house dust mite-free. But once slept on, the house dust mite life cycle can start.
Mattress protectors and toppers commonly claim to be “hypoallergenic”, “anti-allergy” or “allergy free”. But their pore sizes are not small enough to keep house dust mites and their poo out, or shed skin going through.
Sprays claiming to kill mites require so much spray to penetrate the product that it’s likely to become wet, may smell like the spray and, unless dried properly, may grow mould.
Finally, claims that expensive vacuum cleaners can extract all the house dust mites are unsubstantiated.
For more information, visit healthdirect.gov.au or the Australian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy.
Deryn Lee Thompson, Eczema and Allergy Nurse; Lecturer, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
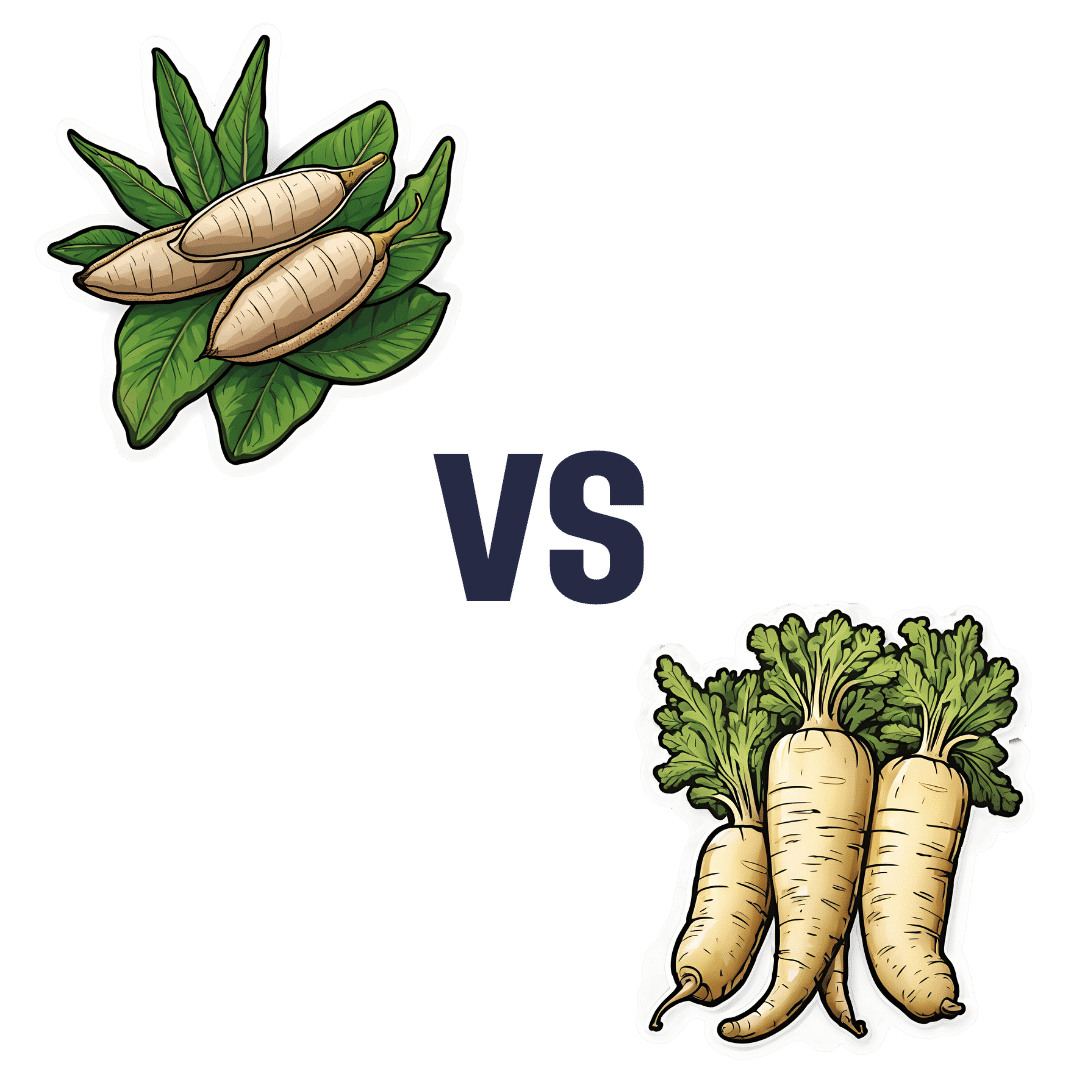
Cassava vs Parsnip – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cassava to parsnips, we picked the parsnips.
Why?
This one wasn’t close!
In terms of macros, cassava has more than 2x the carbs while parsnips have nearly 3x the fiber, making for a very clear win for parsnips.
In the category of vitamins, cassava has more of vitamins B3 and C, while parsnips have more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, B9, E, and K, with very large margins of difference in the latter two cases. Another overwhelming win for parsnips.
Looking at minerals, cassava is not higher in any minerals, while parsnips have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc; a very one-sided win for parsnips!
So, by all means enjoy either or both (diversity is good), but there’s a clear winner here today, and it’s parsnips.
Want to learn more?
You might like:
What Do The Different Kinds Of Fiber Do? 30 Foods That Rank Highest
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: