Can you drink your fruit and vegetables? How does juice compare to the whole food?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do you struggle to eat your fruits and vegetables? You are not alone. Less than 5% of Australians eat the recommended serves of fresh produce each day (with 44% eating enough fruit but only 6% eating the recommended vegetables).
Adults should aim to eat at least five serves of vegetables (or roughly 375 grams) and two serves of fruit (about 300 grams) each day. Fruits and vegetables help keep us healthy because they have lots of nutrients (vitamins, minerals and fibre) and health-promoting bioactive compounds (substances not technically essential but which have health benefits) without having many calories.
So, if you are having trouble eating the rainbow, you might be wondering – is it OK to drink your fruits and vegetables instead in a juice or smoothie? Like everything in nutrition, the answer is all about context.

It might help overcome barriers
Common reasons for not eating enough fruits and vegetables are preferences, habits, perishability, cost, availability, time and poor cooking skills. Drinking your fruits and vegetables in juices or smoothies can help overcome some of these barriers.
Juicing or blending can help disguise tastes you don’t like, like bitterness in vegetables. And it can blitz imperfections such as bruises or soft spots. Preparation doesn’t take much skill or time, particularly if you just have to pour store-bought juice from the bottle. Treating for food safety and shipping time does change the make up of juices slightly, but unsweetened juices still remain significant sources of nutrients and beneficial bioactives.
Juicing can extend shelf life and reduce the cost of nutrients. In fact, when researchers looked at the density of nutrients relative to the costs of common foods, fruit juice was the top performer.
So, drinking my fruits and veggies counts as a serve, right?
How juice is positioned in healthy eating recommendations is a bit confusing. The Australian Dietary Guidelines include 100% fruit juice with fruit but vegetable juice isn’t mentioned. This is likely because vegetable juices weren’t as common in 2013 when the guidelines were last revised.
The guidelines also warn against having juice too often or in too high amounts. This appears to be based on the logic that juice is similar, but not quite as good as, whole fruit. Juice has lower levels of fibre compared to fruits, with fibre important for gut health, heart health and promoting feelings of fullness. Juice and smoothies also release the sugar from the fruit’s other structures, making them “free”. The World Health Organization recommends we limit free sugars for good health.
But fruit and vegetables are more than just the sum of their parts. When we take a “reductionist” approach to nutrition, foods and drinks are judged based on assumptions made about limited features such as sugar content or specific vitamins.
But these features might not have the impact we logically assume because of the complexity of foods and people. When humans eat varied and complex diets, we don’t necessarily need to be concerned that some foods are lower in fibre than others. Juice can retain the nutrients and bioactive compounds of fruit and vegetables and even add more because parts of the fruit we don’t normally eat, like the skin, can be included.

So, it is healthy then?
A recent umbrella review of meta-analyses (a type of research that combines data from multiple studies of multiple outcomes into one paper looked at the relationship between 100% juice and a range of health outcomes.
Most of the evidence showed juice had a neutral impact on health (meaning no impact) or a positive one. Pure 100% juice was linked to improved heart health and inflammatory markers and wasn’t clearly linked to weight gain, multiple cancer types or metabolic markers (such as blood sugar levels).
Some health risks linked to drinking juice were reported: death from heart disease, prostate cancer and diabetes risk. But the risks were all reported in observational studies, where researchers look at data from groups of people collected over time. These are not controlled and do not record consumption in the moment. So other drinks people think of as 100% fruit juice (such as sugar-sweetened juices or cordials) might accidentally be counted as 100% fruit juice. These types of studies are not good at showing the direct causes of illness or death.
What about my teeth?
The common belief juice damages teeth might not stack up. Studies that show juice damages teeth often lump 100% juice in with sweetened drinks. Or they use model systems like fake mouths that don’t match how people drinks juice in real life. Some use extreme scenarios like sipping on large volumes of drink frequently over long periods of time.
Juice is acidic and does contain sugars, but it is possible proper oral hygiene, including rinsing, cleaning and using straws can mitigate these risks.
Again, reducing juice to its acid level misses the rest of the story, including the nutrients and bioactives contained in juice that are beneficial to oral health.

So, what should I do?
Comparing whole fruit (a food) to juice (a drink) can be problematic. They serve different culinary purposes, so aren’t really interchangeable.
The Australian Guide to Healthy Eating recommends water as the preferred beverage but this assumes you are getting all your essential nutrients from eating.
Where juice fits in your diet depends on what you are eating and what other drinks it is replacing. Juice might replace water in the context of a “perfect” diet. Or juice might replace alcohol or sugary soft drinks and make the relative benefits look very different.
On balance
Whether you want to eat your fruits and vegetables or drink them comes down to what works for you, how it fits into the context of your diet and your life.
Smoothies and juices aren’t a silver bullet, and there is no evidence they work as a “cleanse” or detox. But, with society’s low levels of fruit and vegetable eating, having the option to access nutrients and bioactives in a cheap, easy and tasty way shouldn’t be discouraged either.
Emma Beckett, Adjunct Senior Lecturer, Nutrition, Dietetics & Food Innovation – School of Health Sciences, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
5 Ways to Beat Menopausal Weight Gain!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As it turns out, “common” does not mean “inevitable”!
Health Coach Kait’s advice
Her 5 tips are…
- Understand your metabolism: otherwise you’re working the dark and will get random results. Learn about how different foods affect your metabolism, and note that hormonal changes due to menopause can mean that some food types have different effects now.
- Eat enough protein: one thing doesn’t change—protein helps with satiety, thus helping to avoid overeating.
- Focus on sleep: prioritizing sleep is essential for hormone regulation, and that means not just sex hormones, but also food-related hormones such as insulin, ghrelin, and leptin.
- Be smart about carbs: taking a lot of carbs at once can lead to insulin spikes and thus metabolic disorder, which in turn leads to fat in places you don’t want it (especially your liver and belly). Enjoying a low-carb diet, and/or pairing your carbs with proteins and fats, does a lot to help avoid insulin spikes too. Not mentioned in the video, but we’re going to mention here: don’t underestimate fiber’s role either, especially if you take it before the carbs, which is best for blood sugars, as it gives a buffer to the digestive process, thus slowing down absorption of carbs.
- Build muscle: if trying to avoid/lose fat, it’s tempting to focus on cardio, but we generally can’t exercise our way out of having fat, whereas having more muscle increases the body’s metabolic base rate, burning fat just by existing. So for this reason, enjoy muscle-building resistance exercises at least a few times per week.
For more information on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Biological Mind – by Dr. Alan Jasanoff
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How special is our brain? According to Dr. Alan Jasanoff, it’s not nearly as special as we think it is.
In this work, he outlines the case for how we have collectively overstated the brain’s importance. That it’s just another organ like a heart or a kidney, and that who we are is as much a matter of other factors, as what goes on in our brain.
In this reviewer’s opinion, he overcorrects a bit. The heart and kidneys are very simple organs, as organs go. The brain is not. And while everything from our gut microbiota to our environment to our hormones may indeed contribute to what is us, our brain is one thing that can’t just be swapped out.
Nevertheless, this very well-written book can teach us a lot about everything else that makes us us, including many biological factors that many people don’t know about or consider.
Towards the end of the book, he switches into futurist speculation, and his speculation can be summed up as “we cannot achieve anything worthwhile in the future”.
Bottom line: if you’ve an interest in such things as how transplanting glial cells can give a 30% cognitive enhancement, and how a brain transplant wouldn’t result in the same us in a different body, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out The Biological Mind, and learn about yours!
Share This Post
-
25 Healthy Habits That Will Change Your Life
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cori Lefkowith, of “Redefining Strength” and “Strong At Every Age” fame, has compiled a list of the simple habits that make a big difference, and here they are!
The Tips
Her recommendations include…
- The healthy activities you’re most prone to skipping? Do those first
- Create staple meals… Consciously! This means: instead of getting into a rut of cooking the same few things in rotation because it’s what you have the ingredients in for, consciously and deliberately make a list of at least 7 meals that, between them, constitute a healthy balanced diet, and choose to make them your staples. That doesn’t mean don’t eat anything else (indeed, variety is good!) but having a robust collection of healthy staples to fall back on will help you avoid falling into unhealthy eating traps.
- Schedule time for healthy activities that you love. Instead of thinking “it would be nice to…”, actually figure out a timeslot, plan in advance, making it recurring, and do it!
- Have (healthy!) no-spoil food options always available. No-spoil doesn’t have to mean “won’t spoil ever”, but does mean at least that it has a long shelf-life. Nuts are a good example, assuming you’re not allergic. Sundried fruits are good too; not nearly as good as fresh fruit, but a lot better than some random processed snack because it’s what in. If you eat fish, then see if you can get dried fish in; it’s high in protein and keeps for a very long time indeed.
- Stock up on spices! Not only do they all have great health-giving properties (at least, we can’t think of a refutation by counterexample, Arrakis be damned), but also, they literally spice up our culinary repertoire, and bring joy to cooking and eating healthy food.
If you like these, check out the rest:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Further reading
For more about actually making habits stick quickly and reliably,enjoy:
How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Forever Strong – by Dr. Gabrielle Lyon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Obesity kills a lot of people (as does medical neglect and malpractice when it comes to obese patients, but that is another matter), but often the biggest problem is not “too much fat” but rather “too little muscle”. This gets disguised a bit, because these factors often appear in the same people, but it’s a distinction that’s worthy of note.
Dr. Lyon lays out a lot of good hard science in this work, generally in the field of protein metabolism, but also with a keen eye on all manner of blood metrics (triglycerides, LDL/HDL, fasting blood sugars, assorted other biomarkers of metabolic health).
The style of this book is two books in one. It’s a very accessible pop-science book in its primary tone, with an extra layer of precise science and lots of references, for those who wish to dive into that.
In the category of criticism, the diet plan section of the book is rather meat-centric, but the goal of this is protein content, not meat per se, so substitutions can easily be made. That’s just one small section of the book, though, and it’s little enough a downside that even Dr. Mark Hyman (a popular proponent of plant-based nutrition) highly recommends the book.
Bottom line: if you’d like to be less merely fighting decline and more actually becoming healthier as you age, then this book will help you do just that.
Click here to check out Forever Strong, and level up your wellness as you age!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
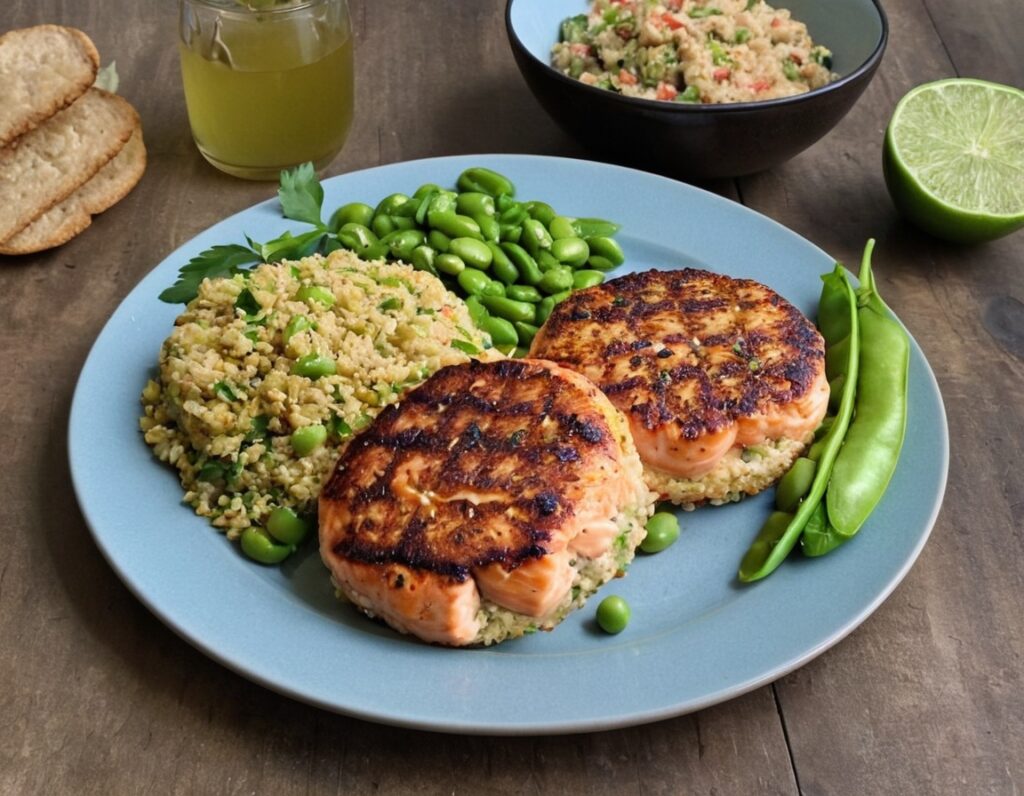
Green Curry Salmon Burgers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These lean and healthy burgers are as quick and easy to make as they are good for entertaining. The serving-bed has its nutritional secrets too! All in all, an especially heart-healthy and brain-healthy dish.
You will need
- 4 skinless salmon fillets, cubed (Vegetarian/Vegan? Consider this Plant-Based Salmon Recipe or, since they are getting blended, simply substitute 1½ cups cooked chickpeas instead with 1 tbsp tahini)
- 2 cloves garlic, chopped
- 2 tbsp thai green curry paste
- juice of two limes, plus wedges to serve
- 1 cup quinoa
- ½ cup edamame beans, thawed if they were frozen
- large bunch fresh cilantro (or parsley if you have the “soap “cilantro tastes like soap” gene), chopped
- extra virgin olive oil, for frying
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the salmon, garlic, curry paste, nutritional yeast, and half the lime juice into a food processor, and blend until smooth.
2) Remove, divide into four parts, and shape into burger patty shapes. Put them in the fridge where they can firm up while we do the next bit.
3) Cook the quinoa with the tablespoon of chia seeds added (which means boiling water and then letting it simmer for 10–15 minutes; when the quinoa is tender and unfurled a little, it’s done).
4) Drain the quinoa with a sieve, and stir in the edamame beans, the rest of the lime juice, the cilantro, and the black pepper. Set aside.
5) Using the olive oil, fry the salmon burgers for about 5 minutes on each side.
6) Serve; we recommend putting the burgers atop the rest, and adding a dash of lime at the table.
(it can also be served this way!)
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Farmed Fish vs Wild–Caught
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Problem With Sweeteners
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The WHO’s view on sugar-free sweeteners
The WHO has released a report offering guidance regards the use of sugar-free sweeteners as part of a weight-loss effort.
In a nutshell, the guidance is: don’t
- Here’s the report itself: Use of non-sugar sweeteners: WHO guideline
- Here’s the WHO’s own press release about it: WHO advises not to use non-sugar sweeteners for weight control in newly released guideline
- And it was based on this huge systematic review: Health effects of the use of non-sugar sweeteners: a systematic review and meta-analysis
They make for interesting reading, so if you don’t have time now, you might want to just quickly open and bookmark them for later!
Some salient bits and pieces:
Besides that some sweeteners can cause gastro-intestinal problems, a big problem is desensitization:
Because many sugar substitutes are many times (in some cases, hundreds of times) sweeter than sugar, this leads to other sweet foods tasting more bland, causing people to crave sweeter and sweeter foods for the same satisfaction level.
You can imagine how that’s not a spiral that’s good for the health!
The WHO recommendation applies to artificial and naturally-occurring non-sugar sweeteners, including:
- Acesulfame K
- Advantame
- Aspartame
- Cyclamates
- Neotame
- Saccharin
- Stevia
Sucralose and erythritol, by the way, technically are sugars, just not “that kind of sugar” so they didn’t make the list of non-sugar sweeteners.
That said, a recent study did find that erythritol was linked to a higher risk of heart attack, stroke, and early death, so it may not be an amazing sweetener either:
Read: The artificial sweetener erythritol and cardiovascular event risk
Want to know a good way of staying healthy in the context of sweeteners?
Just get used to using less. Your taste buds will adapt, and you’ll get just as much pleasure as before, from progressively less sweetening agent.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: