If Your Adult Kid Calls In Crisis…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Parent(s) To The Rescue?
We’ve written before about the very common (yes, really, it is common) phenomenon of estrangement between parents and adult children:
Family Estrangement & How To Fix It
We’ve also written about the juggling act that can be…
Managing Sibling Relationships In Adult Life
…which includes dealing with such situations as supporting each other through difficult times, while still maintaining healthy boundaries.
But what about when one’s [adult] child is in crisis?
When a parent’s job never ends
Hopefully, we have not been estranged (or worse, bereaved) by our children.
In which case, when crisis hits, we are likely to be amongst the first to whom our children will reach out for support. Naturally, we will want to help. But how can we do that, and where (if applicable) to draw the line?
No “helicopter parenting”
If you’ve not heard the term “helicopter parenting”, it refers to the sort of parents who hover around, waiting to swoop in at a moment’s notice.
This is most often applied to parents of kids of university age and downwards, but it’s worth keeping it in mind at any age.
After all, we do want our kids to be able to solve their own problems if possible!
So, if you’ve ever advised your kid to “take a deep breath and count to 10” (or even if you haven’t), then, consider doing that too, and then…
Listen first!
If your first reaction isn’t to join them in panic, it might be to groan and “oh not again”. But for now, quietly shelve that, and listen to whatever it is.
See also: Active Listening (Without Sounding Like A Furby)
And certainly, do your best to maintain your own calm while listening. Your kid is in all likelihood looking to you to be the rock in the storm, so let’s be that.
Empower them, if you can
Maybe they just needed to vent. If so, the above will probably cover it.
More likely, they need help.
Perhaps they need guidance, from your greater life experience. Sometimes things that can seem like overwhelming challenges to one person, are a thing we dealt with 20 or more years ago (it probably felt overwhelming to us at the time, too, but here we are, the other side of it).
Tip: ask “are you looking for my guidance/advice/etc?” before offering it. Doing so will make it much more likely to be accepted rather than rejected as unsolicited advice.
Chances are, they will take the life-ring offered.
It could be that that’s not what they had in mind, and they’re looking for material support. If so…
When it’s about money or similar
Tip: it’s worth thinking about this sort of thing in advance (now is great, if you have adult kids), and ask yourself nowwhat you’d be prepared to give in that regard, e.g:
- if they need money, how much (if any) are you willing and able to provide?
- if they want/need to come stay with you, how prepared are you for that (including: if they want/need to actually move back in with you for a while, which is increasingly common these days)?
Having these answers in your head ready will make the conversation a lot less difficult in the moment, and will avoid you giving a knee-jerk response you might regret (in either direction).
Have a counteroffer up your sleeve if necessary
Maybe:
- you can’t solve their life problem for them, but you can help them find a therapist (if applicable, for example)
- you can’t solve their money problem for them, but you can help them find a free debt advice service (if applicable, for example)
- you can’t solve their residence problem for them, but you can help them find a service that can help with that (if applicable, for example)
You don’t need to brainstorm now for every option; you’re a parent, not Batman. But it’s a lot easier to think through such hypothetical thought-experiments now, than it will be with your fraught kid on the phone later.
Magic words to remember: “Let’s find a way through this for you”
Don’t forget to look after yourself
Many of us, as parents, will tend to not think twice before sacrificing something for our kid(s). That’s generally laudable, but we must avoid accidentally becoming “the giving tree” who has nothing left for ourself, and that includes our mental energy and our personal peace.
That doesn’t mean that when our kid comes in crisis we say “Shh, stop disturbing my personal peace”, but it does mean that we remember to keep at least some boundaries (also figure out now what they are, too!), and to take care of ourselves too.
The following article was written with a slightly different scenario in mind, but the advice remains just as valid here:
How To Avoid Carer Burnout (Without Dropping Care)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
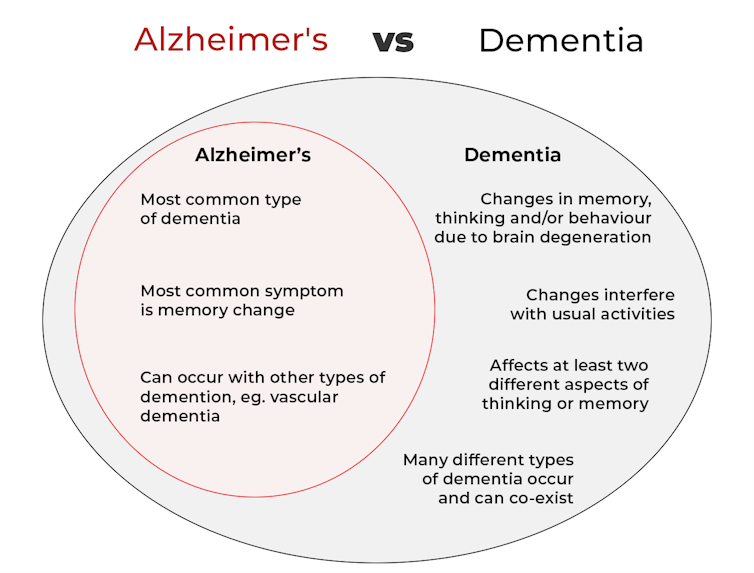
What’s the difference between Alzheimer’s and dementia?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
Changes in thinking and memory as we age can occur for a variety of reasons. These changes are not always cause for concern. But when they begin to disrupt daily life, it could indicate the first signs of dementia.
Another term that can crop up when we’re talking about dementia is Alzheimer’s disease, or Alzheimer’s for short.
So what’s the difference?
Lightspring/Shutterstock What is dementia?
Dementia is an umbrella term used to describe a range of syndromes that result in changes in memory, thinking and/or behaviour due to degeneration in the brain.
To meet the criteria for dementia these changes must be sufficiently pronounced to interfere with usual activities and are present in at least two different aspects of thinking or memory.
For example, someone might have trouble remembering to pay bills and become lost in previously familiar areas.
It’s less-well known that dementia can also occur in children. This is due to progressive brain damage associated with more than 100 rare genetic disorders. This can result in similar cognitive changes as we see in adults.
So what’s Alzheimer’s then?
Alzheimer’s is the most common type of dementia, accounting for about 60-80% of cases.
So it’s not surprising many people use the terms dementia and Alzheimer’s interchangeably.
Changes in memory are the most common sign of Alzheimer’s and it’s what the public most often associates with it. For instance, someone with Alzheimer’s may have trouble recalling recent events or keeping track of what day or month it is.
People with dementia may have trouble keeping track of dates. Daisy Daisy/Shutterstock We still don’t know exactly what causes Alzheimer’s. However, we do know it is associated with a build-up in the brain of two types of protein called amyloid-β and tau.
While we all have some amyloid-β, when too much builds up in the brain it clumps together, forming plaques in the spaces between cells. These plaques cause damage (inflammation) to surrounding brain cells and leads to disruption in tau. Tau forms part of the structure of brain cells but in Alzheimer’s tau proteins become “tangled”. This is toxic to the cells, causing them to die. A feedback loop is then thought to occur, triggering production of more amyloid-β and more abnormal tau, perpetuating damage to brain cells.
Alzheimer’s can also occur with other forms of dementia, such as vascular dementia. This combination is the most common example of a mixed dementia.
Vascular dementia
The second most common type of dementia is vascular dementia. This results from disrupted blood flow to the brain.
Because the changes in blood flow can occur throughout the brain, signs of vascular dementia can be more varied than the memory changes typically seen in Alzheimer’s.
For example, vascular dementia may present as general confusion, slowed thinking, or difficulty organising thoughts and actions.
Your risk of vascular dementia is greater if you have heart disease or high blood pressure.
Frontotemporal dementia
Some people may not realise that dementia can also affect behaviour and/or language. We see this in different forms of frontotemporal dementia.
The behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia is the second most common form (after Alzheimer’s disease) of younger onset dementia (dementia in people under 65).
People living with this may have difficulties in interpreting and appropriately responding to social situations. For example, they may make uncharacteristically rude or offensive comments or invade people’s personal space.
Semantic dementia is also a type of frontotemporal dementia and results in difficulty with understanding the meaning of words and naming everyday objects.
Dementia with Lewy bodies
Dementia with Lewy bodies results from dysregulation of a different type of protein known as α-synuclein. We often see this in people with Parkinson’s disease.
So people with this type of dementia may have altered movement, such as a stooped posture, shuffling walk, and changes in handwriting. Other symptoms include changes in alertness, visual hallucinations and significant disruption to sleep.
Do I have dementia and if so, which type?
If you or someone close to you is concerned, the first thing to do is to speak to your GP. They will likely ask you some questions about your medical history and what changes you have noticed.
Sometimes it might not be clear if you have dementia when you first speak to your doctor. They may suggest you watch for changes or they may refer you to a specialist for further tests.
There is no single test to clearly show if you have dementia, or the type of dementia. A diagnosis comes after multiple tests, including brain scans, tests of memory and thinking, and consideration of how these changes impact your daily life.
Not knowing what is happening can be a challenging time so it is important to speak to someone about how you are feeling or to reach out to support services.
Dementia is diverse
As well as the different forms of dementia, everyone experiences dementia in different ways. For example, the speed dementia progresses varies a lot from person to person. Some people will continue to live well with dementia for some time while others may decline more quickly.
There is still significant stigma surrounding dementia. So by learning more about the various types of dementia and understanding differences in how dementia progresses we can all do our part to create a more dementia-friendly community.
The National Dementia Helpline (1800 100 500) provides information and support for people living with dementia and their carers. To learn more about dementia, you can take this free online course.
Nikki-Anne Wilson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Neuroscience Research Australia (NeuRA), UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
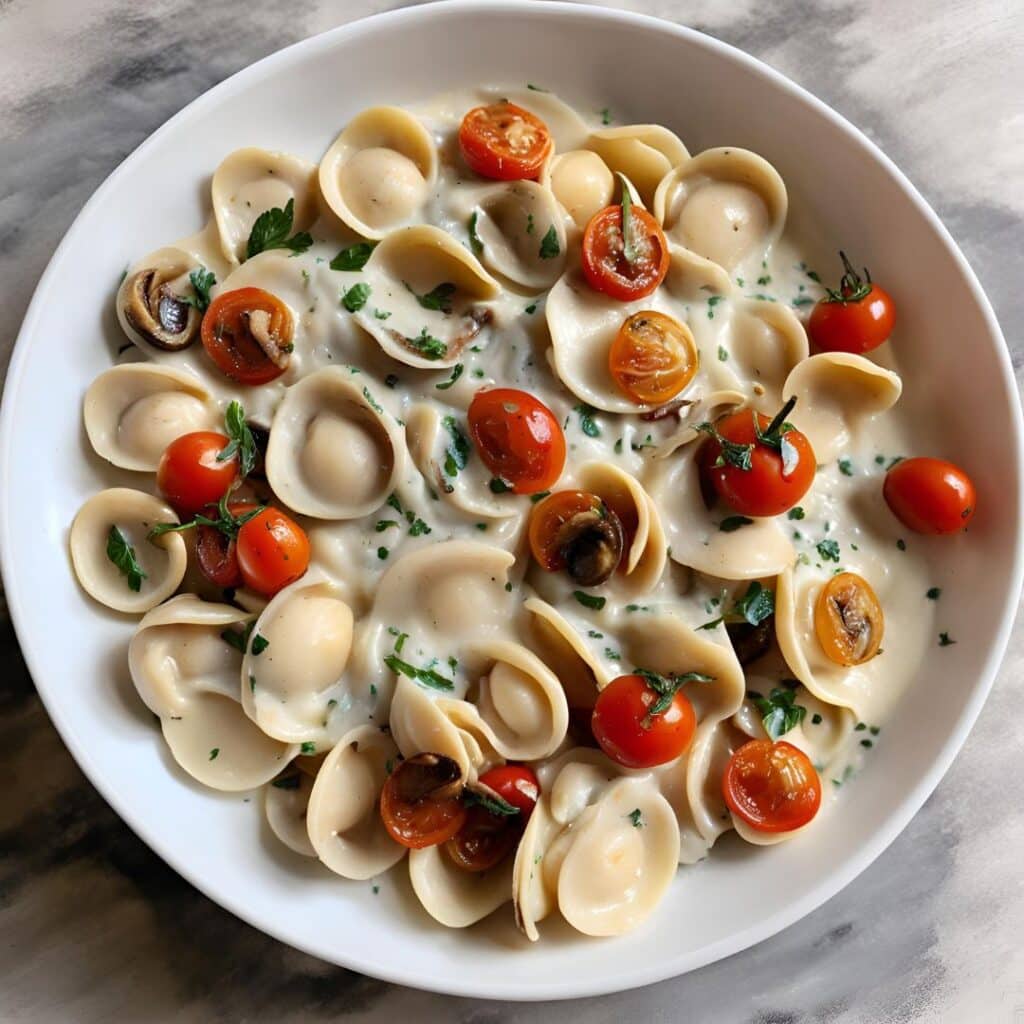
Gut-Healthy Labneh Orecchiette
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Labneh (a sort of yogurt-cheese made from strained yogurt) is a great probiotic, and there’s plenty of resistant starch in this dish too, from how we cook, cool, and reheat the pasta. Add to this the lycopene from the tomatoes, the ergothioneine from the mushrooms, and the healthful properties of the garlic, black pepper, and red chili, and we have a very healthy dish!
You will need
- 10 oz labneh (if you can’t buy it locally, you can make your own by straining Greek yogurt through a muslin cloth, suspended over a bowl to catch the water that drips out, overnight—and yes, plant-based is also fine if you are vegan, and the gut benefits are similar because unlike vegan cheese, vegan yogurt is still fermented)
- 6 oz wholegrain orecchiette (or other pasta, but this shape works well for this sauce)
- ¼ bulb garlic, grated
- Juice of ½ lemon
- Large handful chopped parsley
- Large handful chopped dill
- 9 oz cherry tomatoes, halved
- 9 oz mushrooms (your choice what kind), sliced (unless you went for shiitake or similar, which don’t need it due to already being very thin)
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the pasta as you normally would. Drain, and rinse with cold water. Set aside.
2) Combine the labneh with the garlic, black pepper, dill, parsley, and lemon juice, in a large bowl. Set aside.
3) Heat a little olive oil in a skillet; add the chili flakes, followed by the mushrooms. Cook until soft and browned, then add the tomatoes and fry for a further 1 minute—we want the tomatoes to be blistered, but not broken down. Stir in the MSG/salt, and take off the heat.
4) Refresh the pasta by passing a kettle of boiling water through it in a colander, then add the hot pasta to the bowl of labneh sauce, stirring to coat thoroughly.
5) Serve, spooning the mushrooms and tomatoes over the labneh pasta.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How To Lower Your Blood Pressure (Cardiologists Explain)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Today we enjoy the benefit of input from Dr. Zalzal, Dr. Weeing, and Dr. Hefferman!
If the thought of being in an operating room with three cardiologists in scrubs doesn’t raise your blood pressure too much, the doctors in question have a lot to offer for bringing those numbers down and keeping them down! They recommend…
150 mins of Exercise
This isn’t exactly controversial, but: move your body!
See also: Exercise Less; Move More
Reduce salt
Most people eating the Standard American Diet (SAD) are getting far too much—mostly because it’s in so many processed foods already.
See also: How Too Much Salt May Lead To Organ Failure
Eating habits
There’s a lot more to eating healthily for the heart than just reducing salt, and over all, the Mediterranean diet comes out scoring highest:
- What Is The Mediterranean Diet Anyway? ← a primer for the uncertain
- Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean ← includes a heart-specialized version!
Reduce alcohol
According to the WHO, the only healthy amount of alcohol is zero. According to these cardiologists: at the very least cut down. However much or little you’re drinking right now, less is better.
See also: How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
Maintain healthy weight
While the doctors agree that BMI isn’t a great method of measuring metabolic health, it is clear that carrying excessive weight isn’t good for the heart.
See also: Lose Weight (Healthily!)
No smoking
This one’s pretty straight forward: just don’t.
See also: Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
Reduce stress
Chronic stress has a big impact on chronic health in general and that includes its effect on blood pressure. So, improving one improves the other.
See also: Lower Your Cortisol! (Here’s Why & How)
Good sleep
Quality matters as much as quantity, and that goes for its effect on your blood pressure too, so take the time to invest in your good health!
See also: The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
At The Heart Of Women’s Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A woman’s heart is a particular thing
For the longest time (and still to a large degree now), “women’s health” is assumed to refer to the health of organs found under a bikini. But there’s a lot more to it than that. We are whole people, with such things as brains and hearts and more.
Today (Valentine’s Day!) we’re focusing on the heart.
A quick recap:
We’ve talked previously about some of these sex differences when it comes to the heart, for example:
Heart Attack: His & Hers (Be Prepared!)
…but that’s fairly common knowledge at least amongst those who are attentive to such things, whereas…
…is much less common knowledge, especially with the ways statins are more likely to make things worse for a lot of women (not all though; see the article for some nuance about that).
We also talked about:
What Menopause Does To The Heart
…which is well worth reading too!
A question:
Why are women twice as likely to die from a heart attack as their age-equivalent male peers? Women develop heart disease later, but die from it sooner. Why is that?
That’s been a question scientists have been asking (and tentatively answering, as scientists do—hypotheses, theories, conclusions even sometimes) for 20 years now. Likely contributing factors include:
- A lack of public knowledge of the different symptoms
- A lack of confidence of bystanders to perform CPR on a woman
- A lack of public knowledge (including amongst prescribers) about the sex-related differences for statins
- A lack of women in cardiology, comparatively.
- A lack of attention to it, simply. Men get heart disease earlier, so it’s thought of as a “man thing”, by health providers as much as by individuals. Men get more regular cardiovascular check-ups, women get a mammogram and go.
Statistically, women are much more likely to die from heart disease than breast cancer:
- Breast cancer kills around 0.02% of us.
- Heart disease kills one in three.
And yet…
❝In a nationwide survey, only 22% of primary care doctors and 42% of cardiologists said they feel extremely well prepared to assess cardiovascular risks in women.
We are lagging in implementing risk prevention guidelines for women.
A lot of women are being told to just watch their cholesterol levels and see their doctor in a year. That’s a year of delayed care.❞
Source: The slowly evolving truth about heart disease and women
(there’s a lot more in that article than we have room for in ours, so do check it out!)
Some good news:
The “bystanders less likely to feel confident performing CPR on a woman” aspect may be helped by the deployment of new automatic external defibrillator, that works from four sides instead of one.
It’s called “double sequential external defibrillation”, and you can learn about it here:
A new emergency procedure for cardiac arrests aims to save more lives—here’s how it works
(it’s in use already in Canada and Aotearoa)
Gentlemen-readers, thank you for your attention to this one even if it was mostly not about you! Maybe someone you love will benefit from being aware of this
On a lighter note…
Since it’s Valentine’s Day, a little more on affairs of the heart…
Is chocolate good for the heart? And is it really an aphrodisiac?
We answered these questions and more in our previous main feature:
Chocolate & Health: Fact or Fiction?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Freekeh Tomato Feast
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fiber-dense freekeh stars in this traditional Palestinian dish, and the whole recipe is very gut-healthy, not to mention delicious and filling, as well as boasting generous amounts of lycopene and other phytonutrients:
You will need
- 1 cup dried freekeh (if avoiding gluten, substitute a gluten-free grain, or pseudograin such as buckwheat; if making such a substitution, then also add 1 tbsp nutritional yeast—for the flavor as well as the nutrients)
- 1 medium onion, thinly sliced
- 1 2oz can anchovies (if vegan/vegetarian, substitute 1 can kimchi)
- 1 14oz can cherry tomatoes
- 1 cup halved cherry tomatoes, fresh
- ½ cup black olives, pitted
- 1 5oz jar roasted peppers, chopped
- ½ bulb garlic, thinly sliced
- 2 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 1 sprig fresh thyme
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Place a heavy-based (cast iron, if you have it) sauté pan over a medium heat. Add some olive oil, then the onion, stirring for about 5 minutes.
2) Add the anchovies, herbs and spices (including the garlic), and stir well to combine. The anchovies will probably soon melt into the onion; that’s fine.
3) Add the canned tomatoes (but not the fresh), followed by the freekeh, stirring well again to combine.
4) Add 2 cups boiling water, and simmer with the lid on for about 40 minutes. Stir occasionally and check the water isn’t getting too low; top it up if it’s getting dry and the freekeh isn’t tender yet.
5) Add the fresh chopped cherry tomatoes and the chopped peppers from the jar, as well as the olives. Stir for just another 2 minutes, enough to let the latest ingredients warm through.
6) Serve, adding a garnish if you wish:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Many Health Benefits of Garlic
We’re quite confident you already know what garlic is, so we’re going to leap straight in there with some science today:
First, let’s talk about allicin
Allicin is a compound in garlic that gives most of its health benefits. A downside of allicin is that it’s not very stable, so what this means is:
- Garlic is best fresh—allicin breaks down soon after garlic is cut/crushed
- So while doing the paperwork isn’t fun, buying it as bulbs is better than buying it as granules or similar
- Allicin also breaks down somewhat in cooking, so raw garlic is best
- Our philosophy is: still use it in cooking as well; just use more!
- Supplements (capsule form etc) use typically use extracts and potency varies (from not great to actually very good)
Read more about that:
- Short-term heating reduces the anti-inflammatory effects of fresh raw garlic extracts
- Allicin Bioavailability and Bioequivalence from Garlic Supplements and Garlic Foods
Now, let’s talk benefits…
Benefits to heart health
Garlic has been found to be as effective as the drug Atenolol at reducing blood pressure:
It also lowers LDL (bad cholesterol):
Benefits to the gut
We weren’t even looking for this, but as it turns out, as an add-on to the heart benefits…
Benefits to the immune system
Whether against the common cold or bringing out the heavy guns, garlic is a booster:
- Preventing the common cold with a garlic supplement: a double-blind, placebo-controlled survey
- Supplementation with aged garlic extract improves both NK and γδ-T cell function and reduces the severity of cold and flu symptoms: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled nutrition intervention
Benefits to the youthfulness of body and brain
Garlic is high in antioxidants that, by virtue of reducing oxidative stress, help slow aging. This effect, combined with the cholesterol and blood pressure benefits, means it may also reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia:
- Antioxidant health effects of aged garlic extract
- Effects of garlic consumption on plasma and erythrocyte antioxidant parameters in elderly subjects
- Garlic reduces heart disease and dementia risk
There are more benefits too…
That’s all we have time to dive into study-wise today, but for the visually-inclined, here are yet more benefits to garlic (at a rate of 3–4 cloves per day):
An incredible awesome recipe using lots of garlic:
- Take small potatoes (still in their skins), cut in half
- Add enough peeled cloves of garlic so that you have perhaps a 1:10 ratio of garlic to potato by mass
- Boil (pressure-cooking is ideal) until soft, and drain
- Keeping them in the pan, add a lashing of olive oil, and any additional seasonings per your preference (consider black pepper, rosemary, thyme, parsley)
- Put a lid on the pan, and holding it closed, shake the pan vigorously
- Note: if you didn’t leave the skins on, or you chopped much larger potatoes smaller instead of cutting in half, the potatoes will break up into a rough mash now. This is actually also fine and still tastes (and honestly, looks) great, but it is different, so just be aware, so that you get the outcome you want.
- The garlic, which—unlike the potatoes—didn’t have a skin to hold it together, will now have melted over the potatoes like butter
You can serve like this (it’s delicious already) or finish up in the oven or air-fryer or under the grill, if you prefer a roasted style dish (an amazing option too).
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Garlic is best fresh—allicin breaks down soon after garlic is cut/crushed