What’s the difference between Alzheimer’s and dementia?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
Changes in thinking and memory as we age can occur for a variety of reasons. These changes are not always cause for concern. But when they begin to disrupt daily life, it could indicate the first signs of dementia.
Another term that can crop up when we’re talking about dementia is Alzheimer’s disease, or Alzheimer’s for short.
So what’s the difference?

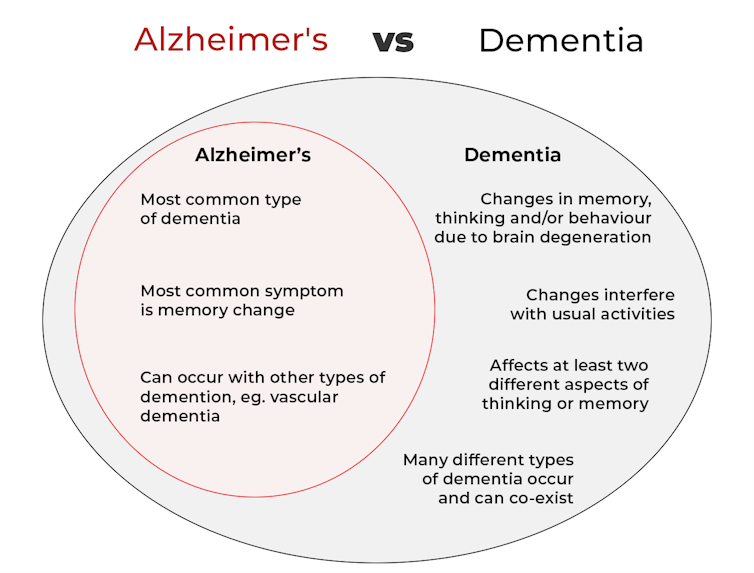
What is dementia?
Dementia is an umbrella term used to describe a range of syndromes that result in changes in memory, thinking and/or behaviour due to degeneration in the brain.
To meet the criteria for dementia these changes must be sufficiently pronounced to interfere with usual activities and are present in at least two different aspects of thinking or memory.
For example, someone might have trouble remembering to pay bills and become lost in previously familiar areas.
It’s less-well known that dementia can also occur in children. This is due to progressive brain damage associated with more than 100 rare genetic disorders. This can result in similar cognitive changes as we see in adults.
So what’s Alzheimer’s then?
Alzheimer’s is the most common type of dementia, accounting for about 60-80% of cases.
So it’s not surprising many people use the terms dementia and Alzheimer’s interchangeably.
Changes in memory are the most common sign of Alzheimer’s and it’s what the public most often associates with it. For instance, someone with Alzheimer’s may have trouble recalling recent events or keeping track of what day or month it is.

We still don’t know exactly what causes Alzheimer’s. However, we do know it is associated with a build-up in the brain of two types of protein called amyloid-β and tau.
While we all have some amyloid-β, when too much builds up in the brain it clumps together, forming plaques in the spaces between cells. These plaques cause damage (inflammation) to surrounding brain cells and leads to disruption in tau. Tau forms part of the structure of brain cells but in Alzheimer’s tau proteins become “tangled”. This is toxic to the cells, causing them to die. A feedback loop is then thought to occur, triggering production of more amyloid-β and more abnormal tau, perpetuating damage to brain cells.
Alzheimer’s can also occur with other forms of dementia, such as vascular dementia. This combination is the most common example of a mixed dementia.
Vascular dementia
The second most common type of dementia is vascular dementia. This results from disrupted blood flow to the brain.
Because the changes in blood flow can occur throughout the brain, signs of vascular dementia can be more varied than the memory changes typically seen in Alzheimer’s.
For example, vascular dementia may present as general confusion, slowed thinking, or difficulty organising thoughts and actions.
Your risk of vascular dementia is greater if you have heart disease or high blood pressure.
Frontotemporal dementia
Some people may not realise that dementia can also affect behaviour and/or language. We see this in different forms of frontotemporal dementia.
The behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia is the second most common form (after Alzheimer’s disease) of younger onset dementia (dementia in people under 65).
People living with this may have difficulties in interpreting and appropriately responding to social situations. For example, they may make uncharacteristically rude or offensive comments or invade people’s personal space.
Semantic dementia is also a type of frontotemporal dementia and results in difficulty with understanding the meaning of words and naming everyday objects.
Dementia with Lewy bodies
Dementia with Lewy bodies results from dysregulation of a different type of protein known as α-synuclein. We often see this in people with Parkinson’s disease.
So people with this type of dementia may have altered movement, such as a stooped posture, shuffling walk, and changes in handwriting. Other symptoms include changes in alertness, visual hallucinations and significant disruption to sleep.
Do I have dementia and if so, which type?
If you or someone close to you is concerned, the first thing to do is to speak to your GP. They will likely ask you some questions about your medical history and what changes you have noticed.
Sometimes it might not be clear if you have dementia when you first speak to your doctor. They may suggest you watch for changes or they may refer you to a specialist for further tests.
There is no single test to clearly show if you have dementia, or the type of dementia. A diagnosis comes after multiple tests, including brain scans, tests of memory and thinking, and consideration of how these changes impact your daily life.
Not knowing what is happening can be a challenging time so it is important to speak to someone about how you are feeling or to reach out to support services.
Dementia is diverse
As well as the different forms of dementia, everyone experiences dementia in different ways. For example, the speed dementia progresses varies a lot from person to person. Some people will continue to live well with dementia for some time while others may decline more quickly.
There is still significant stigma surrounding dementia. So by learning more about the various types of dementia and understanding differences in how dementia progresses we can all do our part to create a more dementia-friendly community.
The National Dementia Helpline (1800 100 500) provides information and support for people living with dementia and their carers. To learn more about dementia, you can take this free online course.
Nikki-Anne Wilson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Neuroscience Research Australia (NeuRA), UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
5 Stretches To Relieve The Pain From Sitting & Poor Posture
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sitting is not good for the health, yes often it’s a necessity of modern life, especially if driving. To make things worse, it can often be difficult to remember to maintain good posture the rest of the time, if it’s not a habit. So, while reducing sitting and improving posture are both very good things to do, here are 5 stretches to mitigate the damage meanwhile:
Daily doses:
These are best done at a rate of 2–3 sets daily:
Cat-Cow Stretch:
- Benefits: eases spinal tension, boosts flexibility, improves posture.
- How to: start on all fours, alternate between arching and rounding your back while syncing with your breath (10-15 times).
Butterfly Stretch:
- Benefits: loosens tight hips, improves lower back flexibility, and enhances mobility for activities like squats.
- How to: sit with soles of feet together, let knees fall toward the floor, lean forward slightly, and hold for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
Supine Twist:
- Benefits: unlocks the spine, relieves post-workout tension, and relaxes the shoulders and hips.
- How to: lie on your back, bend knees, twist to one side while keeping shoulders grounded, and hold for 30 seconds to 1 minute per side.
Calf Stretch:
- Benefits: improves ankle mobility, loosens tight calves, and prevents injuries like Achilles tendinitis.
- How to: stand facing a wall, extend one leg back with the heel on the ground, lean into the stretch, or use a step for deeper stretches. Hold for 30 seconds to 1 minute per leg.
Child’s Pose:
- Benefits: decompresses the spine, relaxes hips, and relieves tension in back and thighs.
- How to: start on hands and knees, sit back onto your heels, stretch arms forward, and rest forehead on the mat. Hold for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
For more on each of these, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
10 Tips To Reduce Morning Pain & Stiffness With Arthritis
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Synergistic Brain-Training
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let The Games Begin (But It Matters What Kind)
Exercise is good for brain health; we’ve written about this before, for example:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk ← there are many advices here, but exercise, especially cardiovascular exercise in this case, is an important item on the list!
Today it’s Psychology Sunday though, and we’re going to talk about looking after brain health by means of brain-training, via games.
“Brain-training” gets a lot of hype and flak:
- Hype: do sudoku every day and soon you will have an IQ of 200 and still have a sharp wit at the age of 120
- Flak: brain-training is usually training only one kind of cognitive function, with limited transferability to the rest of life
The reality is somewhere between the two. Brain training really does improve not just outwardly measurable cognitive function, but also internally measurable improvements visible on brain scans, for example:
- Cognitive training modified age-related brain changes in older adults with subjective memory decline
- Functional brain changes associated with cognitive training in healthy older adults: A preliminary ALE meta-analysis
But what about the transferability?
Let us play
This is where game-based brain-training comes in. And, the more complex the game, the better the benefits, because there is more chance of applicability to life, e.g:
- Sudoku: very limited applicability
- Crosswords: language faculties
- Chess: spatial reasoning, critical path analysis, planning, memory, focus (also unlike the previous two, chess tends to be social for most people, and also involve a lot of reading, if one is keen)
- Computer games: wildly varied depending on the game. While an arcade-style “shoot-em-up” may do little for the brain, there is a lot of potential for a lot of much more relevant brain-training in other kinds of games: it could be planning, problem-solving, social dynamics, economics, things that mirror the day-to-day challenges of running a household, even, or a business.
- It’s not that the skills are useful, by the way. Playing “Stardew Valley” will not qualify you to run a real farm, nor will playing “Civilization” qualify you to run a country. But the brain functions used and trained? Those are important.
It becomes easily explicable, then, why these two research reviews with very similar titles got very different results:
- A Game a Day Keeps Cognitive Decline Away? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Commercially-Available Brain Training Programs in Healthy and Cognitively Impaired Older Adults
- Game-based brain training for improving cognitive function in community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-regression
The first review found that game-based brain-training had negligible actual use. The “games” they looked at? BrainGymmer, BrainHQ, CogMed, CogniFit, Dakim, Lumosity, and MyBrainTrainer. In other words, made-for-purpose brain-trainers, not actual computer games per se.
The second reviewfound that game-based training was very beneficial. The games they looked at? They didn’t name them, but based on the descriptions, they were actual multiplayer online turn-based computer games, not made-for-purpose brain-trainers.
To summarize the above in few words: multiplayer online turn-based computer games outperform made-for-purpose brain-trainers for cognitive improvement.
Bringing synergy
However, before you order that expensive gaming-chair for marathon gaming sessions (research suggests a tail-off in usefulness after about an hour of continuous gaming per session, by the way), be aware that cognitive training and (physical) exercise training combined, performed close in time to each other or simultaneously, perform better than the sum of either alone:
See also:
❝Simultaneous training was the most efficacious approach for cognition, followed by sequential combinations and cognitive training alone, and significantly better than physical exercise.
Our findings suggest that simultaneously and sequentially combined interventions are efficacious for promoting cognitive alongside physical health in older adults, and therefore should be preferred over implementation of single-domain training❞
~ Dr. Hanna Malmberg Gavelin et al.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Bates Method for Better Eyesight Without Glasses − by Dr. William Bates
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a very popular book and method, albeit not a very new one. It was first published in 1920; self-published by Dr. Bates, as the American Medical Association (AMA) considered it quackery.
Of course, our understanding of eyesight has improved a lot in the past 100 years, so, with the benefit of an extra century of ophthalmological research, who was on the right side of history?
As it turns out, all of Dr. Bates’ ideas have been firmly disproven, and eyes simply do not work the way he thought they do (for example, he believed that rather than adjusting the lens for focus, the muscles around the eye elongate the eyeball; this absolutely is not how focusing works, and while how much those muscles squeeze the eye does vary depending on some physiological factors, there are no known exercises that can change them).
Nevertheless, for the interested, his techniques include such things as:
- putting pressure on one’s eyes with one’s hands (which can increase glaucoma risk)
- visualization, rather than actual viewing, of an eye chart (this is ironic, because the book cover promises that an eye chart is included; it is not; perhaps it was hoped that we would visualize it more vividly and thus see it?)
- sunning, which is not only directly looking at the sun, but also using a burning glass to increase the focus of the sunlight onto one’s eye (please do not do this under any circumstances)
His primary thesis in this work, though, is that eyesight problems of all kinds (from short- and long-sightedness, to more serious things like cataracts and glaucoma) are caused by the tension produced by reading books, so relaxation exercises are his prescription for this.
The style is characteristic of its era and then some; bold claims are made with no evidence, there are no references, and the text is (ironically, given his opinions on tension being produced by reading books) quite dense. It certainly doesn’t lend itself well to skimming, for example, because something critical can easily be buried in a wall of text of what is, honestly, mostly waffle.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your eyesight and reduce your dependency on glasses, then we absolutely cannot recommend this book, and would direct you instead to Vision for Life, Revised Edition – by Dr. Meir Schneider, which is much more consistent with actual science.
Click here if you are, nonetheless, curious about Dr. Bates’ book and wish to check it out!
PS: Dr. Bates certainly was an interesting fellow; he disappeared mysteriously, but was found working as a medical assistant a few weeks later by his wife, whom he now claimed to not recognize. Then he disappeared again two days later (his wife never found him, this time, despite trying for many years), only to show up again, 13 years later, shortly after his wife’s death, whereupon he remarried (to his long-time personal assistant). None of this has anything to do with his fascinating opinions on eyesight, but it’s a story worth mentioning.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
In Plain English…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Time!
This is the bit whereby each week, we respond to subscriber questions/requests/etc
Have something you’d like to ask us, or ask us to look into? Hit reply to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom, and a Real Human™ will be glad to read it!
Q: Love to have someone research all the additives in our medicines, (risk of birth control and breast cancer) and what goes in all of our food and beverages. So much info out there, but there are so many variations, you never know who to believe.
That’s a great idea! There are a lot of medicines and food and beverages out there, so that’s quite a broad brief, but! We could well do a breakdown of very common additives, and demystify them, sorting them into good/bad/neutral, e.g:
- Ascorbic acid—Good! This is Vitamin C
- Acetic acid—Neutral! This is vinegar
- Acetylsalicylic acid—Good or Bad! This is aspirin (a painkiller and blood-thinning agent, can be good for you or can cause more problems than it solves, depending on your personal medical situation. If in doubt, check with your doctor)
- Acesulfame K—Generally Neutral! This is a sweetener that the body can’t metabolize, so it’s also not a source of potassium (despite containing potassium) and will generally do nothing. Unless you have an allergy to it, which is rare but is a thing.
- Sucralose—Neutral! This is technically a sugar (as is anything ending in -ose), but the body can’t metabolize it and processes it as a dietary fiber instead. We’d list it as good for that reason, but honestly, we doubt you’re eating enough sucralose to make a noticeable difference to your daily fiber intake.
- Sucrose—Bad! This is just plain sugar
Sometimes words that sound the same can ring alarm bells when they need not, for example there’s a big difference between:
- Potassium iodide (a good source of potassium and iodine)
- Potassium cyanide (the famous poison; 300mg will kill you; half that dose will probably kill you)
- Cyanocobalamine (Vitamin B12)
Let us know if there are particular additives (or particular medications) you’d like us to look at!
While for legal reasons we cannot give medical advice, talking about common contraindications (e.g., it’s generally advised to not take this with that, as one will stop the other from working, etc) is definitely something we could do.
For example! St. John’s Wort, very popular as a herbal mood-brightener, is on the list of contraindications for so many medications, including:
- Antidepressants
- Birth control pills
- Cyclosporine, which prevents the body from rejecting transplanted organs
- Some heart medications, including digoxin and ivabradine
- Some HIV drugs, including indinavir and nevirapine
- Some cancer medications, including irinotecan and imatinib
- Warfarin, an anticoagulant (blood thinner)
- Certain statins, including simvastatin
Q: As I am a retired nurse, I am always interested in new medical technology and new ways of diagnosing. I have recently heard of using the eyes to diagnose Alzheimer’s. When I did some research I didn’t find too much. I am thinking the information may be too new or I wasn’t on the right sites.
(this is in response to last week’s piece on lutein, eyes, and brain health)
We’d readily bet that the diagnostic criteria has to do with recording low levels of lutein in the eye (discernible by a visual examination of macular pigment optical density), and relying on the correlation between this and incidence of Alzheimer’s, but we’ve not seen it as a hard diagnostic tool as yet either—we’ll do some digging and let you know what we find! In the meantime, we note that the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease (which may be of interest to you, if you’re not already subscribed) is onto this:
See also:
- Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease (mixture of free and paid content)
- Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports (open access—all content is free)
Q: As to specific health topics, I would love to see someone address all these Instagram ads targeted to women that claim “You only need to ‘balance your hormones’ to lose weight, get ripped, etc.” What does this mean? Which hormones are they all talking about? They all seem to be selling a workout program and/or supplements or something similar, as they are ads, after all. Is there any science behind this stuff or is it mostly hot air, as I suspect?
Thank you for asking this, as your question prompted yesterday’s main feature, What Does “Balancing Your Hormones” Even Mean?
That’s a great suggestion also about addressing ads (and goes for health-related things in general, not just hormonal stuff) and examining their claims, what they mean, how they work (if they work!), and what’s “technically true but may
be misleading* cause confusion”*We don’t want companies to sue us, of course.
Only, we’re going to need your help for this one, subscribers!
See, here at 10almonds we practice what we preach. We limit screen time, we focus on our work when working, and simply put, we don’t see as many ads as our thousands of subscribers do. Also, ads tend to be targeted to the individual, and often vary from country to country, so chances are good that we’re not seeing the same ads that you’re seeing.
So, how about we pull together as a bit of a 10almonds community project?
- Step 1: add our email address to your contacts list, if you haven’t already
- Step 2: When you see an ad you’re curious about, select “share” (there is usually an option to share ads, but if not, feel free to screenshot or such)
- Step 3: Send the ad to us by email
We’ll do the rest! Whenever we have enough ads to review, we’ll do a special on the topic.
We will categorically not be able to do this without you, so please do join in—Many thanks in advance!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Intelligence Trap – by David Robson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re including this one under the umbrella of “general wellness”, because it happens that a lot of very intelligent people make stunningly unfortunate choices sometimes, for reasons that may baffle others.
The author outlines for us the various reasons that this happens, and how. From the famous trope of “specialized intelligence in one area”, to the tendency of people who are better at acquiring knowledge and understanding to also be better at acquiring biases along the way, to the hubris of “I am intelligent and therefore right as a matter of principle” thinking, and many other reasons.
Perhaps the greatest value of the book is the focus on how we can avoid these traps, narrow our bias blind spots, and play to our strengths while paying full attention to our weaknesses.
The style is very readable, despite having a lot of complex ideas discussed along the way. This is entirely to be expected of this author, an award-winning science writer.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand the array of traps that disproportionately catch out the most intelligent people (and how to spot such), then this is a great book for you.
Click here to check out The Intelligence Trap, and be more wary!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
It’s Not You, It’s Your Hormones – by Nicki Williams, DipION, mBANT, CNHC
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So, first a quick note: this book is very similar to the popular bestseller “The Galveston Diet”, not just in content, but all the way down to its formatting. Some Amazon reviewers have even gone so far as to suggest that “It’s Not You, It’s Your Hormones” (2017) brazenly plagiarized “The Galveston Diet” (2023). However, after carefully examining the publication dates, we feel quite confident that this book is not a copy of the one that came out six years after it. As such, we’ve opted for reviewing the original book.
Nicki Williams’ basic principle is that we can manage our hormonal fluctuations, by managing our diet. Specifically, in three main ways:
- Intermittent fasting
- Anti-inflammatory diet
- Eating more protein and healthy fats
Why should these things matter to our hormones? The answer is to remember that our hormones aren’t just the sex hormones. We have hormones for hunger and satedness, hormones for stress and relaxation, hormones for blood sugar regulation, hormones for sleep and wakefulness, and more. These many hormones make up our endocrine system, and affecting one part of it will affect the others.
Will these things magically undo the effects of the menopause? Well, some things yes, other things no. No diet can do the job of HRT. But by tweaking endocrine system inputs, we can tweak endocrine system outputs, and that’s what this book is for.
The style is very accessible and clear, and Williams walks us through the changes we may want to make, to avoid the changes we don’t want.
In the category of criticism, there is some extra support that’s paywalled, in the sense that she wants the reader to buy her personally-branded online plan, and it can feel a bit like she’s holding back in order to upsell to that.
Bottom line: this book is aimed at peri-menopausal and post-menopausal women. It could also definitely help a lot of people with PCOS too, and, when it comes down to it, pretty much anyone with an endocrine system. It’s a well-evidenced, well-established, healthy way of eating regardless of age, sex, or (most) physical conditions.
Click here to check out It’s Not You, It’s Your Hormones, and take control of yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: