No, vitamin A does not prevent measles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As measles spreads in Texas, New Mexico, and other states, a Texas child died from measles for the first time in the United States since 2015. In a March 2 Fox News editorial, Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. hinted at the importance of vaccination and stated that good nutrition, including vitamin A, is a “best defense against most chronic and infectious illnesses.”
However, doctors and public health professionals say that vitamin A is not a replacement for the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. Vitamin A is sometimes used to treat measles in the hospital—particularly in developing countries where people with poor nutrition tend to be vitamin A deficient. Experts also say that taking vitamin A when your body does not need it can be dangerous.
“It’s really important to distinguish prevention and treatment, and measles can be prevented, and it can be prevented one way: through vaccination,” Dr. Preeti Malani, infectious disease physician and professor at the University of Michigan, tells PGN. “The best treatment is to not get measles in the first place.”
Read on to learn the facts about vitamin A, what it’s used for, its risks, and what you should do to prevent measles.
What is vitamin A, and what does it have to do with measles?
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin, which means that it’s stored in the body’s fatty tissue and in the liver, and it’s absorbed with the fat in a person’s diet. Vitamin A helps with our vision, reproduction, growth, and immunity.
Vitamin A deficiency can increase the risk of death from measles, among other infections. The World Health Organization recommends it as a supplement along with vaccination for children at risk of vitamin A deficiency in developing countries.
However, vitamin A deficiency is rare in the U.S. because most people get enough of it through their diet. (Malani says that’s why research about the use of vitamin A to treat measles is limited in countries like the United States.)
“Vitamin A deficiency is a major problem in developing nations, particularly those that don’t have access to staple foods that have vitamin A,” says Andrea Love, PhD, a biomedical scientist and founder of the health communication organization Immunologic, to PGN. “The problem is that that’s been kind of extrapolated to high-income countries [like the United States], where vitamin A deficiency is really not a concern.”
Under Kennedy’s direction, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently updated its guidance to recommend the use of vitamin A to treat severe measles in young children, but specifically in a hospital setting and under a doctor’s supervision.
Does vitamin A prevent measles?
No. Vitamin A does not prevent measles. The MMR vaccine is the best way to prevent a measles infection.
“Vitamin A is not an alternative to vaccination,” Malani adds. “We have a safe and highly effective vaccine that’s been available for decades—it will protect individuals [and] communities from an outbreak.”
Are there any risks to taking vitamin A?
Yes. If your body doesn’t need extra vitamin A, there are risks.
According to the National Institutes of Health, taking too much vitamin A (specifically, the type found in supplements and some medications) can cause nausea, severe headaches, blurred vision, muscle aches, and problems with coordination. In severe cases, it can also lead to coma and death. Taking too much vitamin A while pregnant can cause birth defects.
“If you’re already getting sufficient vitamin A from your diet, then when you consume more than what you need, those levels are going to build up in your body, in your fat stores, in your tissues, and you’re going to be at risk of both acute and chronic toxicity,” adds Love.
Water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C “get filtered out by your kidneys and you would pee it out, but fat-soluble vitamins [like vitamin A], don’t get processed and excreted as quickly; they start to build up in the body,” she says.
What can I do to protect myself from measles?
The MMR vaccine is the best way to protect yourself from measles. The CDC recommends children get two doses of the MMR vaccine: the first dose between 12 and 15 months and the second one between 4 and 6 years old.
Experts recommend that adults who are not sure about their vaccination or immunity status against measles get at least one dose of the MMR vaccine. Additionally, adults who are at high risk for measles (like health care workers and people who travel internationally) may need two additional doses.
According to the CDC, you can also get an MMR vaccine within 72 hours of initial exposure to measles, which can give you some protection or make your illness less severe. Additionally, there’s an antibody (a protective protein called immunoglobulin) that a doctor may recommend for high-risk people within six days of being exposed to measles.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eat To Avoid (Or Beat) PCOS
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Polycystic ovary syndrome, PCOS, affects very many people; around 1 in 5 women. It can show up unexpectedly, and usually the first-identified sign is irregular vaginal bleeding. We say “vaginal” rather than “menstrual” as it’s not technically menses, although it’ll look (and can feel) the same.
Like many “affects mostly women” conditions, science’s general position is “we don’t know what causes it or how to cure it”.
Quick book recommendation before we continue:
Unwell Women: Misdiagnosis and Myth in a Man-Made World – by Dr. Elinor Cleghorn
…is a top-tier book about medical misogyny. We’d say more here, but well, you can read our review there 🙂
What doesn’t work
Since PCOS is characterized by excessive androgen production, it is reasonable to expect that foods containing phytoestrogens (such as soy) may help. They won’t. The human body can’t use those as estrogen, and in fact, consuming unusually large quantities of phytoestrogens can actually get in the way of your own (or bioidentical) estrogen, by competing for the same receptors but not really doing the job.
But, you won’t get that problem from moderate consumption of soy; the warning is more for those tempted to self-medicate with megadoses, or are opting for dubious supplements such as Pueraria mirifica ← will have to do a research review on that one of these days, but suffice it to say meanwhile, it has some serious drawbacks
See also: What Does “Balance Your Hormones” Even Mean?
What can work
There are some supplement-based approaches that actually can help, and those are the ones that rather than trying to manufacture estrogen out of thin air, work to reduce testosterone and/or reduce the conversion of free testosterone to its more potent form, dihydrogen testosterone (DHT); here are two examples:
- Licorice, Digestion, & Hormones
- One Man’s Saw Palmetto Is Another Woman’s Serenoa Repens ← this one has the most evidence of the two
What will work
…or at least, barring additional confounding factors, what the evidence strongly supports working. Here’s where we get into diet properly, and there are three main dietary approaches:
Low-GI diet: focus on high-fiber, low-carb foods (e.g. whole grains, legumes, berries, leafy greens). Eating this way results in improved insulin sensitivity, lower fasting insulin, cholesterol, triglycerides, waist circumference, and (for women) yes, lower testosterone levels.
See: What Do The Different Kinds Of Fiber Do? 30 Foods That Rank Highest
High antioxidant diet: focus on foods rich in antioxidants (e.g. vitamin A, α-tocopherol specifically, vitamins C and D, and polyphenols) as these lower PCOS incidence.
See: 21 Most Beneficial Polyphenols & What Foods Have Them
Ketogenic diet: focus on high-fat, very low-carb foods (e.g. fatty fish, dairy, leafy greens). This significantly reduces androgen levels, improves insulin sensitivity, and regulates hormones. But… It’s recommended for short-term use only due to its negative health impacts from poor (i.e. narrow) nutritional coverage:
See: Ketogenic Diet: Burning Fat, Or Burning Out?
It is also reasonable to supplement, for example:
❝Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D have powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that significantly improve insulin sensitivity and reduce androgen levels in metabolic syndromes like PCOS. A higher intake of omega-3 and vitamin E also alleviates mental health parameters and gene expression of PPAR-γ, IL-8, and TNF-α in women with PCOS.
Dietary supplements, such as antioxidants like N-acetylcysteine (NAC), vitamin D, inositol, and omega-3 fatty acids, and mineral supplements (zinc, magnesium selenium, and chromium) help in reducing insulin resistance. These supplements also enhance ovulatory function and decrease inflammation in PCOS patients.
Omega-3 fatty acid supplements improve biochemical parameters LH, LH/FSH, lipid profiles, and adiponectin levels and regularize the menstrual cycle in women with PCOS. A recent RCT also indicated that probiotic/symbiotic supplementation significantly improves triglyceride, insulin, and HDL levels in women with PCOS.❞
Source: The Role of Lifestyle Interventions in PCOS Management: A Systematic Review
Want to know more?
You might like this book that we reviewed a little while back:
PCOS Repair Protocol – by Tamika Woods
Take care!
Share This Post
-
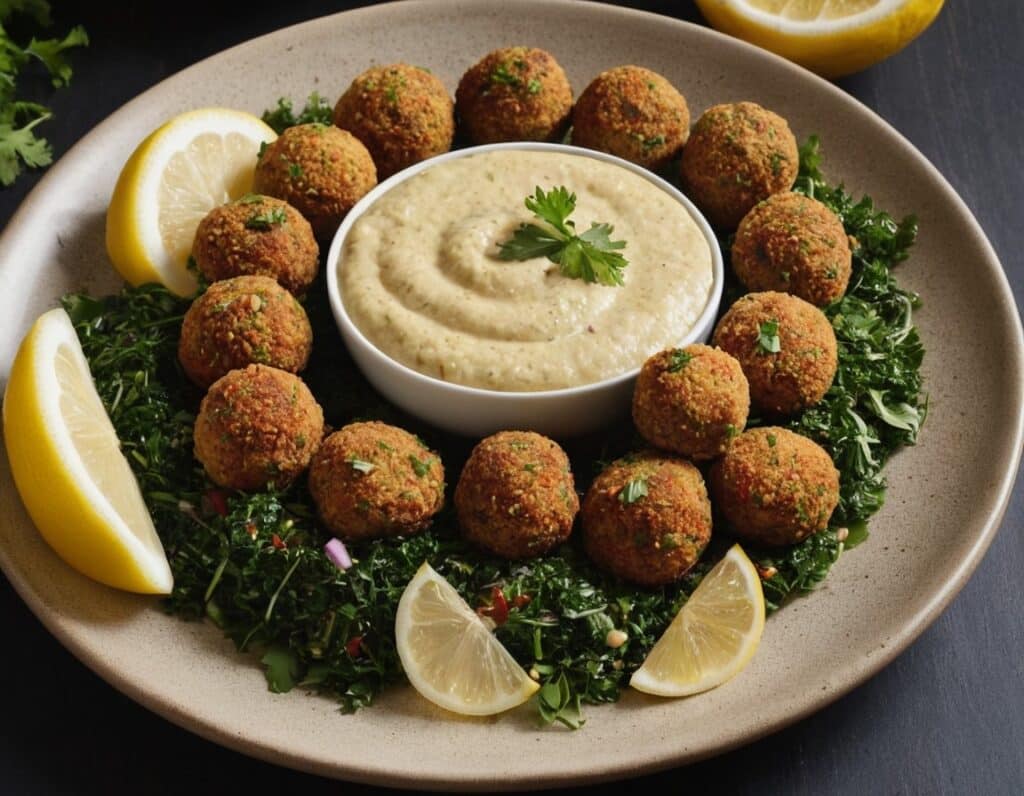
Easy Quinoa Falafel
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Falafel is a wonderful snack or accompaniment to a main, and if you’ve only had shop-bought, you’re missing out. Plus, with this quinoa-based recipe, it’s almost impossible to accidentally make them dry.
You will need
- 1 cup cooked quinoa
- 1 cup chopped fresh parsley
- ½ cup wholewheat breadcrumbs (or rye breadcrumbs if you’re avoiding wheat/gluten)
- 1 can chickpeas, drained
- 4 green onions, chopped
- ½ bulb garlic, minced
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil, plus more for frying
- 2 tbsp tomato paste
- 1 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- 2 tsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp red pepper flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp dried thyme
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend all the ingredients in a food processor until it has an even, but still moderately coarse, texture.
2) Shape into 1″ balls, and put them in the fridge to chill for about 20 minutes.
3) Fry the balls over a medium-high heat until evenly browned—just do a few at a time, taking care to not overcrowd the pan.
4) Serve! Great with salad, hummus, and other such tasty healthy snack items:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in more of what we have going on today:
- Cilantro vs Parsley – Which is Healthier?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- What Matters Most For Your Heart?
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- Hero Homemade Hummus Recipe ← perfect accompaniment!
- Tasty Tabbouleh with Tahini Recipe ← also a great option!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Oxygen Advantage – by Patrick McKeown
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You probably know to breathe through your nose, and use your diaphragm. What else does this book have to offer?
A lot of the book is aimed at fixing specific problems, and optimizing what can be optimized—including with tips and tricks you may not have encountered before. Yet, the offerings are not bizarre either; we don’t need to learn to breathe through our ears while drinking a glass of water upside down or anything.
Rather, such simple things as improving one’s VO₂Max by occasionally holding one’s breath while walking briskly. But, he advises specifically, this should be done by pausing the breath halfway through the exhalation (a discussion of the ensuing physiological response is forthcoming).
Little things like that are woven throughout the book, whose style is mostly anecdotal rather than hard science, yet is consistent with broad scientific consensus in any case.
Bottom line: if you’ve any reason to think your breathing might be anything less than the best it could possibly be, this book is likely to help you to tweak it to be a little better.
Click here to check out The Oxygen Advantage, and get yours!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How Your Sleep Position Changes Dementia Risk
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is not just about sleep duration or even about sleep quality… It really is about which way your body is positioned.
Goodnight, glymphatic system
The association between sleeping position and dementia risk is about glymphatic drainage, which is largely powered by gravity (and thus dependent on which way around your head and neck are oriented), and very important for clearing toxins out of the brain—including beta-amyloid proteins.
This becomes particularly important when the glymphatic system becomes less efficient in midlife, often 15–20 years before cognitive decline symptoms appear.
The video’s thumbnail headline, “SCIENTISTS REVEAL: THE WAY YOUR SLEEP CAN CAUSE DEMENTIA” is overstated and inaccurate, but our adjusted headline “how your sleep position changes dementia risk” is actually representative of the paper on which this video was based; we’ll quote from the paper itself here:
❝This paper concludes that 1. glymphatic clearance plays a major role in Alzheimer’s pathology; 2. the vast majority of waste clearance occurs during sleep; 3. dementias are associated with sleep disruption, alongside an age-related decline in AQP4 polarization; and 4. lifestyle choices such as sleep position, alcohol intake, exercise, omega-3 consumption, intermittent fasting and chronic stress all modulate* glymphatic clearance. Lifestyle choices could therefore alter Alzheimer’s disease risk through improved glymphatic clearance, and could be used as a preventative lifestyle intervention for both healthy brain ageing and Alzheimer’s disease.❞
…and specifically, they found:
❝Glymphatic transport is most efficient in the right lateral sleeping position, with more CSF clearance occurring compared to supine and prone. The average person changes sleeping position 11 times per night, but there was no difference in the number of position changes between neurodegenerative and control groups, making the percentage of time spent in supine position the risk factor, not the number of position changes❞
Read the paper in full here: The Sleeping Brain: Harnessing the Power of the Glymphatic System through Lifestyle Choices
*saying “modulate” here is not as useful as it could be, because they modulate it differently: side-sleeping improves clearance; back sleeping decreases it; front-sleeping isn’t great either. Alcohol intake reduces clearance, exercise (especially cardiovascular exercise) improves it; omega-3 consumption improves it up a degree and does depend on omega-3/6 ratios, intermittent fasting improves it, and chronic stress worsens it.
And for a more pop-science presentation, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Clean Your Brain (Glymphatic Health Primer)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healthy Living in a Contaminated World – by Dr. Donald Hoernschemeyer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a lot going on here, as this book tackles very many kinds of common contaminants, from waste products and industrial chemicals (such as from fracking), pesticides that are banned in most places but not the US, smog and soot from coal and oil power, mercury and other heavy metals, dioxins, Teflon and its close relatives, phthalates, BPA, and other things again regulated out of use in many countries but not entirely in the US (which bans them only in some things, like baby bottles), drinking water issues of various kinds, and much more.
Indeed, there’s a whole chapter on the US and international regulation of toxic substances; the problem is often that on a political level, the same people who are against nebulous “chemicals” are also against environmentalist regulations that would ban them. This is mostly not a political book though, and rather is chiefly a book of chemistry (the author’s field).
It does also cover the medical maladies associated with various contaminants, while the bulk of the data is on the chemistry side of such things as “elimination times for toxic chemicals”, “amounts of pesticides in fruit and vegetables”, “antibiotics and hormones used in animal agriculture”, and so forth.
The style is dense, and/but it is clear the author has made an effort to not be too dry. Still, this is not a fun read; it’s depressing in content and the style is more suited to academia. There are appendices containing glossaries and acronym tables, but reading front-to-back, there’s a lot that’s not explained so unless you also are a PhD chemist, chances are you’ll be needing to leaf forwards and backwards a lot.
Bottom line: this book is not thrilling, but what you don’t know, can kill you.
Click here to check out Healthy Living In A Contaminated World, and improve your odds!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
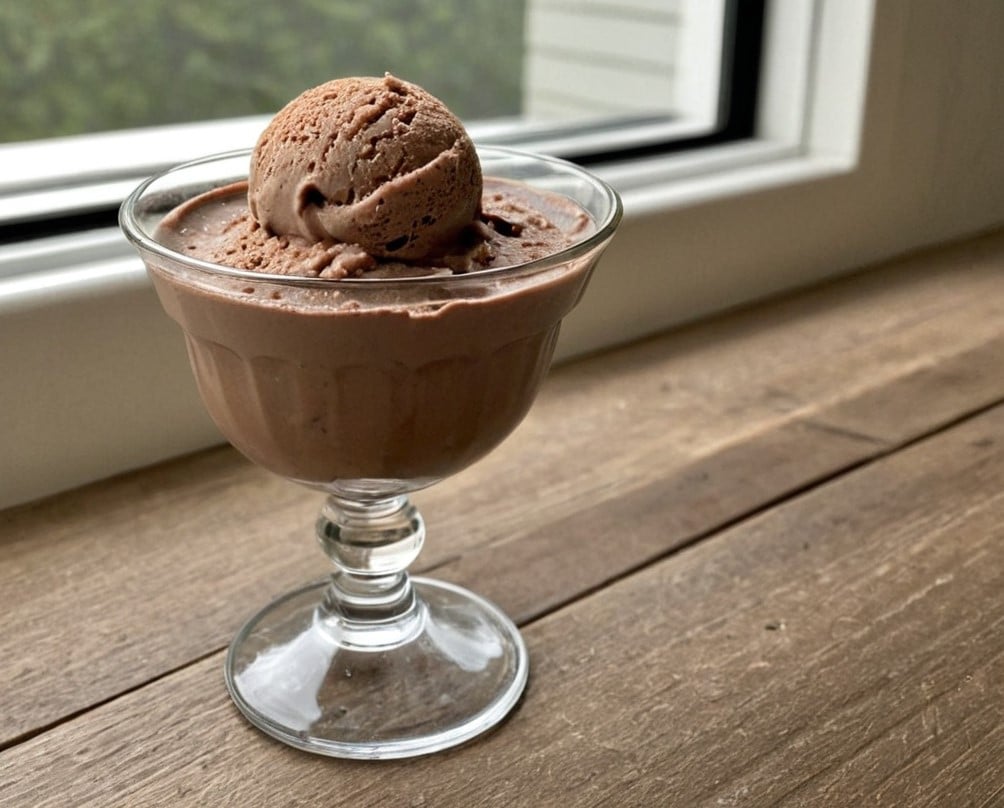
Healthy Choco-Banoffee Ice Cream
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chocolate, banana, and coffee—quite a threesome, whether for breakfast or dessert, and this is healthy enough for breakfast while being decadent enough for dessert! With no dairy or added sugar, and lots of antioxidants, this is a healthy way to start or end your day.
You will need
- 3 bananas
- 2 tbsp cocoa powder, no additives
- 2 shots espresso, chilled
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
- On standby: milk of your choice—we recommend almond or hazelnut
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Peel, slice, and freeze the bananas (let them freeze for at least 2–3 hours)
2) Blend the ingredients, except the milk. Add milk as necessary if the mixture is too thick to blend. Be careful not to add too much at once though, or it will become less of an ice cream and more of a milkshake!
3) Scoop into a sundae glass to serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Which Plant Milk?
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
- Apples vs Bananas – Which is Healthier?
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- Tasty Polyphenols
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: