Paris in spring, Bali in winter. How ‘bucket lists’ help cancer patients handle life and death
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In the 2007 film The Bucket List Jack Nicholson and Morgan Freeman play two main characters who respond to their terminal cancer diagnoses by rejecting experimental treatment. Instead, they go on a range of energetic, overseas escapades.
Since then, the term “bucket list” – a list of experiences or achievements to complete before you “kick the bucket” or die – has become common.
You can read articles listing the seven cities you must visit before you die or the 100 Australian bucket-list travel experiences. https://www.youtube.com/embed/UvdTpywTmQg?wmode=transparent&start=0
But there is a more serious side to the idea behind bucket lists. One of the key forms of suffering at the end of life is regret for things left unsaid or undone. So bucket lists can serve as a form of insurance against this potential regret.
The bucket-list search for adventure, memories and meaning takes on a life of its own with a diagnosis of life-limiting illness.
In a study published this week, we spoke to 54 people living with cancer, and 28 of their friends and family. For many, a key bucket list item was travel.
Why is travel so important?
There are lots of reasons why travel plays such a central role in our ideas about a “life well-lived”. Travel is often linked to important life transitions: the youthful gap year, the journey to self-discovery in the 2010 film Eat Pray Love, or the popular figure of the “grey nomad”.
The significance of travel is not merely in the destination, nor even in the journey. For many people, planning the travel is just as important. A cancer diagnosis affects people’s sense of control over their future, throwing into question their ability to write their own life story or plan their travel dreams.
Mark, the recently retired husband of a woman with cancer, told us about their stalled travel plans:
We’re just in that part of our lives where we were going to jump in the caravan and do the big trip and all this sort of thing, and now [our plans are] on blocks in the shed.
For others, a cancer diagnosis brought an urgent need to “tick things off” their bucket list. Asha, a woman living with breast cancer, told us she’d always been driven to “get things done” but the cancer diagnosis made this worse:
So, I had to do all the travel, I had to empty my bucket list now, which has kind of driven my partner round the bend.
People’s travel dreams ranged from whale watching in Queensland to seeing polar bears in the Arctic, and from driving a caravan across the Nullarbor Plain to skiing in Switzerland.

Nadia, who was 38 years old when we spoke to her, said travelling with her family had made important memories and given her a sense of vitality, despite her health struggles. She told us how being diagnosed with cancer had given her the chance to live her life at a younger age, rather than waiting for retirement:
In the last three years, I think I’ve lived more than a lot of 80-year-olds.
But travel is expensive
Of course, travel is expensive. It’s not by chance Nicholson’s character in The Bucket List is a billionaire.
Some people we spoke to had emptied their savings, assuming they would no longer need to provide for aged care or retirement. Others had used insurance payouts or charity to make their bucket-list dreams come true.
But not everyone can do this. Jim, a 60-year-old whose wife had been diagnosed with cancer, told us:
We’ve actually bought a new car and [been] talking about getting a new caravan […] But I’ve got to work. It’d be nice if there was a little money tree out the back but never mind.
Not everyone’s bucket list items were expensive. Some chose to spend more time with loved ones, take up a new hobby or get a pet.
Our study showed making plans to tick items off a list can give people a sense of self-determination and hope for the future. It was a way of exerting control in the face of an illness that can leave people feeling powerless. Asha said:
This disease is not going to control me. I am not going to sit still and do nothing. I want to go travel.
Something we ‘ought’ to do?
Bucket lists are also a symptom of a broader culture that emphasises conspicuous consumption and productivity, even into the end of life.
Indeed, people told us travelling could be exhausting, expensive and stressful, especially when they’re also living with the symptoms and side effects of treatment. Nevertheless, they felt travel was something they “ought” to do.
Travel can be deeply meaningful, as our study found. But a life well-lived need not be extravagant or adventurous. Finding what is meaningful is a deeply personal journey.
Names of study participants mentioned in this article are pseudonyms.
Leah Williams Veazey, ARC DECRA Research Fellow, University of Sydney; Alex Broom, Professor of Sociology & Director, Sydney Centre for Healthy Societies, University of Sydney, and Katherine Kenny, ARC DECRA Senior Research Fellow, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

154 million lives saved in 50 years: 5 charts on the global success of vaccines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We know vaccines have been a miracle for public health. Now, new research led by the World Health Organization has found vaccines have saved an estimated 154 million lives in the past 50 years from 14 different diseases. Most of these have been children under five, and around two-thirds children under one year old.
In 1974 the World Health Assembly launched the Expanded Programme on Immunization with the goal to vaccinate all children against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), measles, polio, tuberculosis and smallpox by 1990. The program was subsequently expanded to include several other diseases.
The modelling, marking 50 years since this program was established, shows a child aged under ten has about a 40% greater chance of living until their next birthday, compared to if we didn’t have vaccines. And these positive effects can be seen well into adult life. A 50-year-old has a 16% greater chance of celebrating their next birthday thanks to vaccines.
What the study did
The researchers developed mathematical and statistical models which took in vaccine coverage data and population numbers from 194 countries for the years 1974–2024. Not all diseases were included (for example smallpox, which was eradicated in 1980, was left out).
The analysis includes vaccines for 14 diseases, with 11 of these included in the Expanded Programme on Immunization. For some countries, additional vaccines such as Japanese encephalitis, meningitis A and yellow fever were included, as these diseases contribute to major disease burden in certain settings.
The models were used to simulate how diseases would have spread from 1974 to now, as vaccines were introduced, for each country and age group, incorporating data on increasing vaccine coverage over time.
Children are the greatest beneficiaries of vaccines
Since 1974, the rates of deaths in children before their first birthday has more than halved. The researchers calculated almost 40% of this reduction is due to vaccines.
The effects have been greatest for children born in the 1980s because of the intensive efforts made globally to reduce the burden of diseases like measles, polio and whooping cough.
Some 60% of the 154 million lives saved would have been lives lost to measles. This is likely due to its ability to spread rapidly. One person with measles can spread the infection to 12–18 people.
The study also found some variation across different parts of the world. For example, vaccination programs have had a much greater impact on the probability of children living longer across low- and middle-income countries and settings with weaker health systems such as the eastern Mediterranean and African regions. These results highlight the important role vaccines play in promoting health equity.
Vaccine success is not assured
Low or declining vaccine coverage can lead to epidemics which can devastate communities and overwhelm health systems.
Notably, the COVID pandemic saw an overall decline in measles vaccine coverage, with 86% of children having received their first dose in 2019 to 83% in 2022. This is concerning because very high levels of vaccination coverage (more than 95%) are required to achieve herd immunity against measles.
In Australia, the coverage for childhood vaccines, including measles, mumps and rubella, has declined compared to before the pandemic.
This study is a reminder of why we need to continue to vaccinate – not just against measles, but against all diseases we have safe and effective vaccines for.
The results of this research don’t tell us the full story about the impact of vaccines. For example, the authors didn’t include data for some vaccines such as COVID and HPV (human papillomavirus). Also, like with all modelling studies, there are some uncertainties, as data was not available for all time periods and countries.
Nonetheless, the results show the success of global vaccination programs over time. If we want to continue to see lives saved, we need to keep investing in vaccination locally, regionally and globally.
Meru Sheel, Associate Professor and Epidemiologist, Infectious Diseases, Immunisation and Emergencies Group, Sydney School of Public Health, University of Sydney and Alexandra Hogan, Mathematical epidemiologist, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post

Practical Optimism – by Dr. Sue Varma
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about how to get your brain onto a more positive track (without toxic positivity), but there’s a lot more to be said than we can fit into an article, so here’s a whole book packed full with usable advice.
The subtitle claims “the art, science, and practice of…”, but mostly it’s the science of. If there’s art to be found here, then this reviewer missed it, and as for the practice of, well, that’s down to the reader, of course.
However, it is easy to use the contents of this book to translate science into practice without difficulty.
If you’re a fan of acronyms, initialisms, and other mnemonics (such as the rhyming “Name, Claim, Tame, and Reframe”), then you’ll love this book as they come thick and fast throughout, and they contribute to the overall ease of application of the ideas within.
The writing style is conversational but with enough clinical content that one never forgets who is speaking—not in the egotistical way that some authors do, but rather, just, she has a lot of professional experience to share and it shows.
Bottom line: if you’d like to be more optimistic without delving into the delusional, this book can really help a lot with that (in measurable ways, no less!).
Click here to check out Practical Optimism, and brighten up your life!
Share This Post

Revive and Maintain Metabolism
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝How to jump start a inactive metabolism and keep it going? THANKYOU❞
The good news is, if you’re alive, your metabolism is active (it never stops!). So, it may just need perking up a little.
As for keeping it going, well, that’s what we’re here for! We’re all in favor of healthy longevity.
We’ll do a main feature soon on what we can do to influence our metabolism in either direction, but to give some quick notes here:
- A lot of our metabolism is influenced by genes and is unalterable (without modifying our genes, anyway)
- Metabolism isn’t just one thing—it’s many. And sometimes, parts of our metabolism can be much quicker or slower than others.
- When people talk about wanting a “faster metabolism”, they’re usually referring to fat-burning, and that’s just a small part of the picture, but we understand that it’s a focal point for many.
There really is enough material for a whole main feature on metabolic tweaks, though, so watch this space!
Share This Post
Related Posts

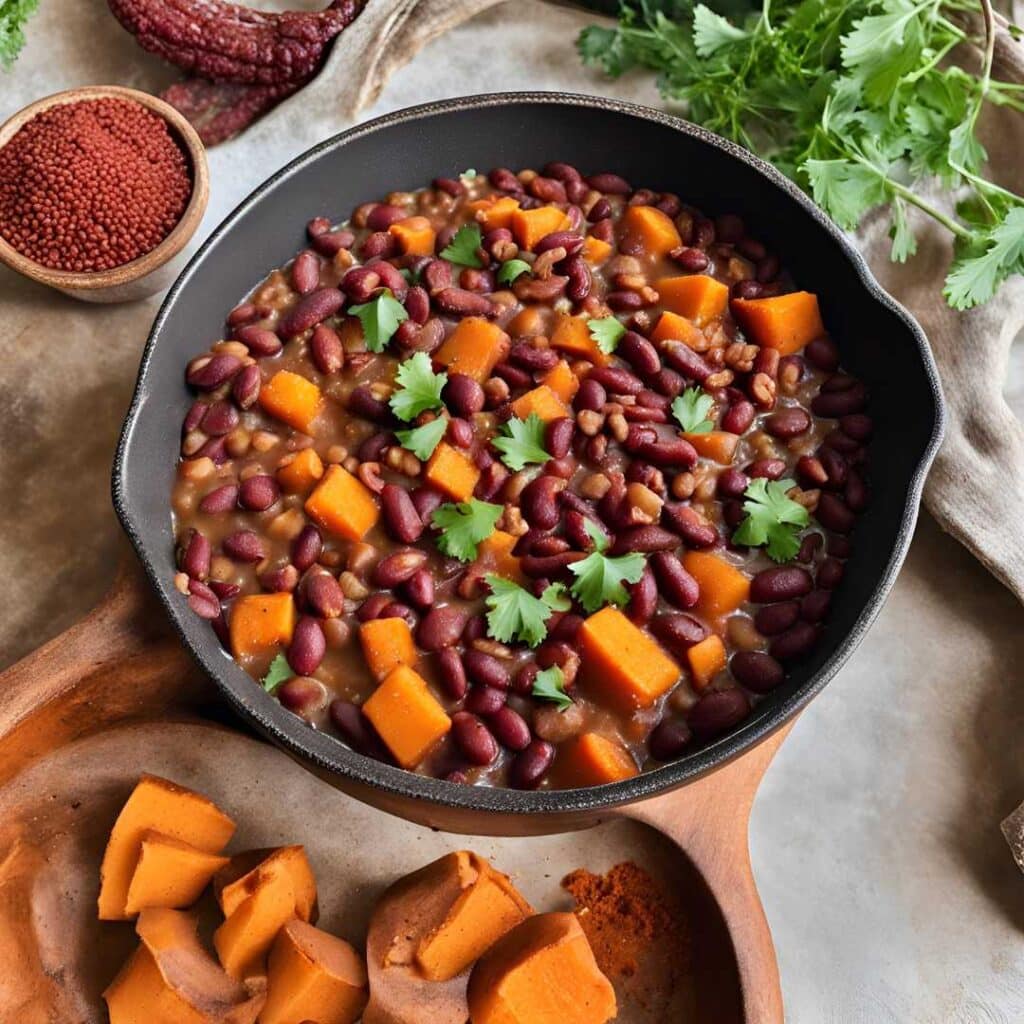
Ghanaian Red Bean & Sweet Potato Groundnut Stew
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a dish popular in principle throughout West Africa. We say “in principle” because that’s a big place, and there is a lot of regional variation. The archetypal peanut stew is from Senegal (as maafe) or Mali (as tigadèguèna), but for its more balanced nutritional profile we’ve chosen one from Ghana—and since there are regional variations within Ghana too, we should specify that this one is from the south.
If you are allergic to nuts, you can substitute a seed butter (or tahini) for the nut butter, and omit the nuts—this will work in culinary terms and be fine healthwise, but we can’t claim it would be the same dish, having lost its defining ingredient. If your allergy is solely to peanuts, then substituting with any oily nut would work. So, not almonds for example, but cashews or even walnuts would be fine.
You will need
- 1½ lbs sweet potatoes, peeled and cut into ½” cubes
- 2 cups low-sodium vegetable stock
- 2 cans kidney beans, drained, cooked, and rinsed (or 2 cups same; cooked, drained, and rinsed)
- 1 can chopped tomatoes
- ½ cup unsalted dry-roasted peanuts
- 1 onion, chopped
- 1 red bell pepper, deseeded and chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 2 heaped tbsp unsalted peanut butter, minimal (ideally: no) additives
- 2 tsp white miso paste
- 2 tsp grated fresh ginger
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp cayenne pepper
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- ½ tsp coarsely ground nigella seeds
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat some oil in a sauté pan, or other pan suitable for both frying and fitting the entire stew in. Fry the onions until softened, turn the heat down low, and add the garlic, ginger, red bell pepper, cumin, cayenne, black pepper, and MSG/salt.
2) Add ¼ cup of the vegetable stock, and the sweet potato, and turn the heat back up, on high for about 30 seconds to get it to temperature, and then take it down to a simmer.
3) Stir in the miso paste and chopped tomatoes.
4) Add most of the rest of the vegetable stock, keeping ¼ cup aside. Simmer for about 20 minutes.
5) Stir in the kidney beans, and simmer for about 30 minutes more—the sweet potato should be soft now; if it isn’t, let it simmer a while longer until it is.
6) Combine the peanut butter with the remaining ¼ cup vegetable stock, and blend until smooth. Stir it into the stew.
7) If the stew is looking more like a soup than a stew, take out 1 cup and blend this 1 cup to a purée, adding it back in.
8) Add half the peanuts unto the stew. Taste, and adjust the seasonings if necessary.
9) Crush the remaining peanuts using a pestle and mortar; not too much though; you want them broken into bits, not pulverised.
10) Garnish with the crushed nuts and nigella seeds, and serve.

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we used 4/5 today!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Mung Beans vs Soy Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing mung beans to soy beans, we picked the soy.
Why?
Mung beans are great, but honestly, it’s not close:
In terms of macronutrients, soy has more than 2x the protein (of which, it’s also a complete protein, containing significant amounts of all essential amino acids) while mung beans have more than 2x the carbs. In their defense, mung beans also have very slightly more fiber, but the carb:fiber ratio is such that soy beans have the lower GI by far.
When it comes to vitamins, mung beans have more of vitamins A, B3, B5, and, B9, while soy beans have more of vitamins B2, B6, C, E, K, and choline, making for a moderate win for soy beans, especially as that vitamin K is more than 7x as much as mung beans have.
In the category of minerals, soy wins even more convincingly; soy beans have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. On the other hand, mung beans have more sodium.
In short, while mung beans are a very respectable option, they don’t come close to meaningfully competing with soy.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
How To Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

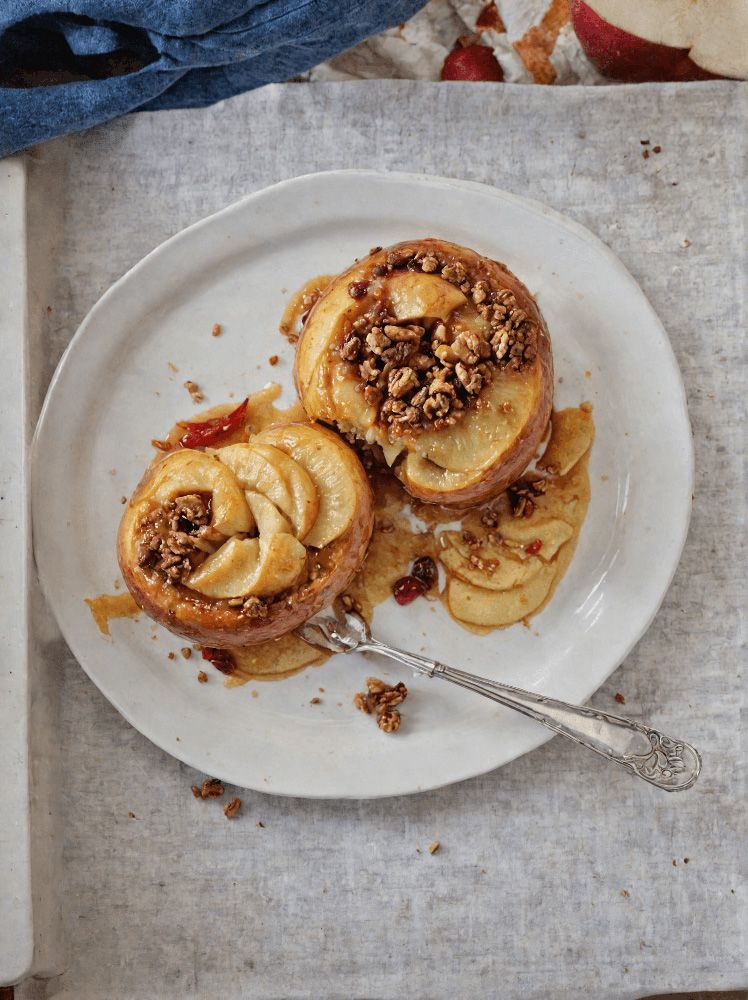
Superfood Baked Apples
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Superfoods, and super-tasty. This is a healthy twist on a classic; your blood sugars will thank you for choosing this tasty sweet delight. It’s also packed with nutrients!
You will need
- 2 large firm baking apples, cored but not peeled
- 1/2 cup chopped walnuts
- 3 tbsp goji berries, rehydrated (soak them in warm water for 10–15minutes and drain)
- 1 tbsp honey, or maple syrup, per your preference (this writer is also a fan of aged balsamic vinegar for its strong flavor and much milder sweetness. If you don’t like things to be too sweet, this is the option for you)
- 2 tsp ground sweet cinnamon
- 1 tsp ground ginger
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 180℃ / 350℉ / gas mark 4
2) Mix the chopped walnuts with the goji berries and the honey (or whatever you used instead of the honey) as well as the sweet cinnamon and the ginger.
3) Place the apples in shallow baking dish, and use the mixture you just made to stuff their holes.
4) Add 1/2 cup water to the dish, around the apples. Cover gently with foil, and bake until soft.
Tip: check them every 20 minutes; they may be done in 40 or it may take 60; in honesty it depends on your oven. If unsure, cook them for longer at a lower temperature.
5) Serve warm.

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose C’s
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- The Sugary Food That Lowers Blood Sugars
- Honey vs Maple Syrup – Which is Healthier?
- A Tale Of Two Cinnamons ← this is important, about why we chose the sweet cinnamon
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: