Sunflower Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sunflower seeds to pumpkin seeds, we picked the pumpkin seeds.
Why?
Both seeds have a good spread of vitamins and minerals, but pumpkin seeds have more. Sunflower seeds come out on top for copper and manganese, but everything else that’s present in either of them (in the category of vitamins and minerals, anyway), pumpkin seeds have more.
There is one other thing that sunflower seeds have more of than pumpkin seeds, and that’s fat. The fat is mostly of healthy varieties, so it’s not a negative factor, but it does mean that if you’re eating a calorie-controlled diet, you’ll get more bang for your buck (i.e. better micronutrient-to-calorie ratio) if you pick pumpkin seeds.
If you’re not concerned about fat/calories, and/or you actively want to consume more of those, then sunflower seeds are still a fine choice.
When it comes down to it, a diverse diet is best, so enjoying both might be the best option of all.
Want to get some?
We don’t sell them, but here for your convenience are example products on Amazon:
Sunflower Seeds | Pumpkin Seeds
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Primary Care Is Being Disrupted: A Video Primer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How patients are seeing their doctor is changing, and that could shape access to and quality of care for decades to come.
More than 100 million Americans don’t have regular access to primary care, a number that has nearly doubled since 2014. Yet demand for primary care is up, spurred partly by record enrollment in Affordable Care Act plans. Under pressure from increased demand, consolidation, and changing patient expectations, the model of care no longer means visiting the same doctor for decades.
KFF Health News senior correspondent Julie Appleby breaks down what is happening — and what it means for patients.
More From This Investigation
Primary Care Disrupted
Known as the “front door” to the health system, primary care is changing. Under pressure from increased demand, consolidation, and changing patient expectations, the model of care no longer means visiting the same doctor for decades. KFF Health News looks at what this means for patients.
Credits
Hannah Norman Video producer and animator Oona Tempest Illustrator and creative director KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
Food and Nutrition – by Dr. P.K. Newby
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The “What Everyone Needs To Know” part of the title is the name of a series of books, of which this one, “Food and Nutrition”, is one.
In this case, the title is apt, and/or could have been “What Everyone Really Should Know”, or “What Everyone Would Like To Think They Know But Have Often Just Been Bluffing Their Way Through The Supermarket Aisles”.
The chapter and section headings are all in the forms of questions, such that all-together in such volume in the table of contents, they’re reminiscent of the “Jonathan Frakes Asks You Things” meme.
But, this serves a dual purpose—for one, it makes the whole book one big FAQ, which is a very convenient format. Furthermore, it prompts a little thought on the part of the reader before each section, if we indeed question for ourselves:
- Are fertilizers in farming friend or foe?
- How have the Digital Revolution and Information Age impacted our diet?
- Are canned and frozen foods inferior to fresh?
- Does snacking or meal timing matter?
- What are cereal grains and “pseudograins”?
…And so many more. But what’s best about this is:
Dr. Newby doesn’t reference her own preferences, or even have a particular way of eating she’d like us to adopt. She just lays out the science to answer each question, as discovered by high-quality studies and a general weight of evidence.
Bottom line: this book can level-up your nutritional knowledge from bluffing to really knowing! A worthy addition to anyone’s bookshelf.
Share This Post
-
7 Invisible Eating Disorders
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s easy to assume that anyone with an eating disorder can be easily recognized by the resultantly atypical body composition, but it’s often not so.
Beyond the obvious
We’ll not keep them a mystery; the 7 invisible eating disorders discussed by therapist Kati Morton in this video are:
- OSFED (Other Specified Feeding or Eating Disorder): a catch-all diagnosis for those who don’t meet the criteria for more specific eating disorders but still have significant eating disorder behaviors.
- Atypical Anorexia: characterized by all the symptoms of anorexia nervosa (especially: intense fear of gaining weight, and body image distortion) except that the individual’s weight remains in a normal range.
- Atypical Bulimia: similar to bulimia nervosa, but the frequency or duration of binge-purge behaviors does not meet the usual diagnostic criteria and thus can fly under the radar.
- Atypical Binge-Eating Disorder: has episodes of consuming large amounts of food without compensatory behaviors (e.g. purging), but the episodes are less frequent and/or intense than typical binge-eating disorder.
- Purging Disorder: purging behaviors such as self-induced vomiting or laxative abuse without having binge-eating episodes (thus, this not being binging, and nothing obvious is happening outside of the bathroom).
- Night Eating Syndrome: consuming excessive amounts of food during the night while being fully aware of the nature of the eating episodes, which disrupts sleep and leads to guilt.
- Rumination Disorder: repeatedly regurgitating food, which may be rechewed, reswallowed, or spat out, without nausea or involuntary retching, often as a self-soothing mechanism.
For more on each of these, along with a case study-style example of each, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Eating Disorders: More Varied (And Prevalent) Than People Think
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
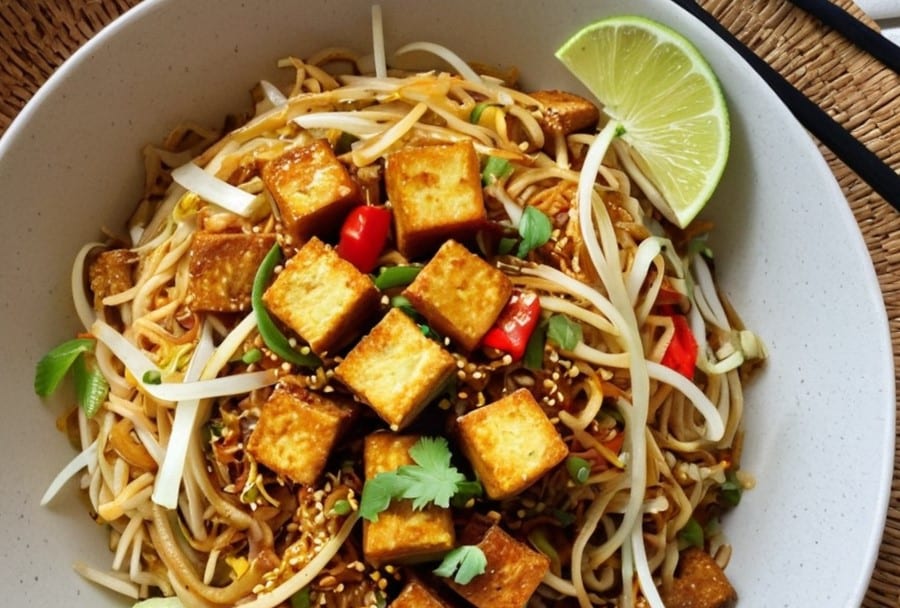
Crispy Tofu Pad Thai
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Easy to make, delicious to enjoy, and packed with phytonutrients, this dish is a great one to add to your repertoire:
You will need
- 10 oz ready-to-wok rice noodles, or 6 oz dry
- 5 oz silken tofu
- 5 oz firm or extra firm tofu, cut into small cubes
- 1 oz arrowroot (or cornstarch if you don’t have arrowroot)
- 4 scallions, sliced
- ¼ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 1″ piece fresh ginger, grated
- 1 red chili, chopped (multiply per your heat preferences)
- 1 red bell pepper, deseeded and thinly sliced
- 4 oz bok choi, thinly sliced
- 4 oz mung bean sprouts
- 1 tbsp tamari (or other, but tamari is traditional) soy sauce
- 1 tbsp sweet chili sauce
- Juice of ½ lime
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Avocado oil, or your preferred oil for stir-frying
- To serve: lime wedges
- Optional garnish: crushed roasted peanuts (if allergic, substitute sesame seeds; peanuts are simply traditional, that’s all)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Scramble the silken tofu. For guidance and also additional seasoning pointers, see our Tasty Tofu Scramble recipe, but omit the thyme.
2) Cook the noodles if necessary (i.e. if they are the dry type and need boiling, as opposed to “ready-to-wok” noodles that don’t), drain, and set aside.
4) Prepare the tofu cubes: if the tofu cubes are dry to the touch, toss them gently in a little oil to coat. If they’re wet to the touch, no need. Dust the tofu cubes with the arrowroot and MSG/salt; you can do this in a bowl, tossing gently to distribute the coating evenly.
4) Heat some oil in a wok over a high heat, and fry the tofu on each side until golden and crispy all over, and set aside.
5) Stir-fry the scallions, garlic, ginger, chili, and bell pepper for about 2 minutes.
6) Add the bean sprouts and bok choi, and keep stir-frying for another 2 minutes.
7) Add everything that’s not already in the pan except the lime wedges and peanuts (i.e., add the things you set aside, plus the remaining as-yet-untouched ingredients) and stir-fry for a further 2 minutes.
8) Serve hot, garnished with the crushed peanuts if using, and with the lime wedges on the side:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc
- Which Bell Peppers To Pick? A Spectrum Of Specialties
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sunflower Oil vs Canola Oil – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sunflower oil to canola oil, we picked the sunflower oil.
Why?
They’re both terrible! But canola oil is worse. Sunflower oil is marketed as being higher in polyunsaturated fats, which it is, albeit not by much.
Canola oil is very bad for the heart, and sunflower oil is only moderately bad for the heart, to the point that it can be heart-neutral if used sparingly.
As seed oils, they are both sources of vitamin E, but you’d need to drink a cup of oil to get your daily dose, so please just eat some seeds (or nuts, or fruit, or something) instead. It can even be sunflower seeds if you like! Rapeseed* itself (the seed that canola oil is made from) isn’t really sold as a foodstuff, so that one’s less of an option.
*Fun fact: if you’re N. American and wondering what this “rapeseed” is, know that most of the rest of the Anglosphere calls canola oil “rapeseed oil”, as it’s made from rapeseed, which comes from a plant called rape, whose name is unrelated to the crime of the same name, and comes from rāpa, the Latin word for turnip. Anyway, “canola” is a portmanteau of “Canadian” and “Ola” meaning oil, and is a trademark that has made its way into generic use throughout N. America, as a less alarming name.
Back to health matters: while sunflower seeds are healthy in moderation, the ultraprocessed and refined sunflower and canola oils are not.
Canola oil has also been found to be implicated in age-related cognitive decline, whereas sunflower oil has had mixed results in that regard.
In summary
Sunflower oil is relatively, and we stress relatively, healthier than canola oil. Please use a healthier oil than either if you can. Olive oil is good for most things, and if you need something with a higher smoke point (and/or less distinctive flavor), consider avocado oil, which is also very healthy and whose smoke point is even higher than the seed oils we’ve been discussing today.
Want to know more?
Check out:
Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
All of your hepatitis B vaccine questions answered
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that can cause liver disease in people of any age or background. Vaccination is 95 percent effective against the virus. But in recent years, false claims, rumors, and myths about the hepatitis B vaccine have become increasingly common.
Here’s everything you need to know about the lifesaving hepatitis B vaccine.
What is hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. The virus attacks the liver, causing severe short-term and long-term infections.
Short-term hepatitis B infections may cause “fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, jaundice (yellow skin or eyes, dark urine, clay-colored bowel movements), and pain in the muscles, joints, and stomach,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A long-term hepatitis B infection occurs when the virus stays in the body beyond the initial infection, causing chronic illness. Hepatitis B infections become chronic in 90 percent of infected infants, half of infected young children, and between 5 to 10 percent of infected adults.
“Most people who go on to develop chronic hepatitis B do not have symptoms, but it is still very serious and can lead to liver damage (cirrhosis), liver cancer, and death. Chronically infected people can spread hepatitis B virus to others, even if they do not feel or look sick themselves,” says the CDC.
How does the hepatitis B virus spread?
The hepatitis B virus is spread through body fluids, including blood, semen, and saliva. It can also be transmitted from birthing parent to child during pregnancy and childbirth.
“While hepatitis B is an infection that lives in bodily fluids, it can survive outside the human body for several days, which means that sharing contaminated household products is a possible source of infection,” said Dr. Christopher Labos, a McGill University cardiologist and epidemiologist, in a 2019 article.
In 2022, over 250 million people worldwide had chronic hepatitis B, and 1.1 million died from the disease. Most of the deaths were from liver damage and liver cancer. Less than 15 percent of people living with hepatitis B have been diagnosed.
How well does the vaccine protect against hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B vaccination is up to 95 percent effective, providing lasting—and possibly lifelong—protection against the virus. Depending on when the first dose is given, the complete vaccine series consists of two to three doses.
The vaccine is most effective for infants and children. The CDC recommends that infants receive it at birth for the most protection.
The first dose is followed by two to three additional doses administered before 18 months. Children, adolescents, and adults who weren’t vaccinated as infants should also receive the vaccine.
Vaccination is particularly important for high-risk groups, including health workers and those who are in close contact with individuals living with chronic hepatitis B, people who use intravenous drugs, and people receiving blood transfusions, dialysis, or organ transplants.
Is the vaccine safe?
Vaccines against hepatitis B were first developed in the 1980s, and they have been proven safe for decades. They have a low risk of serious side effects and are safe enough to be given to newborns, pregnant people, and immunocompromised people.
We also know hepatitis B vaccines work: “Between 1990 (about the time when universal hepatitis B vaccinations started) and 2006, the rate of hepatitis B infection fell by 81 percent to the lowest level ever recorded, and the decline was greatest among children,” added Labos.
Hepatitis B rates have continued to decline across all age groups, with the U.S. exceeding its goal of reducing new hepatitis B infections by 20 percent.
Why do doctors recommend the vaccine for babies?
Hepatitis B vaccination helps protect infants from a lifetime of potentially life-threatening infections and complications. Nine out of 10 unvaccinated infants infected with hepatitis B will develop chronic infections, which increases their risk of liver failure and liver cancer.
The hepatitis B vaccine is administered at birth to help prevent the virus from being transmitted from birthing parent to child. It also helps protect infants who might be in close contact with someone with hepatitis B. This is particularly important because most people who have hepatitis are undiagnosed.
Have more questions? Talk to your health care provider to learn more about hepatitis B vaccination.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: