Body Scrubs: Benefits, Risks, and Guidance
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I was wondering whether I should be using a body scrub in the shower, rather than just soap. What should guide me in the choice of a body scrub, and are there any risks to be aware of?❞
Body scrubs are great for giving skin a healthy glow, but are best used sparingly—over-exfoliation leads to the opposite effect (unhappy skin, premature skin aging, etc).
As for contents:
- microplastics are now banned in most places, but you might want to check any products (and their containers!) are BPA-free, pthalate free, etc.
- fragrances in body scrubs are usually a bad idea, and many essential oils have been shown to be endocrine-disruptors, which you do not want:
About the microplastics, harmful artificial chemicals in general, and what constitutes “etc”:
About the fragrances’ (including “natural” essential oils’) endocrine-disrupting shenanigans:
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: an Endocrine Society scientific statement
So, what might you want to use instead?
If you’re feeling adventurous, you might like to try treating yourself to a pineapple-based mask instead (a muslin cloth soaked in pineapple juice will work just fine; please don’t waterboard yourself though), as the bromelain enzymes (found very generously in pineapple juice) break down dead cells without the need for scrubbing.
Another option is a homemade salt- or sugar-scrub. Put your salt or sugar into a jar, add enough warm water to cover it, leave it for about a day, adding more water if it seems in danger of drying out, until it recrystallizes with a high water content keeping it malleable to the touch; congratulations, you now have a very simple scrub. This should still not be used more than, say, once per week, though.
Last but not least, you might consider investing in a konjac sponge; they gently remove dead skin without damaging living skin. Here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience
For more on gentle-yet-effective skincare, you might like to read:
Clean: The New Science of Skin and the Beauty of Doing Less
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What to Know About Stillbirths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Series: Stillbirths:When Babies Die Before Taking Their First Breath
The U.S. has not prioritized stillbirth prevention, and American parents are losing babies even as other countries make larger strides to reduce deaths late in pregnancy.
Every year, more than 20,000 pregnancies in the U.S. end in a stillbirth, the death of an expected child at 20 weeks or more of pregnancy. Research shows as many as 1 in 4 stillbirths may be preventable. We interviewed dozens of parents of stillborn children who said their health care providers did not tell them about risk factors or explain what to watch for while pregnant. They said they felt blindsided by what followed. They did not have the information needed to make critical decisions about what happened with their baby’s body, about what additional testing could have been done to help determine what caused the stillbirth, or about how to navigate the process of requesting important stillbirth documents.
This guide is meant to help fill the void of information on stillbirths. It’s based on more than 150 conversations with parents, health care providers, researchers and other medical experts.
Whether you’re trying to better prepare for a pregnancy or grieving a loss, we hope this will help you and your family. This guide does not provide medical advice. We encourage you to seek out other reliable resources and consult with providers you trust.
We welcome your thoughts and questions at mailto:[email protected]. You can share your experience with stillbirth with us. If you are a health care provider interested in distributing this guide, let us know if we can help.
Table of contents:
- What Is Stillbirth?
- Are Stillbirths Preventable?
- What to Expect After a Stillbirth.
- Grieving After a Stillbirth.
- What You Might Say and Do After a Loved One Experiences a Stillbirth.
What Is Stillbirth?
Many people told us that the first time they heard the term stillbirth was after they delivered their stillborn baby. In many cases, the lack of information and awareness beforehand contributed to their heartache and guilt afterward.
Stillbirth is defined in the U.S. as the death of a baby in the womb at 20 weeks or more of pregnancy. Depending on when it happens, stillbirth is considered:
- Early: 20-27 weeks of pregnancy.
- Late: 28-36 weeks of pregnancy.
- Term: 37 or more weeks of pregnancy.
About half of all stillbirths in the U.S. occur at 28 weeks or later.
What is the difference between a stillbirth and a miscarriage?
Both terms describe pregnancy loss. The distinction is when the loss occurs. A miscarriage is typically defined as a loss before the 20th week of pregnancy, while stillbirth is after that point.
How common is stillbirth?
Each year, about 1 in 175 deliveries in the U.S. are stillbirths — that’s about 60 stillborn babies every day — making it one of the most common adverse pregnancy outcomes, but it is rarely discussed.
If you are surprised by that fact, you are not alone. Many people we spoke to did not know how common stillbirths are. Leandria Lee of Texas said she spent her 2021 pregnancy unaware that her daughter, Zuri Armoni, could die in the last phase of her pregnancy.
“If I was prepared to know that something could happen, I don’t think it would have been as bad. But to not know and then it happens, it affects you,” she said of her stillbirth at 35 weeks.
Some doctors have told us they don’t introduce the possibility of a stillbirth because they don’t want to create additional anxiety for patients.
Other doctors say withholding information leaves patients unprepared.
“We have this idea that we can’t scare the patient, which to me is very paternalistic,” said Dr. Heather Florescue, an OB-GYN near Rochester, New York, who works to inform doctors and patients about stillbirth prevention.
What causes stillbirths?
There is a lot we don’t know about stillbirths because there hasn’t been enough research. The cause of the stillbirth is unknown in about 1 in 3 cases.
What we do know is that a number of factors may cause or increase the risk of a stillbirth, including:
- The baby not growing as expected.
- Placental abnormalities or problems with the umbilical cord.
- Genetic or structural disorders that cause developmental issues.
- High blood pressure before pregnancy or preeclampsia, a potentially fatal complication that usually appears late in pregnancy and causes high blood pressure.
- Diabetes before or during pregnancy.
- An infection in the fetus, the placenta or the pregnant person.
- Smoking.
- Being 35 or older.
- Obesity.
- Being pregnant with more than one baby.
But not all doctors, hospitals or health departments perform tests to identify the potential cause of a stillbirth or determine if it could have been prevented. Even when a cause is identified, fetal death records are rarely updated. This means data is sometimes inaccurate. Researchers strongly encourage doctors to perform a stillbirth evaluation, which includes an examination of the placenta and umbilical cord, a fetal autopsy and genetic testing.
If your hospital or doctor does not proactively offer one or more of these exams, you can ask them to conduct the tests. Research shows that placental exams may help establish a cause of death or exclude a suspected one in about 65% of stillbirths, while autopsies were similarly useful in more than 40% of cases.
Are Stillbirths Preventable?
Not all stillbirths are preventable, but some are. For pregnancies that last 37 weeks or more, one study found that nearly half of stillbirths are potentially preventable.
Dr. Joanne Stone, who last year was president of the Society of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, leads the country’s first Rainbow Clinic at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York. The clinic is modeled on similar facilities in the United Kingdom that care for people who want to conceive again after a stillbirth. She said many doctors used to think there was nothing they could do to prevent stillbirth.
“People just looked at it like, ‘Oh, it was an accident, couldn’t have been prevented,’” said Stone, who also is the system chair of the obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive science department at the Icahn School of Medicine. “But we know now there are things that we can do to try to prevent that from happening.”
She said doctors can:
- More closely monitor patients with certain risk factors, like high blood pressure, diabetes or obesity.
- Ask about prior infant loss or other obstetrical trauma.
- Carefully assess whether a baby’s growth is normal.
- Work to diagnose genetic anomalies.
- Teach patients how to track their baby’s movements and encourage them to speak up if they notice activity has slowed or stopped.
- Deliver at or before 39 weeks if there are concerns.
What are the risks of stillbirth over the course of a pregnancy?
The risk of a stillbirth increases significantly toward the end of pregnancy, especially after 39 weeks. The risk is higher for people who get pregnant at 35 or older. The risk begins to climb even earlier, around 36 weeks, for people pregnant with twins.
What you and your doctor can do to reduce the risk of stillbirth.
While federal agencies in the U.S. have yet to come up with a checklist that may help reduce the risk of stillbirth, the Stillbirth Centre of Research Excellence in Australia has adopted a Safer Baby Bundle that lists five recommendations:
- Stop smoking.
- Regularly monitor growth to reduce the risk of fetal growth restriction, when the fetus is not growing as expected.
- Understand the importance of acting quickly if fetal movement decreases.
- Sleep on your side after 28 weeks.
- Talk to your doctor about when to deliver. Depending on your situation, it may be before your due date.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has compiled a list of tests and techniques doctors can use to try to reduce the risk of a stillbirth. They include:
- A risk assessment to identify prenatal needs.
- A nonstresstest, which checks the fetus’s heart rate and how it changes as the fetus moves.
- A biophysical profile, which is done with an ultrasound to measure body movement, muscle tone and breathing, along with amniotic fluid volume.
The group stressed that there is no test that can guarantee a stillbirth won’t happen and that individual circumstances should determine what tests are run.
Are some people at higher risk for stillbirth?
Black women are more than twice as likely to have a stillbirth as white women. There are a number of possible explanations for that disparity, including institutional bias and structural racism, and a patient’s pre-pregnancy health, socioeconomic status and access to health care. In addition, research shows that Black women are more likely than white women to experience multiple stressful life events while pregnant and have their concerns ignored by their health care provider. Similar racial disparities drive the country’s high rate of maternal mortality.
How to find a provider you trust.
Finding a doctor to care for you during your pregnancy can be a daunting process. Medical experts and parents suggest interviewing prospective providers before you decide on the right one.
Here is a short list of questions you might want to ask a potential OB-GYN:
- What is the best way to contact you if I have questions or concerns?
- How do you manage inquiries after hours and on weekends? Do you see walk-ins?
- How do you manage prenatal risk assessments?
- What should I know about the risks of a miscarriage or stillbirth?
- How do you decide when a patient should be induced?
If a provider doesn’t answer your questions to your satisfaction, don’t be reluctant to move on. Dr. Ashanda Saint Jean, chair of the obstetrics and gynecology department at HealthAlliance Hospitals of the Hudson Valley in New York, said she encourages her patients to find the provider that meets their needs.
“Seek out someone that is like-minded,” said Saint Jean “It doesn’t have to be that they’re the same ethnicity or the same race, but like-minded in terms of the goals of what that patient desires for their own health and prosperity.”
What to know in the last trimester.
The last trimester can be an uncomfortable and challenging time as the fetus grows and you get increasingly tired. During this critical time, your provider should talk to you about the following topics:
- Whether you need a nonstress test to determine if the fetus is getting enough oxygen.
- The best way to track fetal movements.
- What to do if your baby stops moving.
- Whether you are at risk for preeclampsia or gestational diabetes.
Rachel Foran’s child, Eoin Francis, was stillborn at 41 weeks and two days. Foran, who lives in New York, said she believes that if her doctor had tracked her placenta, and if she had understood the importance of fetal movement, she and her husband might have decided to deliver sooner.
She remembers that her son was “very active” until the day before he was stillborn.
“I would have gone in earlier if someone had told me, ‘You’re doing this because the baby could die,’” she said of tracking fetal movement. “That would have been really helpful to know.”
Researchers are looking at the best way to measure the health, blood flow and size of the placenta, but studies are still in their early stages.
“If someone had been doing that with my son’s,” Foran said, “my son would be alive.”
A placental exam and an autopsy showed that a small placenta contributed to Foran’s stillbirth.
How often should you feel movement?
Every baby and each pregnancy are different, so it is important to get to know what levels of activity are normal for you. You might feel movement around 20 weeks. You’re more likely to feel movement when you’re sitting or lying down. Paying attention to movement during the third trimester is particularly important because research shows that changes, including decreased movement or bursts of excessive activity, are associated with an increased risk of stillbirth. Most of the time, it’s nothing. But sometimes it can be a sign that your baby is in distress. If you’re worried, don’t rely on a home fetal doppler to reassure you. Reach out to your doctor.
Saint Jean offers a tip to track movement: “I still tell patients each day to lay on their left side after dinner and record how many times their baby moves, because then that will give you an idea of what’s normal for your baby,” she said.
Other groups recommend using the Count the Kicks app as a way of tracking fetal movements and establishing what is normal for that pregnancy. Although there is no scientific consensus that counting kicks can prevent stillbirths, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and other groups recommend that patients be aware of fetal movement patterns.
Dr. Karen Gibbins is a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Oregon Health & Science University who in 2018 had stillborn son named Sebastian. She said the idea that babies don’t move as much at the end of pregnancy is a dangerous myth.
“You might hear that babies slow down at the end,” she said. “They don’t slow down. They just have a little less space. So their movements are a little different, but they should be as strong and as frequent.”
What to Expect After a Stillbirth
What might happen at the hospital?
Parents are often asked to make several important decisions while they are still reeling from the shock and devastation of their loss. It’s completely understandable if you need to take some time to consider them.
Some other things you can ask for (if medical personnel don’t offer them) are:
- Blood work, a placental exam, an autopsy and genetic testing.
- A social worker or counselor, bereavement resources and religious or chaplain support.
- The option to be isolated from the labor rooms.
- Someone to take photos of you and your baby, typically either a nurse or an outside group.
- A small cooling cot that allows parents to spend more time with their babies after a stillbirth. If one is not available, you can ask for ice packs to put in the swaddle or the bassinet.
- A mold of your baby’s hands and feet.
- Information about burial or cremation services.
- Guidance on what to do if your milk comes in.
Getting an autopsy after a stillbirth.
Whether to have an autopsy is a personal decision. It may not reveal a cause of death, but it might provide important information about your stillbirth and contribute to broader stillbirth research. Autopsies can be useful if you are considering another pregnancy in the future. Families also told us that an autopsy can help parents feel they did everything they could to try to understand why their baby died.
But several families told us their health care providers didn’t provide them with the right information to help with that decision. Some aren’t trained in the advantages of conducting an autopsy after a stillbirth, or in when and how to sensitively communicate with parents about it. Some, for example, don’t explain that patients can still have an open-casket funeral or other service after an autopsy because the incisions can easily be covered by clothing. Others may not encourage an autopsy because they think they already know what caused the stillbirth or don’t believe anything could have been done to prevent it. In addition, not all hospitals have the capacity to do an autopsy, but there may be private autopsy providers that can perform one at an additional cost.
You can read more about autopsies in our reporting.
Paying for an autopsy after a stillbirth.
If you decide you want an autopsy, you may wonder whether you need to pay out-of-pocket for it. Several families told us their providers gave them incomplete or incorrect information. Many larger or academic hospitals offer autopsies at no cost to patients. Some insurance companies also cover the cost of an autopsy after a stillbirth.
When hospitals don’t provide an autopsy, they may give you names of private providers. That was the case for Rachel Foran. The hospital gave her and her husband a list of numbers to call if they wanted to pay for an autopsy themselves. The process, she said, shocked her.
“I had just delivered and we had to figure out what to do with his body,” Foran said. “It felt totally insane that that was what we had to do and that we had to figure it out on our own.”
An independent autopsy, records show, cost them $5,000.
What is a certificate of stillbirth and how do I get one?
A fetal death certificate is the official legal document that records the death. This is the document used to gather data on and track the number of stillbirths in the country. Many states also issue a certificate of stillbirth or a certificate of birth resulting in stillbirth, which acknowledge the baby’s birth. Families told us they appreciated having that document, since typical birth certificates are not issued for stillbirths. You can usually request a certificate from the vital records office.
Grieving After a Stillbirth
What are the effects of stillbirths on parents and families?
Over and over, families told us the effects of losing a baby can reverberate for a lifetime.
Bereavement support groups may help provide a space to share experiences and resources. Hospitals and birth centers may suggest a local grief group.
We talked with Anna Calix, a maternal health expert who became active in perinatal loss prevention after her son Liam was stillborn on his due date in 2016. Calix leads grief support groups for people of color in English and Spanish.
She suggested rededicating the time you would have spent taking care of a new baby to the grief process.
“You can do that by addressing your own thoughts and feelings and really experiencing those feelings,” Calix said. “We like to push those feelings away or try to do something to distract and avoid, but no matter what we do, the feelings are there.”
It’s important, she said, to give yourself permission to grow your connection with your child and work through thoughts of guilt or blame.
What You Might Say and Do After a Loved One Experiences a Stillbirth
Finding the right words can be difficult. The following are a few suggestions from parents who went through a stillbirth.
Helpful:
- Acknowledge the loss and offer condolences.
- Ask if the baby was named and use the name.
- Allow space for the family to talk about their baby.
Unhelpful:
- Avoid talking about the baby.
- Minimize the loss or compare experiences.
- Start statements with “at least.”
Suggested phrases to avoid:
- “You’re young. You can have more kids.”
- “At least you have other children.”
- “These things just happen.”
- “Your baby is in a better place now.”
Share This Post
-
Early Dementia Screening From Your Blood & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dementia is, statistically speaking, the most feared disease in the US. Notwithstanding…
- heart disease killing more
- COVID being more of a lottery
- cancer being the “yes you can modify risk factors but it can come for anyone” life-changing (and often life-ending) disease,
…it’s still dementia that Americans report fearing the most.
And yet… Early dementia screening is seriously underused
It may be a case of a head-in-sand approach to avoid unwanted news, or it could be a case of not knowing what’s available.
So, with that in mind…
How to watch out: first line warning signs
You walk into a room of your house, and suddenly stop: “what did I come in here for?”, you wonder.
A moment later, you’re worrying whether this is a sign of age-related cognitive decline.
The good news: it usually isn’t. In fact, you did that when you were younger, too, you just didn’t pay enough attention at the time to remember it now.
Dementia-related memory loss is less “where did I put my car keys?”, and more “what is this thing for?” (it’s your car keys). Or at a less advanced stage: “whose are these car keys?” (they are yours).
You can read about some of the nuances here:
Is It Dementia? Spot The Signs (Because None Of Us Are Immune) ← If you’d like an objective test of memory and other cognitive impairments, this article also has a link to the industry’s gold standard test (it’s free)
(The Self-Administered Gerocognitive Exam (SAGE) is designed to detect early signs of cognitive, memory or thinking impairments)
Tests you can’t do at home
We wrote a little while back about how one kind of blood testing for Alzheimer’s disease works:
The Brain Alarm Signs That Warn Of Dementia
Why “Brain Alarm Signs” if it’s a blood test? Because the blood gets (in very lay terms) bits of broken brain in it. Or more specifically, they tested the blood for density of cerebrovascular endothelial extracellular vesicles (CEEVs), which are bits of the cells from the lining of blood vessels in the brain. These cerebrovascular endothelial extracellular vesicles should not, ideally, be falling off and riding around your bloodstream, and the greater the density of them, the greater likelihood of mild cognitive impairment now, and by extension, dementia later.
It’s not the only blood test available though, see:
Highly accurate blood test for Alzheimer’s disease is similar or superior to clinical cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tests ← this one checks the ratio of phosporylated-tau217 to non-phosphorylated tau (which is a protein antibody), which equalled or outperformed FDA-approved CSF tests in classifying amyloid-β positron emission topography (PET, as in a PET scan) status, with a confidence interval as high as, or better than, industry standards.
If you don’t like having your blood taken, trust us that you’d find having your cerebrospinal fluid taken even less enjoyable, so this is a very welcome improvement!
In case you’re curious about how the CSF test works, here you go: NPTX2 in Cerebrospinal Fluid Predicts the Progression From Normal Cognition to Mild Cognitive Impairment ← NPTX2 is a protein biomarker of Alzheimer’s risk
…but again, we really think the blood test is preferable.
Tests beyond the physiological
There are, of course, psychological tests that can be done, including a linguistic analysis of your conversation, compared with a vast database of other people’s conversations, with and without various degrees of cognitive impairment
As Dr. Ioannis Paschalidis explains:
❝We wanted to predict what would happen in the next six years—and we found we can reasonably make that prediction with relatively good confidence and accuracy.
Rather than using acoustic features of speech, like enunciation or speed, the model is just pulling from the content of the interview—the words spoken, how they’re structured.
You can think of the score as the likelihood, the probability, that someone will remain stable or transition to dementia. It had significant predictive ability.
Digital is the new blood. You can collect it, analyze it for what is known today, store it, and reanalyze it for whatever new emerges tomorrow.❞
You can read the full paper here: Prediction of Alzheimer’s disease progression within 6 years using speech: A novel approach leveraging language models
See also: AI: The Doctor That Never Tires?
What if the news isn’t good?
While bad news is never welcome per se, it is preferable to not knowing, insofar as we can then take steps to manage the situation.
You may be wondering: what can be done that I wouldn’t already be doing to minimize my dementia risk in the first place?
And the answer is: yes, do continue those things of course, but there is more to do:
See: Beyond Guarding Against Dementia: When Age’s Brain-Changes Come Knocking
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Zuranolone: What to know about the pill for postpartum depression
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In the year after giving birth, about one in eight people who give birth in the U.S. experience the debilitating symptoms of postpartum depression (PPD), including lack of energy and feeling sad, anxious, hopeless, and overwhelmed.
Postpartum depression is a serious, potentially life-threatening condition that can affect a person’s bond with their baby. Although it’s frequently confused with the so-called “baby blues,” it’s not the same.
The baby blues include similar, temporary symptoms that affect up to 80 percent of people who have recently given birth and usually go away within the first few weeks. PPD usually begins within the first month after giving birth and can last for months and interfere with a person’s daily life if left untreated. Thankfully, PPD is treatable and there is help available.
On August 4, the FDA approved zuranolone, branded as Zurzuvae, the first-ever oral medication to treat PPD. Until now, besides other common antidepressants, the only medication available to treat PPD specifically was the IV injection brexanolone, which is difficult to access and expensive and can only be administered in a hospital or health care setting.
Read on to find out more about zuranolone: what it is, how it works, how much it costs, and more.
What is zuranolone?
Zurzuvae is the brand name for zuranolone, an oral medication to treat postpartum depression. Developed by Sage Therapeutics in partnership with Biogen, it’s now available in the U.S. Zurzuvae is typically prescribed as two 25 mg capsules a day for 14 days. In clinical trials, the medication showed to be fast-acting, improving PPD symptoms in just three days.
How does zuranolone work?
Zuranolone is a neuroactive steroid, a type of medication that helps the neurotransmitter GABA’s receptors, which affect how the body reacts to anxiety, stress, and fear, function better.
“Zuranolone can be thought of as a synthetic version of [the neuroactive steroid] allopregnanolone,” says Dr. Katrina Furey, a reproductive psychiatrist, clinical instructor at Yale University, and co-host of the Analyze Scripts podcast. “Women with PPD have lower levels of allopregnenolone compared to women without PPD.”
How is it different from other antidepressants?
“What differentiates zuranolone from other previously available oral antidepressants is that it has a much more rapid response and a shorter course of treatment,” says Dr. Asima Ahmad, an OB-GYN, reproductive endocrinologist, and founder of Carrot Fertility.
“It can take effect as early as on day three of treatment, versus other oral antidepressants that can take up to six to 12 weeks to take full effect.”
What are Zurzuvae’s side effects?
According to the FDA, the most common side effects of Zurzuvae include dizziness, drowsiness, diarrhea, fatigue, the common cold, and urinary tract infection. Similar to other antidepressants, the medication may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and actions in people 24 and younger. However, NPR noted that this type of labeling is required for all antidepressants, and researchers didn’t see any reports of suicidal thoughts in their trials.
“Drug trials also noted that the side effects for zuranolone were not as severe,” says Ahmad. “[There was] no sudden loss of consciousness as seen with brexanolone or weight gain and sexual dysfunction, which can be seen with other oral antidepressants.”
She adds: “Given the lower incidence of side effects and more rapid-acting onset, zuranolone could be a viable option for many,” including those looking for a treatment that offers faster symptom relief.
Can someone breastfeed while taking zuranolone?
It’s complicated. In clinical trials, participants were asked to stop breastfeeding (which, according to Furey, is common in early clinical trials).
A small study of people who were nursing while taking zuranolone found that 0.3 percent of the medication dose was passed on to breast milk, which, Furey says, is a pretty low amount of exposure for the baby. Ahmad says that “though some data suggests that the risk of harm to the baby may be low, there is still overall limited data.”
Overall, people should talk to their health care provider about the risks and benefits of breastfeeding while on the medication.
“A lot of factors will need to be weighed, such as overall health of the infant, age of the infant, etc., when making this decision,” Furey says.
How much does Zurzuvae cost?
Zurzuvae’s price before insurance coverage is $15,900 for the 14-day treatment. However, the Policy Center for Maternal Mental Health says insurance companies and Medicaid are expected to cover it because it’s the only drug of its kind.
Less than 1 percent of U.S. insurers have issued coverage guidelines so far, so it’s still unknown how much it will cost patients after insurance. Some insurers require patients to try another antidepressant first (like the more common SSRIs) before covering Zurzuvae. For uninsured and underinsured people, Sage Therapeutics said it will offer copay assistance.
The hefty price tag and potential issues with coverage may widen existing health disparities, says Ahmad. “We need to ensure that we are seeking out solutions to enable wide-scale access to all PPD treatments so that people have access to whatever treatment may work best for them.”
If you or anyone you know is considering suicide or self-harm or is anxious, depressed, upset, or needs to talk, call the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or text the Crisis Text Line at 741-741. For international resources, here is a good place to begin.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Are Brain Chips Safe?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ready For Cyborgization?
In yesterday’s newsletter, we asked you for your views on Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs), such as the Utah Array and Neuralink’s chips on/in brains that allow direct communication between brains and computers, so that (for example) a paralysed person can use a device to communicate, or manipulate a prosthetic limb or two.
We didn’t get as many votes as usual; it’s possible that yesterday’s newsletter ended up in a lot of spam filters due to repeated use of a word in “extra ______ olive oil” in its main feature!
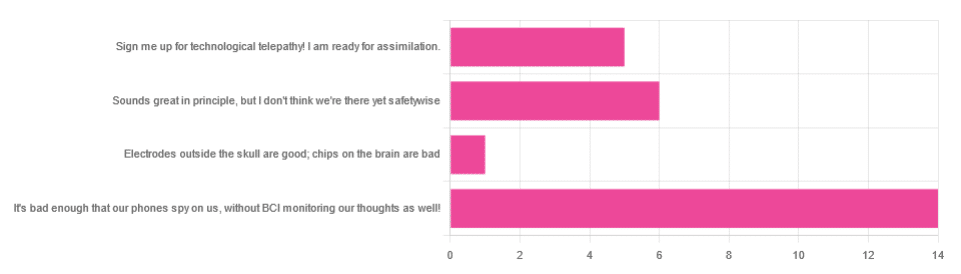
However, of the answers we did get…
- About 54% said “It’s bad enough that our phones spy on us, without BCI monitoring our thoughts as well!”
- About 23% said “Sounds great in principle, but I don’t think we’re there yet safetywise”
- About 19% said “Sign me up for technological telepathy! I am ready for assimilation”
- One (1) person said “Electrode outside the skull are good; chips on the brain are bad”
But what does the science say?
We’re not there yet safetywise: True or False?
True, in our opinion, when it comes to the latest implants, anyway. While it’s very difficult to prove a negative (it could be that everything goes perfectly in human trials), “extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence”, and so far this seems to be lacking.
The stage before human trials is usually animal trials, starting with small creatures and working up to non-human primates if appropriate, before finally humans.
- Good news: the latest hot-topic BCI device (Neuralink) was tested on animals!
- Bad news: to say it did not go well would be an understatement
The Gruesome Story of How Neuralink’s Monkeys Actually Died
The above is a Wired article, and we tend to go for more objective sources, however we chose this one because it links to very many objective sources, including an open letter from the Physicians’ Committee for Responsible Medicine, which basically confirms everything in the Wired article. There are lots of links to primary (medical and legal) sources, too.
Electrodes outside the skull are good; chips on/in the brain are bad: True or False?
True or False depending on how they’re done. The Utah Array (an older BCI implant, now 20 years old, though it’s been updated many times since) has had a good safety record, after being used by a few dozen people with paralysis to control devices:
How the Utah Array is advancing BCI science
The Utah Array works on the same general principle as Neuralink, but the mechanics of its implementation are very different:
- The Utah Array involves a tiny bundle of microelectrodes (held together by a rigid structure that looks a bit like a nanoscale hairbrush) put in place by a brain surgeon, and that’s that.
- The Neuralink has a dynamic web of electrodes, implanted by a little robot that acts like a tiny sewing machine to implant many polymer threads, each containing its own a bunch of electrodes.
In theory, the latter is much more advanced. In practice, so far, the former has a much better safety record.
I am right to be a little worried about giving companies access to my brain: True or False?
True or False, depending on the nature of your concern.
For privacy: current BCI devices have quite simple switches operated consciously by the user. So while technically any such device that then runs its data through Bluetooth or WiFi could be hacked, this risk is no greater than using a wireless mouse and/or keyboard, because it has access to about the same amount of information.
For safety: yes, probably there is cause to be worried. Likely the first waves of commercial users of any given BCI device will be severely disabled people who are more likely to waive their rights in the hope of a life-changing assistance device, and likely some of those will suffer if things go wrong.
Which on the one hand, is their gamble to make. And on the other hand, makes rushing to human trials, for companies that do that, a little more predatory.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Signs That Are Present When Someone Is Dying
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You’ve probably been there a few times, although given the emotional nature of the thing, it’s likely that you weren’t taking notes. Hospice workers, on the other hand, do take notes, so here are some things you might want to know, and if anything makes the next time even a little easier, that’ll be good:
Last stages
Here are the discussed signs of the “active dying” phase:
- Increasing unconsciousness:
- The person will be mostly unresponsive most of the time.
- Eyes may be open or partially open but not making eye contact.
- Mouth will likely remain open due to muscle relaxation.
- Cessation of food and water intake
- The person will likely not eat or drink for several days.
- This is a natural process and does not cause suffering per se (e.g. thirst, hunger).
- Dryness of mouth, however, can be treated with a little moistening, for comfort.
- Changes in breathing
- Breathing patterns will change and may be irregular.
- This is a natural metabolic response, and is not a sign of distress.
- Terminal secretions (“death rattle”) may occur:
- A gurgling sound caused by saliva buildup due to loss of swallowing reflex.
- Not painful or distressing for the person.
- Can be managed by repositioning or using medication to dry secretions.
- Skin color changes / mottling:
- First appears on fingers and toes (purple or gray discoloration).
- May spread to knees, nose, or other extremities.
- Temperature fluctuations:
- The body loses its ability to regulate temperature.
- Person may feel hot but be cold (or vice versa).
- Fevers are common—cooling measures and/or Tylenol can help.
A person in discomfort may appear restless, have a furrowed brow, or show physical agitation. If on the other hand they appear peaceful and unresponsive, they are almost certainly not in distress. At such times, it’s best to focus on just keeping them clean and comfortable.
For more on all of these, see:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Managing Mortality: When Planning Is a Matter of Life and Death
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Increasing unconsciousness:
-
Wise Old Fool
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How old is this dish? Well, let’s put it this way, it used to be called “𓅮𓏏𓈖” and remnants of it have been found at neolithic burial sites in Egypt. Nowadays it’s called “فول مدمس”, which gets rendered a lot of different ways in the Latin alphabet, but “fūl mudammas” is one option. For short, it’s just called “fūl”, which is pronounced like the English word “fool”, and it’s about the beans.
From chana masala with poori to frijoles refritos to beans on toast, lots of cultures have some version of this breakfast food, and all can be great (yes, even the beans on toast). But today we’re about this particular kind of morning protein, fiber, fats, and healthful spices.
You will need
- 2x 14 oz cans fava beans (other kinds of beans work as substitute; kidney beans are common substitution, but this writer prefers black beans personally if she doesn’t have fava in), drained
- 4 garlic cloves, crushed
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 teaspoon sweet cinnamon (or ½ sweet cinnamon stick)
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 1 tsp paprika
- 1 tsp black pepper
- Juice of ½ lemon
- For the relish: 1 medium tomato, finely chopped; 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil; 2 tbsp parsley, finely chopped
- To serve: 4 pitta breads, 2 eggs (omit if vegan), and a selection of pickled vegetables, drained
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add the olive oil to a saucepan over a medium heat; add the garlic, cumin seeds, and cinnamon. Keep these moving for a minute or two before moving to the next step.
2) Add the fava beans, as well as the other seasonings (chili flakes, paprika, black pepper), and mix thoroughly
3) Add 1 cup boiling water, and keep everything on a simmer for about 20 minutes, stirring often. Add the lemon juice while it’s simmering; when the beans start to break down and the mixture starts to thicken, it’s ready.
4) Mix the relish ingredients (finely chopped tomato, olive oil, parsley) thoroughly in a small bowl
5) Toast the pitta breads, and if using, soft-boil the eggs.
6) Serve! We suggest: fūl in a bowl, with one half of a soft-boiled egg per bowl, topped with the relish, and served with the pitta bread and pickled vegetables on the side.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Less Obvious Probiotic Benefits ← the pickled vegetables contain the probiotics here, while the beans are a great source of prebiotic fiber; this is why they work so well together
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- A Tale Of Two Cinnamons
- Eggs: All Things In Moderation?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: