Altered Traits – by Dr. Daniel Goleman & Dr. Richard Davidson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We know that meditation helps people to relax, but what more than that?This book explores the available science.
We say “explore the available science”, but it’d be remiss of us not to note that the authors have also expanded the available science, conducting research in their own lab.
From stress tests and EEGs to attention tests and fMRIs, this book looks at the hard science of what different kinds of meditation do to the brain. Not just in terms of brain state, either, but gradual cumulative anatomical changes, too. Powerful stuff!
The style is very pop-science in presentation, easily comprehensible to all. Be aware though that this is an “if this, then that” book of science, not a how-to manual. If you want to learn to meditate, this isn’t the book for that.
Bottom line: if you’d like to understand more about how different kinds of meditation affect the brain differently, this is the book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Fall Asleep Faster: CBT-Insomnia Treatment
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Insomnia affects a lot of people, and is even more common as we get older. Happily, therapist Emma McAdam is here with a drug-free solution that will work for most people most of the time.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBTI)
While people think of causes of insomnia as being things such as stress, anxiety, overthinking, disturbances, and so forth, these things affect sleep in the short term, but don’t directly cause chronic insomnia.
We say “directly”, because chronic insomnia is usually the result of the brain becoming accustomed to the above, and thus accidentally training itself to not sleep.
The remedy: cut the bad habit of staying in bed while awake. Lying in bed awake trains the brain to associate lying in bed with wakefulness (and any associated worrying, etc). In essence, we lie down, and the brain thinks “Aha, we know this one; this is the time and place for worrying, ok, let’s get to work”.
So instead: if you’re in bed and not asleep within 15 minutes, get up and do something non-stimulating until you feel sleepy, then return to bed. This may cause some short term tiredness, but it will usually correct the chronic insomnia within a week.
For more details, tips, and troubleshooting with regard to the above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How to Fall Back Asleep After Waking Up in the Middle of the Night
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Bromelain vs Inflammation & Much More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let’s Get Fruity
Bromelain is an enzyme* found in pineapple (and only in pineapple), that has many very healthful properties, some of them unique to bromelain.
*actually a combination of enzymes, but most often referred to collectively in the singular. But when you do see it referred to as “they”, that’s what that means.
What does it do?
It does a lot of things, for starters:
❝Various in vivo and in vitro studies have shown that they are anti-edematous, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancerous, anti-thrombotic, fibrinolytic, and facilitate the death of apoptotic cells. The pharmacological properties of bromelain are, in part, related to its arachidonate cascade modulation, inhibition of platelet aggregation, such as interference with malignant cell growth; anti-inflammatory action; fibrinolytic activity; skin debridement properties, and reduction of the severe effects of SARS-Cov-2❞
Some quick notes:
- “facilitate the death of apoptotic cells” may sound alarming, but it’s actually good; those cells need to be killed quickly; see for example: Fisetin: The Anti-Aging Assassin
- If you’re wondering what arachidonate cascade modulation means, that’s the modulation of the cascade reaction of arachidonic acid, which plays a part in providing energy for body functions, and has a role in cell structure formation, and is the precursor of assorted inflammatory mediators and cell-signalling chemicals.
- Its skin debridement properties (getting rid of dead skin) are most clearly seen when using bromelain topically (one can literally just make a pineapple poultice), but do occur from ingestion also (because of what it can do from the inside).
- As for being anti-thrombotic and fibrinolytic, let’s touch on that before we get to the main item, its anti-inflammatory properties.
If you want to read more of the above before moving on, though, here’s the full text:
Anti-thrombotic and fibrinolytic
While it does have anti-thrombotic effects, largely by its fibrinolytic action (i.e., it dissolves the fibrin mesh holding clots together), it can have a paradoxically beneficial effect on wound healing, too:
For more specifically on its wound-healing benefits:
In Vitro Effect of Bromelain on the Regenerative Properties of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Anti-inflammatory
Bromelain is perhaps most well-known for its anti-inflammatory powers, which are so diverse that it can be a challenge to pin them all down, as it has many mechanisms of action, and there’s a large heterogeneity of studies because it’s often studied in the context of specific diseases. But, for example:
❝Bromelain reduced IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α secretion when immune cells were already stimulated in an overproduction condition by proinflammatory cytokines, generating a modulation in the inflammatory response through prostaglandins reduction and activation of cascade reactions that trigger neutrophils and macrophages, in addition to accelerating the healing process❞
~ Dr. Taline Alves Nobre et al.
Read in full:
Bromelain as a natural anti-inflammatory drug: a systematic review
Or if you want a more specific example, here’s how it stacks up against arthritis:
❝The results demonstrated the chondroprotective effects of bromelain on cartilage degradation and the downregulation of inflammatory cytokine (tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8) expression in TNF-α–induced synovial fibroblasts by suppressing NF-κB and MAPK signaling❞
~ Dr. Perephan Pothacharoen et al.
Read in full:
More?
Yes more! You’ll remember from the first paper we quoted today, that it has a long laundry list of benefits. However, there’s only so much we can cover in one edition, so that’s it for today
Is it safe?
It is generally recognized as safe. However, its blood-thinning effect means it should be avoided if you’re already on blood-thinners, have some sort of bleeding disorder, or are about to have a surgery.
Additionally, if you have a pineapple allergy, this one may not be for you.
Aside from that, anything can have drug interactions, so do check with your doctor/pharmacist to be sure (with the pharmacist usually being the more knowledgeable of the two, when it comes to drug interactions).
Want to try some?
You can just eat pineapples, but if you don’t enjoy that and/or wouldn’t want it every day, bromelain is available in supplement form too.
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Fruit, Fiber, & Leafy Greens… On A Low-FODMAP Diet!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fiber For FODMAP-Avoiders
First, let’s quickly cover: what are FODMAPs?
FODMAPs are fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols.
In plainer English: they’re carbohydrates that are resistant to digestion.
This is, for most people most of the time, a good thing, for example:
When Is A Fiber Not A Fiber? When It’s A Resistant Starch.
Not for everyone…
However, if you have inflammatory bowel syndrome (IBS), including ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, or similar, then suddenly a lot of common dietary advice gets flipped on its head:
While digestion-resistant carbohydrates making it to the end parts of our digestive tract are good for our bacteria there, in the case of people with IBS or similar, it can be a bit too good for our bacteria there.
Which can mean gas (a natural by-product of bacterial respiration) accumulation, discomfort, water retention (as the pseudo-fiber draws water in and keeps it), and other related symptoms, causing discomfort, and potentially disease such as diarrhea.
Again: for most people this is not so (usually: quite the opposite; resistant starches improve things down there), but for those for whom it’s a thing, it’s a Big Bad Thing™.
Hold the veg? Hold your horses.
A common knee-jerk reaction is “I will avoid fruit and veg, then”.
Superficially, this can work, as many fruit & veg are high in FODMAPs (as are fermented dairy products, by the way).
However, a diet free from fruit and veg is not going to be healthy in any sustainable fashion.
There are, however, options for low-FODMAP fruit & veg, such as:
Fruits: bananas (if not overripe), kiwi, grapefruit, lemons, limes, melons, oranges, passionfruit, strawberries
Vegetables: alfalfa, bell peppers, bok choy, carrots, celery, cucumbers, eggplant, green beans, kale, lettuce, olives, parsnips, potatoes (and sweet potatoes, yams etc), radishes, spinach, squash, tomatoes*, turnips, zucchini
*our stance: botanically it’s a fruit, but culinarily it’s a vegetable.
For more on the science of this, check out:
Strategies for Producing Low FODMAPs Foodstuffs: Challenges and Perspectives ← table 2 is particularly informative when it comes to the above examples, and table 3 will advise about…
Bonus
Grains: oats, quinoa, rice, tapioca
…and wheat if the conditions in table 3 (linked above) are satisfied
(worth mentioning since grains also get a bad press when it comes to IBS, but that’s mostly because of wheat)
See also: Gluten: What’s The Truth?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
5 Steps To Beat Overwhelm
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dealing With Overwhelm
Whether we live a hectic life in general, or we usually casually take each day as it comes but sometimes several days gang up on us at once, everyone gets overwhelmed sometimes.
Today we’re going to look at how to deal with it healthily.
Step 1: Start anywhere
It’s easy to get stuck in “analysis paralysis” and not know how to tackle an unexpected large problem. An (unhealthy) alternative is to try to tackle everything at once, and end up doing nothing very well.
Even the most expert juggler will not successfully juggle 10 random things thrown unexpectedly at them.
So instead, just pick any part of the the mountain of to-dos, and start.
If you do want a little more finesse though, check out:
Procrastination, And How To Pay Off The To-Do List Debt
Step 2: Accept what you’re capable of
This one works both ways. It means being aware of your limitations yes, but also, of your actual abilities:
- Is the task ahead of you really beyond what you are capable of?
- Could you do it right now without hesitation if a loved one’s life depended on it?
- Could you do it, but there’s a price to pay (e.g. you can do it but it’ll wipe you out in some other life area)?
Work out what’s possible and acceptable to you, and make a decision. And remember, it could be that someone else could do it, but everyone has taken the “if you want something doing, give it to someone busy” approach. It’s flattering that people have such confidence in our competence, but it is also necessary to say “no” sometimes, or at least enlisting help.
Step 3: Listen to your body
…like a leader listening to an advisory council. Your perception of tiredness, pain, weakness, and all your emotions are simply messengers. Listen to the message! And then say “thank you for the information”, and proceed accordingly.
Sometimes that will be in the way the messengers seem to be hoping for!
Sometimes, however, maybe we (blessed with a weighty brain and not entirely a slave to our limbic system) know better, and know when it’s right to push through instead.
Similarly, that voice in your head? You get to decide where it goes and doesn’t. On which note…
Step 4: Be responsive, not reactive
We wrote previously on the difference between these:
A Bone To Pick… Up And Then Put Back Where We Found It
Measured responses will always be better than knee-jerk reactions, unless it is literally a case of a split-second making a difference. 99% of our problems in life are not so; usually the problem will still be there unchanged after a moment’s mindful consideration, so invest in that moment.
You’ve probably heard the saying “give me six hours to chop down a tree, and I’ll spend the first four sharpening the axe”. In this case, that can be your mind. Here’s a good starting point:
No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
And if your mental state is already worse than that, mind racing with threats (real or perceived) and doom-laden scenarios, here’s how to get out of that negative spiral first, so that you can apply the rest of this:
Do remember to turn it on again afterwards, though
Step 5: Transcend discomfort
This is partly a callback to step 3, but it’s now coming from a place of a clear ready mind, so the territory should be looking quite different now. Nevertheless, it’s entirely possible that your clear view shows discomfort ahead.
You’re going to make a conscious decision whether or not to proceed through the discomfort (and if you’re not, then now’s the time to start calmly and measuredly looking at alternative plans; delegating, ditching, etc).
If you are going to proceed through discomfort, then it can help to frame the discomfort as simply a neutral part of the path to getting where you want. Maybe you’re going to be going way out of your comfort zone in order to deal with something, and if that’s the case, make your peace with it now, in advance.
“Certainly it hurts” / “Well, what’s the trick then?” / “The trick, William Potter, is not minding that it hurts”
(lines from a famous scene from the 1962 movie Lawrence of Arabia)
It’s ok to say to yourself (if it’s what you decide is the right thing to do) “Yep, this experience is going to suck terribly, but I’m going to do it anyway”.
See also (this being about Radical Acceptance):
What’s The Worst That Could Happen?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Sun Exposure Dilemma
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Sun Exposure Dilemma
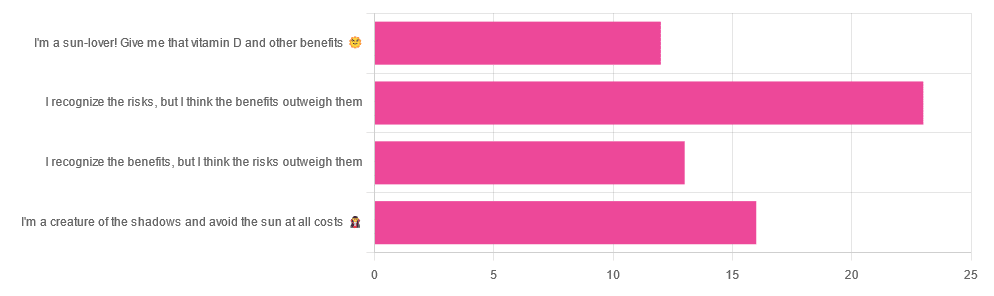
Yesterday, we asked you about your policy on sun exposure, and got the above-pictured, below-described, set of answers:
- A little over a third of respondents chose “I recognize the risks, but I think the benefits outweigh them”
- A quarter of respondents chose “I am a creature of the shadows and I avoid the sun at all costs”
- A little over a fifth of respondents chose “I recognize the benefits, but I think the risks outweigh them”
- A little under a fifth of respondents chose “I’m a sun-lover! Give me that vitamin D and other benefits!”
All in all, this is perhaps the most even spread of answers we’ve had for Friday mythbuster polls—though the sample size was smaller than it often is.
Of those who added comments, common themes were to mention your local climate, and the importance of sunscreen and/or taking vitamin D supplements.
One subscriber mentioned having lupus and living in Florida, which is a particularly unfortunate combination:
Lupus Foundation | Lupus & UV exposure: What you need to know
Another subscriber wrote:
❝Use a very good sunscreen with a high SPF all the time. Reapply after swimming or as needed! I also wear polarized sunglasses anytime I’m outside.❞
…which are important things to note too, and a lot of people forget!
See also: Who Screens The Sunscreens? (on fearing chemical dangers, vs the protection given)
But, onto today’s science for the topic at hand…
We need to get plenty of sun to get plenty of vitamin D: True or False?
True or False, depending on so many factors—to the point that many people get it wildly wrong in either direction.
Whether we are getting enough vitamin D depends on many circumstances, including:
- The climate (and depending on latitude, time of year) where we live
- Our genes, and especially (but not only) our skintone
- The clothes we wear (or don’t)
- Our diet (and not just “how much vitamin D do we consume”)
- Chronic diseases that affect vitamin D metabolism and/or requirements and/or sensitivity to the sun
For a rundown on these factors and more, check out:
Should I be getting my vitamin D levels checked?
Notably, on the topic of whether you should stay in the sun for longer to get more vitamin D…
❝The body can only produce a certain amount of vitamin D at the time, so staying in the sun any longer than needed (which could be just a few minutes, in a sunny climate) is not going to help increase your vitamin D levels, while it will increase your risk of skin cancer.❞
In contrast, she does also note:
❝During winter, catching enough sun can be difficult, especially if you spend your days confined indoors. Typically, the required exposure increases to two to three hours per week in winter. This is because sunlight exposure can only help produce vitamin D if the UVB rays reach us at the correct angle. So in winter we should regularly spend time outside in the middle of the day to get our dose of vitamin D.❞
See also: Vitamin D & Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
We can skip the sun and get our vitamin D from diet/supplements: True or False?
True! However, vitamin D is not the only health benefit of sun exposure.
Not only is sunlight-induced serotonin production important for many things ranging from mood to circadian rhythm (which in turn affects many other aspects of health), but also…
While too much sun can cause skin cancer, too little sun could cause other kinds of cancer:
Benefits of Sunlight: A Bright Spot for Human Health
Additionally, according to new research, the circadian rhythm benefits we mentioned above may also have an impact on type 2 diabetes:
Can catching some rays help you fight off type 2 diabetes?
Which way to jump?
A lot of it depends on who you are, ranging from the factors we mentioned earlier, to even such things as “having many moles” or “having blonde hair”.
This latter item, blonde hair, is a dual thing: it’s a matter of genetic factors that align with being prone to being more sensitive to the sun, as well as being a lesser physical barrier to the sun’s rays than dark hair (that can block some UV rays).
So for example, if two people have comparably gray hair now, but one of them used to have dark hair and the other blonde, there will still be a difference in how they suffer damage, or don’t—and yes, even if their skin is visually of the same approximate skintone.
You probably already know for yourself whether you are more likely to burn or tan in the sun, and the former group are less resistant to the sun’s damage… But the latter group are more likely to spend longer in the sun, and accumulate more damage that way.
If you’d like a very comprehensive downloadable, here are the guidelines issued by the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence:
NICE Guidelines | Sunlight exposure: risks and benefits
…and skip to “At risk groups”, if you don’t want to read the whole thing; “Skin type” is also an important subsection, which also uses your hair and eye color as indicators.
Writer’s note: genetics are complicated and not everyone will fall neatly into categories, which is why it’s important to know the individual factors.
For example, I am quite light-skinned with slightly graying dark hair and gray-blue eyes, and/but also have an obscure Sámi gene that means my skin makes vitamin D easily, while simultaneously being unusually resistant to burning (I just tan). Basically: built for the midnight sun of the Arctic circle.
And yet! My hobbies include not getting skin cancer, so I tend to still be quite mindful of UV levels in different weathers and times of day, and make choices (schedule, clothing, sunscreen or not) accordingly.
Bottom line:
That big self-perpetuating nuclear explosion in the sky is responsible for many things, good and bad for our health, so be aware of your own risk factors, especially for vitamin D deficiency, and skin cancer.
- If you have a predisposition to both, that’s unfortunate, but diet and supplementation at least can help with the vitamin D while getting modest amounts of sun at most.
- Remember that you can only make so much vitamin D at once, so sunbathing for health benefits need only take a few minutes
- Remember that sunlight is important for our circadian rhythm, which is important for many things.
- That’s governed by specific photoreceptor cells, though, so we don’t need our skin to be exposed for that; we just need to be able to see sunlight.
- If you’re going to be out in the sun, and not covered up, sunscreen is your friend, and yes, that goes for clear cold days under the winter sun too.
- Most phone weather apps these days have a UV index score as part of the data they give. Get used to checking it as often as you’d check for rain.
Stay safe, both ways around!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How light tells you when to sleep, focus and poo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is the next article in our ‘Light and health’ series, where we look at how light affects our physical and mental health in sometimes surprising ways. Read other articles in the series.
Exposure to light is crucial for our physical and mental health, as this and future articles in the series will show.
But the timing of that light exposure is also crucial. This tells our body to wake up in the morning, when to poo and the time of day to best focus or be alert. When we’re exposed to light also controls our body temperature, blood pressure and even chemical reactions in our body.
But how does our body know when it’s time to do all this? And what’s light got to do with it?
nymphoenix/Shutterstock What is the body clock, actually?
One of the key roles of light is to re-set our body clock, also known as the circadian clock. This works like an internal oscillator, similar to an actual clock, ticking away as you read this article.
But rather than ticking you can hear, the body clock is a network of genes and proteins that regulate each other. This network sends signals to organs via hormones and the nervous system. These complex loops of interactions and communications have a rhythm of about 24 hours.
In fact, we don’t have one clock, we have trillions of body clocks throughout the body. The central clock is in the hypothalamus region of the brain, and each cell in every organ has its own. These clocks work in concert to help us adapt to the daily cycle of light and dark, aligning our body’s functions with the time of day.
However, our body clock is not precise and works to a rhythm of about 24 hours (24 hours 30 minutes on average). So every morning, the central clock needs to be reset, signalling the start of a new day. This is why light is so important.
The central clock is directly connected to light-sensing cells in our retinas (the back of the eye). This daily re-setting of the body clock with morning light is essential for ensuring our body works well, in sync with our environment.
In parallel, when we eat food also plays a role in re-setting the body clock, but this time the clock in organs other than the brain, such as the liver, kidneys or the gut.
So it’s easy to see how our daily routines are closely linked with our body clocks. And in turn, our body clocks shape how our body works at set times of the day.
What time of day?
Matt Garrow/The Conversation. Adapted from Delos, CC BY Let’s take a closer look at sleep
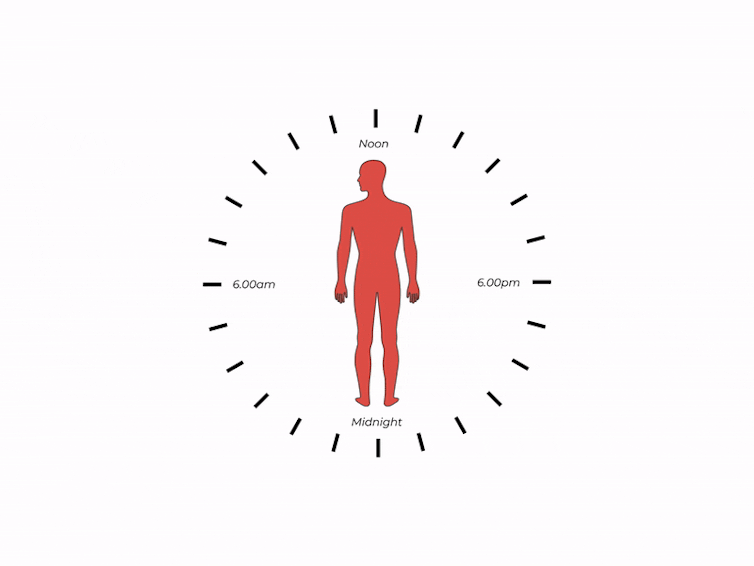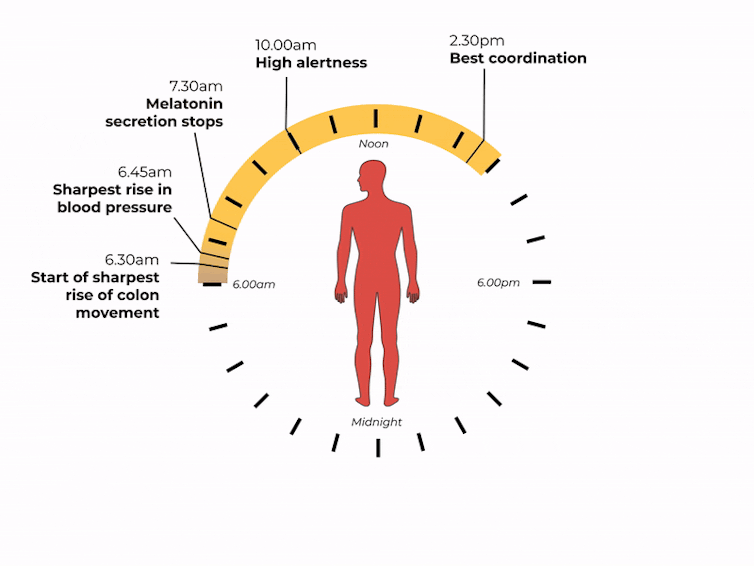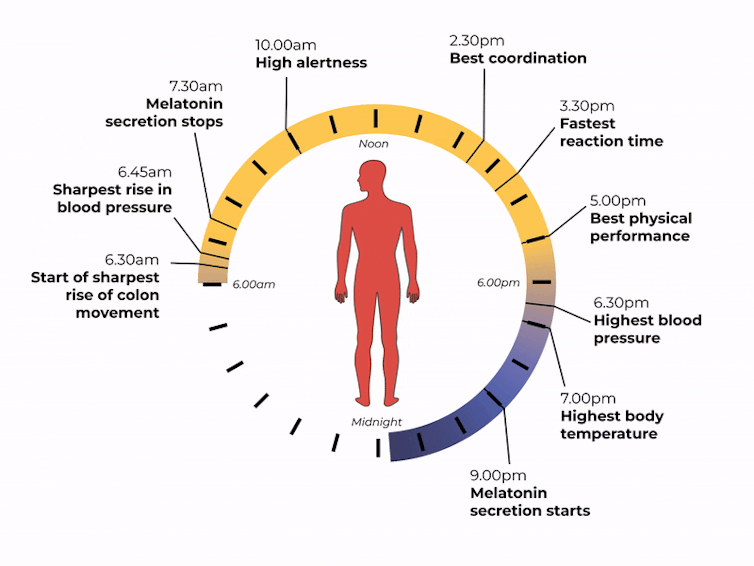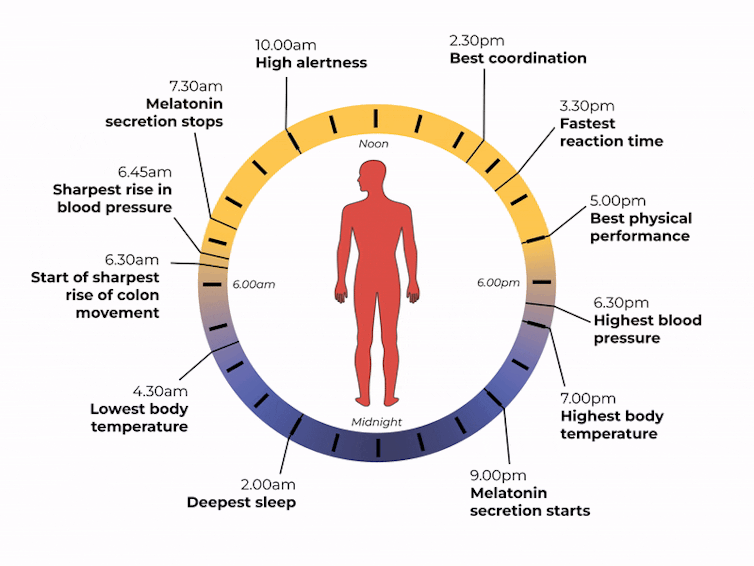
The naturally occurring brain hormone melatonin is linked to our central clock and makes us feel sleepy at certain times of day. When it’s light, our body stops making melatonin (its production is inhibited) and we are alert. Closer to bedtime, the hormone is made, then secreted, making us feel drowsy.
Our sleep is also partly controlled by our genes, which are part of our central clock. These genes influence our chronotype – whether we are a “lark” (early riser), “night owl” (late sleeper) or a “dove” (somewhere in between).
But exposure to light at night when we are supposed to be sleeping can have harmful effects. Even dim light from light pollution can impair our heart rate and how we metabolise sugar (glucose), may lead to psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety and bipolar disorder, and increases the overall risk of premature death.
The main reason for these harmful effects is that light “at the wrong time” disturbs the body clock, and these effects are more pronounced for “night owls”.
This “misaligned” exposure to light is also connected to the detrimental health effects we often see in people who work night shifts, such as an increased risk of cancer, diabetes and heart disease.
How about the gut?
Digestion also follows a circadian rhythm. Muscles in the colon that help move waste are more active during the day and slow down at night.
The most significant increase in colon movement starts at 6.30am. This is one of the reasons why most people feel the urge to poo in the early morning rather than at night.
The gut’s day-night rhythm is a direct result of the action of the gut’s own clock and the central clock (which synchronises the gut with the rest of the body). It’s also influenced by when we eat.
At 6.30am, your gut really begins to get going for the day. Rendra Dria Septia Aji/Shutterstock How about focusing?
Our body clock also helps control our attention and alertness levels by changing how our brain functions at certain times of day. Attention and alertness levels improve in the afternoon and evening but dip during the night and early morning.
Those fluctuations impact performance and can lead to decreased productivity and an increased risk of errors and accidents during the less-alert hours.
So it’s important to perform certain tasks that require our attention at certain times of day. That includes driving. In fact, disruption of the circadian clock at the start of daylight savings – when our body hasn’t had a chance to adapt to the clocks changing – increases the risk of a car accident, particularly in the morning.
What else does our body clock control?
Our body clock influences many other aspects of our biology, including:
- physical performance by controlling the activity of our muscles
- blood pressure by controlling the system of hormones involved in regulating our blood volume and blood vessels
- body temperature by controlling our metabolism and our level of physical activity
- how our body handles drugs and toxins by controlling enzymes involved in how the liver and kidneys eliminate these substances from the body.
If you can, avoid driving long distances at night, as you’ll be less alert. trendobjects/Shutterstock Morning light is important
But what does this all mean for us? Exposure to light, especially in the morning, is crucial for synchronising our circadian clock and bodily functions.
As well as setting us up for a good night’s sleep, increased morning light exposure benefits our mental health and reduces the risk of obesity. So boosting our exposure to morning light – for example, by going for a walk, or having breakfast outside – can directly benefit our mental and metabolic health.
However, there are other aspects about which we have less control, including the genes that control our body clock.
Frederic Gachon, Associate Professor, Physiology of Circadian Rhythms, Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland and Benjamin Weger, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: