Frozen/Thawed/Refrozen Meat: How Much Is Safety, And How Much Is Taste?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What You Can (And Can’t) Safely Do With Frozen Meat
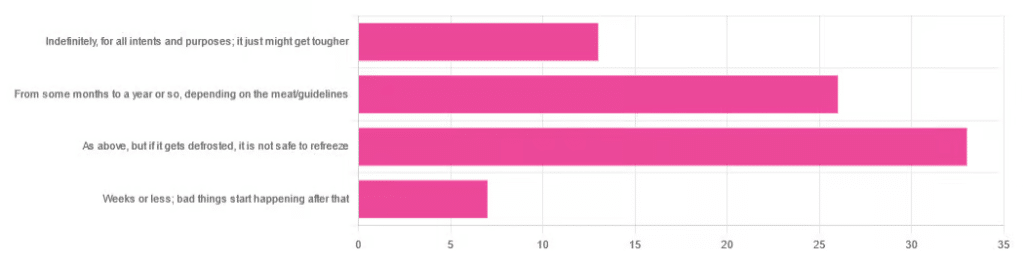
Yesterday, we asked you:
❝You have meat in the freezer. How long is it really safe to keep it?❞
…and got a range of answers, mostly indicating to a) follow the instructions (a very safe general policy) and b) do not refreeze if thawed because that would be unsafe. Fewer respondents indicated that meat could be kept for much longer than guidelines say, or conversely, that it should only be kept for weeks or less.
So, what does the science say?
Meat can be kept indefinitely (for all intents and purposes) in a freezer; it just might get tougher: True or False?
False, assuming we are talking about a normal household electrical freezer that bottoms out at about -18℃ / 0℉.
Fun fact: cryobiologists cryopreserve tissue samples (so basically, meat) at -196℃ / -320℉, and down at those temperatures, the tissues will last a lot longer than you will (and, for all practical purposes: indefinitely). There are other complications with doing so (such as getting the sample through the glass transition point without cracking it during the vitrification process) but those are beyond the scope of this article.
If you remember back to your physics or perhaps chemistry classes at school, you’ll know that molecules move more quickly at higher temperatures, and more slowly at lower ones, only approaching true stillness as they near absolute zero (-273℃ / -459℉ / 0K ← we’re not saying it’s ok, although it is; rather, that is zero kelvin; no degree sign is used with kelvins)
That means that when food is frozen, the internal processes aren’t truly paused; it’s just slowed to a point of near imperceptibility.
So, all the way up at the relatively warm temperatures of a household freezer, a lot of processes are still going on.
What this means in practical terms: those guidelines saying “keep in the freezer for up to 4 months”, “keep in the freezer for up to 9 months”, “keep in the freezer for up to 12 months” etc are being honest with you.
More or less, anyway! They’ll usually underestimate a little to be on the safe side—but so should you.
Bad things start happening within weeks at most: True or False?
False, for all practical purposes. Again, assuming a normal and properly-working household freezer as described above.
(True, technically but misleadingly: the bad things never stopped; they just slowed down to a near imperceptible pace—again, as described above)
By “bad” here we should clarify we mean “dangerous”. One subscriber wrote:
❝Meat starts losing color and flavor after being in the freezer for too long. I keep meat in the freezer for about 2 months at the most❞
…and as a matter of taste, that’s fair enough!
It is unsafe to refreeze meat that has been thawed: True or False?
False! Assuming it has otherwise been kept chilled, just the same as for fresh meat.
Food poisoning comes from bacteria, and there is nothing about the meat previously having been frozen that will make it now have more bacteria.
That means, for example…
- if it was thawed (but chilled) for a period of time, treat it like you would any other meat that has been chilled for that period of time (so probably: use it or freeze it, unless it’s been more than a few days)
- if it was thawed (and at room temperature) for a period of time, treat it like you would any other meat that has been at room temperature for that period of time (so probably: throw it out, unless the period of time is very small indeed)
The USDA gives for 2 hours max at room temperature before considering it unsalvageable, by the way.
However! Whenever you freeze meat (or almost anything with cells, really), ice crystals will form in and between cells. How much ice crystallization occurs depends on several variables, with how much water there is present in the food is usually the biggest factor (remember that animal cells are—just like us—mostly water).
Those ice crystals will damage the cell walls, causing the food to lose structural integrity. When you thaw it out, the ice crystals will disappear but the damage will be left behind (this is what “freezer burn” is).
So if your food seems a little “squishy” after having been frozen and thawed, that’s why. It’s not rotten; it’s just been stabbed countless times on a microscopic level.
The more times you freeze and thaw and refreeze food, the more this will happen. Your food will degrade in structural integrity each time, but the safety of it won’t have changed meaningfully.
Want to know more?
Further reading:
You can thaw and refreeze meat: five food safety myths busted
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Much Does A Vegan Diet Affect Biological Aging?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Slow Your Aging, One Meal At A Time
This one’s a straightforward one today, and the ““life hack” can be summed up:
Enjoy a vegan diet to enjoy younger biological age.
First, what is biological age?
Biological age is not one number, but a collection of numbers, as per different biomarkers of aging, including:
- Visual markers of aging (e.g. wrinkles, graying hair)
- Performative markers of aging (e.g. mobility tests)
- Internal functional markers of aging (e.g. tests for cognitive decline, eyesight, hearing, etc)
- Cellular markers of aging (e.g. telomere length)
We wrote more about this here:
Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
A vegan diet may well impact multiple of those categories of aging, but today we’re highlighting a study (hot off the press; published only a few days ago!) that looks at its effect on that last category: cellular markers of aging.
There’s an interesting paradox here, because this category is:
- the most easily ignorable; because we all feel it if our knees are giving out or our skin is losing elasticity, but who notices if telomeres’ T/S ratio changed by 0.0407? ← the researchers, that’s who, as this difference is very significant
- the most far-reaching in its impact, because cellular aging in turn has an effect on all the other markers of aging
Second, how much difference does it make, and how do we know?
The study was an eight-week interventional identical twin study. This means several things, to start with:
- Eight weeks is a rather short period of time to accumulate cellular aging, let alone for an intervention to accumulate a significant difference in cellular aging—but it did. So, just imagine what difference it might make in a year or ten!
- Doing an interventional study with identical twin pairs already controlled for a lot of factors, that are usually confounding variables in population / cohort / longitudinal / observational studies.
Factors that weren’t controlled for by default by using identical twins, were controlled for in the experiment design. For example, twin pairs were rejected if one or more twin in a given pair already had medical conditions that could affect the outcome:
❝Inclusion criteria involved participants aged ≥18, part of a willing twin pair, with BMI <40, and LDL-C <190 mg/dL. Exclusions included uncontrolled hypertension, metabolic disease, diabetes, cancer, heart/renal/liver disease, pregnancy, lactation, and medication use affecting body weight or energy.
Eligibility was determined via online screening, followed by an orientation meeting and in-person clinic visit. Randomization occurred only after completing baseline visits, dietary recalls, and questionnaires for both twins❞
~ Dr. Varun Dwaraka et al. ← there’s a lot of “et al.” to this one; the paper had 16 collaborating authors!
As to the difference it made over the course of the 8 weeks…
❝Various measures of epigenetic age acceleration (PC GrimAge, PC PhenoAge, DunedinPACE) were assessed, along with system-specific effects (Inflammation, Heart, Hormone, Liver, and Metabolic).
Distinct responses were observed, with the vegan cohort exhibiting significant decreases in overall epigenetic age acceleration, aligning with anti-aging effects of plant-based diets. Diet-specific shifts were noted in the analysis of methylation surrogates, demonstrating the influence of diet on complex trait prediction through DNA methylation markers.❞
~ Ibid.
You can read the whole paper here (it goes into a lot more detail than we have room to here, and also gives infographics, charts, numbers, the works):
Were they just eating more healthily, though?
Well, arguably yes, as the results show, but to be clear:
The omnivorous diet compared to the vegan diet in this study was also controlled; both groups were given a healthy meal plan for their respective diet. So this wasn’t a case of “any omnivorous diet vs healthy vegan diet”, but rather “healthy omnivorous diet vs healthy vegan diet”.
Again, the paper itself has the full details—a short version is that it involved a healthy meal kit delivery service, followed by ongoing dietician involvement in an equal and carefully-controlled fashion.
So, aside from that one group had an omnivorous meal plan and the other vegan, both groups received the same level of “healthy eating” support, guidance, and oversight.
But isn’t [insert your preferred animal product here] healthy?
Quite possibly! For general health, general scientific consensus is that eating at least mostly plants is best, red meat is bad, poultry is neutral in moderation, fish is good in moderation, dairy is good in moderation if fermented, eggs are good in moderation if not fried.
This study looked at the various biomarkers of aging that we listed, and not every possible aspect of health—there’s more science yet to be done, and the researchers themselves are calling for it.
It also bears mentioning that for some (relatively few, but not insignificantly few) people, extant health conditions may make a vegan diet unhealthy or otherwise untenable. Do speak with your own doctor and/or dietician if unsure.
See also: Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy?
We would hypothesize, by the way, that the anti-aging benefits of a vegan diet are probably proportional to abstention from animal products—meaning that even if you simply have some “vegan days”, while still consuming animal products other days, you’ll still get benefit for the days you abstained. That’s just our hypothesis though.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Physical Exercises That Build Your Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Jim Kwik: from broken brain to brain coach
Image from Kwik Learning This is Jim Kwik. He suffered a traumatic brain injury as a small child, and later taught himself to read and write by reading comic books. He became fascinated with the process of learning, and in his late 20s he set up Kwik Learning, to teach accelerated learning in classrooms and companies, which he continued until 2009 when he launched his online learning platform. His courses have now been enjoyed by people in 195 countries.
So, since accelerated learning is his thing, you might wonder…
What does he have to share that we can benefit from in the next five minutes?
Three brain exercises to improve memory and concentration
A lot of problems we have with working memory are a case of executive dysfunction, but there are tricks we can use to get our brains into gear and make them cumulatively stronger:
First exercise
You can strengthen your corpus callosum (the little bridge between the two hemispheres of the brain) by performing a simple kinesiological exercise, such as alternating touching your left elbow to your right knee, and touching your right elbow to your left knee.
Do it for about a minute, but the goal here is not a cardio exercise, it’s accuracy!
You want to touch your elbow and opposite knee to each other as precisely as possible each time. Not missing slightly off to the side, not falling slightly short, not hitting it too hard.
Second exercise
Put your hands out in front of you, as though you’re about to type at a keyboard. Now, turn your hands palm-upwards. Now back to where they were. Now palm-upwards again. Got it? Good.
That’s not the exercise, the exercise is:
You’re now going to do the same thing, but do it twice as quickly with one hand than the other. So they’ll still be flipping to the same basic “beat”, put it in musical terms, the tempo on one hand will now be twice that of the other. When you get the hang of that, switch hands and do the other side.
This is again about the corpus callosum, but it’s now adding an extra level of challenge because of holding the two rhythms separately, which is also working the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex.
The pre-frontal cortex in particular is incredibly important to executive function, self-discipline, and being able to “do” delayed gratification. So this exercise is really important!
Third exercise
This one works the same features of the brain, but most people find it harder. So, consider it a level-up on the previous:
Imagine there’s a bicycle wheel in front of you (as though the bike is facing you at chest-height). Turn the wheel towards you with your hands, one on each side.
Now, do the same thing, but each of your hands is going in the opposite direction. So one is turning the wheel towards you; the other is turning it away from you.
Now, do the same thing, but one hand goes twice as quickly as the other.
Switch sides.
Why is this harder for most people than the previous? Because the previous involved processing discrete (distinct from each other) movements while this one involves analog continuous movements.
It’s like reading an analog clock vs a digital clock, but while using both halves of your brain, your corpus callosum, your pre-frontal cortex, and the motor cortex too.
Want to learn more?
You might enjoy his book, which as well as offering exercises like the above, also offers a lot about learning strategies, memory processes, and generally building a quicker more efficient brain:
Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life
Share This Post
-
All About Olive Oil
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Skip the video & tell more about olive oil please.❞
We love requests!
We can’t really do anti-requests (e.g. “skip the video”) because for every one person who doesn’t care for one particular element of the newsletter, there will be thousands who do—and indeed, the video segment is a popular one, so it will certainly remain.
However! Let us reassure you that you personally are not obliged to watch the video if you don’t want to 🙂 In fact, our general hope with 10almonds is that there will be at least one feature that is of value to each reader, each day.
Writer’s note: I’m a very bookish person, and in honesty do not love videos personally either. You know what I do love though? Olive oil. So let’s get onto that 😎
Why olive oil?
Let’s quickly address the taste/culinary side of things first, and then spend more time on the health aspects. Olive oil’s strong punchy flavor (as oils go, anyway) makes it a big winner with those of us who love strong punchy flavors. However, it does mean that it can overwhelm some more delicate dishes if one isn’t careful, meaning that it’s not perfect for everything all the time.
Healthwise, olive oil is one of the healthiest oils around, along with avocado oil. In fact, we compared them previously:
Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
…and it’s worth noting that their (excellent) lipids profiles are very similar, meaning that the main factor between them is that olive oil usually retains vitamins that avocado oil doesn’t.
Meanwhile, another popular contender for “healthy oil” is coconut oil, but this doesn’t have nearly as unambiguously good a lipids profile, because of coconut oil’s high saturated fat content—though lauric acid can have a cardioprotective effect, so the jury is out on that one:
Olive Oil vs Coconut Oil – Which is Healthier?
Interestingly, this article from The Conversation considered seed oils (canola, sunflower, sesame) to be next-best options:
I can’t afford olive oil. What else can I use?
…but it’s worth noting that the way those seed oils are made varies a lot from country to country, and can affect their health impact considerably.
It’s not just about the fats
Olives, especially green olives with their stronger more pungent flavor, are rich in assorted polyphenols that have many health-giving properties:
Black Olives vs Green Olives – Which is Healthier
…and olive oil is almost always made from green olives. Note that while we picked black olives in the above comparison, that’s mainly because green olives are “cured” for longer and thus are much higher in sodium… Which, guess what, isn’t in olive oil, so with olive oil we can enjoy all of the polyphenols with almost none of the sodium!
Let’s talk virginity
When it comes to olive oil, definitely not everything labelled as olive oil in the supermarket is of the same quality. Mostly, however, it’s not whether it’s “extra virgin” (i.e. the oil from the first mechanical pressing) or not that actually makes the biggest health difference, so much as that olive oils are often adulterated with other cheaper oils, so it’s important to check labels for that, even when they say “extra virgin”, in case it’s something like:
a blend of
EXTRA VIRGIN OLIVE OIL
and other oilsWe talk about this, and the various different levels of quality of olive oil and how you can tell them apart for yourself in the supermarket (and be wise to the ways they may try to trick you), here:
What to enjoy it with?
Olive oil is the single largest source of fat in the Mediterranean diet, and by that we mean not just “food that is eaten in the Mediterranean”, but rather, the well-defined dietary approach that has for a long time now been considered “the gold standard” of what a healthy diet looks like, scientifically. You can read more about what is and isn’t included in the definition, here:
Mediterranean Diet: What Is It Good For? ← what isn’t it good for!
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Seven Circles – by Chelsey Luger & Thosh Collins
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
At first glance, this can seem like an unscientific book—you won’t find links to studies in this one, for sure! However, if we take a look at the seven circles in question, they are:
- Food
- Movement
- Sleep
- Ceremony
- Sacred Space
- Land
- Community
Regular 10almonds readers may notice that these seven items contain five of the things strongly associated with the “supercentenarian Blue Zones”. (If you are wondering why Native American reservations are not Blue Zones, the answer there lies less in health science and more in history and sociology, and what things have been done to a given people).
The authors—who are Native American, yes—present in one place a wealth of knowledge and know-how. Not even just from their own knowledge and their own respective tribes, but gathered from other tribes too.
Perhaps the strongest value of this book to the reader is in the explanation of noting the size of each of those circles, how they connect with each other, and providing a whole well-explained system for how we can grow each of them in harmony with each other.
Or to say the same thing in sciencey terms: how to mindfully improve integrated lifestyle factors synergistically for greater efficacy and improved health-adjusted quality-of-life years.
Bottom line: if you’re not averse to something that mostly doesn’t use sciencey terms of have citations to peer-reviewed studies peppered through the text, then this book has wisdom that’s a) older than the pyramids of Giza, yet also b) highly consistent with our current best science of Blue Zone healthy longevity.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Physical Exercises That Build Your Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Jim Kwik: from broken brain to brain coach
Image from Kwik Learning This is Jim Kwik. He suffered a traumatic brain injury as a small child, and later taught himself to read and write by reading comic books. He became fascinated with the process of learning, and in his late 20s he set up Kwik Learning, to teach accelerated learning in classrooms and companies, which he continued until 2009 when he launched his online learning platform. His courses have now been enjoyed by people in 195 countries.
So, since accelerated learning is his thing, you might wonder…
What does he have to share that we can benefit from in the next five minutes?
Three brain exercises to improve memory and concentration
A lot of problems we have with working memory are a case of executive dysfunction, but there are tricks we can use to get our brains into gear and make them cumulatively stronger:
First exercise
You can strengthen your corpus callosum (the little bridge between the two hemispheres of the brain) by performing a simple kinesiological exercise, such as alternating touching your left elbow to your right knee, and touching your right elbow to your left knee.
Do it for about a minute, but the goal here is not a cardio exercise, it’s accuracy!
You want to touch your elbow and opposite knee to each other as precisely as possible each time. Not missing slightly off to the side, not falling slightly short, not hitting it too hard.
Second exercise
Put your hands out in front of you, as though you’re about to type at a keyboard. Now, turn your hands palm-upwards. Now back to where they were. Now palm-upwards again. Got it? Good.
That’s not the exercise, the exercise is:
You’re now going to do the same thing, but do it twice as quickly with one hand than the other. So they’ll still be flipping to the same basic “beat”, put it in musical terms, the tempo on one hand will now be twice that of the other. When you get the hang of that, switch hands and do the other side.
This is again about the corpus callosum, but it’s now adding an extra level of challenge because of holding the two rhythms separately, which is also working the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex.
The pre-frontal cortex in particular is incredibly important to executive function, self-discipline, and being able to “do” delayed gratification. So this exercise is really important!
Third exercise
This one works the same features of the brain, but most people find it harder. So, consider it a level-up on the previous:
Imagine there’s a bicycle wheel in front of you (as though the bike is facing you at chest-height). Turn the wheel towards you with your hands, one on each side.
Now, do the same thing, but each of your hands is going in the opposite direction. So one is turning the wheel towards you; the other is turning it away from you.
Now, do the same thing, but one hand goes twice as quickly as the other.
Switch sides.
Why is this harder for most people than the previous? Because the previous involved processing discrete (distinct from each other) movements while this one involves analog continuous movements.
It’s like reading an analog clock vs a digital clock, but while using both halves of your brain, your corpus callosum, your pre-frontal cortex, and the motor cortex too.
Want to learn more?
You might enjoy his book, which as well as offering exercises like the above, also offers a lot about learning strategies, memory processes, and generally building a quicker more efficient brain:
Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is chocolate milk a good recovery drink after a workout? A dietitian reviews the evidence
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Whether you enjoy chocolate milk regularly, as a weekend treat, or as an occasional dose of childhood nostalgia, it probably wouldn’t be the first option you think of for post-workout recovery.
Unless you’re on TikTok, perhaps. According to many people on the social media platform, chocolate milk is not only delicious, but it offers benefits comparable to sports drinks after a workout.
So is there any evidence to support this? Let’s take a look.
eldar nurkovic/Shutterstock Rehydrating after a workout is important
Water accounts for somewhere between 50% and 60% of our body weight. Water has many important functions in the body, including helping to keep our body at the right temperature through sweating.
We lose water naturally from our bodies when we sweat, as well as through our breathing and when we go to the toilet. So it’s important to stay hydrated to replenish the water we lose.
When we don’t, we become dehydrated, which can put a strain on our bodies. Signs and symptoms of dehydration can range from thirst and dizziness to low blood pressure and confusion.
Athletes, because of their higher levels of exertion, lose more water through sweating and from respiration (when their breathing rate gets faster). If they’re training or competing in hot or humid environments they will sweat even more.
Dehydration impacts athletes’ performance and like for all of us, can affect their health.
So finding ways to ensure athletes rehydrate quickly during and after they train or compete is important. Fortunately, sports scientists and dietitians have done research looking at the composition of different fluids to understand which ones rehydrate athletes most effectively.
The beverage hydration index
The best hydrating drinks are those the body retains the most of once they’ve been consumed. By doing studies where they give people different drinks in standardised conditions, scientists have been able to determine how various options stack up.
To this end, they’ve developed something called the beverage hydration index, which measures to what degree different fluids hydrate a person compared to still water.
According to this index beverages with similar fluid retention to still water include sparkling water, sports drinks, cola, diet cola, tea, coffee, and beer below 4% alcohol. That said, alcohol is probably best avoided when recovering from exercise.
Beverages with superior fluid retention to still water include milk (both full-fat and skim), soy milk, orange juice and oral rehydration solutions.
This body of research indicates that when it comes to rehydration after exercise, unflavoured milk (full fat, skim or soy) is better than sports drinks.
But what about chocolate milk?
A small study looked at the effects of chocolate milk compared to plain milk on rehydration and exercise performance in futsal players (futsal is similar to soccer but played on a court indoors). The researchers found no difference in rehydration between the two. There’s no other published research to my knowledge looking at how chocolate milk compares to regular milk for rehydration during or after exercise.
But rehydration isn’t the only thing athletes look for in sports drinks. In the same study, drinking chocolate milk after play (referred to as the recovery period) increased the time it took for the futsal players to become exhausted in further exercise (a shuttle run test) four hours later.
This was also shown in a review of several clinical trials. The analysis found that, compared to different placebos (such as water) or other drinks containing fat, protein and carbohydrates, chocolate milk lengthened the time to exhaustion during exercise.
What’s in chocolate milk?
Milk contains protein, carbohydrates and electrolytes, each of which can affect hydration, performance, or both.
Protein is important for building muscle, which is beneficial for performance. The electrolytes in milk (including sodium and potassium) help to replace electrolytes lost through sweating, so can also be good for performance, and aid hydration.
Compared to regular milk, chocolate milk contains added sugar. This provides extra carbohydrates, which are likewise beneficial for performance. Carbohydrates provide an immediate source of energy for athletes’ working muscles, where they’re stored as glycogen. This might contribute to the edge chocolate milk appears to have over plain milk in terms of athletic endurance.
The added sugar in chocolate milk provides extra carbohydrates. Brent Hofacker/Shutterstock Coffee-flavoured milk has an additional advantage. It contains caffeine, which can improve athletic performance by reducing the perceived effort that goes into exercise.
One study showed that a frappe-type drink prepared with filtered coffee, skim milk and sugar led to better muscle glycogen levels after exercise compared to plain milk with an equivalent amount of sugar added.
So what’s the verdict?
Evidence shows chocolate milk can rehydrate better than water or sports drinks after exercise. But there isn’t evidence to suggest it can rehydrate better than plain milk. Chocolate milk does appear to improve athletic endurance compared to plain milk though.
Ultimately, the best drink for athletes to consume to rehydrate is the one they’re most likely to drink.
While many TikTok trends are not based on evidence, it seems chocolate milk could actually be a good option for recovery from exercise. And it will be cheaper than specialised sports nutrition products. You can buy different brands from the supermarket or make your own at home with a drinking chocolate powder.
This doesn’t mean everyone should look to chocolate milk when they’re feeling thirsty. Chocolate milk does have more calories than plain milk and many other drinks because of the added sugar. For most of us, chocolate milk may be best enjoyed as an occasional treat.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: