52 Weeks to Better Mental Health – by Dr. Tina Tessina
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about the health benefits of journaling, but how to get started, and how to make it a habit, and what even to write about?
Dr. Tessina presents a year’s worth of journaling prompts with explanations and exercises, and no, they’re not your standard CBT flowchart things, either. Rather, they not only prompt genuine introspection, but also are crafted to be consistently uplifting—yes, even if you are usually the most disinclined to such positivity, and approach such exercises with cynicism.
There’s an element of guidance beyond that, too, and as such, this book is as much a therapist-in-a-book as you might find. Of course, no book can ever replace a competent and compatible therapist, but then, competent and compatible therapists are often harder to find and can’t usually be ordered for a few dollars with next-day shipping.
Bottom line: if undertaken with seriousness, this book will be an excellent investment in your mental health and general wellbeing.
Click here to check out 52 Weeks to Better Mental Health, and get on the best path for you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eyes for Alzheimer’s Diagnosis: New?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Time!
This is the bit whereby each week, we respond to subscriber questions/requests/etc
Have something you’d like to ask us, or ask us to look into? Hit reply to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom, and a Real Human™ will be glad to read it!
Q: As I am a retired nurse, I am always interested in new medical technology and new ways of diagnosing. I have recently heard of using the eyes to diagnose Alzheimer’s. When I did some research I didn’t find too much. I am thinking the information may be too new or I wasn’t on the right sites.
(this is in response to last week’s piece on lutein, eyes, and brain health)
We’d readily bet that the diagnostic criteria has to do with recording low levels of lutein in the eye (discernible by a visual examination of macular pigment optical density), and relying on the correlation between this and incidence of Alzheimer’s, but we’ve not seen it as a hard diagnostic tool as yet either—we’ll do some digging and let you know what we find! In the meantime, we note that the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease (which may be of interest to you, if you’re not already subscribed) is onto this:
See also:
- Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease (mixture of free and paid content)
- Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports (open access—all content is free)
Share This Post
-
Older people’s risk of abuse is rising. Can an ad campaign protect them?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Elder abuse is an emerging public health and safety issue for communities of high-income countries.
The most recent data from Australia’s National Elder Abuse Prevalence Study, which surveyed 7,000 older people living in the community, found one in six self-reported being a victim of some form of abuse. But this did not include older people living in residential aged care or those with cognitive impairment, such as dementia – so is likely an underestimate.
This week the Australian government announced a multi-million dollar advertising campaign it hopes will address this serious and abhorrent abuse.
But is investing in community awareness of elder abuse the best use of scarce resources?
Nuttapong punna/Shutterstock What is elder abuse?
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines elder abuse as
[…] a single, or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust which causes harm or distress to an older person.
Australia usually defines older people as those over 65. The exact age varies between countries depending on the overall health status of a nation and its vulnerable population groups. The WHO definitions of an older adult for sub-Saharan Africa, for example, is over 50. And there are communities with poorer health status and shorter lifespans within country borders, including our First Nations people.
Elder abuse can take on many different forms including physical, sexual, psychological, emotional, or financial abuse and neglect.
Living longer and wealthier
The number of older people in our society is greater than it has ever been. Around 17% Australians are aged 65 and over. By 2071, older Australians will make up between 25% and 27% of the total population.
People are living longer, accumulating substantial wealth and are vulnerable to abuse due to cognitive, physical or functional limitations.
Longer lifespans increase the time of possible exposure to abuse. Australian men aged 65 can expect to live another 20.2 years, while women aged 65 are likely to live another 22.8 years. (Life expectancy for First Nations men and women remains significantly shorter.)
Australian men are now 143 times more likely to reach the age of 100 than they were in 1901. Women are 82 times more likely.
Older people hold a large proportion of our nation’s wealth, making them vulnerable to financial abuse. Recent research by the Australian Council of Social Service and UNSW Sydney reveals older households (with people over 65) are 25% wealthier than the average middle-aged household and almost four times as wealthy as the average under-35 household.
Finally, older people have higher levels of impairment in their thinking, reasoning and physical function. Cognitive impairment, especially dementia, increases from one in 67 Australians under 60 to almost one in two people aged over 90.
Over half of Australians aged 65 years and over have disability. A particularly vulnerable group are the 258,374 older Australians who receive government-funded home care.
Who perpetrates elder abuse?
Sadly, most of the perpetrators of elder abuse are known to their victims. They are usually a member of the family, such as a life partner, child or grandchild.
Elder abuse causes significant illness and even early death. Financial abuse (across all ages) costs the community billions of dollars. Specific data for financial elder abuse is limited but indicates massive costs to individual survivors and the community.
Despite this, the level of awareness of elder abuse is likely to be much lower than for family violence or child abuse. This is partly due to the comparatively recent concept of elder abuse, with global awareness campaigns only developed over the past two decades.
Is an advertising campaign the answer?
The federal government has allocated A$4.8 million to an advertising campaign on television, online and in health-care clinics to reach the broader community. For context, last year the government spent $131.4 million on all media campaigns, including $32.6 million on the COVID vaccination program, $2 million on Japanese encephalitis and $3.2 million on hearing health awareness.
The campaign will likely benefit a small number of people who may be victims and have the capacity to report their perpetrators to authorities. It will generate some heartbreaking anecdotes. But it is unlikely to achieve broad community or systemic change.
There is little research evidence to show media campaigns alter the behaviour of perpetrators of elder abuse. And suggesting the campaign raises awareness of the issue for older people who are survivors of abuse sounds more like blaming victims than empowering them.
We don’t know how the government will judge the success of the campaign, so taxpayers won’t know whether a reasonable return on this investment was achieved. There may also be opportunity costs associated with the initiative – that is, lost opportunities for other actions and strategies. It could be more effective and efficient to target high-risk subgroups or to allocate funding to policy, practice reform or research that has direct tangible benefits for survivors. https://www.youtube.com/embed/DeK2kaqplTI?wmode=transparent&start=0 The Australian Human Rights Commission’s campaign from last year.
But the campaign can’t hurt, right?
Actually, the dangers that could come with an advertising campaign are two-fold.
First it may well oversimplify a highly complex issue. Identifying and managing elder abuse requires an understanding of the person’s vulnerabilities, their decision-making capacity and ability to consent, the will and preferences of victim and the role of perpetrator in the older person’s life. Abuse happens in the context of family and social networks. And reporting abuse can have consequences for the victim’s quality of life and care.
Consider the complexities of a case where an older person declines to have her grandson reported to police for stealing her money and medication because of her fear of becoming socially isolated. She might even feel responsible for the behaviour having raised the grandson and not want him to have a criminal record.
Secondly, a public campaign can create the illusion government and our institutions have the matter “in hand”. This might slow the opportunity for real change.
Ideally, the campaign will strengthen the argument for better policies, reporting procedures, policing, prosecution and judgements that are aligned. But these ends will also need investment in more research to build better communities that take good care of older people.
Joseph Ibrahim, Professor, Aged Care Medical Research Australian Centre for Evidence Based Aged Care, La Trobe University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
What you need to know about FLiRT, an emerging group of COVID-19 variants
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- COVID-19 wastewater levels are currently low, but a recent group of variants called FLiRT is making headlines.
- KP.2 is one of several FLiRT variants, and early lab tests suggest that it’s more infectious than JN.1.
- Getting infected with any COVID-19 variant can cause severe illness, heart problems, and death.
KP.2, a new COVID-19 variant, is now dominant in the United States. Lab tests suggest that it may be more infectious than JN.1, the variant that was dominant earlier this year.
Fortunately, there’s good news: Current wastewater data shows that COVID-19 infection rates are low. Still, experts are closely watching KP.2 to see if it will lead to an uptick in infections.
Read on to learn more about KP.2 and how to stay informed about COVID-19 cases in your area.
Where can I find data on COVID-19 cases in my area?
Hospitals are no longer required to report COVID-19 hospital admissions or hospital capacity to the Department of Health and Human Services. However, wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) estimates the number of COVID-19 infections in a community based on the amount of COVID-19 viral particles detected in local wastewater.
View this map of wastewater data from the CDC to visualize COVID-19 infection rates throughout the U.S., or look up COVID-19 wastewater trends in your state.
What do we know so far about the new variant?
Early lab tests suggest that KP.2—one of a group of emerging variants called FLiRT—is similar to the previously dominant variant, JN.1, but it may be more infectious. If you had JN.1, you may still get reinfected with KP.2, especially if it’s been several months or longer since your last COVID-19 infection.
A CDC spokesperson said they have no reason to believe that KP.2 causes more severe illness than other variants. Experts are closely watching KP.2 to see if it will lead to an uptick in COVID-19 cases.
How can I protect myself from COVID-19 variants?
Staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines reduces your risk of severe illness, long COVID, heart problems, and death. The CDC recommends that people 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring.
Wearing a high-quality, well-fitting mask reduces your risk of contracting COVID-19 and spreading it to others. At indoor gatherings, improving ventilation by opening doors and windows, using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, and building your own Corsi-Rosenthal box can also reduce the spread of COVID-19.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Outlive – by Dr. Peter Attia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We know, we know; this diet, that exercise, don’t smoke or drink, get decent sleep”—a lot of books don’t go beyond this level of advice!
What Dr. Attia offers is a multi-vector approach that covers the above and a lot more.
Themes of the book include:
- The above-mentioned things, of course
- Rethinking medicine for the age of chronic disease
- The pros and cons of…
- caloric restriction
- dietary restriction
- intermittent fasting
- Pre-emptive interventions for…
- specific common cause-of-death conditions
- specific common age-related degenerative conditions
- The oft-forgotten extra pillar of longevity: mental health
The last one in the list there is covered mostly in the last chapter of the book, but it’s there as a matter of importance, not as an afterthought. As Dr. Attia puts it, not only are you less likely to take care of your physical health if you are (for example) depressed, but also… “Longevity is meaningless if your life sucks!”
So, it’s important to do things that promote and maintain good physical and mental health.
Bottom line: if you’re interested in happy, healthy, longevity, this is a book for you.
Click here to check out Dr. Attia’s “Outlive” on Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Resveratrol & Healthy Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Resveratrol & Healthy Aging
Resveratrol is the compound found in red grapes, and thus in red wine, that have resulted in red wine being sometimes touted as a heart-healthy drink.
However, at the levels contained in red wine, you’d need to drink 100–1000 glasses of wine per day (depending on the wine) to get the dose of resveratrol that was associated with heart health benefits in mouse studies.
Which also means: if you are not a mouse, you might need to drink even more than that!
Further reading: can we drink to good health?
Resveratrol supplementation
Happily, resveratrol supplements exist. But what does resveratrol do?
It lowers blood pressure:
Effect of resveratrol on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
It improves blood lipid levels:
It improves insulin sensitivity:
It has neuroprotective effects too:
Resveratrol promotes clearance of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta peptides
Is it safe?
For most people, it is generally recognized as safe. However, if you are on blood-thinners or otherwise have a bleeding disorder, you might want to skip it:
Antiplatelet activity of synthetic and natural resveratrol in red wine
You also might want to check with your pharmacist/doctor, if you’re on blood pressure meds, anxiety meds, or immunosuppressants, as it can increase the amount of these drugs that will then stay in your system:
Resveratrol modulates drug- and carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes in a healthy volunteer study
And as ever, of course, if unsure just check with your pharmacist/doctor, to be on the safe side.
Where to get it?
We don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon for your convenience
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
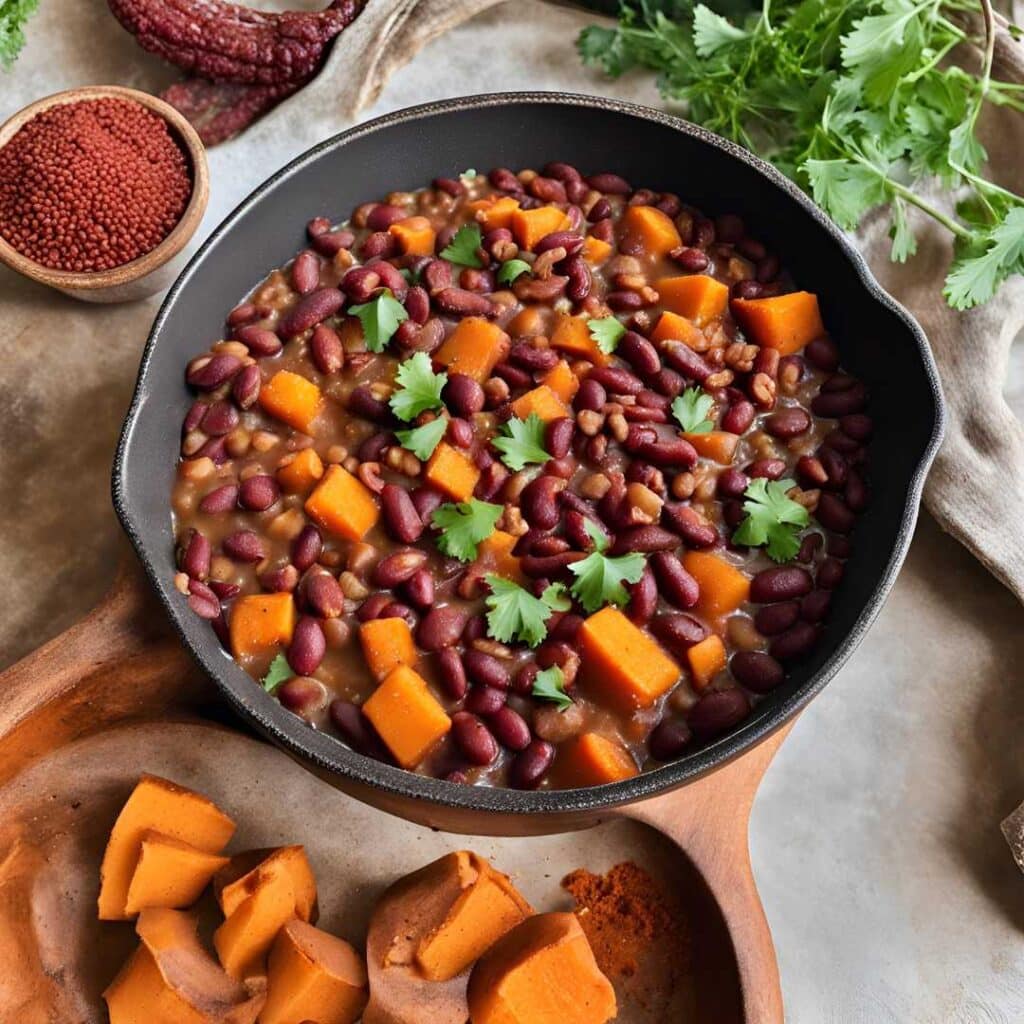
Ghanaian Red Bean & Sweet Potato Groundnut Stew
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a dish popular in principle throughout West Africa. We say “in principle” because that’s a big place, and there is a lot of regional variation. The archetypal peanut stew is from Senegal (as maafe) or Mali (as tigadèguèna), but for its more balanced nutritional profile we’ve chosen one from Ghana—and since there are regional variations within Ghana too, we should specify that this one is from the south.
If you are allergic to nuts, you can substitute a seed butter (or tahini) for the nut butter, and omit the nuts—this will work in culinary terms and be fine healthwise, but we can’t claim it would be the same dish, having lost its defining ingredient. If your allergy is solely to peanuts, then substituting with any oily nut would work. So, not almonds for example, but cashews or even walnuts would be fine.
You will need
- 1½ lbs sweet potatoes, peeled and cut into ½” cubes
- 2 cups low-sodium vegetable stock
- 2 cans kidney beans, drained, cooked, and rinsed (or 2 cups same; cooked, drained, and rinsed)
- 1 can chopped tomatoes
- ½ cup unsalted dry-roasted peanuts
- 1 onion, chopped
- 1 red bell pepper, deseeded and chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 2 heaped tbsp unsalted peanut butter, minimal (ideally: no) additives
- 2 tsp white miso paste
- 2 tsp grated fresh ginger
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp cayenne pepper
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- ½ tsp coarsely ground nigella seeds
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat some oil in a sauté pan, or other pan suitable for both frying and fitting the entire stew in. Fry the onions until softened, turn the heat down low, and add the garlic, ginger, red bell pepper, cumin, cayenne, black pepper, and MSG/salt.
2) Add ¼ cup of the vegetable stock, and the sweet potato, and turn the heat back up, on high for about 30 seconds to get it to temperature, and then take it down to a simmer.
3) Stir in the miso paste and chopped tomatoes.
4) Add most of the rest of the vegetable stock, keeping ¼ cup aside. Simmer for about 20 minutes.
5) Stir in the kidney beans, and simmer for about 30 minutes more—the sweet potato should be soft now; if it isn’t, let it simmer a while longer until it is.
6) Combine the peanut butter with the remaining ¼ cup vegetable stock, and blend until smooth. Stir it into the stew.
7) If the stew is looking more like a soup than a stew, take out 1 cup and blend this 1 cup to a purée, adding it back in.
8) Add half the peanuts unto the stew. Taste, and adjust the seasonings if necessary.
9) Crush the remaining peanuts using a pestle and mortar; not too much though; you want them broken into bits, not pulverised.
10) Garnish with the crushed nuts and nigella seeds, and serve.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we used 4/5 today!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: