Try This At Home: ABI Test For Clogged Arteries
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Arterial plaque is a big deal, and statistically it’s more of a risk as we get older, often coming to a head around age 72 for women and 65 for men—these are the median ages at which people who are going to get heart attacks, get them. Or get it, because sometimes one is all it takes.
The Ankle-Brachial Index Test
Dr. Brewer recommends a home test for detecting arterial plaque called the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI), which uses a blood pressure monitor. The test involves measuring blood pressure in both the arms and ankles, then calculating the ratio of these measurements:
- A healthy ABI score is between 1.0 and 1.4; anything outside this range may indicate arterial problems.
- Low ABI scores (below 0.8) suggest plaque is likely obstructing blood flow
- High ABI scores (above 1.4) may indicate artery hardening
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), associated with poor ABI results (be they high or low), can cause a whole lot of problems that are definitely better tackled sooner rather than later—remember that atherosclerosis is a self-worsening thing once it gets going, because narrower walls means it’s even easier for more stuff to get stuck in there (and thus, the new stuff that got stuck also becomes part of the walls, and the problem gets worse).
If you need a blood pressure monitor, by the way, here’s an example product on Amazon.
Do note also that yes, if you have plaque obstructing blood flow and hardened arteries, your scores may cancel out and give you a “healthy” score, despite your arteries being very much not healthy. For this reason, this test can be used to raise the alarm, but not to give the “all clear”.
For more on all of the above, plus a demonstration and more in-depth explanation of the test, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Diet Tips for Crohn’s Disease
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Doctors are great at saving lives like mine. I’m a two time survivor of colon cancer and have recently been diagnosed with Chron’s disease at 62. No one is the health system can or is prepared to tell me an appropriate diet to follow or what to avoid. Can you?❞
Congratulations on the survivorship!
As to Crohn’s, that’s indeed quite a pain, isn’t it? In some ways, a good diet for Crohn’s is the same as a good diet for most other people, with one major exception: fiber
…and unfortunately, that changes everything, in terms of a whole-foods majority plant-based diet.
What stays the same:
- You still ideally want to eat a lot of plants
- You definitely want to avoid meat and dairy in general
- Eating fish is still usually* fine, same with eggs
- Get plenty of water
What needs to change:
- Consider swapping grains for potatoes or pasta (at least: avoid grains)
- Peel vegetables that are peelable; discard the peel or use it to make stock
- Consider steaming fruit and veg for easier digestion
- Skip spicy foods (moderate spices, like ginger, turmeric, and black pepper, are usually fine in moderation)
Much of this latter list is opposite to the advice for people without Crohn’s Disease.
*A good practice, by the way, is to keep a food journal. There are apps that you can get for free, or you can do it the old-fashioned way on paper if prefer.
But the important part is: make a note not just of what you ate, but also of how you felt afterwards. That way, you can start to get a picture of patterns, and what’s working (or not) for you, and build up a more personalized set of guidelines than anyone else could give to you.
We hope the above pointers at least help you get going on the right foot, though!
Share This Post
-
The Exercises That Can Fix Sinus Problems (And More)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Who nose what benefits you will gain today?
This is James Nestor, a science journalist and author. He’s written for many publications, including Scientific American, and written a number of books, most notably Breath: The New Science Of A Lost Art.
Today we’ll be looking at what he has to share about what has gone wrong with our breathing, what problems this causes, and how to fix it.
What has gone wrong?
When it comes to breathing, we humans are the pugs of the primate world. In a way, we have the opposite problem to the squashed-faced dogs, though. But, how and why?
When our ancestors learned first tenderize food, and later to cook it, this had two big effects:
- We could now get much more nutrition for much less hunting/gathering
- We now did not need to chew our food nearly so much
Getting much more nutrition for much less hunting/gathering is what allowed us to grow our brains so large—as a species, we have a singularly large brain-to-body size ratio.
Not needing to chew our food nearly so much, meanwhile, had even more effects… And these effects have become only more pronounced in recent decades with the rise of processed food making our food softer and softer.
It changed the shape of our jaw and cheekbones, just as the size of our brains taking up more space in our skull moved our breathing apparatus around. As a result, our nasal cavities are anatomically ridiculous, our sinuses are a crime against nature (not least of all because they drain backwards and get easily clogged), and our windpipes are very easily blocked and damaged due to the unique placement of our larynx; we’re the only species that has it there. It allowed us to develop speech, but at the cost of choking much more easily.
What problems does this cause?
Our (normal, to us) species-wide breathing problems have resulted in behavioral adaptations such as partial (or in some people’s cases, total or near-total) mouth-breathing. This in turn exacerbates the problems with our jaws and cheekbones, which in turn exacerbates the problems with our sinuses and nasal cavities in general.
Results include such very human-centric conditions as sleep apnea, as well as a tendency towards asthma, allergies, and autoimmune diseases. Improper breathing also brings about a rather sluggish metabolism for how many calories we consume.
How are we supposed to fix all that?!
First, close your mouth if you haven’t already, and breathe through your nose.
In and out.
Both are important, and unless you are engaging in peak exercise, both should be through your nose. If you’re not used to this, it may feel odd at first, but practice, and build up your breathing ability.
Six seconds in and six seconds out is a very good pace.
If you’re sitting doing a breathing exercise, also good is four seconds in, four seconds hold, four seconds out, four seconds hold, repeat.
But those frequent holds aren’t practical in general life, so: six seconds in, six seconds out.
Through your nose only.
This has benefits immediately, but there are other more long-term benefits from doing not just that, but also what has been called (by Nestor, amongst many others), “Mewing”, per the orthodontist, Dr. John Mew, who pioneered it.
How (and why) to “mew”:
Place your tongue against the roof of your mouth. It should be flat against the palate; you’re not touching it with the tip here; you’re creating a flat seal.
Note: if you were mouth-breathing, you will now be unable to breathe. So, important to make sure you can breathe adequately through your nose first.
This does two things:
- It obliges nose-breathing rather than mouth-breathing
- It creates a change in how the muscles of your face interact with the bones of your face
In a battle between muscle and bone, muscle will always win.
Aim to keep your tongue there as much as possible; make it your new best habit. If you’re not eating, talking, or otherwise using your tongue to do something, it should be flat against the roof of your mouth.
You don’t have to exert pressure; this isn’t an exercise regime. Think of it more as a postural exercise, just, inside your mouth.
Quick note: read the above line again, because it’s important. Doing it too hard could cause the opposite problems, and you don’t want that. You cannot rush this by doing it harder; it takes time and gentleness.
Why would we want to do that?
The result, over time, will tend to be much healthier breathing, better sinus health, freer airways, reduced or eliminated sleep apnea, and, as a bonus, what is generally considered a more attractive face in terms of bone structure. We’re talking more defined cheekbones, straighter teeth, and a better mouth position.
Want to learn more?
This is the “Mewing” technique that Nestor encourages us to try:
Share This Post
-
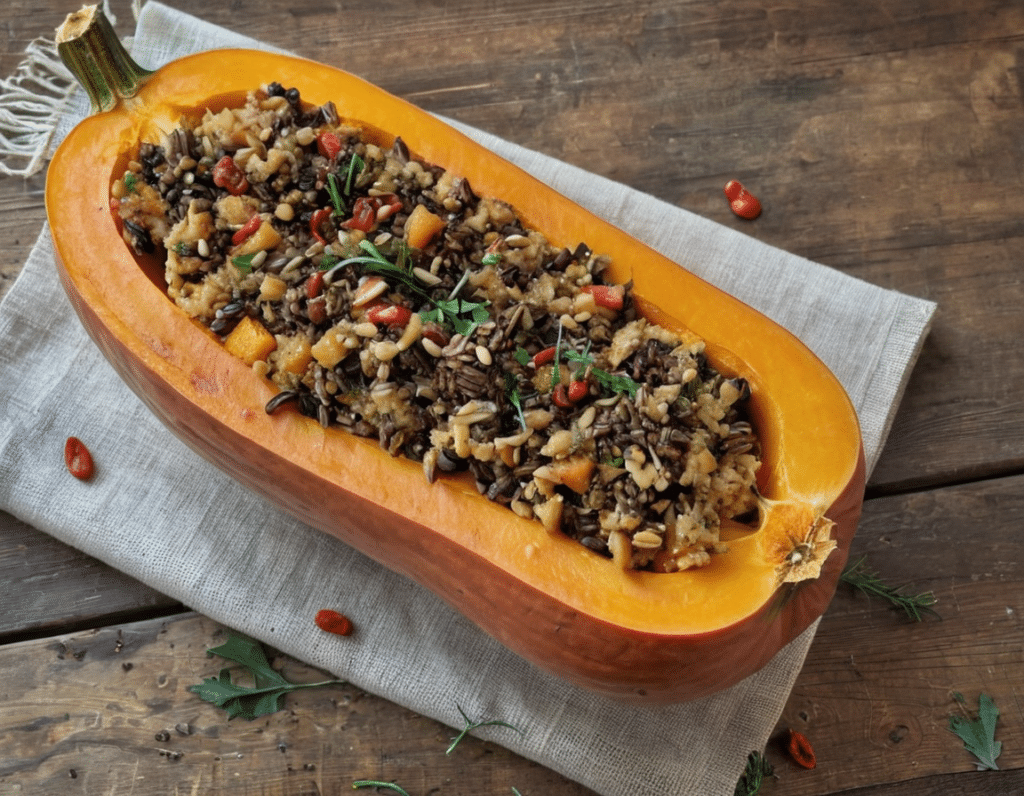
Superfood-Stuffed Squash
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This stuffed squash recipe is packed with so many nutrient-dense ingredients, yet it feels delightfully decadent—a great recipe to have up your sleeve ready for fall.
You will need
- 1 large or two medium butternut squashes, halved lengthways and seeds removed (keep them; they are full of nutrients! You can sprout them, or dry them to use them at your leisure), along with some of the flesh from the central part above where the seeds are, so that there is room for stuffing
- 2 cups low-sodium vegetable stock
- 1 cup wild rice, rinsed
- 1 medium onion, finely chopped
- ½ cup walnuts, roughly chopped
- ½ cup dried
cranberriesgoji berries ← why goji berries? They have even more healthful properties than cranberries, and cranberries are hard to buy without so much added sugar that the ingredients list looks like “cranberries (51%), sugar (39%), vegetable oil (10%)”, whereas when buying goji berries, the ingredients list says “goji berries”, and they do the same culinary job. - ¼ cup pine nuts
- ½ bulb garlic, minced
- 1 tbsp dried thyme or 2 tsp fresh thyme, destalked
- 1 tbsp dried rosemary or 2 tsp fresh rosemary, destalked
- 1 generous handful fresh parsley, chopped
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil, for brushing and frying
- Aged balsamic vinegar, to serve (failing this, make a balsamic vinegar reduction and use that; it should have a thicker texture but still taste acidic and not too sweet; the thickness should come from the higher concentration of grape must and its natural sugars; no need to add sugar)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400°F / 200°C.
2) Brush the cut sides of the squash with olive oil; sprinkle with a pinch of MSG/salt and a little black pepper (grind it directly over the squash if you are using a grinder; hold the grinder high though so that it distributes evenly—waiters in restaurants aren’t just being dramatic when they do that with pepper or Parmesan or such)
3) Arrange them cut-sides-down on a baking tray lined with baking paper, and roast for at least 30 minutes or until tender.
4) While that is roasting, add the chia seeds to the wild rice, and cook them in the low-sodium vegetable stock, using a rice cooker if available. It should take about the same length of time, but if the rice is done first, set it aside, and if the squash is done first, turn the oven down low to keep it warm.
5) Heat some oil in a sauté pan (not a skillet without high sides; we’re going to need space in a bit), and fry the chopped onion until translucent and soft. We could say “about 5 minutes” but honestly it depends on your pan as well as the heat and other factors.
6) Add the seasonings (herbs, garlic, black pepper, MSG/salt, nooch), and cook for a further 2 minutes, stirring thoroughly to distribute evenly.
7) Add the rice, berries, and nuts, cooking for a further 2 minutes, stirring constantly, ensuring everything is heated evenly.
8) Remove the squash halves from the oven, turn them over, and spoon the mixture we just made into them, filling generously.
9) Drizzle a lashing of the aged balsamic vinegar (or balsamic vinegar reduction), to serve.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Brown Rice vs Wild Rice – Which is Healthier?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- Chia: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Lost Art of Silence – by Sarah Anderson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From “A Room Of One’s Own” to “Silent Mondays”, from spiritual retreats to noise-cancelling headphones, this book covers the many benefits of silence—and a couple of downsides too.
In an age where most things are available at the touch of a button, a little peaceful solitude can come at quite a premium, but what it offers can effect all manner of physical changes, from reduced stress responses to increased neurogenesis (growing new brain cells).
The tone throughout is a combination of personal and pop-science, and it’s very motivating to find a little more space-between-the-things in life.
The book is best enjoyed in a quiet room.
Bottom line: if you get the feeling sometimes that you could rest and recover fully and properly if you could just find the downtime, this book will help you find exactly that.
Click here to check out the Lost Art of Silence, and find peace and strength in it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Rebuild Your Neurons’ Myelin Sheaths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
PS: We Love You
Phosphatidylserine, or “PS” for short, is a phospholipid found in the brain. In other words, a kind of fatty compound that is such stuff as our brains are made of.
In particular, it’s required for healthy nerve cell membranes and myelin (the protective sheath that neurons live in—basically, myelin sheaths do for neurons what telomere caps do for DNA).
For an overview that’s more comprehensive than we have room for here, check out:
Phosphatidylserine and the human brain
Many people take it as a supplement.
Does taking it as a supplement work?
This is a valid question, as a lot of supplements can’t be absorbed well, and/or can’t pass the blood-brain barrier. But, as the above-linked study notes:
❝Exogenous PS (300-800 mg/d) is absorbed efficiently in humans, crosses the blood-brain barrier, and safely slows, halts, or reverses biochemical alterations and structural deterioration in nerve cells. It supports human cognitive functions, including the formation of short-term memory, the consolidation of long-term memory, the ability to create new memories, the ability to retrieve memories, the ability to learn and recall information, the ability to focus attention and concentrate, the ability to reason and solve problems, language skills, and the ability to communicate. It also supports locomotor functions, especially rapid reactions and reflexes.❞
(“Exogenous” means “coming from outside of the body”, as opposed to “endogenous”, meaning “made inside the body”. Effectively, in this context “exogenous” means “taken as a supplement”.)
Why do people take it?
The health claims for phosphatidylserine fall into two main categories:
- Neuroprotection (helping your brain to avoid age-related decline in the long term)
- Cognitive enhancement (helping your brain work better in the short term)
What does the science say?
There’s a lot of science that’s been done on the neuroprotective properties of PS, and there are thousands of studies we could draw from here. The upshot is that regular phosphatidylserine supplementation (most often 300mg/day, but studies are also found for 100–500mg/day) is strongly associated with a reduction in cognitive decline over the course of 12 weeks (a common study duration). Here are a some spotlight studies showing this:
- Effects of phosphatidylserine in Alzheimer’s disease
- Double-blind cross-over study of phosphatidylserine vs. placebo in patients with early dementia of the Alzheimer type
- Effect of Phosphatidylserine on Cerebral Glucose Metabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease
- The effect of soybean-derived phosphatidylserine on cognitive performance in elderly with subjective memory complaints
Note: PS can be derived from various sources, with the two most common forms being bovine (i.e., from cow brains) or soy-derived.
There is no established difference in the efficacy of these.
There have been some concerns raised about the risk of CJD (the human form of BSE, as in “mad cow disease”) from consuming brain matter from cows, but studies have not found any evidence of this actually happening.
There is also some evidence that phosphatidyserine significantly boosts cognitive performance, even in young people with no extant cognitive decline, for example:
(as the title suggests, they did also test for its effect on mood and endocrine response, but found it made no difference to those, just the cognitive function—which enjoyed a boost before exercise, as well as after it, meaning that the boost wasn’t dependent on the exercise)
PS for cognitive enhancement in the young and healthy is not nearly so well-explored as its use as a later-life guard against age-related cognitive decline. However, just because the studies in younger people are dwarfed in number by the studies in older people, doesn’t detract from the validity of the studies in younger people.
Basically: its use in older people has been studied the most, but all available evidence points to it being beneficial to brain health at all ages.
Where can we get it?
We don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience, here’s an example product on Amazon.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Rapid Rise in Syphilis Hits Native Americans Hardest
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From her base in Gallup, New Mexico, Melissa Wyaco supervises about two dozen public health nurses who crisscross the sprawling Navajo Nation searching for patients who have tested positive for or been exposed to a disease once nearly eradicated in the U.S.: syphilis.
Infection rates in this region of the Southwest — the 27,000-square-mile reservation encompasses parts of Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah — are among the nation’s highest. And they’re far worse than anything Wyaco, who is from Zuni Pueblo (about 40 miles south of Gallup) and is the nurse consultant for the Navajo Area Indian Health Service, has seen in her 30-year nursing career.
Syphilis infections nationwide have climbed rapidly in recent years, reaching a 70-year high in 2022, according to the most recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That rise comes amid a shortage of penicillin, the most effective treatment. Simultaneously, congenital syphilis — syphilis passed from a pregnant person to a baby — has similarly spun out of control. Untreated, congenital syphilis can cause bone deformities, severe anemia, jaundice, meningitis, and even death. In 2022, the CDC recorded 231 stillbirths and 51 infant deaths caused by syphilis, out of 3,761 congenital syphilis cases reported that year.
And while infections have risen across the U.S., no demographic has been hit harder than Native Americans. The CDC data released in January shows that the rate of congenital syphilis among American Indians and Alaska Natives was triple the rate for African Americans and nearly 12 times the rate for white babies in 2022.
“This is a disease we thought we were going to eradicate not that long ago, because we have a treatment that works really well,” said Meghan Curry O’Connell, a member of the Cherokee Nation and chief public health officer at the Great Plains Tribal Leaders’ Health Board, who is based in South Dakota.
Instead, the rate of congenital syphilis infections among Native Americans (644.7 cases per 100,000 people in 2022) is now comparable to the rate for the entire U.S. population in 1941 (651.1) — before doctors began using penicillin to cure syphilis. (The rate fell to 6.6 nationally in 1983.)
O’Connell said that’s why the Great Plains Tribal Leaders’ Health Board and tribal leaders from North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, and Iowa have asked federal Health and Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra to declare a public health emergency in their states. A declaration would expand staffing, funding, and access to contact tracing data across their region.
“Syphilis is deadly to babies. It’s highly infectious, and it causes very severe outcomes,” O’Connell said. “We need to have people doing boots-on-the-ground work” right now.
In 2022, New Mexico reported the highest rate of congenital syphilis among states. Primary and secondary syphilis infections, which are not passed to infants, were highest in South Dakota, which had the second-highest rate of congenital syphilis in 2022. In 2021, the most recent year for which demographic data is available, South Dakota had the second-worst rate nationwide (after the District of Columbia) — and numbers were highest among the state’s large Native population.
In an October news release, the New Mexico Department of Health noted that the state had “reported a 660% increase in cases of congenital syphilis over the past five years.” A year earlier, in 2017, New Mexico reported only one case — but by 2020, that number had risen to 43, then to 76 in 2022.
Starting in 2020, the covid-19 pandemic made things worse. “Public health across the country got almost 95% diverted to doing covid care,” said Jonathan Iralu, the Indian Health Service chief clinical consultant for infectious diseases, who is based at the Gallup Indian Medical Center. “This was a really hard-hit area.”
At one point early in the pandemic, the Navajo Nation reported the highest covid rate in the U.S. Iralu suspects patients with syphilis symptoms may have avoided seeing a doctor for fear of catching covid. That said, he doesn’t think it’s fair to blame the pandemic for the high rates of syphilis, or the high rates of women passing infections to their babies during pregnancy, that continue four years later.
Native Americans are more likely to live in rural areas, far from hospital obstetric units, than any other racial or ethnic group. As a result, many do not receive prenatal care until later in pregnancy, if at all. That often means providers cannot test and treat patients for syphilis before delivery.
In New Mexico, 23% of patients did not receive prenatal care until the fifth month of pregnancy or later, or received fewer than half the appropriate number of visits for the infant’s gestational age in 2023 (the national average is less than 16%).
Inadequate prenatal care is especially risky for Native Americans, who have a greater chance than other ethnic groups of passing on a syphilis infection if they become pregnant. That’s because, among Native communities, syphilis infections are just as common in women as in men. In every other ethnic group, men are at least twice as likely to contract syphilis, largely because men who have sex with men are more susceptible to infection. O’Connell said it’s not clear why women in Native communities are disproportionately affected by syphilis.
“The Navajo Nation is a maternal health desert,” said Amanda Singer, a Diné (Navajo) doula and lactation counselor in Arizona who is also executive director of the Navajo Breastfeeding Coalition/Diné Doula Collective. On some parts of the reservation, patients have to drive more than 100 miles to reach obstetric services. “There’s a really high number of pregnant women who don’t get prenatal care throughout the whole pregnancy.”
She said that’s due not only to a lack of services but also to a mistrust of health care providers who don’t understand Native culture. Some also worry that providers might report patients who use illicit substances during their pregnancies to the police or child welfare. But it’s also because of a shrinking network of facilities: Two of the Navajo area’s labor and delivery wards have closed in the past decade. According to a recent report, more than half of U.S. rural hospitals no longer offer labor and delivery services.
Singer and the other doulas in her network believe New Mexico and Arizona could combat the syphilis epidemic by expanding access to prenatal care in rural Indigenous communities. Singer imagines a system in which midwives, doulas, and lactation counselors are able to travel to families and offer prenatal care “in their own home.”
O’Connell added that data-sharing arrangements between tribes and state, federal, and IHS offices vary widely across the country, but have posed an additional challenge to tackling the epidemic in some Native communities, including her own. Her Tribal Epidemiology Center is fighting to access South Dakota’s state data.
In the Navajo Nation and surrounding area, Iralu said, IHS infectious disease doctors meet with tribal officials every month, and he recommends that all IHS service areas have regular meetings of state, tribal, and IHS providers and public health nurses to ensure every pregnant person in those areas has been tested and treated.
IHS now recommends all patients be tested for syphilis yearly, and tests pregnant patients three times. It also expanded rapid and express testing and started offering DoxyPEP, an antibiotic that transgender women and men who have sex with men can take up to 72 hours after sex and that has been shown to reduce syphilis transmission by 87%. But perhaps the most significant change IHS has made is offering testing and treatment in the field.
Today, the public health nurses Wyaco supervises can test and treat patients for syphilis at home — something she couldn’t do when she was one of them just three years ago.
“Why not bring the penicillin to the patient instead of trying to drag the patient in to the penicillin?” said Iralu.
It’s not a tactic IHS uses for every patient, but it’s been effective in treating those who might pass an infection on to a partner or baby.
Iralu expects to see an expansion in street medicine in urban areas and van outreach in rural areas, in coming years, bringing more testing to communities — as well as an effort to put tests in patients’ hands through vending machines and the mail.
“This is a radical departure from our past,” he said. “But I think that’s the wave of the future.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: