Superfood-Stuffed Squash
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This stuffed squash recipe is packed with so many nutrient-dense ingredients, yet it feels delightfully decadent—a great recipe to have up your sleeve ready for fall.
You will need
- 1 large or two medium butternut squashes, halved lengthways and seeds removed (keep them; they are full of nutrients! You can sprout them, or dry them to use them at your leisure), along with some of the flesh from the central part above where the seeds are, so that there is room for stuffing
- 2 cups low-sodium vegetable stock
- 1 cup wild rice, rinsed
- 1 medium onion, finely chopped
- ½ cup walnuts, roughly chopped
- ½ cup dried
cranberriesgoji berries ← why goji berries? They have even more healthful properties than cranberries, and cranberries are hard to buy without so much added sugar that the ingredients list looks like “cranberries (51%), sugar (39%), vegetable oil (10%)”, whereas when buying goji berries, the ingredients list says “goji berries”, and they do the same culinary job. - ¼ cup pine nuts
- ½ bulb garlic, minced
- 1 tbsp dried thyme or 2 tsp fresh thyme, destalked
- 1 tbsp dried rosemary or 2 tsp fresh rosemary, destalked
- 1 generous handful fresh parsley, chopped
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil, for brushing and frying
- Aged balsamic vinegar, to serve (failing this, make a balsamic vinegar reduction and use that; it should have a thicker texture but still taste acidic and not too sweet; the thickness should come from the higher concentration of grape must and its natural sugars; no need to add sugar)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400°F / 200°C.
2) Brush the cut sides of the squash with olive oil; sprinkle with a pinch of MSG/salt and a little black pepper (grind it directly over the squash if you are using a grinder; hold the grinder high though so that it distributes evenly—waiters in restaurants aren’t just being dramatic when they do that with pepper or Parmesan or such)
3) Arrange them cut-sides-down on a baking tray lined with baking paper, and roast for at least 30 minutes or until tender.
4) While that is roasting, add the chia seeds to the wild rice, and cook them in the low-sodium vegetable stock, using a rice cooker if available. It should take about the same length of time, but if the rice is done first, set it aside, and if the squash is done first, turn the oven down low to keep it warm.
5) Heat some oil in a sauté pan (not a skillet without high sides; we’re going to need space in a bit), and fry the chopped onion until translucent and soft. We could say “about 5 minutes” but honestly it depends on your pan as well as the heat and other factors.
6) Add the seasonings (herbs, garlic, black pepper, MSG/salt, nooch), and cook for a further 2 minutes, stirring thoroughly to distribute evenly.
7) Add the rice, berries, and nuts, cooking for a further 2 minutes, stirring constantly, ensuring everything is heated evenly.
8) Remove the squash halves from the oven, turn them over, and spoon the mixture we just made into them, filling generously.
9) Drizzle a lashing of the aged balsamic vinegar (or balsamic vinegar reduction), to serve.
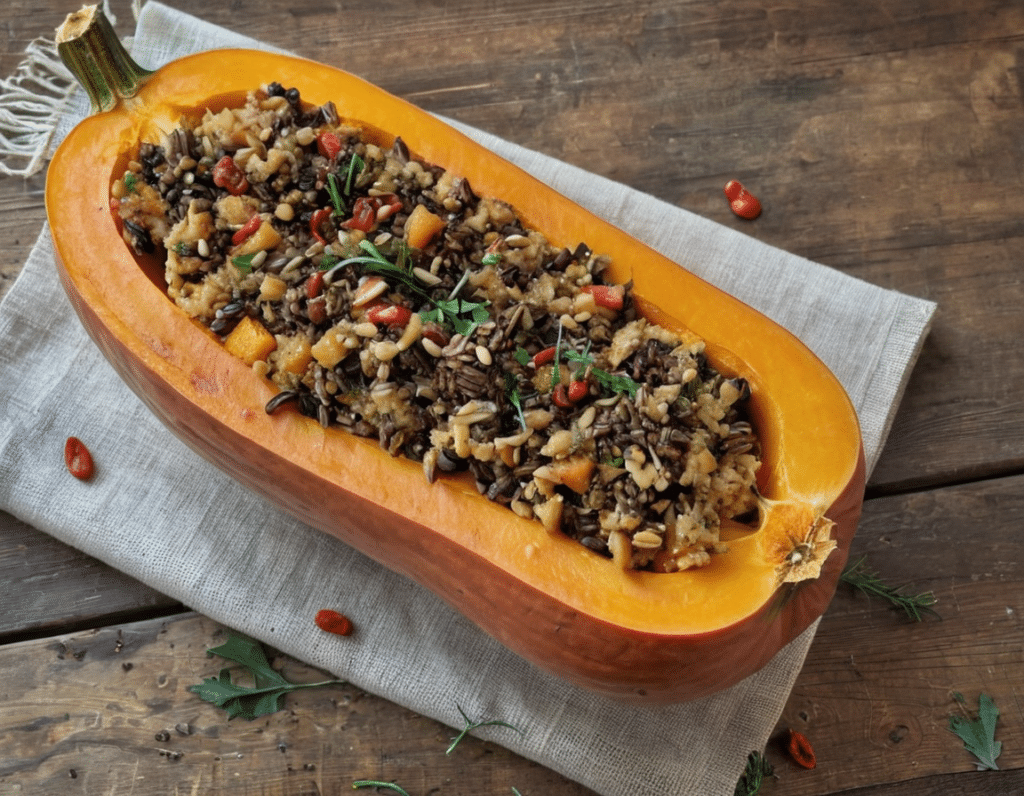

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Brown Rice vs Wild Rice – Which is Healthier?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- Chia: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Self-Care for Tough Times – by Suzy Reading
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A note on the author: while not “Dr. Reading”, she is a “CPsychol, B Psych (Hons), M Psych”; a Chartered Psychologist specializing in wellbeing, stress management and facilitation of healthy lifestyle change. So this is coming from a place of research and evidence!
The kinds of “tough times” she has in mind are so numerous that listing them takes two pages in the book, so we won’t try here. But suffice it to say, there are a lot of things that can go wrong for us as humans, and this book addresses how to take care of ourselves mindfully in light of them.
The author takes a “self-care is health care” approach, and goes about things with a clinical mindset and/but a light tone, offering both background information, and hands-on practical advice.
Bottom line: there may be troubles ahead (and maybe you’re in the middle of troubles right now), but there’s always room for a little sunshine too.
Click here to check out Self-Care For Tough Times, and care for yourself in tough times!
Share This Post
-
Procrastination, and how to pay off the to-do list debt
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Procrastination, and how pay off the to-do list debt
Sometimes we procrastinate because we feel overwhelmed by the mountain of things we are supposed to be doing. If you look at your to-do list and it shows 60 overdue items, it’s little wonder if you want to bury your head in the sand!
“What difference does it make if I do one of these things now; I will still have 59 which feels as bad as having 60”
So, treat it like you might a financial debt, and make a repayment plan. Now, instead of 60 overdue items today, you have 1/day for the next 60 days, or 2/day for the next 30 days, or 3/day for the next 20 days, etc. Obviously, you may need to work out whether some are greater temporal priorities and if so, bump those to the top of the list. But don’t sweat the minutiae; your list doesn’t have to be perfectly ordered, just broadly have more urgent things to the top and less urgent things to the bottom.
Note: this repayment plan means having set repayment dates.
Up front, sit down and assign each item a specific calendar date on which you will do that thing.
This is not a deadline! It is your schedule. You’ll not try to do it sooner, and you won’t postpone it for later. You will just do that item on that date.
A productivity app like ToDoist can help with this, but paper is fine too.
What’s important here, psychologically, is that each day you’re looking not at 60 things and doing the top item; you’re just looking at today’s item (only!) and doing it.
Debt Reduction/Cancellation
Much like you might manage a financial debt, you can also look to see if any of your debts could be reduced or cancelled.
We wrote previously about the “Getting Things Done” system. It’s a very good system if you want to do that; if not, no worries, but you might at least want to borrow this one idea….
Sort your items into:
Do / Defer / Delegate / Ditch
- Do: if it can be done in under 2 minutes, do it now.
- Defer: defer the item to a specific calendar date (per the repayment plan idea we just talked about)
- Delegate: could this item be done by someone else? Get it off your plate if you reasonably can.
- Ditch: sometimes, it’s ok to realize “you know what, this isn’t that important to me anymore” and scratch it from the list.
As a last resort, consider declaring bankruptcy
Towards the end of the dot-com boom, there was a fellow who unintentionally got his 5 minutes of viral fame for “declaring email bankruptcy”.
Basically, he publicly declared that his email backlog had got so far out of hand that he would now not reply to emails from before the declaration.
He pledged to keep on top of new emails only from that point onwards; a fresh start.
We can’t comment on whether he then did, but if you need a fresh start, that can be one way to get it!
In closing…
Procrastination is not usually a matter of laziness, it’s usually a matter of overwhelm. Hopefully the above approach will help reframe things, and make things more manageable.
Sometimes procrastination is a matter of perfectionism, and not starting on tasks because we worry we won’t do them well enough, and so we get stuck in a pseudo-preparation rut. If that’s the case, our previous main feature on perfectionism may help:
Share This Post
-
The Whys and Hows of Cutting Meats Out Of Your Diet
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it’s time to tell the meat to beat it…
Meat in general, and red meat and processed meat in particular, have been associated with so many health risks, that it’s very reasonable to want to reduce, if not outright eliminate, our meat consumption.
First, in case anyone’s wondering “what health risks?”
The aforementioned culprits tend to turn out to be a villain in the story of every second health-related thing we write about here. To name just a few:
- Processed Meat Consumption and the Risk of Cancer: A Critical Evaluation of the Constraints of Current Evidence from Epidemiological Studies
- Red Meat Consumption (Heme Iron Intake) and Risk for Diabetes and Comorbidities?
- Health Risks Associated with Meat Consumption: A Review of Epidemiological Studies
- Associations of Processed Meat, Unprocessed Red Meat, Poultry, or Fish Intake With Incident Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality
- Meat consumption: Which are the current global risks? A review of recent (2010-2020) evidences
Seasoned subscribers will know that we rarely go more than a few days without recommending the very science-based Mediterranean Diet which studies find beneficial for almost everything we write about. The Mediterranean Diet isn’t vegetarian per se—by default it consists of mostly plants but does include some fish and a very small amount of meat from land animals. But even that can be improved upon:
- A Pesco-Mediterranean Diet With Intermittent Fasting
- Mediterranean, vegetarian and vegan diets as practical outtakes of EAS and ACC/AHA recommendations for lowering lipid profile
- A Mediterranean Low-Fat Vegan Diet to Improve Body Weight and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Randomized, Cross-over Trial
So that’s the “why”; now for the “how”…
It’s said that with a big enough “why” you can always find a “how”, but let’s make things easy!
Meatless Mondays
One of the biggest barriers to many people skipping the meat is “what will we even eat?”
The idea of “Meatless Mondays” means that this question need only be answered once a week, and in doing that a few Mondays in a row, you’ll soon find you’re gradually building your repertoire of meatless meals, and finding it’s not so difficult after all.
Then you might want to expand to “meat only on the weekends”, for example.
Flexitarian
This can be met with derision, “Yes and I’m teetotal, apart from wine”, but there is a practical aspect here:
The idea is “I will choose vegetarian options, unless it’s really inconvenient for me to do so”, which wipes out any difficulty involved.
After doing this for a while, you might find that as you get more used to vegetarian stuff, it’s almost never inconvenient to eat vegetarian.
Then you might want to expand it to “I will choose vegan options, unless it’s really inconvenient for me to do so”
Like-for-like substitutions
Pretty much anything that can come from an animal, one can get a plant-based version of it nowadays. The healthiness (and cost!) of these substitutions can vary, but let’s face it, meat is neither the healthiest nor the cheapest thing out there these days either.
If you have the money and don’t fancy leaping to lentils and beans, this can be a very quick and easy zero-effort change-over. Then once you’re up and running, maybe you can—at your leisure—see what all the fuss is about when it comes to tasty recipes with lentils and beans!
That’s all we have time for today, but…
We’re thinking of doing a piece making your favorite recipes plant-based (how to pick the right substitutions so the meal still tastes and “feels” the same), so let us know if you’d like that? Feel free to mention your favorite foods/meals too, as that’ll help us know what there’s a market for!
You can do that by hitting reply to any of our emails, or using the handy feedback widget at the bottom!
Curious to know more while you wait?
Check out: The Vegan Diet: A Complete Guide for Beginners ← this is a well-sourced article from Healthline, who—just like us—like to tackle important health stuff in an easy-to-read, well-sourced format
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Stop Self-Sabotage – by Dr. Judy Ho
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of books of this genre identify one particular kind of self-sabotage, for example, they might pick one out of:
- Bad habits
- Limiting self-beliefs
- Poor goal-setting
- Procrastination
…etc, slap a quick fix on whatever they chose to focus on, and call it a day. Not so with Dr. Ho!
Here we have a much more comprehensive approach to tackling the problem of unintentional self-sabotage. With a multi-vector method, of which all angles can be improved simultaneously, it becomes much less like “whack-a-mole”… And much more like everything actually getting into order and staying that way.
The main approach here is CBT, but far beyond what most pop-psychology CBT books go for, with more techniques and resources.
On which note…
There are many great exercises that Dr. Ho recommends we do while reading… So you might want to get a nice notebook alongside this book if you don’t already have one! And what is more inspiring of optimism than a new notebook?
Bottom line: this is a great, well-organized guide to pruning the “why am I still doing this to myself?” aspects out of your life for a much more intentional, purposeful, effective way of living.
Click here to check it out on Amazon today, and stop sabotaging yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Infections, Heart Failure, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some health news to round off the week:
The Infection That Leads To Heart Failure
It’s long been held that, for example, flossing reduces heart disease risk, with the hypothesis being that if plaque bacteria enter the blood stream, well, that’s an even worse place for plaque bacteria to be. Now, with much more data, attention has turned to
- actual infections, and
- actual heart failure
Way to up the ante! And, it holds true regardless of what kind of infection. So, you might think that a UTI, for example, is surely “downstream” and should not affect the heart, but it does. Because of this, researchers currently believe that it is not the infection itself, so much as the body’s inflammation response to infection, that leads to the heart failure. Which is reasonable, because, for example, atherosclerosis is made mostly not of cholesterol itself, but rather mostly of dead immune cells that got stuck in the cholesterol.
Moreover, it’s not so much about the acute inflammatory response (which is almost always a good thing, circumstantially), but rather that after cases where an infection managed to take hold, the immune system can then often stay on high alert for many years alter. Long COVID is an obvious recent example of this, but it’s hardly a new phenomenon; see for example post-polio syndrome, and consider how many more such post-infection maladies are likely to exist that never got a name because they flew under the radar or got diagnosed as fibromyalgia or something (fibromyalgia is a common diagnosis doctors give when they acknowledge something’s wrong, and it causes pain and exhaustion, but they don’t know what, and it appears to be stable—so while it can be helpful to put a name to the collection of symptoms, it’s a non-diagnosis diagnosis on the doctors’ part. It’s saying “I diagnose you with hurty tiredness”).
The take-away from all this? Avoid infections, for your heart’s sake, and if you do get an infection, take it seriously even if it’s minor. The safe amount of infection is “no infection”.
Read in full: Study uncovers new link between infections and heart failure
Cold Water Immersion: Hot Or Not?
The evidence is clear for some benefits; for others, not so much:
- It’s great (if you’re already in fair health, and definitely not if you have a heart condition) to improve circulation and stress response
- There may be some benefits to immune function, but however reasonable the hypothesis, actual evidence is thin on the ground
- The oft-hyped mood benefits are a) marginal b) short-lived, with benefits fading after 3 months of regular cold baths/showers/etc
Read in full: The big chill: Is cold-water immersion good for our health?
Related: Ice Baths: To Dip Or Not To Dip?
The Unspoken Trials Of Going To The Gym (While Being A Woman)
Public health decision-makers often think that getting people to go to the gym more is a matter of public information, or perhaps branding. Some who have their thinking heads on might even realize that there may be economic factors for many. But for women, there’s an additional factor—or rather, an additionally prominent factor. The study we’ll link started with this observation (please read it in the voice of your favorite nature documentary narrator):
❝Despite an increase in gym memberships, women are less active than men and little is known about the barriers women face when navigating gym spaces.❞
What then, of these shy, elusive creatures that make up a mere 51% of the world’s population?
A medium-sized (n=279) study of women, of whom 84% being current gym-goers, reported often feeling “judged for their appearance or performance, as well as having to fight for space in the gym and to be taken seriously, while navigating harassment and unsolicited comments from men”
Even gym attire becomes an issue:
❝Aligning with previous literature, women often chose attire based on comfort and functionality. However, their choices were also influenced by comparisons with others or fear of judgement for wearing non-branded attire or looking too put together. Many women also chose gym attire to hide perceived problem areas or avoid appearance concerns, including visible sweat stains.❞
…which main seem silly; you’re at the gym, of course you’re going to sweat, but if you’re the only one with visible sweat stains, then there can be social consequences (bad ones).
Similarly, there’s a “damned if you do; damned if you don’t” when it comes to working out while fat—on the one hand, society conflates fatness with laziness; on the other, it can be extra intimidating to be the only fat person in a gym full of people who look like they’re going to audition for a superhero movie.
❝In the gym, just like in other areas of life, women often feel stuck between being seen as ‘too much’ and ‘not enough’, dealing with judgement about how they look, how they perform, and even how much space they take up. Even though the pressure to be super thin is decreasing, the growing focus on being muscular and athletic is creating new challenges. It is pushing unrealistic standards that can negatively affect women’s body image and overall well-being.❞
Writer’s note: I live a few minutes walk from my nearest gym, and I work out at home instead. This way, if I want to do yoga in my pajamas, I can. If I want to use my treadmill naked and watch my T+A bounce in the mirror, I can. If I want to lift weights in the dress I happened to be wearing, I can. Alas that I can’t swim at home!
Read in full: Women face multiple barriers while exercising in gyms
Related: Body Image Dissatisfaction/Appreciation Across The Ages
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What are compound exercises and why are they good for you?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So you’ve got yourself a gym membership or bought a set of home weights. Now what? With the sheer amount of confusing exercise advice out there, it can be hard to decide what to include in a weights routine.
It can help to know there are broadly two types of movements in resistance training (lifting weights): compound exercises and isolation exercises.
So what’s the difference? And what’s all this got to do with strength, speed and healthy ageing?
What’s the difference?
Compound exercises involve multiple joints and muscle groups working together.
In a push up, for example, your shoulder and elbow joints are moving together. This targets the muscles in the chest, shoulder and triceps.
When you do a squat, you’re using your thigh and butt muscles, your back, and even the muscles in your core.
It can help to think about compound movements by grouping them by primary movement patterns.
For example, some lower body compound exercises follow a “squat pattern”. Examples include bodyweight squats, weighted squats, lunges and split squats.
A Bulgarian split squat is a type of compound movement exercise. Evelin Montero/Shutterstock We also have “hinge patterns”, where you hinge from a point on your body (such as the hips). Examples include deadlifts, hip thrusts and kettle bell swings.
Upper body compounded exercises can be grouped into “push patterns” (such as vertical barbell lifts) or “pull patterns” (such as weighted rows, chin ups or lat pull downs, which is where you use a pulley system machine to lift weights by pulling a bar downwards).
In contrast, isolation exercises are movements that occur at a single joint.
For instance, bicep curls only require movement at the elbow joint and work your bicep muscles. Tricep extensions and lateral raises are other examples of isolation exercises.
Many compound exercises mimic movements we do every day. Photo by Ketut Subiyanto/Pexels Compound exercises can make daily life easier
Many compound exercises mimic movements we do every day.
Hinge patterns mimic picking something off the floor. A vertical press mimics putting a heavy box on a high shelf. A squat mimics standing up from the couch or getting on and off the toilet.
That might sound ridiculous to a young, fit person (“why would I need to practise getting on and off a toilet?”).
Unfortunately, we lose strength and muscle mass as we age. Men lose about 5% of their muscle mass per decade, while for women the figure is about 4% per decade.
When this decline begins can vary widely. However, approximately 30% of an adult’s peak muscle mass is lost by the time they are 80.
The good news is resistance training can counteract these age-related changes in muscle size and strength.
So building strength through compound exercise movements may help make daily life feel a bit easier. In fact, our ability to perform compound movements are a good indicator how well we can function as we age.
Want to be able to get stuff down from high shelves when you’re older? Practising compound exercises like a vertical press could help. Galina_Lya/Shutterstock What about strength and athletic ability?
Compound exercises use multiple joints, so you can generally lift heavier weights than you could with isolation exercises. Lifting a heavier weight means you can build muscle strength more efficiently.
One study divided a group of 36 people into two. Three times a week, one group performed isolation exercises, while the other group did compound exercises.
After eight weeks, both groups had lost fat. But the compound exercises group saw much better results on measures of cardiovascular fitness, bench press strength, knee extension strength, and squat strength.
If you play a sport, compound movements can also help boost athletic ability.
Squat patterns require your hip, knee, and ankle to extend at the same time (also known as triple extension).
Our bodies use this triple extension trick when we run, sprint, jump or change direction quickly. In fact, research has found squat strength is strongly linked to being able to sprint faster and jump higher.
Isolation exercises are still good
What if you’re unable to do compound movements, or you just don’t want to?
Don’t worry, you’ll still build strength and muscle with isolation exercises.
Isolation exercises are also typically easier to learn as there is no skill required. They are an easy and low risk way to add extra exercise at the end of the workout, where you might otherwise be too tired to do more compound exercises safely and with correct form.
In fact, both isolation and compound exercises seem to be equally effective in helping us lose body fat and increase fat-free muscle mass when total intensity and volume of exercises are otherwise equal.
Some people also do isolation exercises when they want to build up a particular muscle group for a certain sport or for a bodybuilding competition, for example.
Isolation exercises have their role to play. Photo by Kampus Production/Pexels I just want a time efficient workout
Considering the above factors, you could consider prioritising compound exercises if you’re:
- time poor
- keen to lift heavier weights
- looking for an efficient way to train many muscles in the one workout
- interested in healthy ageing.
That said, most well designed workout programs will include both compound and isolation movements.
Correction: This article has been amended to reflect the fact a weighted row is a pull pattern, not a push pattern.
Mandy Hagstrom, Senior Lecturer, Exercise Physiology. School of Health Sciences, UNSW Sydney and Anurag Pandit, PhD Candidate in Exercise Physiology, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: