Toasted Chick’n Mango Tacos
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tacos aren’t generally held up as the world’s healthiest food, but they can be! There’s so much going on in this dish today, healthwise, in a good way, that it’s hard to know where to start. But suffice it to say, these tacos are great for your gut, heart, blood sugars, and more.
You will need
For the chickpeas:
- 1 can chickpeas, drained
- 1 tbsp ras el-hanout*
- 1 tsp red pepper flakes
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
*You can easily make this yourself; following our recipe (linked above in the ingredients list) will be better than buying it ready-made, and if you have strong feelings about any of the ingredients, you can adjust per your preference.
For the tahini sauce:
- ⅓ cup tahini
- 2 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- 2 tbsp finely chopped fresh dill
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced
- 1 tsp red pepper flakes
- ½ tsp black pepper, coarse ground
It may seem like salt is conspicuous by its absence, but there is already enough in the chickpeas component; you do not want to overwhelm the dish. Trust us that enjoying these things together will be well-balanced and delicious as written.
For the mango relish:
- ½ mango, pitted, peeled, and cubed
- 2 tsp apple cider vinegar
- 2 tsp cilantro, finely chopped (substitute with parsley if you have the “cilantro tastes like soap” gene)
- 1 tsp red pepper flakes
For building the taco:
- Soft corn tortillas
- Handful of arugula
- 1 avocado, pitted, peeled, and sliced
- ½ red onion, sliced
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat a sauté pan with a little olive oil in; add the chickpeas and then the rest of the ingredients from the chickpea section; cook for about 5 minutes, stirring frequently, and set aside.
2) Combine the tahini sauce ingredients in a small bowl, stirring in ¼ cup water, and set aside.
3) Combine the mango relish ingredients in a separate small bowl, and set aside. You can eat the other half of the mango if you like.
4) Lightly toast the tortillas in a dry skillet, or using a grill.
5) Assemble the tacos; we recommend the order: tortillas, arugula, avocado slices, chickpeas, mango relish, red onion slices, tahini sauce.
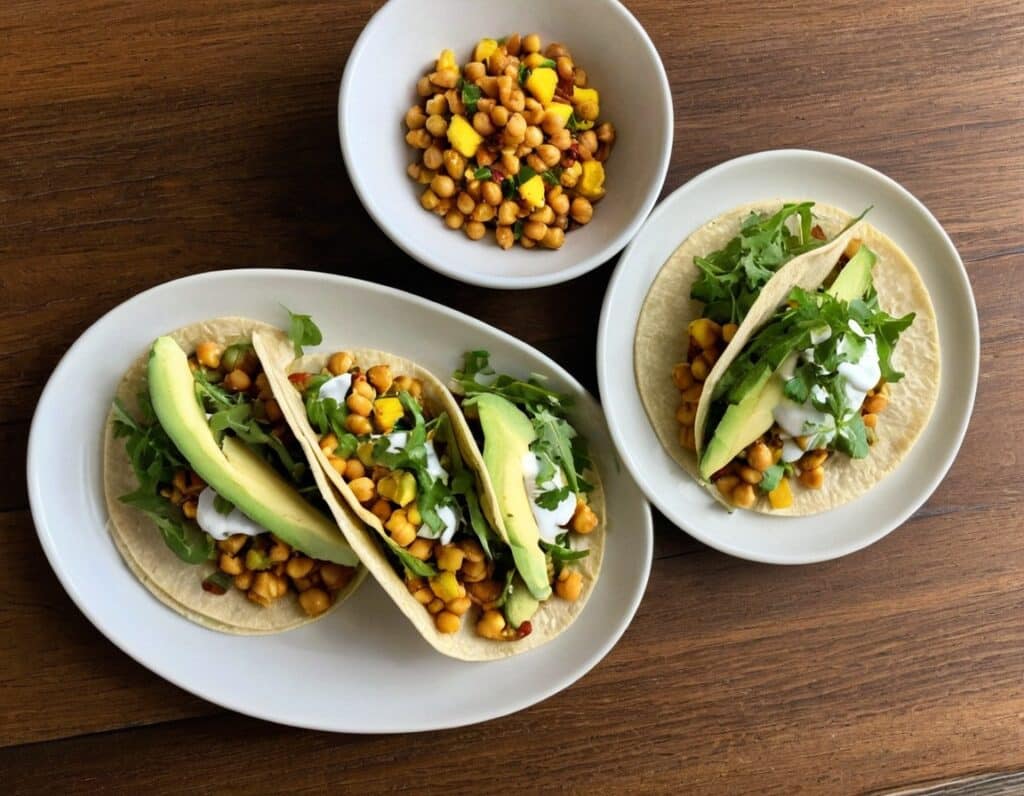

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we hit all five today! Yay!
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- Coconut vs Avocado – Which is Healthier?
- Lettuce vs Arugula – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pomegranate vs Cherries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pomegranate to cherries, we picked the pomegranate.
Why?
In terms of macros, pomegranate is slightly higher in carbs, and/but 4x higher in fiber. That’s already a good start for pomegranates. Lest we be accused of cherry-picking, though, we’ll mention that pomegranate is also slightly higher in protein and fat, for what it’s worth—which is not a lot. As with most fruits, the protein and fat numbers are low importance next to the carb:fiber ratio.
When it comes to vitamins, pomegranate has more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, B9. E. K, and choline. On the other hand, cherries have more of vitamins A and B3. The two fruits are equal in vitamin C. This all makes for a clear win for pomegranate.
In the category of minerals, pomegranate boasts more copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. In contrast, cherries have slightly more calcium. Another win for pomegranate.
Both of these fruits have beneficial polyphenols, each with a slightly different profile, but neither pressingly better than the other.
In short: as ever with healthy foods, enjoy both—diversity is good! But if you’re going to pick on, we recommend the pomegranate.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Pomegranate Peel’s Potent Potential ← so don’t throw it away!
- Cherries’ Very Healthy Wealth Of Benefits!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Which Tea Is Best, By Science?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What kind of tea is best for the health?
It’s popular knowledge that tea is a healthful drink, and green tea tends to get the popular credit for “healthiest”.
Is that accurate? It depends on what you’re looking for…
Black
Its strong flavor packs in lots of polyphenols, often more than other kinds of tea. This brings some great benefits:
As well as effects beyond the obvious:
…and its cardioprotective benefits aren’t just about lowering blood pressure; it improves triglyceride levels as well as improving the LDL to HDL ratio:
The effect of black tea on risk factors of cardiovascular disease in a normal population
Finally (we could say more, but we only have so much room), black tea usually has the highest caffeine content, compared to other teas.
That’s good or bad depending on your own physiology and preferences, of course.
White
White tea hasn’t been processed as much as other kinds, so this one keeps more of its antioxidants, but that doesn’t mean it comes out on top; in this study of 30 teas, the white tea options ranked in the mid-to-low 20s:
White tea is also unusual in its relatively high fluoride content, which is consider a good thing:
White tea: A contributor to oral health
In case you were wondering about the safety of that…
Water Fluoridation: Is It Safe, And How Much Is Too Much?
Green
Green tea ranks almost as high as black tea, on average, for polyphenols.
Its antioxidant powers have given it a considerable anti-cancer potential, too:
- Green tea consumption and breast cancer risk or recurrence: a meta-analysis
- Green tea consumption and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study
…and many others, but you get the idea. Notably:
Green Tea Catechins: Nature’s Way of Preventing and Treating Cancer
…or to expand on that:
About green tea’s much higher levels of catechins, they also have a neuroprotective effect:
Green tea of course is also a great source of l-theanine, which we could write a whole main feature about, and we did:
Red
Also called “rooibos” or (literally translated from Afrikaans to English) “redbush”, it’s quite special in that despite being a “true tea” botanically and containing many of the same phytochemicals as the other teas, it has no caffeine.
There’s not nearly as much research for this as green tea, but here’s one that stood out:
However, in the search for the perfect cup of tea (in terms of phytochemical content), another set of researchers found:
❝The optimal cup was identified as sample steeped for 10 min or longer. The rooibos consumers did not consume it sufficiently, nor steeped it long enough. ❞
Read in full: Rooibos herbal tea: an optimal cup and its consumers
Bottom line
Black, white, green, and red teas all have their benefits, and ultimately the best one for you will probably be the one you enjoy drinking, and thus drink more of.
If trying to choose though, we offer the following summary:
- 🖤 Black tea: best for total beneficial phytochemicals
- 🤍 White tea:best for your oral health
- 💚 Green tea: best for your brain
- ❤️ Red tea: best if you want naturally caffeine-free
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Top Foods Against Neuroinflammation
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chronic inflammation is something you might feel in your joints, but it will usually be in the brain too. There, neuroinflammation can disrupt brain function, affecting stress responses, mood, cognition, and even alter brain structure. It’s also heavily implicated in the pathogenesis of various forms of dementia.
What to do about it
Dr. Tracey Marks, psychiatrist, bids us eat:
- Fatty fish: omega-3-rich fish like salmon reduce neuroinflammation.
- Leafy greens: spinach, kale, and collards protect brain cells and support neurotransmitter production.
- Berries: blueberries and strawberries improve memory and protect neurons.
- Nuts and seeds: walnuts, almonds, and flaxseeds support brain health and reduce inflammation.
- Turmeric: curcumin combats inflammation and supports neuron growth (best with supplements).
- Fermented foods: yogurt and sauerkraut improve gut health, benefiting the brain via the gut-brain axis; not just the vagus nerve, but also, remember that various neurotransmitters (including serotonin) are made in the gut.
Of course, you should also avoid alcohol, nicotine, red meat, processed meat, and ideally also white flour products, and sugary foods (unless they are also rich in fiber, like whole fruit).
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
3 Appetite Suppressants Better Than Ozempic
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Annette Bosworth gives her recommendations, and explains why:
What and how
We’ll get straight to it; the recommendations are:
- Coffee, black, unsweetened: not only suppresses the appetite but also boosts the metabolism, increasing fat burn.
- Salt: especially for when fasting (as under such circumstances we may lose salts without replenishing them), a small taste of this can help satisfy taste buds while replenishing sodium and—depending on the salt—other minerals. For example, if you buy “low-sodium salt” in the supermarket, this is generally sodium chloride cut with potassium chloride and/or occasionally magnesium sulfate.
- Ketones (MCT oil): ketones can suppress hunger, particularly when fasting causes blood sugar levels to drop. Supplementing with MCT oil promotes ketone production in the liver, training the body to produce more ketones naturally, thus curbing appetite.
For more on these including the science of them, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Ozempic vs Five Natural Supplements
- Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety
- The Fruit That Can Specifically Reduce Belly Fat
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Whole – by Dr. T. Colin Campbell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most of us have at least a broad idea of what we’re supposed to be eating, what nutrients we should be getting. Many of us look at labels, and try to get our daily dose of this and that and the other.
And what we don’t get from food? There are supplements.
Dr. Campbell thinks we can do better:
Perhaps most critical in this book, where it stands out from others (we may already know, for example, that we should try to eat diverse plants and whole foods) is its treatment of why many supplements aren’t helpful.
We tend to hear “supplements are a waste of money” and sometimes they are, sometimes they aren’t. How to know the difference?
Key: things directly made from whole food sources will tend to be better. Seems reasonable, but… why? The answer lies in what else those foods contain. An apple may contain a small amount of vitamin C, less than a vitamin C tablet, but also contains a whole host of other things—tiny phytonutrients, whose machinations are mostly still mysteries to us—that go with that vitamin C and help it work much better. Lab-made supplements won’t have those.
There’s a lot more to the book… A chunk of which is a damning critique of the US healthcare system (the author argues it would be better named a sicknesscare system). We also learn about getting a good balance of macro- and micronutrients from our diet rather than having to supplement so much.
The style is conversational, while not skimping on the science. The author has had more than 150 papers published in peer-reviewed journals, and is no stranger to the relevant academia. Here, however, he focuses on making things easily comprehensible to the lay reader.
In short: if you’ve ever wondered how you’re doing at getting a good nutritional profile, and how you could do better, this is definitely the book for you.
Click here to check out “Whole” on Amazon today, and level up your daily diet!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why We Get Fat: And What to Do About It – by Gary Taubes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Taubes’ “The Case Against Sugar“. What does this one bring differently?
Mostly, it’s a different focus. Unsurprisingly, Taubes’ underlying argument is the same: sugar is the biggest dietary health hazard we face. However, this book looks at it specifically through the lens of weight loss, or avoiding weight gain.
Taubes argues for low-carb in general; he doesn’t frame it specifically as the ketogenic diet here, but that is what he is advocating. However, he also acknowledges that not all carbs are created equal, and looks at several categories that are relatively better or worse for our insulin response, and thus, fat management.
If the book has a fault it’s that it does argue a bit too much for eating large quantities of meat, based on Weston Price’s outdated and poorly-conducted research. However, if one chooses to disregard that, the arguments for a low-carb diet for weight management remain strong.
Bottom line: if you’d like to cut some fat without eating less (or exercising more), this book offers a good, well-explained guide for doing so.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: