The Book Of Hormones – by Dr. Shweta Patel
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The subtitle promising “through every stage of life” is a slight overstatement, as the book barely touches on puberty, but we know that the vast majority of our readers have left that one far behind in the past, so probably this is not such an issue.
Where the book gives more attention is in general adult life, through the years of potential fertility, into menopause and beyond. This means lots about the hormonal fluctuations inherent to the menstrual cycle (both the normal, and the still-quite-commonly abnormal, e.g. in cases of PCOS etc), the before-during-after of pregnancy, and many hormonal matters that are not related to sex hormones, such as stress-related hormones and food-related hormones. As such, the book certainly lives up to its title; it is indeed “the book of hormones”.
The style is light and conversational; we get a lot of lessons in chemistry here, but it never feels like it, and there’s certainly no hard science, just clear and easy explanations.
Bottom line: if you’d like to understand hormones quite comprehensively but in a light-hearted manner, this book is a very pleasant and educational read.
Click here to check out The Book Of Hormones, and understand them!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hit A Weight Loss Plateau? Here’s What To Do
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Around this time of year (early April, at time of writing) it’s especially common for people to hit a plateau in our progress towards various goals.
When it comes to weight loss specifically, a large (n=24,035) study of mostly women (19.972/24,035 = 83.09%) aged 31–70 (with more than half being in the 51–70 range) has good news about this:
Most people who sustainably lose weight weight over the course of a year, have a plateau at some point, usually at least one three-month plateau.
The top three weight loss patterns were:
- 15% lost weight for 6 months, then maintained their weight for a further 6 months, resulting in an average 11kg weight loss after a year (12% of their starting body weight)
- 11% lost weight in the first 3 months, then maintained for 9 months, losing 5kg after a year (nearly 6% of their starting body weight)
- 9% lost weight for 9 months, followed by 3 months of maintenance, resulting in an average 16kg loss (17% of their starting body weight)
You can read the full paper here: Weight Loss Patterns and Outcomes Over 12 Months on a Commercial Weight Management Program (CSIRO Total Wellbeing Diet Online): Large-Community Cohort Evaluation Study
Did you notice the reframe there? What may be seen (and not welcomed) by the individual is a plateau, but what it also is objectively, is weight loss maintenance. In other words, not regaining weight, as we all know can be all too easy for many.
You may be thinking: “but I want to continue losing weight!”
And that’s fine. The trick is to use the maintenance phase (or plateau, if you want to call it that) as an opportunity to assess what’s working for you and what’s not, and where you want to go from here.
The chances are good that your metabolism has simply adapted to whatever diet/exercises changes you made to your lifestyle… And that’s good!
Three months ago, you wanted your body to have this new “set point”, and now you have it. Congratulations on the improved metabolism!
Now, imagine yourself starting again, but this time you’re starting with a better metabolism than last time you started. What will you do next to up the ante?
Whatever you do, we recommend making sure to do it healthily, for example: How To Lose Weight (Healthily!)
You might even want to coast for a little in a maintenance phase, and use the opportunity to improve related areas of your health, before diving back into your next weight loss phase.
For example, you might want to: Stop Trying To Lose Weight (And Do This Instead) ← this is about metabolic health in a more general fashion, and is very important
Alternatively, you might want to take the opportunity to build a little muscle (which in turn will improve your metabolic health, because muscle “costs” calories to maintain, while fat cues your body to dial down the metabolism to survive the famine for which it thinks you were preparing).
If you want to do that, then check out: Can You Gain Muscle & Lose Fat At The Same Time?
And if at any point your weight loss journey (or perhaps a plateau somewhere along such) is getting you down, then… You know the saying “have fun and be yourself”? The trick here is to have fun and be your best self. Seriously! Mindset is actually really important, not just for your mental health, but also for your physical health, and yes, also for weight loss specifically, if that’s your goal.
See: 8 Pillars of Weight Loss Explained ← Surprise, diet is #6 and exercise is #7, while emotional freedom and resilience is #1 😎
Want to know more?
Check out this trio of articles that’ll keep you on the right path:
- How To Plan For The Unplannable & Always Follow Through
- How To Avoid Slipping Into (Bad) Old Habits
- How To Keep On Keeping On… Long Term!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Fight Inflammation & Protect Your Brain, With Quercetin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Querying Quercetin
Quercetin is a flavonoid (and thus, antioxidant) pigment found in many plants. Capers, radishes, and coriander/cilantro score highly, but the list is large:
USDA Database for the Flavonoid Content of Selected Foods
Indeed,
❝Their regular consumption is associated with reduced risk of a number of chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease (CVD) and neurodegenerative disorders❞
~ Dr. Aleksandra Kozłpwsla & Dr. Dorota Szostak-Wegierek
Read more: Flavonoids—food sources and health benefits
For this reason, quercetin is often sold/consumed as a supplement on the strength of its health-giving properties.
But what does the science say?
Quercetin and inflammation
In short, it helps:
❝500 mg per day quercetin supplementation for 8 weeks resulted in significant improvements in clinical symptoms, disease activity, hs-TNFα, and Health Assessment Questionnaire scores in women with rheumatoid athritis❞
Quercetin and blood pressure
It works, if antihypertensive (i.e., blood pressure lowering) effect is what you want/need:
❝…significant effect of quercetin supplementation in the reduction of BP, possibly limited to, or greater with dosages of >500 mg/day.❞
~ Dr. Maria-Corina Serban et al.
Quercetin and diabetes
We’re less confident to claim this one, because (almost?) all of the research so far as been in non-human animals or in vitro. As one team of researchers put it:
❝Despite the wealth of in animal research results suggesting the anti-diabetic and its complications potential of quercetin, its efficacy in diabetic human subjects is yet to be explored❞
Quercetin and neuroprotection
Research has been done into the effect of quercetin on the risk of Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, and they found…
❝The data indicate that quercetin is the major neuroprotective component in coffee against Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease❞
Read more: Quercetin, not caffeine, is a major neuroprotective component in coffee
Summary
Quercetin is a wonderful flavonoid that can be enjoyed as part of one’s diet and by supplementation. In terms of its popular health claims:
- It has been found very effective for lowering inflammation
- It has a moderate blood pressure lowering effect
- It may have anti-diabetes potential, but the science is young
- It has been found to have a potent neuroprotective effect
Want to get some?
We don’t sell it, but for your convenience, here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
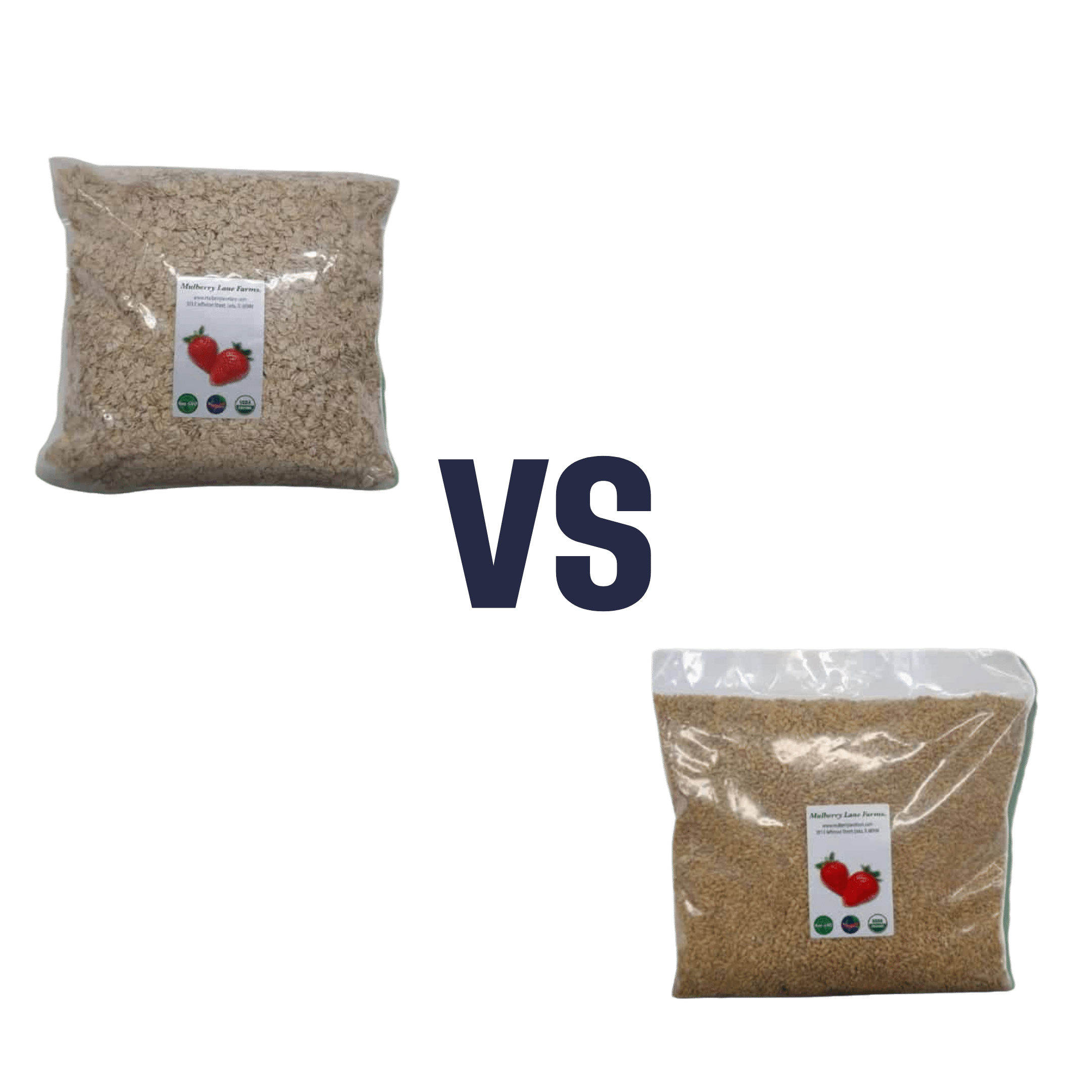
Red Lentils vs Green Lentils – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing red lentils to green lentils, we picked the green.
Why?
Yes, they’re both great. But there are some clear distinctions!
First, know: red lentils are, secretly, hulled brown lentils. Brown lentils are similar to green lentils, just a little less popular and with (very) slightly lower nutritional values, as a rule.
By hulling the lentils, the first thing that needs mentioning is that they lose some of their fiber, since this is what was removed. While we’re talking macros, this does mean that red lentils have proportionally more protein, because of the fiber weight lost. However, because green lentils are still a good source of protein, we think the fat that green lentils have much more fiber is a point in their favor.
In terms of micronutrients, they’re quite similar in vitamins (mostly B-vitamins, of which, mostly folate / vitamin B9), and when it comes to minerals, they’re similarly good sources of iron, but green lentils contain more magnesium and potassium.
Green lentils also contain more antixoidants.
All in all, they both continue to be very respectable parts of anyone’s diet—but in a head-to-head, green lentils do come out on top (unless you want to prioritize slightly higher protein above everything else, in which case, red).
Want to get some in? Here are the specific products we featured today:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure ← incidentally, the potassium content of green lentils also helps minimize the harm done by sodium in one’s diet
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Debunking the myth that vaccines cause autism
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The myth that autism is linked to childhood vaccines first appeared in a 1998 study by British physician Dr. Andrew Wakefield. The study was later retracted, and Wakefield was discredited. But nearly three decades after the study’s publication, the myth persists, championed by activists, political leaders, and even potential health officials.
There is overwhelming evidence that there is no link between vaccines and autism. “No one has any real or solid evidence that vaccines cause autism,” says Catherine Lord, a psychologist and autism researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Here are just some of the many reasons that we know vaccines don’t cause autism.
The Wakefield study has been thoroughly discredited
In 1998, the Lancet published a study describing a small group of children who reportedly had bowel inflammation and developed autism within a month of getting the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. The study proposed that the vaccination triggered bowel inflammation and developmental delays, including autism. Lead author Andrew Wakefield coined the term “autistic enterocolitis” to describe the condition he and his colleagues claimed to have discovered.
The study received significant media attention and immediate criticism from scientists, who pointed out the study’s small size, lack of controls, and insufficient evidence to support its conclusions.
Subsequent research published over the next few years refuted Wakefield’s findings. A 1999 Lancet study found no link between autism and the MMR vaccine, and a 2001 study found no evidence of a link or the existence of so-called autistic enterocolitis.
In 2010, the Lancet finally retracted Wakefield’s fraudulent study, noting that “several elements” of the study were “incorrect” and that the experiments carried out on children had not been approved by an ethics board. The journal’s editor called the paper’s conclusions “utterly false.”
A few months later, Wakefield was stripped of his medical license by the United Kingdom’s General Medical Council. The council deemed Wakefield “dishonest and irresponsible” and concluded that he conducted unethical experiments on children.
The committee’s investigation also revealed that, less than a year before he published his study claiming that the MMR vaccine was linked to bowel inflammation that triggered autism, Wakefield filed a patent for a standalone measles vaccine and inflammatory bowel disease treatment.
Thimerosal was removed from childhood vaccines in 2001—with no effect on autism rates
A 2003 study published by a conservative group known for promoting anti-science myths—including that HIV doesn’t cause AIDS—first proposed that the preservative thimerosal in childhood vaccines is linked to autism. This supposed link was subsequently disproven.
Thimerosal is added in small amounts to some vaccines to prevent dangerous bacterial and fungal contamination. The substance contains ethylmercury, a form of mercury that the body quickly and safely processes in small doses.
Ethylmercury is different from methylmercury, a far more dangerous form of mercury that is toxic at low doses. By contrast, the small amount of thimerosal in some vaccines is harmless to humans and is equal to the amount of mercury in a can of tuna.
The preservative was removed from childhood vaccines as a precautionary measure in 2001. With the exception of some flu shots, no childhood vaccine contains the preservative and hasn’t for more than two decades. Autism rates have not decreased as a result of thimerosal being removed from childhood immunization vaccines. While some types of the annual flu vaccine contain thimerosal, you can get one without it.
Extensive research also shows that neither thimerosal nor methylmercury at any dose is linked to autism. A 2008 study of statewide California data found that autism rates “increased consistently for children born from 1989 through 2003, inclusive of the period when exposure to [thimerosal-containing vaccines] has declined.”
Autism rates are the same in vaccinated and unvaccinated children
Vaccine opponents often falsely claim that vaccinated children are more likely than unvaccinated children to develop autism. Decades of research disprove this false claim.
A 2002 analysis of every child born in Denmark over eight years found that children who received MMR vaccines were no more likely to be diagnosed with autism than unvaccinated children.
A 2015 study of over 95,000 U.S. siblings found that MMR vaccination is not associated with increased autism diagnosis. This was true even among the siblings of children with autism, who are seven times more likely to develop autism than children without an autistic sibling.
And a 2018 study found some evidence that children with autism—and their siblings—were more likely to be unvaccinated or under-vaccinated than children without autism.
Vaccination also has no impact on autism rates at the population level, regardless of the age at which children get vaccinated.
“In comparing countries that have different timing and levels of vaccination … there’s no difference in autism,” says Lord. “You can look at different countries with different rates of autism, and there’s no relationship between the rates of autism and vaccinations.”
Countries such as Taiwan, Tunisia, Turkey, and Morocco, which have some of the world’s lowest autism rates, have childhood immunization rates that are nearly identical to countries with the highest autism rates, including Sweden, Japan, Brunei, and Singapore.
Improved awareness and diagnosis play a role in rising autism rates
Autism was first described in 1911 when it was considered to be a form of severe schizophrenia. Over a century later, our understanding of autism has changed drastically, as have diagnostic standards.
A 2013 scientific article describing how medical and social perceptions of autism have evolved explains that “the diagnoses of schizophrenia, psychosis and autism in children were largely interchangeable during the 1940s and 1950s.” Beginning in the 1960s, methods of diagnosing autism improved, “increasing the number of children who were considered to display autistic traits.”
The autism diagnosis was changed to autism spectrum disorder in 2013. “This category is now very broad, which was an intentional choice to help provide services to the greatest number of people who might need them,” writes Gideon Meyerowitz-Katz, an epidemiologist and creator of the popular Health Nerd blog.
“Rather than the severe intellectual disability of the 1940s and 50s, [autism spectrum disorder] is a group of behaviours that can be any severity as long as they are persistent and impact people’s daily functioning in a significant way.”
For more information about autism, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Optimism Seriously Increases Longevity!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Always look on the bright side for life
❝I’m not a pessimist; I’m a realist!❞
~ every pessimist ever
To believe self-reports, the world is divided between optimists and realists. But how does your outlook measure up, really?
Below, we’ve included a link to a test, and like most free online tests, this is offered “as-is” with the usual caveats about not being a clinical diagnostic tool, this one actually has a fair amount of scientific weight behind it:
❝Empirical testing has indicated the validity of the Optimism Pessimism Instrument as published in the scientific journal Current Psychology: Research and Reviews.
The IDRlabs Optimism/Pessimism Test (IDR-OPT) was developed by IDRlabs. The IDR-OPT is based on the Optimism/Pessimism Instrument (OPI) developed by Dr. William Dember, Dr. Stephanie Martin, Dr. Mary Hummer, Dr. Steven Howe, and Dr. Richard Melton, at the University of Cincinnati.❞
Take This Short (1–2 mins) Test
How did you score? And what could you do to improve on that score?
We said before that we’d do a main feature on this sometime, and today’s the day! Fits with the theme of Easter too, as for those who observe, this is a time for a celebration of hope, new beginnings, and life stepping out of the shadows.
On which note, before we go any further, let’s look at a very big “why” of optimism…
There have been many studies done regards optimism and health, and they generally come to the same conclusion: optimism is simply good for the health.
Here’s an example. It’s a longitudinal study, and it followed 121,700 women (what a sample size!) for eight years. It controlled for all kinds of other lifestyle factors (especially smoking, drinking, diet, and exercise habits, as well as pre-existing medical conditions), so this wasn’t a case of “people who are healthy are more optimistic as a result. And, in the researchers’ own words…
❝We found strong and statistically significant associations of increasing levels of optimism with decreasing risks of mortality, including mortality due each major cause of death, such as cancer, heart disease, stroke, respiratory disease, and infection.
Importantly, findings were maintained after close control for potential confounding factors, including sociodemographic characteristics and depression❞
Read: Optimism and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Prospective Cohort Study
So that’s the why. Now for the how…
Positive thinking is not what you think it is
A lot of people think of “think positive thoughts” as a very wishy-washy platitude, but positive thinking isn’t about ignoring what’s wrong, or burying every negative emotion.
Rather, it is taking advantage of the basic CBT, DBT, and, for that matter, NLP principles:
- Our feelings are driven by our thoughts
- Our thoughts can be changed by how we frame things
This is a lot like the idea that “there’s not such thing as bad weather; only the wrong clothes”. Clearly written by someone who’s never been in a hurricane, but by and large, the principle stands true.
For example…
- Most problems can be reframed as opportunities
- Replace “I have to…” with “I get to…”
- Will the task be arduous? It’ll be all the better looking back on it.
- Did you fail abjectly? Be proud that you lived true to your values anyway.
A lot of this is about focusing on what you can control. If you live your life by your values (first figure out what they are, if you haven’t already), then that will become a reassuring thing that you can always count on, no matter what.
Practice positive self-talk (eliminate the negative)
We often learn, usually as children, to be self deprecatory so as to not appear immodest. While modesty certainly has its place, we don’t have to trash ourselves to do that!
There are various approaches to this, for example:
- Replacing a self-criticism (whether it was true or not) with a neutral or positive statement that you know is true. “I suck at xyz” is just putting yourself down, “Xyz is a challenge for me” asks the question, how will you rise to it?
- Replacing a self-criticism with irony. It doesn’t matter how dripping with sarcasm your inner voice is, the words will still be better. “Glamorous as ever!” after accidentally putting mascara in your eye. “So elegant and graceful!” after walking into furniture. And so on.
Practice radical acceptance
This evokes the “optimistic nihilism” approach to life. It’s perhaps not best in all scenarios, but if you’re consciously and rationally pretty sure something is going to be terrible (and/or know it’s completely outside of your control), acknowledging that possibility (or even, likelihood) cheerfully. Borrowing from the last tip, this can be done with as much irony as you find necessary. For example:
Facing a surgery the recovery from which you know categorically will be very painful: with a big smile “Yep, I am going to be in a lot of pain, so that’s going to be fun!” (fun fact: psychological misery will not make the physical pain any less painful, so you might as well see the funny side) ← see link for additional benefits laughter can add to health-related quality of life)
Plan for the future with love
You know the whole “planting trees in whose shade you’ll never sit”, thing, but: actually for yourself too. Plan (and act!) now, out of love and compassion for your future self.
Simple example: preparing (or semi-preparing, if appropriate) breakfast for yourself the night before, when you know in the morning you’ll be tired, hungry, and/or pressed for time. You’ll wake up, remember that you did that, and…
Tip: at moments like that, take a moment to think “Thanks, past me”. (Or call yourself by your name, whatever works for you. For example I, your writer here, might say to myself “Thanks, past Nastja!”)
This helps to build a habit of gratitude for your past self and love for your future self.
This goes for little things like the above, but it also goes for things whereby there’s much longer-term delayed gratification, such as:
- Healthy lifestyle changes (usually these see slow, cumulative progress)
- Good financial strategies (usually these see slow, cumulative progress)
- Long educational courses (usually these see slow, cumulative progress)
Basically: pay it forward to your future self, and thank yourself later!
Some quick ideas of systems and apps that go hard on the “long slow cumulative progress” approach that you can look back on with pride:
- Noom—nutritional program with a psychology-based approach to help you attain and maintain your goals, long term
- You Need A Budget—we’ve recommended it before and we’ll recommend it again. This is so good. If you click through, you can see a short explanation of what makes it so different to other budgeting apps.
- Duolingo—the famously persistence-motivational language learning app
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hormones & Health, Beyond The Obvious
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Wholesome Health
This is Dr. Sara Gottfried, who some decades ago got her MD from Harvard and specialized as an OB/GYN at MIT. She’s since then spent the more recent part of her career educating people (mostly: women) about hormonal health, precision, functional, & integrative medicine, and the importance of lifestyle medicine in general.
What does she want us to know?
Beyond “bikini zone health”
Dr. Gottfried urges us to pay attention to our whole health, in context.
“Women’s health” is often thought of as what lies beneath a bikini, and if it’s not in those places, then we can basically treat a woman like a man.
And that’s often not actually true—because hormones affect every living cell in our body, and as a result, while prepubescent girls and postmenopausal women (specifically, those who are not on HRT) may share a few more similarities with boys and men of similar respective ages, for most people at most ages, men and women are by default quite different metabolically—which is what counts for a lot of diseases! And note, that difference is not just “faster” or “slower””, but is often very different in manner also.
That’s why, even in cases where incidence of disease is approximately similar in men and women when other factors are controlled for (age, lifestyle, medical history, etc), the disease course and response to treatment may vary considerable. For a strong example of this, see for example:
- The well-known: Heart Attack: His & Hers ← most people know these differences exist, but it’s always good to brush up on what they actually are
- The less-known: Statins: His & Hers ← most people don’t know these differences exist, and it pays to know, especially if you are a woman or care about one
Nor are brains exempt from his…
The female brain (kinda)
While the notion of an anatomically different brain for men and women has long since been thrown out as unscientific phrenology, and the idea of a genetically different brain is… Well, it’s an unreliable indicator, because technically the cells will have DNA and that DNA will usually (but not always; there are other options) have XX or XY chromosomes, which will usually (but again, not always) match apparent sex (in about 1/2000 cases there’s a mismatch, which is more common than, say, red hair; sometimes people find out about a chromosomal mismatch only later in life when getting a DNA test for some unrelated reason), and in any case, even for most of us, the chromosomal differences don’t count for much outside of antenatal development (telling the default genital materials which genitals to develop into, though this too can get diverted, per many intersex possibilities, which is also a lot more common than people think) or chromosome-specific conditions like colorblindness…
The notion of a hormonally different brain is, in contrast to all of the above, a reliable and easily verifiable thing.
See for example:
Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear
Dr. Gottfried urges us to take the above seriously!
Because, if women get Alzheimer’s much more commonly than men, and the disease progresses much more quickly in women than men, but that’s based on postmenopausal women not on HRT, then that’s saying “Women, without women’s usual hormones, don’t do so well as men with men’s usual hormones”.
She does, by the way, advocate for bioidentical HRT for menopausal women, unless contraindicated for some important reason that your doctor/endocrinologist knows about. See also:
Menopausal HRT: A Tale Of Two Approaches (Bioidentical vs Animal)
The other very relevant hormone
…that Dr. Gottfried wants us to pay attention to is insulin.
Or rather, its scrubbing enzyme, the prosaically-named “insulin-degrading enzyme”, but it doesn’t only scrub insulin. It also scrubs amyloid beta—yes, the same that produces the amyloid beta plaques in the brain associated with Alzheimer’s. And, there’s only so much insulin-degrading enzyme to go around, and if it’s all busy breaking down excess insulin, there’s not enough left to do the other job too, and thus can’t break down amyloid beta.
In other words: to fight neurodegeneration, keep your blood sugars healthy.
This may actually work by multiple mechanisms besides the amyloid hypothesis, by the way:
The Surprising Link Between Type 2 Diabetes & Alzheimer’s
Want more from Dr. Gottfried?
You might like this interview with Dr. Gottfried by Dr. Benson at the IMCJ:
Integrative Medicine: A Clinician’s Journal | Conversations with Sara Gottfried, MD
…in which she discusses some of the things we talked about today, and also about her shift from a pharmaceutical-heavy approach to a predominantly lifestyle medicine approach.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: