Keep Your Wits About You – by Dr. Vonetta Dotson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Dotson sets out to provide the reader with the tools to maintain good brain health at any age, though she does assume the reader to be in midlife or older.
She talks us through the most important kinds of physical activity, mental activity, and social activity, as well as a good grounding in brain-healthy nutrition, and how to beat the often catch-22 situation of poor sleep.
If you are the sort of person who likes refreshers on what you have just read, you’ll enjoy that the final two chapters repeat the information from chapters 2–6. If not, then well, if you skip the final 2 chapters the book will be 25% shorter without loss of content.
The style is enthusiastic; when it comes to her passion for the brain, Dr. Dotson both tells and shows, in abundance. While some authors may take care to break down the information in a way that can be understood from skimming alone, Dr. Dotson assumes that the reader’s interest will match hers, and thus will not mind a lot of lengthy prose with in-line citations. So, provided that’s the way you like to read, it’ll suit you too.
Bottom line: if you are looking for a book on maintaining optimal brain health that covers the basics without adding advice that is out of the norm, then this is a fine option for that!
Click here to check out Keep Your Wits About You, and keep your wits about you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Case of the Armadillo: Is It Spreading Leprosy in Florida?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — In an open-air barn at the edge of the University of Florida, veterinarian Juan Campos Krauer examines a dead armadillo’s footpads and ears for signs of infection.
Its claws are curled tight and covered in blood. Campos Krauer thinks it was struck in the head while crossing a nearby road.
He then runs a scalpel down its underside. He removes all the important organs: heart, liver, kidneys. Once the specimens are bottled up, they’re destined for an ultra-cold freezer in his lab at the college.
Campos Krauer plans to test the armadillo for leprosy, an ancient illness also known as Hansen’s disease that can lead to nerve damage and disfigurement in humans. He and other scientists are trying to solve a medical mystery: why Central Florida has become a hot spot for the age-old bacteria that cause it.
Leprosy remains rare in the United States. But Florida, which often reports the most cases of any state, has seen an uptick in patients. The epicenter is east of Orlando. Brevard County reported a staggering 13% of the nation’s 159 leprosy cases in 2020, according to a Tampa Bay Times analysis of state and federal data.
Many questions about the phenomenon remain unanswered. But leprosy experts believe armadillos play a role in spreading the illness to people. To better understand who’s at risk and to prevent infections, about 10 scientists teamed up last year to investigate. The group includes researchers from the University of Florida, Colorado State University, and Emory University in Atlanta.
“How this transmission is happening, we really don’t know,” said Ramanuj Lahiri, chief of the laboratory research branch for the National Hansen’s Disease Program, which studies the bacteria involved and cares for leprosy patients across the country.
‘Nothing Was Adding Up’
Leprosy is believed to be the oldest human infection in history. It probably has been sickening people for at least 100,000 years. The disease is highly stigmatized — in the Bible, it was described as a punishment for sin. In more modern times, patients were isolated in “colonies” around the world, including in Hawaii and Louisiana.
In mild cases, the slow-growing bacteria cause a few lesions. If left untreated, they can paralyze the hands and feet.
But it’s actually difficult to fall ill with leprosy, as the infection isn’t very contagious. Antibiotics can cure the ailment in a year or two. They’re available for free through the federal government and the World Health Organization, which launched a campaign in the 1990s to eliminate leprosy as a public health problem.
In 2000, reported U.S. cases dropped to their lowest point in decades with 77 infections. But they later increased, averaging about 180 per year from 2011 to 2020, according to data from the National Hansen’s Disease Program.
During that time, a curious trend emerged in Florida.
In the first decade of the 21st century, the state logged 67 cases. Miami-Dade County noted 20 infections — the most of any Florida county. The vast majority of its cases were acquired outside the U.S., according to a Times analysis of Florida Department of Health data.
But over the next 10 years, recorded cases in the state more than doubled to 176 as Brevard County took center stage.
The county, whose population is about a fifth the size of Miami-Dade’s, logged 85 infections during that time — by far the most of any county in the state and nearly half of all Florida cases. In the previous decade, Brevard noted just five cases.
Remarkably, at least a quarter of Brevard’s infections were acquired within the state, not while the individuals were abroad. India, Brazil, and Indonesia diagnose more leprosy cases than anywhere, reporting over 135,000 infections combined in 2022 alone. People were getting sick even though they hadn’t traveled to such areas or been in close contact with existing leprosy patients, said Barry Inman, a former epidemiologist at the Brevard health department who investigated the cases and retired in 2021.
“Nothing was adding up,” Inman said.
A few patients recalled touching armadillos, which are known to carry the bacteria. But most didn’t, he said. Many spent a lot of time outdoors, including lawn workers and avid gardeners. The cases were usually mild.
It was difficult to nail down where people got the illness, he added. Because the bacteria grow so slowly, it can take anywhere from nine months to 20 years for symptoms to begin.
Amoeba or Insect Culprits?
Heightened awareness of leprosy could play a role in Brevard’s groundswell of cases.
Doctors must report leprosy to the health department. Yet Inman said many in the county didn’t know that, so he tried to educate them after noticing cases in the late 2000s.
But that’s not the sole factor at play, Inman said.
“I don’t think there’s any doubt in my mind that something new is going on,” he said.
Other parts of Central Florida have also recorded more infections. From 2011 to 2020, Polk County logged 12 cases, tripling its numbers compared with the previous 10 years. Volusia County noted 10 cases. It reported none the prior decade.
Scientists are honing in on armadillos. They suspect the burrowing critters may indirectly cause infections through soil contamination.
Armadillos, which are protected by hard shells, serve as good hosts for the bacteria, which don’t like heat and can thrive in the animals whose body temperatures range from a cool 86-95 degrees.
Colonists probably brought the disease to the New World hundreds of years ago, and somehow armadillos became infected, said Lahiri, the National Hansen’s Disease Program scientist. The nocturnal mammals can develop lesions from the illness just as humans can. More than 1 million armadillos occupy Florida, estimated Campos Krauer, an assistant professor in the University of Florida’s Department of Large Animal Clinical Sciences.
How many carry leprosy is unclear. A study published in 2015 of more than 600 armadillos in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, and Mississippi found that about 16% showed evidence of infection. Public health experts believe leprosy was previously confined to armadillos west of the Mississippi River, then spread east.
Handling the critters is a known hazard. Lab research shows that single-cell amoebas, which live in soil, can also carry the bacteria.
Armadillos love to dig up and eat earthworms, frustrating homeowners whose yards they damage. The animals may shed the bacteria while hunting for food, passing it to amoebas, which could later infect people.
Leprosy experts also wonder if insects help spread the disease. Blood-sucking ticks might be a culprit, lab research shows.
“Some people who are infected have little to no exposure to the armadillo,” said Norman Beatty, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Florida. “There is likely another source of transmission in the environment.”
Campos Krauer, who’s been searching Gainesville streets for armadillo roadkill, wants to gather infected animals and let them decompose in a fenced-off area, allowing the remains to soak into a tray of soil while flies lay eggs. He hopes to test the dirt and larvae to see if they pick up the bacteria.
Adding to the intrigue is a leprosy strain found only in Florida, according to scientists.
In the 2015 study, researchers discovered that seven armadillos from the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which is mostly in Brevard but crosses into Volusia, carried a previously unseen version of the pathogen.
Ten patients in the region were stricken with it, too. At the genetic level, the strain is similar to another type found in U.S. armadillos, said Charlotte Avanzi, a Colorado State University researcher who specializes in leprosy.
It’s unknown if the strain causes more severe disease, Lahiri said.
Reducing Risk
The public should not panic about leprosy, nor should people race to euthanize armadillos, researchers warn.
Scientists estimate that over 95% of the global human population has a natural ability to ward off the disease. They believe months of exposure to respiratory droplets is needed for person-to-person transmission to occur.
But when infections do happen, they can be devastating.
“If we better understand it,” Campos Krauer said, “the better we can learn to live with it and reduce the risk.”
The new research may also provide insight for other Southern states. Armadillos, which don’t hibernate, have been moving north, Campos Krauer said, reaching areas like Indiana and Virginia. They could go farther due to climate change.
People concerned about leprosy can take simple precautions, medical experts say. Those working in dirt should wear gloves and wash their hands afterward. Raising garden beds or surrounding them with a fence may limit the chances of soil contamination. If digging up an armadillo burrow, consider wearing a face mask, Campos Krauer said.
Don’t play with or eat the animals, added John Spencer, a scientist at Colorado State University who studies leprosy transmission in Brazil. They’re legal to hunt year-round in Florida without a license.
Campos Krauer’s team has so far examined 16 dead armadillos found on Gainesville area roads, more than 100 miles from the state’s leprosy epicenter, trying to get a preliminary idea of how many carry the bacteria.
None has tested positive yet.
This article was produced through a partnership between KFF Health News and the Tampa Bay Times.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
What does lion’s mane mushroom actually do, anyway?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may know it as an ingredient in nootropic supplements. You may have heard of lion’s mane mushroom coffee. You may know it as the big shaggy white mushroom that grows in nature and can look very impressive.
What’s special about it?
The lion’s mane mushroom, or Hericium erinaceus (we mention, as studies we’ll cite often use the botanical name) is an adaptogenic agent that has an established ability to promote nerve regeneration through nerve growth factor neurotrophic activity. In other words, it helps (re)grow neurons.
In a 2023 study, researchers wondered if its abilities (well-established in the peripheral nervous system) would work in the central nervous system too, namely the brain, specifically the hippocampus (responsible for memory).
To boil what they found down to a single line, they concluded:
❝[Lion’s mane extract] therefore acts through a novel pan-neurotrophic signaling pathway, leading to improved cognitive performance.❞
You can read the full study for yourself (with pictures!) here:
Limitations of the study
It’s worth noting that the above study was performed on mice brains, not those of humans. As there is a shortage of human volunteers willing to have their brains sliced and examined under microscopes, we do not expect this study to be repeated with humans any time soon.
So, are there human studies that have been done?
There are! Particularly promising was this 2020 study of people with Alzheimer’s disease, wherein supplementation with 1g of lion’s mane mushroom daily for 49 weeks significantly increased cognitive test scores compared with a placebo; you can read about it here:
Additionally, this 2019 study showed that taking 1.2g daily for eight weeks helped relieve depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders in overweight or obese patiences:
Are there other health benefits?
It seems so! Unfortunately, most of its other health claims are only supported by animal studies so far, aside from one small study funded by a supplement company for their supplement that contained mostly Agaricus blazei (a different mushroom) with 14% lion’s mane.
However, in animal studies, lion’s mane has also shown promise:
- For digestion
- Against inflammation
- For cardiovascular health
- For diabetes management
- Against cancer
- Against aging
Where can I get it?
We don’t sell it (or anything else, for that matter) but if you’d like to try it, here’s an example product for your convenience:
Share This Post
-
Yes, adults can develop food allergies. Here are 4 types you need to know about
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you didn’t have food allergies as a child, is it possible to develop them as an adult? The short answer is yes. But the reasons why are much more complicated.
Preschoolers are about four times more likely to have a food allergy than adults and are more likely to grow out of it as they get older.
It’s hard to get accurate figures on adult food allergy prevalence. The Australian National Allergy Council reports one in 50 adults have food allergies. But a US survey suggested as many as one in ten adults were allergic to at least one food, with some developing allergies in adulthood.
What is a food allergy
Food allergies are immune reactions involving immunoglobulin E (IgE) – an antibody that’s central to triggering allergic responses. These are known as “IgE-mediated food allergies”.
Food allergy symptoms that are not mediated by IgE are usually delayed reactions and called food intolerances or hypersensitivity.
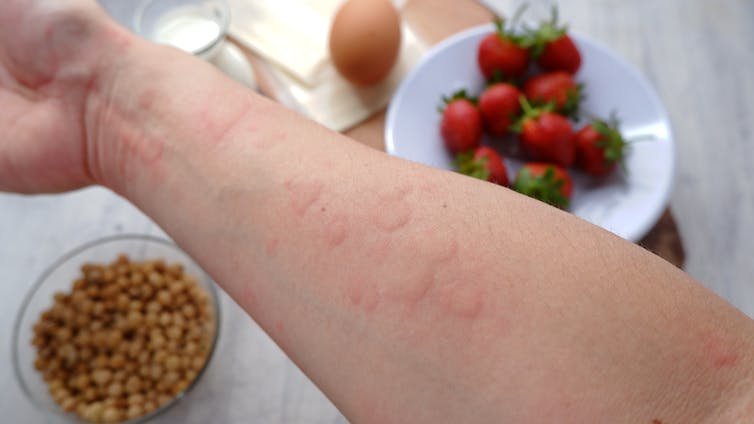
Food allergy symptoms can include hives, swelling, difficulty swallowing, vomiting, throat or chest tightening, trouble breathing, chest pain, rapid heart rate, dizziness, low blood pressure or anaphylaxis.
Symptoms include hives. wisely/Shutterstock IgE-mediated food allergies can be life threatening, so all adults need an action management plan developed in consultation with their medical team.
Here are four IgE-mediated food allergies that can occur in adults – from relatively common ones to rare allergies you’ve probably never heard of.
1. Single food allergies
The most common IgE-mediated food allergies in adults in a US survey were to:
- shellfish (2.9%)
- cow’s milk (1.9%)
- peanut (1.8%)
- tree nuts (1.2%)
- fin fish (0.9%) like barramundi, snapper, salmon, cod and perch.
In these adults, about 45% reported reacting to multiple foods.
This compares to most common childhood food allergies: cow’s milk, egg, peanut and soy.
Overall, adult food allergy prevalence appears to be increasing. Compared to older surveys published in 2003 and 2004, peanut allergy prevalence has increased about three-fold (from 0.6%), while tree nuts and fin fish roughly doubled (from 0.5% each), with shellfish similar (2.5%).
While new adult-onset food allergies are increasing, childhood-onset food allergies are also more likely to be retained into adulthood. Possible reasons for both include low vitamin D status, lack of immune system challenges due to being overly “clean”, heightened sensitisation due to allergen avoidance, and more frequent antibiotic use.
Some adults develop allergies to cow’s milk, while others retain their allergy from childhood. Sarah Swinton/Unsplash 2. Tick-meat allergy
Tick-meat allergy, also called α-Gal syndrome or mammalian meat allergy, is an allergic reaction to galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose, or α-Gal for short.
Australian immunologists first reported links between α-Gal syndrome and tick bites in 2009, with cases also reported in the United States, Japan, Europe and South Africa. The US Centers for Disease Control estimates about 450,000 Americans could be affected.
The α-Gal contains a carbohydrate molecule that is bound to a protein molecule in mammals.
The IgE-mediated allergy is triggered after repeated bites from ticks or chigger mites that have bitten those mammals. When tick saliva crosses into your body through the bite, antibodies to α-Gal are produced.
When you subsequently eat foods that contain α-Gal, the allergy is triggered. These triggering foods include meat (lamb, beef, pork, rabbit, kangaroo), dairy products (yoghurt, cheese, ice-cream, cream), animal-origin gelatin added to gummy foods (jelly, lollies, marshmallow), prescription medications and over-the counter supplements containing gelatin (some antibiotics, vitamins and other supplements).
Tick-meat allergy reactions can be hard to recognise because they’re usually delayed, and they can be severe and include anaphylaxis. Allergy organisations produce management guidelines, so always discuss management with your doctor.
3. Fruit-pollen allergy
Fruit-pollen allergy, called pollen food allergy syndrome, is an IgE-mediated allergic reaction.
In susceptible adults, pollen in the air provokes the production of IgE antibodies to antigens in the pollen, but these antigens are similar to ones found in some fruits, vegetables and herbs. The problem is that eating those plants triggers an allergic reaction.
The most allergenic tree pollens are from birch, cypress, Japanese cedar, latex, grass, and ragweed. Their pollen can cross-react with fruit and vegetables, including kiwi, banana, mango, avocado, grapes, celery, carrot and potato, and some herbs such as caraway, coriander, fennel, pepper and paprika.
Fruit-pollen allergy is not common. Prevalence estimates are between 0.03% and 8% depending on the country, but it can be life-threatening. Reactions range from itching or tingling of lips, mouth, tongue and throat, called oral allergy syndrome, to mild hives, to anaphylaxis.
4. Food-dependent, exercise-induced food allergy
During heavy exercise, the stomach produces less acid than usual and gut permeability increases, meaning that small molecules in your gut are more likely to escape across the membrane into your blood. These include food molecules that trigger an IgE reaction.
If the person already has IgE antibodies to the foods eaten before exercise, then the risk of triggering food allergy reactions is increased. This allergy is called food-dependent exercise-induced allergy, with symptoms ranging from hives and swelling, to difficulty breathing and anaphylaxis.
This type of allergy is extremely rare. Ben O’Sullivan/Unsplash Common trigger foods include wheat, seafood, meat, poultry, egg, milk, nuts, grapes, celery and other foods, which could have been eaten many hours before exercising.
To complicate things even further, allergic reactions can occur at lower levels of trigger-food exposure, and be more severe if the person is simultaneously taking non-steroidal inflammatory medications like aspirin, drinking alcohol or is sleep-deprived.
Food-dependent exercise-induced allergy is extremely rare. Surveys have estimated prevalence as between one to 17 cases per 1,000 people worldwide with the highest prevalence between the teenage years to age 35. Those affected often have other allergic conditions such as hay fever, asthma, allergic conjunctivitis and dermatitis.
Allergies are a growing burden
The burden on physical health, psychological health and health costs due to food allergy is increasing. In the US, this financial burden was estimated as $24 billion per year.
Adult food allergy needs to be taken seriously and those with severe symptoms should wear a medical information bracelet or chain and carry an adrenaline auto-injector pen. Concerningly, surveys suggest only about one in four adults with food allergy have an adrenaline pen.
If you have an IgE-mediated food allergy, discuss your management plan with your doctor. You can also find more information at Allergy and Anaphylaxis Australia.
Clare Collins, Laureate Professor in Nutrition and Dietetics, University of Newcastle
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Fast-Mimicking Diet
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Live, Fast, Live Long
This is Dr. Valter Longo. He’s a biogerontologist and cell biologist, whose work has focused on fasting and nutrient response genes, and how we can leverage them against diseases and aging in general.
We reviewed his book recently:
What does he want us to know?
What to eat
Dr. Longo recommends a mostly plant-based diet (especially vegetables, whole grains, and legumes), but also having some fish. The bulk of our dietary fats, however, he says are best coming from olive oil and nuts.
He also advises aiming for nutritional density of vitamins and minerals in our diet, and/but supplementing with a multivitamin once every few days to cover any gaps.
If in doubt choosing between plant-based whole foods, he recommends that we choose those our ancestors will have eaten.
Read more: Longevity Diet For Adults
When to eat
Dr. Longo recommends time-restricted eating within a 12-hour window per day.
See also: Intermittent Fasting: We Sort The Science From The Hype
However, he also recommends (additionally or separately; it’s up to us; additionally is better but the point is it still has excellent benefits separately too) his “fast-mimicking diet” (FMD), which involves eating according to what we said in “What to eat”, but restricting it to 750 kcal per day, 5 days in a row, but not necessarily 5 days per week.
For example, the following was a 3-month study that involved doing this for only one 5-day cycle per month:
❝Three FMD cycles reduced body weight, trunk, and total body fat; lowered blood pressure; and decreased insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). No serious adverse effects were reported.
A post hoc analysis of subjects from both FMD arms showed that body mass index, blood pressure, fasting glucose, IGF-1, triglycerides, total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and C-reactive protein were more beneficially affected in participants at risk for disease than in subjects who were not at risk.
Thus, cycles of a 5-day FMD are safe, feasible, and effective in reducing markers/risk factors for aging and age-related diseases.❞
~ Dr. Min Wei et al. ← Dr. Longo was
Note: the introduction mentions FMD in mice, but this is just referencing previous studies. This study is about FMD in humans!
Read in full: Fasting-mimicking diet and markers/risk factors for aging, diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular disease
Want to know more?
You might like this (text-based) interview with Dr. Longo, with the Health Sciences Academy:
Eat, fast and live longer? Interview with Professor Valter Longo
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What are nootropics and do they really boost your brain?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Humans have long been searching for a “magic elixir” to make us smarter, and improve our focus and memory. This includes traditional Chinese medicine used thousands of years ago to improve cognitive function.
Now we have nootropics, also known as smart drugs, brain boosters or cognitive enhancers.
You can buy these gummies, chewing gums, pills and skin patches online, or from supermarkets, pharmacies or petrol stations. You don’t need a prescription or to consult a health professional.
But do nootropics actually boost your brain? Here’s what the science says.
LuckyStep/Shutterstock What are nootropics and how do they work?
Romanian psychologist and chemist Cornelius E. Giurgea coined the term nootropics in the early 1970s to describe compounds that may boost memory and learning. The term comes from the Greek words nӧos (thinking) and tropein (guide).
Nootropics may work in the brain by improving transmission of signals between nerve cells, maintaining the health of nerve cells, and helping in energy production. Some nootropics have antioxidant properties and may reduce damage to nerve cells in the brain caused by the accumulation of free radicals.
But how safe and effective are they? Let’s look at four of the most widely used nootropics.
1. Caffeine
You might be surprised to know caffeine is a nootropic. No wonder so many of us start our day with a coffee. It stimulates our nervous system.
Caffeine is rapidly absorbed into the blood and distributed in nearly all human tissues. This includes the brain where it increases our alertness, reaction time and mood, and we feel as if we have more energy.
For caffeine to have these effects, you need to consume 32-300 milligrams in a single dose. That’s equivalent to around two espressos (for the 300mg dose). So, why the wide range? Genetic variations in a particular gene (the CYP1A2 gene) can affect how fast you metabolise caffeine. So this can explain why some people need more caffeine than others to recognise any neurostimulant effect.
Unfortunately too much caffeine can lead to anxiety-like symptoms and panic attacks, sleep disturbances, hallucinations, gut disturbances and heart problems.
So it’s recommended adults drink no more than 400mg caffeine a day, the equivalent of up to three espressos.
Caffeine can make you feel alert and can boost your mood. That makes it a nootropic. LHshooter/Shutterstock 2. L-theanine
L-theanine comes as a supplement, chewing gum or in a beverage. It’s also the most common amino acid in green tea.
Consuming L-theanine as a supplement may increase production of alpha waves in the brain. These are associated with increased alertness and perception of calmness.
However, it’s effect on cognitive functioning is still unclear. Various studies including those comparing a single dose with a daily dose for several weeks, and in different populations, show different outcomes.
But taking L-theanine with caffeine as a supplement improved cognitive performance and alertness in one study. Young adults who consumed L-theanine (97mg) plus caffeine (40mg) could more accurately switch between tasks after a single dose, and said they were more alert.
Another study of people who took L-theanine with caffeine at similar doses to the study above found improvements in several cognitive outcomes, including being less susceptible to distraction.
Although pure L-theanine is well tolerated, there are still relatively few human trials to show it works or is safe over a prolonged period of time. Larger and longer studies examining the optimal dose are also needed.
The amino acid L-theanine is also in green tea. grafvision/Shutterstock 3. Ashwaghanda
Ashwaghanda is a plant extract commonly used in Indian Ayurvedic medicine for improving memory and cognitive function.
In one study, 225-400mg daily for 30 days improved cognitive performance in healthy males. There were significant improvements in cognitive flexibility (the ability to switch tasks), visual memory (recalling an image), reaction time (response to a stimulus) and executive functioning (recognising rules and categories, and managing rapid decision making).
There are similar effects in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
But we should be cautious about results from studies using Ashwaghanda supplements; the studies are relatively small and only treated participants for a short time.
Ashwaghanda is a plant extract commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine. Agnieszka Kwiecień, Nova/Wikimedia, CC BY-SA 4. Creatine
Creatine is an organic compound involved in how the body generates energy and is used as a sports supplement. But it also has cognitive effects.
In a review of available evidence, healthy adults aged 66-76 who took creatine supplements had improved short-term memory.
Long-term supplementation may also have benefits. In another study, people with fatigue after COVID took 4g a day of creatine for six months and reported they were better able to concentrate, and were less fatigued. Creatine may reduce brain inflammation and oxidative stress, to improve cognitive performance and reduce fatigue.
Side effects of creatine supplements in studies are rarely reported. But they include weight gain, gastrointestinal upset and changes in the liver and kidneys.
Where to now?
There is good evidence for brain boosting effects of caffeine and creatine. But the jury is still out on the efficacy, optimal dose and safety of most other nootropics.
So until we have more evidence, consult your health professional before taking a nootropic.
But drinking your daily coffee isn’t likely to do much harm. Thank goodness, because for some of us, it is a magic elixir.
Nenad Naumovski, Professor in Food Science and Human Nutrition, University of Canberra; Amanda Bulman, PhD candidate studying the effects of nutrients on sleep, University of Canberra, and Andrew McKune, Professor, Exercise Science, University of Canberra
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
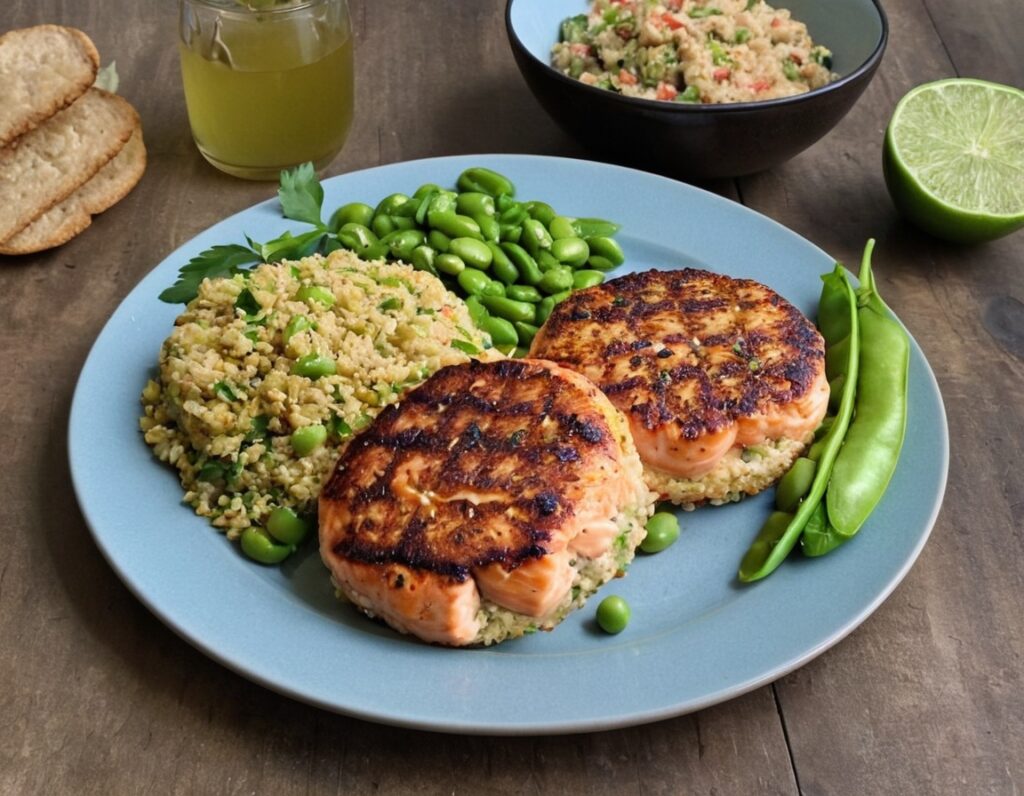
Green Curry Salmon Burgers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These lean and healthy burgers are as quick and easy to make as they are good for entertaining. The serving-bed has its nutritional secrets too! All in all, an especially heart-healthy and brain-healthy dish.
You will need
- 4 skinless salmon fillets, cubed (Vegetarian/Vegan? Consider this Plant-Based Salmon Recipe or, since they are getting blended, simply substitute 1½ cups cooked chickpeas instead with 1 tbsp tahini)
- 2 cloves garlic, chopped
- 2 tbsp thai green curry paste
- juice of two limes, plus wedges to serve
- 1 cup quinoa
- ½ cup edamame beans, thawed if they were frozen
- large bunch fresh cilantro (or parsley if you have the “soap “cilantro tastes like soap” gene), chopped
- extra virgin olive oil, for frying
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the salmon, garlic, curry paste, nutritional yeast, and half the lime juice into a food processor, and blend until smooth.
2) Remove, divide into four parts, and shape into burger patty shapes. Put them in the fridge where they can firm up while we do the next bit.
3) Cook the quinoa with the tablespoon of chia seeds added (which means boiling water and then letting it simmer for 10–15 minutes; when the quinoa is tender and unfurled a little, it’s done).
4) Drain the quinoa with a sieve, and stir in the edamame beans, the rest of the lime juice, the cilantro, and the black pepper. Set aside.
5) Using the olive oil, fry the salmon burgers for about 5 minutes on each side.
6) Serve; we recommend putting the burgers atop the rest, and adding a dash of lime at the table.
(it can also be served this way!)
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Farmed Fish vs Wild–Caught
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: