How to Vary Breakfast for Digestion?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Would appreciate your thoughts on how best to promote good digestion. For years, my breakfast has consisted of flaxseeds, sunflower seeds, and almonds – all well ground up – eaten with a generous amount of kefir. This works a treat as far as my digestion is concerned. But I sometimes wonder whether it would be better for my health if I varied or supplemented this breakfast. How might I do this without jeopardising my good digestion?❞
Sounds like you’re already doing great! Those ingredients are all very nutrient-dense, and grinding them up improves digestion greatly, to the point that you’re getting nutrients your body couldn’t get at otherwise. And the kefir, of course, is a top-tier probiotic.
Also, you’re getting plenty of protein and healthy fats in with your carbs, which results in the smoothest blood sugar curve.
As for variety…
Variety is good in diet, but variety within a theme. Our gut microbiota change according to what we eat, so sudden changes in diet are often met with heavy resistance from our gut.
- For example, people who take up a 100% plant-based diet overnight often spend the next day in the bathroom, and wonder what happened.
- Conversely, a long-time vegan who (whether by accident or design) consumes meat or dairy will likely find themself quickly feeling very unwell, because their gut microbiota have no idea what to do with this.
So, variety yes, but within a theme, and make any changes gradual for the easiest transition.
All in all, the only obvious suggestion for improvement is to consider adding some berries. These can be fresh, dried, or frozen, and will confer many health benefits (most notably a lot of antioxidant activity).
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
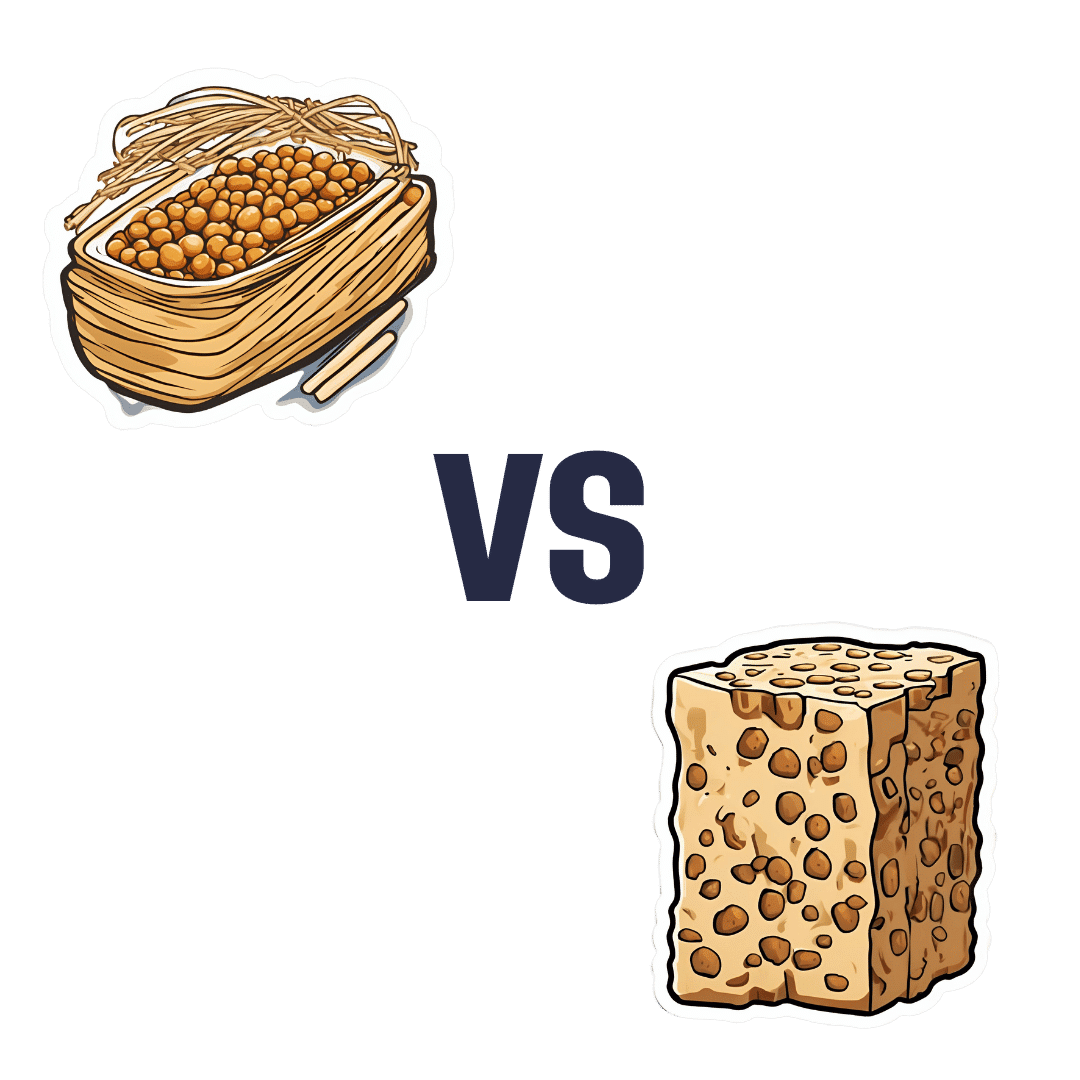
Natto vs Tempeh – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing nattō to tempeh, we picked the nattō.
Why?
Both are great, but in the battle of fermented soybeans vs fermented soybeans with extra steps, it turns out that the simplest option is the best, even if tempeh was a close runner-up:
In terms of macros, nattō has more carbs and fiber for the same protein and fat; we’ll call this category a tie or a marginal win for nattō.
In the category of vitamins, nattō has more of vitamins B1, C, E, K, and choline, while tempeh has more of vitamins B2, B3, B6, and B9. A clearer, yet still modest, win for nattō.
Minerals, however, are what really set them apart: nattō has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while tempeh has more phosphorus. An overwhelming win for nattō this time.
In short: enjoy either or both, but nattō is the more nutritionally dense option!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
21% Stronger Bones in a Year at 62? Yes, It’s Possible (No Calcium Supplements Needed!) ← nattō is featured as part of the diet 😎
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Sleeping on Your Back after 50; Yay or Nay?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sleeping Differently After 50
Sleeping is one of those things that, at any age, can be hard to master. Some of our most popular articles have been on getting better sleep, and effective sleep aids, and we’ve had a range of specific sleep-related questions, like whether air purifiers actually improve your sleep.
But perhaps there’s an underlying truth hidden in our opening sentence…is sleeping consistently difficult because the way we sleep should change according to our age?
Inspired by Brad and Mike’s video below (which was published to their 5 million+ subscribers!), there are 4 main elements to consider when sleeping on your back after you’ve hit the 50-year mark:
- Degenerative Disk Disease: As you age, your spine may start to show signs of wear and tear, which directly affects comfort while lying on your back.
- Sleep Apnea and Snoring: Sleep Apnea and snoring become more of an issue with age, and sleeping on your back can exacerbate these problems; when you sleep on your back, the soft tissues in your throat, as well as your tongue, “fall back” and partly obstruct your the airway.
- Spinal Stenosis: Spinal Stenosis–the often-age-related narrowing of your spinal canal–can put pressure on the nerves that travel through the spine, which equally makes back-sleeping harder.
- GERD: The all-too-familiar gastroesophageal reflux disease can be more problematic when lying flat on your back, as doing so can allow easy access for stomach acid to move upwards.
Alternatives to Back Sleeping
Referencing the Mayo Clinic’s Sleep Facility’s director, Dr. Virend Somers, today’s video suggests a simple solution: sleeping on your side. The video goes into a bit more detail but, as you know, here at 10almonds we like to cut to the chase.
Modifications for Back Sleeping
If you’re a lifelong back-sleeping and cannot bear the idea of changing to your side, or your stomach, then there are a few modifications that you can make to ease any pain and discomfort.
Most solutions revolve around either leg wedges or pillow adjustments. For instance, if you’re suffering from back pain, try propping your knees up. Or if GERD is your worst enemy, a wedge pillow could help keep that acid down.
As can be expected, the video dives into more detail:
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Share This Post
-
The Sweet Truth About Diabetes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s A Lot Of Confusion About Diabetes!
For those readers who are not diabetic, nor have a loved one who is diabetic, nor any other pressing reason to know these things, first a quick 101 rundown of some things to understand the rest of today’s main feature:
- Blood sugar levels: how much sugar is in the blood, measured in mg/dL or mmol/L
- Hyperglycemia or “hyper” for short: too much sugar in the blood
- Hypoglycemia or “hypo” for short: too little sugar in the blood
- Insulin: a hormone that acts as a gatekeeper to allow sugar to pass, or not pass, into various parts of the body
- Type 1 diabetes (sometimes capitalized, and/or abbreviated to “T1D”) is an autoimmune disorder that prevents the pancreas from being able to supply the body with insulin. This means that taking insulin consistently is necessary for life.
- Type 2 diabetes is a matter of insulin resistance. The pancreas produces plenty of insulin, but the body has become desensitized to it, so it doesn’t work properly. Taking extra insulin may sometimes be necessary, but for many people, it can be controlled by means of a careful diet and other lifestyle factors.
With that in mind, on to some very popular myths…
Diabetes is caused by having too much sugar
While sugar is not exactly a health food, it’s not the villain of this story either.
- Type 1 diabetes has a genetic basis, triggered by epigenetic factors unrelated to sugar.
- Type 2 diabetes comes from a cluster of risk factors which, together, can cause a person to go through pre-diabetes and acquire type 2 diabetes.
- Those risk factors include:
- A genetic predisposition
- A large waist circumference
- (this is more relevant than BMI or body fat percentage)
- High blood pressure
- A sedentary lifestyle
- Age (the risk starts rising at 35, rises sharply at 45, and continues upwards with increasing age)
- Those risk factors include:
Read more: Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetics can’t have sugar
While it’s true that diabetics must be careful about sugar (and carbs in general), it’s not to say that they can’t have them… just: be mindful and intentional about it.
- Type 1 diabetics will need to carb-count in order to take the appropriate insulin bolus. Otherwise, too little insulin will result in hyperglycemia, or too much insulin will result in hypoglycemia.
- Type 2 diabetics will often be able to manage their blood sugar levels with diet alone, and slow-release carbs will make this easier.
In either case, having quick release sugars will increase blood sugar levels (what a surprise), and sometimes (such as when experiencing a hypo), that’s what’s needed.
Also, when it comes to sugar, a word on fruit:
Not all fruits are equal, and some fruits can help maintain stable blood sugar levels! Read all about it:
Fruit Intake to Prevent and Control Hypertension and Diabetes
Artificial sweeteners are must-haves for diabetics
Whereas sugar is a known quantity to the careful diabetic, some artificial sweeteners can impact insulin sensitivity, causing blood sugars to behave in unexpected ways. See for example:
The Impact of Artificial Sweeteners on Body Weight Control and Glucose Homeostasis
If a diabetic person is hyper, they should exercise to bring their blood sugar levels down
Be careful with this!
- In the case of type 2 diabetes, it may (or may not) help, as the extra sugar may be used up.
- Type 1 diabetes, however, has a crucial difference. Because the pancreas isn’t making insulin, a hyper (above a certain level, anyway) means more insulin is needed. Exercising could do more harm than good, as unlike in type 2 diabetes, the body has no way to use that extra sugar, without the insulin to facilitate it. Exercising will just pump the syrupy hyperglycemic blood around the body, potentially causing damage as it goes (all without actually being able to use it).
There are other ways this can be managed that are outside of the scope of this newsletter, but “be careful” is rarely a bad approach.
Read more, from the American Diabetes Association:
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Why STIs Are On The Rise In Older Adults
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Three Little Words
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) are often thought of as something that predominantly plagues younger people… The truth, however, is different:
❝Rising divorce rates, forgoing condoms as there is no risk of pregnancy, the availability of drugs for sexual dysfunction, the large number of older adults living together in retirement communities, and the increased use of dating apps are likely to have contributed to the growing incidence of STIs in the over-50s.
These data likely underestimate the true extent of the problem as limited access to sexual health services for the over 50s, and trying to avoid the stigma and embarrassment both on the part of older people and healthcare professionals, is leading to this age group not seeking help for STIs.❞
Read more: Managing The Rise In STIs Among Older Adults
That said, there is a gender gap when it comes to the increased risk, for example:
❝A retrospective study from the USA involving 420,790 couples aged 67 to 99 years, found that widowhood was associated with an increased risk of STIs in older men, but not women❞
~ US Dept of Health & Human Services
Source: CDC: | Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance
Is abstinence the best preventative, then?
It is inarguably the most effective, but not necessarily the best for everyone.
This is because for most adults, a healthy sex life is an important part of overall wellbeing.
See also: Mythbusting The Big O
Even in this case there is a gender gap in:
- the level of importance placed on frequency of sexual interactions
- what act(s) of sexuality are held to be most important:
❝Among sexually active men, frequent (≥2 times a month) sexual intercourse (P < .001) and frequent kissing, petting, or fondling (P < .001) were associated with greater enjoyment of life.
Among sexually active women, frequent kissing, petting, or fondling was also associated with greater enjoyment of life (P < .001), but there was no significant association with frequent intercourse (P = .101).
Concerns about one’s sex life and problems with sexual function were strongly associated with lower levels of enjoyment of life in men and to a lesser extent in women.❞
Source: Sexual Activity is Associated with Greater Enjoyment of Life in Older Adults
If you have the time to go into it much more deeply, this paper from the Journal of Gerontology is much more comprehensive, looking also at related lifestyle factors, religious/political backgrounds, views on monogamy or non-monogamy (of various kinds), hormonal considerations, the impact of dementia or other long-term disabilities that may affect things, widowhood, and many other elements:
The National Social Life, Health, and Aging Project: An Introduction
What’s the best preventative, then?
Regular health screening for yourself and your partner(s) is an important key to preventative health when it comes to STIs.
You can Google search for a local STI clinic, and worry not, they are invariably discreet and are well-used to everybody coming in. They’re just glad you’re being responsible about things. It’s also not their job to judge your sexual activities, even if it’s something you might have reason to wish to be secretive about, try to be honest there.
Secondly, most of the usual advice about safe sex still goes, even when there’s no risk of pregnancy. For example, if there’s at least one penis involved, then condoms remain the #1 barrier to all manner of potential infections (we know, almost nobody likes condoms, but sometimes the truth isn’t what we want to hear).
Lastly, if there’s at least one vagina involved, then please for the love of all that is holey, do not put anything there that could cause a yeast infection.
What can cause a yeast infection? Pretty much anything with sugar, which includes but is not limited to:
- Most kinds of food that Cosmo-style “liven things up in the bedroom” advice columns might suggest using (including fruit, honey, chocolate sauce, whipped cream, etc)
- Hands that are not clean (watch out for bacteria too)
- A mouth that has recently been eating or drinking anything with sugar in it, and that includes many kinds of alcohol, as well as milk or hot drinks that had milk in
Yeast infections are not nearly so serious as the STIs the other measures are there to avoid, but they’re not fun either, so some sensible policies in that regard are always good!
On a related note, see also: How To Avoid UTIs
Recap on the single most important part of this article:
At all ages, it remains a good health practice—unless one is absolutely celibate—to regularly get oneself and one’s partner(s) checked for STIs.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Plant-Based Diet Revolution – by Dr. Alan Desomond
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is this just another gut-healthy cooking guide? Not entirely…
For a start, it’s not just about giving you a healthy gut; it also covers a healthy heart and a healthy brain. There’s lots of science in here!
It’s also aimed as a transitional guide to eating more plants and fewer animal products, if you so choose. And if you don’t so choose, at least having the flexibility to cook both ways.
The recipes themselves (organized into basics, breakfasts, lunches, mains, desserts) are clear and easy while also being calculated to please readers (and their families) who are used to eating more meat. There are, for instance, plenty of healthy proteins, healthy fats, and comfort foods.
The “28 days” of the title refers to a meal plan using the recipes from the book; it’s not a big feature of the book though, so use it or don’t, but the cooking advice itself is more than worth the price of the book and the recipes are certainly great.
Bottom line: if you’re thinking of taking a “Meatless Mondays” approach to making your diet healthier, this book can help you do that in style!
Click here to check out The Plant-Based Diet Revolution, and upgrade your culinary repertoire!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
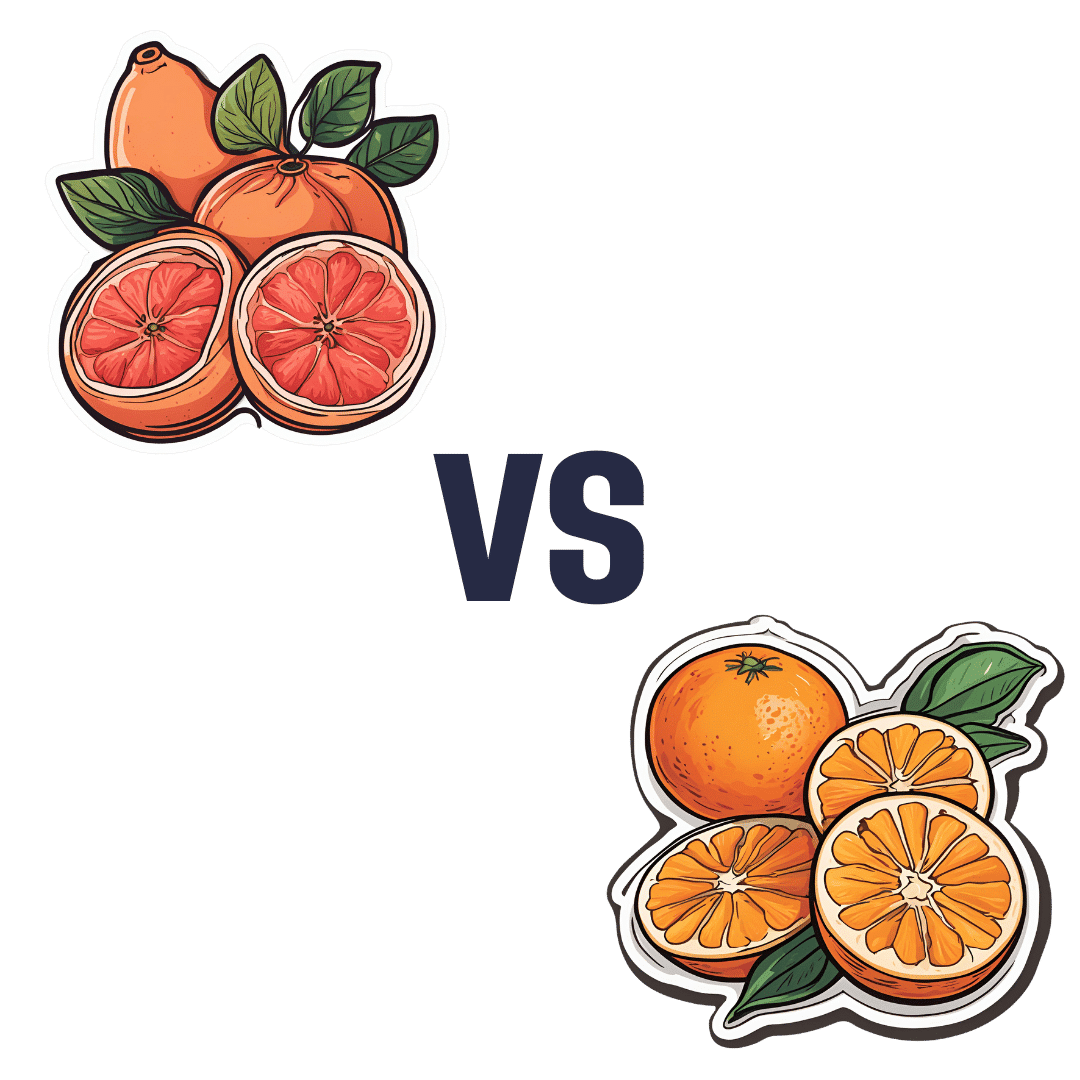
Grapefruit vs Orange – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing grapefruit to orange, we picked the orange.
Why?
It’s easy, when guessing which is the healthier out of two things, to guess that the more expensive or perhaps less universally available one is the healthier. But it’s not always so, and today is one of those cases!
In terms of macros, they are very similar fruits, with almost identical levels of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, as well as water. Looking more carefully, we find that grapefruit’s sugars contain a slightly high proportion of fructose; not enough to make it unhealthy by any means (indeed, no whole unprocessed fruit is unhealthy unless it’s literally poisonous), but it is a thing to note if we’re micro-analysing the macronutrients. Also, oranges have slightly more fiber, which is always a plus.
When it comes to vitamins, oranges stand out with more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, C, and E, while grapefruit boasts more vitamin A (hence its color). Still, we’re calling this category another win for oranges.
In the category of minerals, oranges again sweep with more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, and selenium, while grapefruit has just a little more phosphorus. So, another easy win for oranges.
One final consideration that’s not shown in the nutritional values, is that grapefruit contains furanocoumarin, which can inhibit cytochrome P-450 3A4 isoenzyme and P-glycoptrotein transporters in the intestine and liver—slowing down their drug metabolism capabilities, thus effectively increasing the bioavailability of many drugs manifold. It can also be found in lower quantities in Seville (sour) oranges, and it’s not present (or at least, if it is, it’s in truly tiny quantities) in most oranges.
This may sound superficially like a good thing (improving bioavailability of things we want), but in practice it means that in the case of many drugs, if you take them with (or near in time to) grapefruit or grapefruit juice, then congratulations, you just took an overdose. This happens with a lot of meds for blood pressure, cholesterol (including statins), calcium channel-blockers, anti-depressants, benzo-family drugs, beta-blockers, and more. Oh, and Viagra, too. Which latter might sound funny, but remember, Viagra’s mechanism of action is blood pressure modulation, and that is not something you want to mess around with unduly. So, do check with your pharmacist to know if you’re on any meds that would be affected by grapefruit or grapefruit juice!
All in all, today’s sections add up to an overwhelming win for oranges!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: