How To Reduce Cortisol Levels Naturally
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cortisol is a hormone that is important for us (we’d struggle to get up in the morning without it, for a start), but in this modern world we often have too much of it, too much of the time. How can we rebalance it? Dr. Mindy Pelz explains:
Lifestyle adjustments
A note in advance: the video makes frequent reference to things that “spike cortisol levels”, but this is probably intended as a stand-in for “raise cortisol levels”. Because, unlike for some things, in the case of cortisol, spikes aren’t usually a problem (indeed, they can be beneficial, and this is a large part of why cold showers and ice baths can be healthy; it’s an artificially induced cortisol spike, and this hormesis has an assortment of healthy benefits, each related to improving our body’s ability to switch quickly between states as appropriate); rather, it’s chronically high cortisol levels that are the problem. However, the video discusses things that can increase resting cortisol levels, so where she says “spike”, we suggest to read “raise”.
Dr. Pelz, an advocate of intermittent fasting, mentions that done incorrectly and/or for the same way for too long, fasting can raise cortisol levels and thus sabotage our efforts—so varying our fasting style can help avoid that. For example, 16:8, 5:2, longer fasts less frequently, etc.
On the topic of food, she also warns us of the dangers of ultra-processed food, harmful oils, and foods with added sugar, as these can all raise cortisol levels.
When it comes to exercise, she notes that intense exercise without adequate recovery can raise cortisol levels, so again it’s good to mix up one’s methods, vary one’s exercise routine, and allow each well-worked muscle-group adequate rest afterwards.
Dr. Pelz also talks mindset, and has her own interesting way of framing the well-established science that chronic stress means chronically high stress hormone (cortisol) levels; Dr. Pelz prefers to see it as negative vs positive thoughts, environments, etc.
Any discussion of cortisol management would be incomplete without discussing the importance of good quality sleep. Dr. Pelz doesn’t mention this at all in her video, but it’s important to bear in mind too!
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Lower Your Cortisol! (Here’s Why & How)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can you get sunburnt or UV skin damage through car or home windows?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When you’re in a car, train or bus, do you choose a seat to avoid being in the sun or do you like the sunny side?
You can definitely feel the sun’s heat through a window. But can you get sunburn or skin damage when in your car or inside with the windows closed?
Let’s look at how much UV (ultraviolet) radiation passes through different types of glass, how tinting can help block UV, and whether we need sunscreen when driving or indoors.
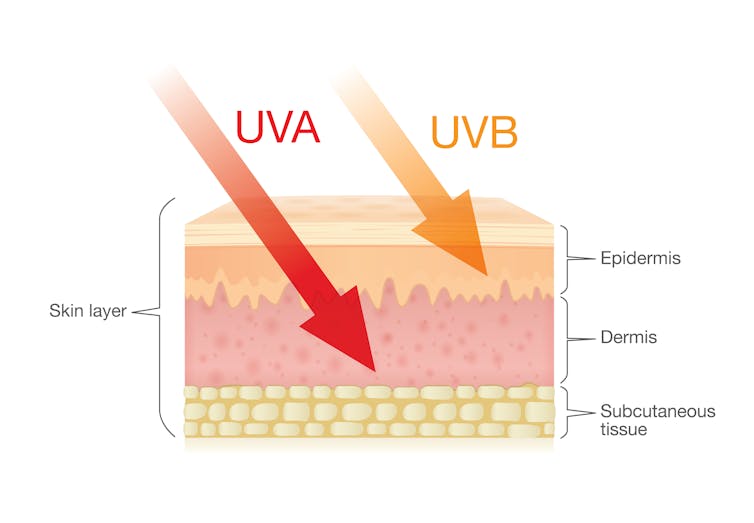
Zac Harris/Unsplash What’s the difference between UVA and UVB?
Of the total UV radiation that reaches Earth, about 95% is UVA and 5% is UVB.
UVB only reaches the upper layers of our skin but is the major cause of sunburn, cataracts and skin cancer.
UVA penetrates deeper into our skin and causes cell damage that leads to skin cancer.
UVA penetrates deeper than UVB. Shutterstock/solar22 Glass blocks UVA and UVB radiation differently
All glass used in house, office and car windows completely blocks UVB from passing through.
But only laminated glass can completely block UVA. UVA can pass through other glass used in car, house and office windows and cause skin damage, increasing the risk of cancer.
Car windscreens block UVA, but the side and rear windows don’t
A car’s front windscreen lets in lots of sunshine and light. Luckily it blocks 98% of UVA radiation because it is made of two layers of laminated glass.
But the side and rear car windows are made of tempered glass, which doesn’t completely block UVA. A study of 29 cars found a range from 4% to almost 56% of UVA passed through the side and rear windows.
The UVA protection was not related to the car’s age or cost, but to the type of glass, its colour and whether it has been tinted or coated in a protective film. Grey or bronze coloured glass, and window tinting, all increase UVA protection. Window tinting blocks around 95% of UVA radiation.
In a separate study from Saudi Arabia, researchers fitted drivers with a wearable radiation monitor. They found drivers were exposed to UV index ratings up to 3.5. (In Australia, sun protection is generally recommended when the UV index is 3 or above – at this level it takes pale skin about 20 minutes to burn.)
So if you have your windows tinted, you should not have to wear sunscreen in the car. But without tinted windows, you can accumulate skin damage.
UV exposure while driving increases skin cancer risk
Many people spend a lot of time in the car – for work, commuting, holiday travel and general transport. Repeated UVA radiation exposure through car side windows might go unnoticed, but it can affect our skin.
Indeed, skin cancer is more common on the driver’s side of the body. A study in the United States (where drivers sit on the left side) found more skin cancers on the left than the right side for the face, scalp, arm and leg, including 20 times more for the arm.
Another US study found this effect was higher in men. For melanoma in situ, an early form of melanoma, 74% of these cancers were on the on the left versus 26% on the right.
Earlier Australian studies reported more skin damage and more skin cancer on the right side.
Cataracts and other eye damage are also more common on the driver’s side of the body.
What about UV exposure through home or office windows?
We see UV damage from sunlight through our home windows in faded materials, furniture or plastics.
Most glass used in residential windows lets a lot of UVA pass through, between 45 and 75%.
Residential windows can let varied amounts of UVA through. Sherman Trotz/Pexels Single-pane glass lets through the most UVA, while thicker, tinted or coated glass blocks more UVA.
The best options are laminated glass, or double-glazed, tinted windows that allow less than 1% of UVA through.
Skylights are made from laminated glass, which completely stops UVA from passing through.
Most office and commercial window glass has better UVA protection than residential windows, allowing less than 25% of UVA transmission. These windows are usually double-glazed and tinted, with reflective properties or UV-absorbent chemicals.
Some smart windows that reduce heat using chemical treatments to darken the glass can also block UVA.
So when should you wear sunscreen and sunglasses?
The biggest risk with skin damage while driving is having the windows down or your arm out the window in direct sun. Even untinted windows will reduce UVA exposure to some extent, so it’s better to have the car window up.
For home windows, window films or tint can increase UVA protection of single pane glass. UVA blocking by glass is similar to protection by sunscreen.
When you need to use sunscreen depends on your skin type, latitude and time of the year. In a car without tinted windows, you could burn after one hour in the middle of the day in summer, and two hours in the middle of a winter’s day.
But in the middle of the day next to a home window that allows more UVA to pass through, it could take only 30 minutes to burn in summer and one hour in winter.
When the UV index is above three, it is recommended you wear protective sunglasses while driving or next to a sunny window to avoid eye damage.
Theresa Larkin, Associate Professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
An Addiction Expert’s Insights On Festive Drinking
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Christopher Kahler. He’s Professor of Behavioral and Social Sciences, Director of Alcohol and Addiction Studies, Professor of Psychiatry and Human Behavior, all at Brown University.
What does he want us to know?
It’s the trickiest time of the year
Per stats, alcohol sales peak in December, with the heaviest drinking being from mid-December (getting an early start on the Christmas cheer) to New Year’s Eve. As for why, there’s a collection of reasons, as he notes:
❝The main challenge is there’s an extra layer of stress, with a lot of obligations and expectations from friends and family. We’re around people who maybe we’re not usually around, and in larger groups. It’s also a time of heightened emotion and, for some people, loneliness.
On top of that, alcohol use is built into a lot of our winter holiday traditions. It’s often marketed as part of the “good life.” We’re expected to have alcohol when we celebrate.❞
As for how much alcohol is safe to drink… According to the World Health Organization, the only safe amount of alcohol is zero:
Dr. Kahler acknowledges, however, that many people will wish to imbibe anyway, and indeed, he himself does drink a little, but endeavours to do so mindfully, and as such, he recommends that we…
HALT!
Dr. Kahler counsels us against making decisions (including the decision to drink alcohol), on occasions when we are one or more of the following:
- Hungry
- Angry
- Lonely
- Tired
He also notes that around this time of year, often our normal schedules and habits are disrupted, which introduces more microdecisions to our daily lives, which in turn means more “decision fatigue”, and the greater chance of making bad decisions.
We share some practical tips on how to reduce the chances of thusly erring, here:
Set your intentions now
He bids us figure out what our goal is, and really think it through, including not just “how many drinks to have” if we’re drinking, but also such things as “what feelings are likely to come up”. Because, if we’ve historically used alcohol as a maladaptive coping mechanism, we’re going to need a different, better, healthier coping mechanism (we talked more about that in our above-linked article about reducing or quitting alcohol, too, with some examples).
He also suggests that we memorize our social responses—exactly what we’re going to say if offered a drink, for example:
❝It’s important to know what you’re going to say about your alcohol use. If someone asks if they can get you a drink, good responses could be: “A glass of water would be great” or “Do you have any non-alcoholic cider?” You don’t have to explain yourself. Just ask for what you want, because saying no to someone can be difficult.❞
See also:
December’s Traps To Plan Around
Mix it up and slow it down
No, that doesn’t mean mix yourself a sloe gin cocktail. But rather, it’s about alternating alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks, to give your body half a chance to process the alcohol, and also to rehydrate a little along the way.
We talk about this and other damage-limitation methods, here:
How To Reduce The Harm Of Festive Drinking (Without Abstaining)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Genetic Risk Factors For Long COVID
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some people, after getting COVID, go on to have Long COVID. There are various contributing factors to this, including:
- Lifestyle factors that impact general disease-proneness
- Immune-specific factors such as being immunocompromised already
- Genetic factors
We looked at some modifiable factors to improve one’s disease-resistance, yesterday:
And we’ve taken a more big-picture look previously:
Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
Along with some more systemic issues:
Why Some People Get Sick More (And How To Not Be One Of Them)
But, for when the “don’t get COVID” ship has sailed, one of the big remaining deciding factors with regard to whether one gets Long COVID or not, is genetic
The Long COVID Genes
For those with their 23andMe genetic data to hand…
❝Study findings revealed that three specific genetic loci, HLA-DQA1–HLA-DQB1, ABO, and BPTF–KPAN2–C17orf58, and three phenotypes were at significantly heightened risk, highlighting high-priority populations for interventions against this poorly understood disease.❞
For those who don’t, then first: you might consider getting that! Here’s why:
Genetic Testing: Health Benefits & Methods
But also, all is not lost meanwhile:
The same study also found that individuals with genetic predispositions to chronic fatigue, depression, and fibromyalgia, as well as other phenotypes such as autoimmune conditions and cardiometabolic conditions, are at significantly higher risk of long-COVID than individuals without these conditions.
Good news, bad news
Another finding was that women and non-smokers were more likely to get Long COVID, than men and smokers, respectively.
Does that mean that those things are protective against Long COVID, which would be very counterintuitive in the case of smoking?
Well, yes and no; it depends on whether you count “less likely to get Long COVID because of being more likely to just die” as protective against Long COVID.
(Incidentally, estrogen is moderately immune-enhancing, while testosterone is moderately immune-suppressing, so the sex thing was not too surprising. It’s also at least contributory to why women get more autoimmune disorders, while men get more respiratory infections such as colds and the like)
Want to know more?
You can read the paper itself, here:
*GWAS = Genome-Wide Association Study
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Uses of Delusion – by Dr. Stuart Vyse
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most of us try to live rational lives. We try to make the best decisions we can based on the information we have… And if we’re thoughtful, we even try to be aware of common logical fallacies, and overcome our personal biases too. But is self-delusion ever useful?
Dr. Stuart Vyse, psychologist and Fellow for the Committee for Skeptical Inquiry, argues that it can be.
From self-fulfilling prophecies of optimism and pessimism, to the role of delusion in love and loss, Dr. Vyse explores what separates useful delusion from dangerous irrationality.
We also read about such questions as (and proposed answers to):
- Why is placebo effect stronger if we attach a ritual to it?
- Why are negative superstitions harder to shake than positive ones?
- Why do we tend to hold to the notion of free will, despite so much evidence for determinism?
The style of the book is conversational, and captivating from the start; a highly compelling read.
Bottom line: if you’ve ever felt yourself wondering if you are deluding yourself and if so, whether that’s useful or counterproductive, this is the book for you!
Click here to check out The Uses of Delusion, and optimize yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Revive and Maintain Metabolism
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝How to jump start a inactive metabolism and keep it going? THANKYOU❞
The good news is, if you’re alive, your metabolism is active (it never stops!). So, it may just need perking up a little.
As for keeping it going, well, that’s what we’re here for! We’re all in favor of healthy longevity.
We’ll do a main feature soon on what we can do to influence our metabolism in either direction, but to give some quick notes here:
- A lot of our metabolism is influenced by genes and is unalterable (without modifying our genes, anyway)
- Metabolism isn’t just one thing—it’s many. And sometimes, parts of our metabolism can be much quicker or slower than others.
- When people talk about wanting a “faster metabolism”, they’re usually referring to fat-burning, and that’s just a small part of the picture, but we understand that it’s a focal point for many.
There really is enough material for a whole main feature on metabolic tweaks, though, so watch this space!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cows’ Milk, Bird Flu, & You
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to dairy products, generally speaking, fermented ones (such as most cheeses and yogurts) are considered healthy in moderation, and unfermented ones have their pros and cons that can be argued and quibbled “until the cows come home”. We gave a broad overview, here:
Furthermore, you may recall that there’s some controversy/dissent about when human babies can have cows’ milk:
When can my baby drink cow’s milk? It’s sooner than you think
So, what about bird flu now?
Earlier this year, the information from the dairy industry was that it was nothing to be worried about for the time being:
Bird Flu Is Bad for Poultry and Dairy Cows. It’s Not a Dire Threat for Most of Us — Yet.
More recently, the latest science has found:
❝We found a first-order decay rate constant of −2.05 day–1 equivalent to a T99 of 2.3 days. Viral RNA remained detectable for at least 57 days with no degradation. Pasteurization (63 °C for 30 min) reduced infectious virus to undetectable levels and reduced viral RNA concentrations, but reduction was less than 1 log10.
The prolonged persistence of viral RNA in both raw and pasteurized milk has implications for food safety assessments and environmental surveillance❞
You can find the study here:
Infectivity and Persistence of Influenza A Virus in Raw Milk
In short: raw milk keeps the infectious virus; pasteurization appears to render it uninfectious, though viral RNA remains present.
This is relevant, because of the bird flu virus being found in milk:
World Health Organization | H5N1 strain of bird flu found in milk
To this end, a moratorium has been placed on the sale of raw milk, first by the California Dept of Public Health (following an outbreak in California):
California halts sales of raw milk due to bird flu virus contamination
And then, functionally, by the USDA, though rather than an outright ban, it’s requiring testing for the virus:
USDA orders testing of milk supply for presence of bird flu virus
So, is pasteurized milk safe?
The official answer to this, per the FDA, is… Honestly, a lot of hand-wringing and shrugging. What we do know is:
- the bird flu virus has been found in pasteurized milk too
- the test for this is very sensitive, and has the extra strength/weakness that viral fragments will flag it as a positive
- it is assumed that the virus was inactivated by the pasteurization process
- it could, however, have been the entire virus, the test simply does not tell us which
In the FDA’s own words:
❝The pasteurization process has served public health well for more than 100 years. Even if the virus is detected in raw milk, pasteurization is generally expected to eliminate pathogens to a level that does not pose a risk to consumer health❞
So, there we have it: the FDA does not have a reassurance exactly, but it does have a general expectation.
Source: US Officials: Bird flu viral fragments found in pasteurized milk
Want to know more?
You might like this mythbusting edition we did a little while back:
Pasteurization: What It Does And Doesn’t Do ← this is about its effect on risks and nutrients
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: