Healthy Choco-Banoffee Ice Cream
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chocolate, banana, and coffee—quite a threesome, whether for breakfast or dessert, and this is healthy enough for breakfast while being decadent enough for dessert! With no dairy or added sugar, and lots of antioxidants, this is a healthy way to start or end your day.
You will need
- 3 bananas
- 2 tbsp cocoa powder, no additives
- 2 shots espresso, chilled
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
- On standby: milk of your choice—we recommend almond or hazelnut
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Peel, slice, and freeze the bananas (let them freeze for at least 2–3 hours)
2) Blend the ingredients, except the milk. Add milk as necessary if the mixture is too thick to blend. Be careful not to add too much at once though, or it will become less of an ice cream and more of a milkshake!
3) Scoop into a sundae glass to serve:
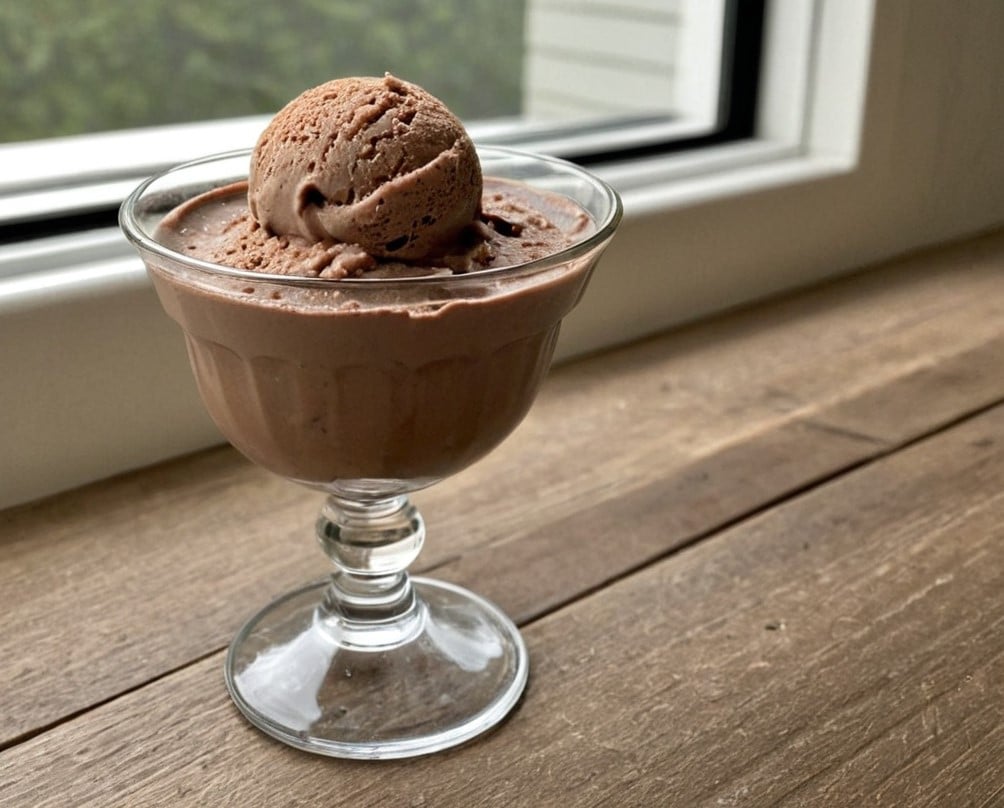

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Which Plant Milk?
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
- Apples vs Bananas – Which is Healthier?
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- Tasty Polyphenols
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tinnitus: Quieting The Unwanted Orchestra In Your Ears
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tinnitus—When a “minor” symptom becomes disruptive
Tinnitus (typically: ringing in the ears) is often thought of less as a condition in and of itself, and more a symptom related to other hearing-related conditions. Paradoxically, it can be associated with hearing loss as well as with hyperacusis (hearing supersensitivity, which sounds like a superpower, but can be quite a problem too).
More than just ringing
Tinnitus can manifest not just as ringing, but also as whistling, hissing, pulsing, buzzing, hooting, and more.
For those who don’t suffer from this, it can seem very trivial; for those who do… Sometimes it can seem trivial too!
But sometimes it’s hard to carry on a conversation when at random moments it suddenly sounds like someone is playing a slide-whistle directly into your earhole, or like maybe a fly got stuck in there.
It’s distracting, to say the least.
What causes it?
First let’s note, tinnitus can be acute or chronic. So, some of these things may just cause tinnitus for a while, whereas some may give you tinnitus for life. In some cases, it depends on how long the thing in question persisted for.
A lot of things can cause it, but common causes include:
- Noise exposure (e.g. concerts, some kinds of industrial work, war)
- High blood pressure
- Head/neck injuries
- Ear infection
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g. Type 1 Diabetes, Lupus, Multiple Sclerosis)
So what can be done about it?
Different remedies will work (or not) for different people, depending on the cause and type of tinnitus.
Be warned also: some things that will work for one person’s tinnitus will make another person’s worse, so you might need to try a degree of experimentation and some of it might not be fun!
That in mind, here are some things you might want to try if you haven’t already:
- Earplugs or noise-canceling headphones—while tinnitus is an internal sound, not external, it often has to do with some part(s) of your ears being unduly sensitive, so giving them less stimulus may ease the tinnitus that occurs in reaction to external noise.
- A great option (that this writer uses personally and considers a life-changer) is silicon earplugs that live in a little case on a keyring when not in use—no more heart-racing fleeing from supermarket checkout boops or pedestrian crossing bips or traffic noises or babies crying or (etc)
- White noise—if you also have hyperacusis, a lower frequency range will probably not hurt the way a higher range might. If you don’t also have hyperacusis, you have more options here and this is a popular remedy. Either way, white noise outperforms “relaxing” soundscapes.
- Hearing aids—counterintuitively, for some people whose tinnitus has developed in response to hearing loss, hearing aids can help bring things “back to normal” and eliminate tinnitus in the process.
- Customized sound machines—if you have the resources to get fancy, science currently finds this to be best of all. They work like white noise, but are tailored to your specific tinnitus.
Share This Post
-
Accidentally Overweight – by Dr. Libby Weaver
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book’s main premise is that for most people who become overweight especially in midlife or later, if there wasn’t an obvious lifestyle change to precipitate this (e.g. started living on fast food for some reason), then in most cases, what’s needed is not drastic action, so much as some metabolic tweaks to correct things that have gone off-piste a little in our physiology.
The book covers nine factors that make an impact, and how each can be managed. They are:
- Insulin
- Stress hormones
- Calories
- Thyroid function
- Nervous system
- Emotions
- Sex hormones
- Liver function
- Gut bacteria
Some will be obvious, but as Dr. Weaver explains, are relative trivial compared to the others; “calories” in one such example of this “yes, it’s a factor, but very overrated” category.
Others are things that most people don’t think too much about, like liver function. And yet, it is indeed very much critical, and a major player in metabolism and adiposity.
The style is on the very light end of pop-science, but she does bring her professional knowledge to bear on topic (her doctorate is a PhD in biochemistry, so a lot of explanations come from that angle).
Bottom line: if you’ve found yourself “accidentally overweight”, and would like to tip the scales back in the other direction without doing anything extreme, then this book provides the tweaks that no amount of cardio or restrictive dieting will.
Click here to check out Accidentally Overweight, and re-adjust it back the other way!
Share This Post
-
Beetroot vs Sweet Potato – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing beetroot to sweet potato, we picked the sweet potato.
Why?
Quite a straightforward one today!
In terms of macros, sweet potato has more protein, carbs, and fiber. The glycemic index of both of these root vegetables is similar (and in each case varies similarly depending on how it is cooked), so we’ll call the winner the one that’s more nutritionally dense—the sweet potato.
Looking at vitamins next, beetroot has more vitamin B9 (and is in fact a very good source of that, unlike sweet potato), and/but sweet potato is a lot higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, C, E, K, and choline. And we’re talking for example more than 582x more vitamin A, more than 17x more vitamin E, more than a 10x more vitamin K, and at least multiples more of the other vitamins mentioned. So this category’s not a difficult one to call for sweet potato.
When it comes to minerals, beetroot has more selenium, while sweet potato has more calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium. They’re approximately equal in iron and zinc. Another win for sweet potato.
Of course, enjoy both. But if you’re looking for the root vegetable that’ll bring the most nutrients, it’s the sweet potato.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
No, beetroot isn’t vegetable Viagra. But here’s what else it can do
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Deskbound – by Kelly Starrett and Glen Cordoza
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve all heard that “sitting is the new smoking”, and whether or not that’s an exaggeration (the jury’s out), one thing that is clear is that sitting is very bad.
Popular advice is “here’s how to sit with good posture and stretch your neck sometimes”… but that advice tends to come from companies that pay people to sit for a long time. They might not be the a very unbiased source.
Starrett and Cordoza offer better. After one opening chapter covering the multifarious ways sitting ruins our health, the rest of the book is all advice, covering:
- The principles of how the body is supposed to be
- The most important movements that we should be doing
- A dynamic workstation setup
- This is great, because “get a standing desk” tends to present more questions than answers, and can cause as much harm as good if done wrong
- The authors also cover how to progressively cut down on sitting, rather than try to go cold-turkey.
- They also recognize that not everyone can stand at all, and…
- Optimizing the sitting position, for when we must sit
- Exercises to maintain our general mobility and compensate about as well as we can for the body-unfriendly nature of modern life.
The book is mostly explanations, so at 682 pages, you can imagine it’s not just “get up, lazybones!”. Rather, things are explained in such detail (and with many high-quality medical diagrams) so that we can truly understand them.
Most of us have gone through life knowing we should have “better posture” and “move more”… but without the details, that can be hard to execute correctly, and worse, we can even sabotage our bodies unknowingly with incorrect form.
This book straightens all that out very comprehensively, and we highly recommend it.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Natural Remedies and Foods for Osteoarthritis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Natural solutions for osteoarthritis. Eg. Rosehip tea, dandelion root tea. Any others??? What foods should I absolutely leave alone?❞
We’ll do a main feature on arthritis (in both its main forms) someday soon, but meanwhile, we recommend eating for good bone/joint health and against inflammation. To that end, you might like these main features we did on those topics:
- We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of (collagen for bone and joint health)
- The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis (eating for bone health generally)
- Keep Inflammation At Bay (dietary tips for minimizing inflammation—also, our all-time most popular article to date!)
Of these, probably the last one is the most critical, and also will have the speediest effects if implemented.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Do we need animal products to be healthy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
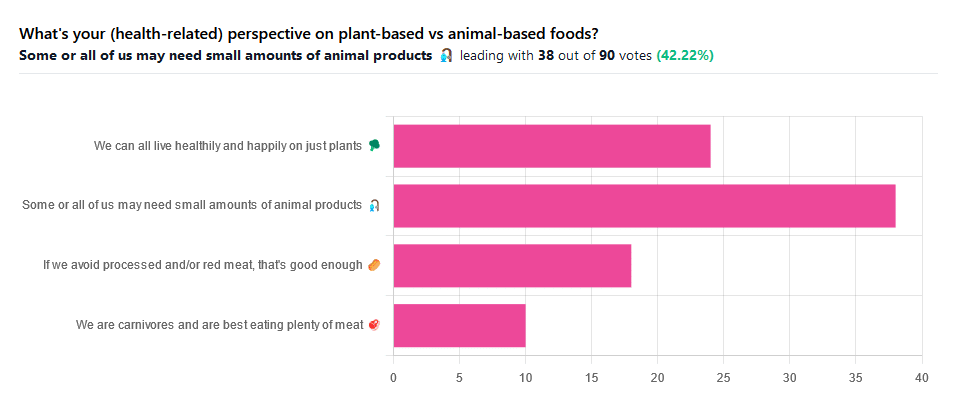
Do we need animal products to be healthy?
We asked you for your (health-related) perspective on plant-based vs anima-based foods, and got the above-pictured spread of answers.
“Some or all of us may need small amounts of animal products” came out on top with more votes than the two more meat-eatery options combined, and the second most popular option was the hard-line “We can all live healthily and happily on just plants”.
Based on these answers, it seems our readership has quite a lot of vegans, vegetarians, and perhaps “flexitarians” who just have a little of animal products here and there.
Perhaps we should have seen this coming; the newsletter is “10almonds”, not “10 rashers of bacon”, after all.
But what does the science say?
We are carnivores and are best eating plenty of meat: True or False?
False. Let’s just rip the band-aid off for this one.
In terms of our anatomy and physiology, we are neither carnivores nor herbivores:
- We have a mid-length digestive tract (unlike carnivores and herbivores who have short and long ones, respectively)
- We have a mouthful of an assortment of teeth; molars and premolars for getting through plants from hard nuts to tough fibrous tubers, and we have incisors for cutting into flesh and (vestigial, but they’re there) canines that really serve us no purpose now but would have been a vicious bite when they were bigger, like some other modern-day primates.
- If we look at our closest living relatives, the other great apes, they are mostly frugivores (fruit-eaters) who supplement their fruity diet with a small quantity of insects and sometimes other small animals—of which they’ll often eat only the fatty organ meat and discard the rest.
And then, there’s the health risks associated with meat. We’ll not linger on this as we’ve talked about it before, but for example:
- Processed Meat Consumption and the Risk of Cancer: A Critical Evaluation of the Constraints of Current Evidence from Epidemiological Studies
- Red Meat Consumption (Heme Iron Intake) and Risk for Diabetes and Comorbidities?
- Health Risks Associated with Meat Consumption: A Review of Epidemiological Studies
- Associations of Processed Meat, Unprocessed Red Meat, Poultry, or Fish Intake With Incident Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality
- Meat consumption: Which are the current global risks? A review of recent (2010-2020) evidences
If we avoid processed and/or red meat, that’s good enough: True or False?
True… Ish.
Really this one depends on one’s criteria for “good enough”. The above-linked studies, and plenty more like them, give the following broad picture:
- Red and/or processed meats are unequivocally terrible for the health in general
- Other mammalian meats, such as from pigs, are really not much better
- Poultry, on the other hand, the science is less clear on; the results are mixed, and thus so are the conclusions. The results are often barely statistically significant. In other words, when it comes to poultry, in the matter of health, the general consensus is that you can take it or leave it and will be fine. Some studies have found firmly for or against it, but the consensus is a collective scientific shrug.
- Fish, meanwhile, has almost universally been found to be healthful in moderation. You may have other reasons for wanting to avoid it (ethics, environmentalism, personal taste) but those things are beyond the scope of this article.
Some or all of us may need small amounts of animal products: True or False?
True! With nuances.
Let’s divide this into “some” and “all”. Firstly, some people may have health conditions and/or other mitigating circumstances that make an entirely plant-based diet untenable.
We’re going light on quotations from subscriber comments today because otherwise this article will get a bit long, but here’s a great example that’s worth quoting, from a subscriber who voted for this option:
❝I have a rare genetic disease called hereditary fructose intolerance. It means I lack the enzyme, Aldolase B, to process fructose. Eating fruits and veggies thus gives me severe hypoglycemia. I also have anemia caused by two autoimmune diseases, so I have to eat meat for the iron it supplies. I also supplement with iron pills but the pills alone can’t fix the problem entirely.❞
And, there’s the thing. Popular vegan talking-points are very good at saying “if you have this problem, this will address it; if you have that problem, that will address it”, etc. For every health-related objection to a fully plant-based diet there’s a refutation… Individually.
But actual real-world health doesn’t work like that; co-morbidities are very common, and in some cases, like our subscriber above, one problem undermines the solution to another. Add a third problem and by now you really just have to do what you need to do to survive.
For this reason, even the Vegan Society’s definition of veganism includes the clause “so far as is possible and practicable”.
Now, as for the rest of us “all”.
What if we’re really healthy and are living in optimal circumstances (easy access to a wide variety of choice of food), can we live healthily and happily just on plants?
No—on a technicality.
Vegans famously need to supplement vitamin B12, which is not found in plants. Ironically, much of the B12 in animal products comes from the animals themselves being given supplements, but that’s another matter. However, B12 can also be enjoyed from yeast. Popular options include the use of yeast extract (e.g. Marmite) and/or nutritional yeast in cooking.
Yeast is a single-celled microorganism that’s taxonomically classified as a fungus, even though in many ways it behaves like an animal (which series of words may conjure an amusing image, but we mean, biologically speaking).
However, it’s also not technically a plant, hence the “No—on a technicality”
Bottom line:
By nature, humans are quite versatile generalists when it comes to diet:
- Most of us can live healthily and happily on just plants if we so choose.
- Some people cannot, and will require varying kinds (and quantities) of animal products.
- As for red and/or processed meats, we’re not the boss of you, but from a health perspective, the science is clear: unless you have a circumstance that really necessitates it, just don’t.
- Same goes for pork, which isn’t red and may not be processed, but metabolically it’s associated with the same problems.
- The jury is out on poultry, but it strongly appears to be optional, healthwise, without making much of a difference either way
- Fish is roundly considered healthful in moderation. Enjoy it if you want, don’t if you don’t.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: