Freekeh Tomato Feast
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fiber-dense freekeh stars in this traditional Palestinian dish, and the whole recipe is very gut-healthy, not to mention delicious and filling, as well as boasting generous amounts of lycopene and other phytonutrients:
You will need
- 1 cup dried freekeh (if avoiding gluten, substitute a gluten-free grain, or pseudograin such as buckwheat; if making such a substitution, then also add 1 tbsp nutritional yeast—for the flavor as well as the nutrients)
- 1 medium onion, thinly sliced
- 1 2oz can anchovies (if vegan/vegetarian, substitute 1 can kimchi)
- 1 14oz can cherry tomatoes
- 1 cup halved cherry tomatoes, fresh
- ½ cup black olives, pitted
- 1 5oz jar roasted peppers, chopped
- ½ bulb garlic, thinly sliced
- 2 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 1 sprig fresh thyme
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Place a heavy-based (cast iron, if you have it) sauté pan over a medium heat. Add some olive oil, then the onion, stirring for about 5 minutes.
2) Add the anchovies, herbs and spices (including the garlic), and stir well to combine. The anchovies will probably soon melt into the onion; that’s fine.
3) Add the canned tomatoes (but not the fresh), followed by the freekeh, stirring well again to combine.
4) Add 2 cups boiling water, and simmer with the lid on for about 40 minutes. Stir occasionally and check the water isn’t getting too low; top it up if it’s getting dry and the freekeh isn’t tender yet.
5) Add the fresh chopped cherry tomatoes and the chopped peppers from the jar, as well as the olives. Stir for just another 2 minutes, enough to let the latest ingredients warm through.
6) Serve, adding a garnish if you wish:
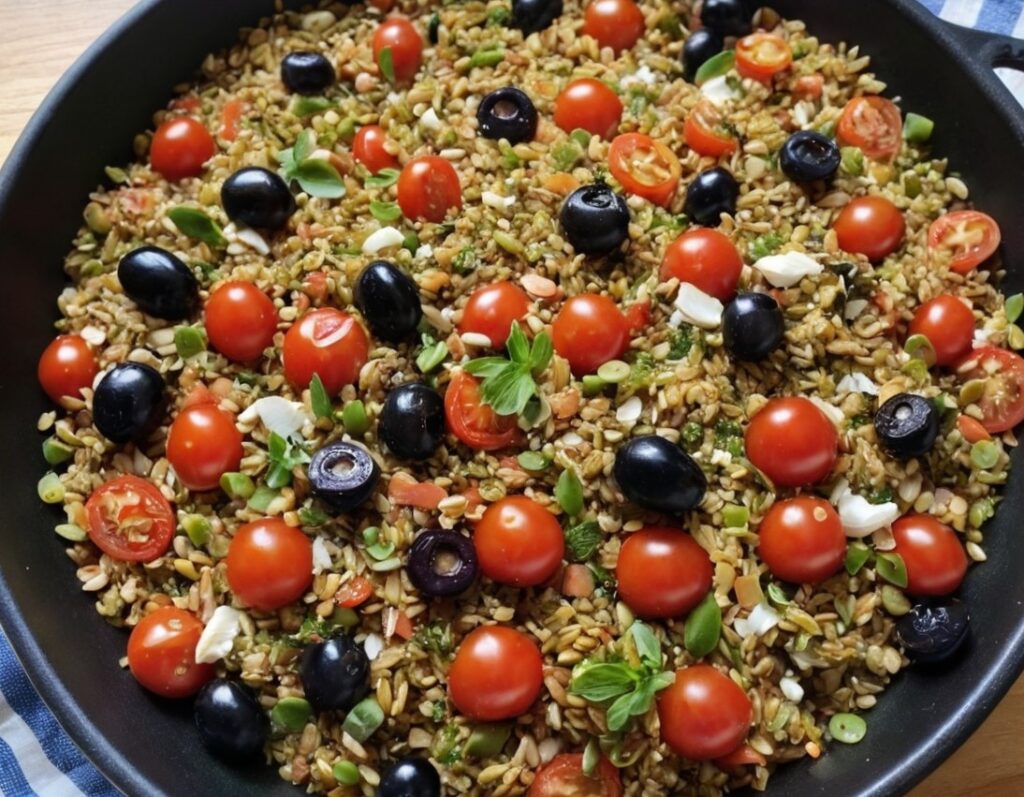

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Microplastics found in artery plaque linked with higher risk of heart attack, stroke and death
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Microplastics and nanoplastics are everywhere in our environment – including in our oceans and lakes, farmland, and even Arctic ice algae.
Microplastics have also been found inside of us – with studies detecting them in various tissues including in the lungs, blood, heart and placenta. Understandably, concern is rising about the potential risks of microplastics on our health.
However, while a growing body of research has focused on microplastics and nanoplastics, there’s still a lack of direct evidence that their presence in human tissues is harmful to our health – and it’s uncertain if they are related to particular diseases.
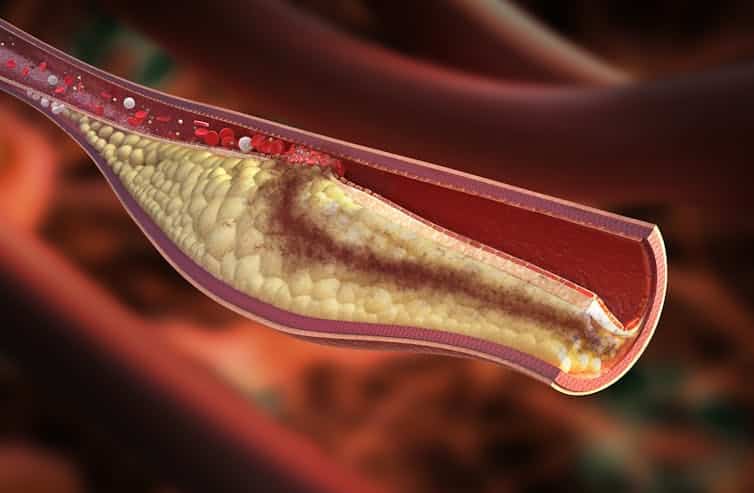
A new study has uncovered a correlation between microplastics and heart health, though. The researchers found that people who had detectable microplastics and nanoplastics in the plaque in their arteries had a higher risk of heart attack, stroke and death.
Heart health
The researchers looked at 257 people altogether. All of the patients were already undergoing preventative surgery to remove plaque from their carotid arteries (the main arteries that supply the brain with blood). This allowed the researchers to collect plaque samples and perform a chemical analysis. They then followed up with participants 34 months later.
Of the 257 participants, 150 were found to have the presence of microplastics and nanoplastics in their arterial plaque – mainly fragments of two of the most commonly used plastics in the world, polyethylene (used in grocery bags, bottles and food packaging) and polyvinyl chloride (used in flooring, cladding and pipes).
A statistical analysis of this data found that patients with microplastics and nanoplastics in their plaque had a higher risk of suffering a heart attack, stroke or death from any cause, compared with those who had no microplastics or nanoplastics in their plaque.
The researchers also analysed the macrophages (a type of immune cell that helps remove pathogens from the body) in the patients’ arteries. They found that participants who’d had microplastics and nanoplastics in their plaque also had evidence of plastic fragments in their macrophages.
They also looked at whether certain genes associated with inflammation (which can be a sign of disease) were switched on in the participants. They found that the participants who’d had microplastics and nanoplastics in their plaque also had signs of inflammation in their genes.
The microplastics were found in samples of plaque extracted from the carotid artery. Rocos/ Shutterstock These results may suggest an accumulation of nanoplastics and microplastics in carotid plaque could partly trigger inflammation. This inflammation may subsequently change the way plaque behaves in the body, making it less stable and triggering it to form a blood clot – which can eventually block blood flow, leading to heart attacks and strokes.
Interestingly, the researchers also found the presence of nanoplastics and microplastics was more common in participants who had diabetes and cardiovascular disease. This raises a lot of questions which have yet to be answered – such as why microplastics were more common in these participants, and if there may be a correlation between other diseases and the presence of microplastics in the body.
Other health risks
This study only focused on patients who had carotid artery disease and were already having surgery to remove the build-up of plaque. As such, it’s unclear whether the findings of this study can be applied to a larger population of people.
However, it isn’t the first study to show a link between microplastics and nanoplastics with poor health. Research suggests some of this harm may be due to the way microplastics and nanoplastics interact with proteins in the body.
For example, some human proteins adhere to the surface of polystyrene nanoplastics, forming a layer surrounding the nanoparticle. The formation of this layer may influence the activity and transfer of nanoplastics in human organs.
Another study suggested that nanoplastics can interact with a protein called alpha-synuclein, which in mouse studies has been shown to play a crucial role in facilitating communication between nerve cells. These clumps of nanoplastics and protein may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease.
My published PhD research in chicken embryos found that nanoplastics may cause congenital malformations due to the way they interact with a protein called cadherin6B. Based on the interactions myself and fellow researchers saw, these malformations may affect the embryo’s eyes and neural tube, as well as the heart’s development and function.
Given the fact that nanoplastics and microplastics are found in carotid plaque, we now need to investigate how these plastics got into such tissues.
In mice, it has been demonstrated that gut macrophages (a type of white blood cell) can absorb microplastics and nanoplastics into their cell membrane. Perhaps a similar mechanism is taking place in the arteries, since nanoplastics have been identified in samples of carotid plaque macrophages.
The findings from this latest study add to a growing body of evidence showing a link between plastic products and our health. It is important now for researchers to investigate the specific mechanisms by which microplastics and nanoplastics cause harm in the body.
Meiru Wang, Postdoctoral Researcher, Molecular Biology and Nanotoxicology, Leiden University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Toe-Tapping Tip For Better Balance
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Balance is critical for health especially in older age, since it’s amazing how much else can go dramatically and suddenly wrong after a fall. So, here’s an exercise to give great balance and stability:
How to do it
You will need:
- Something to hold onto, such as a countertop
- A target on the floor, such as a mark or a coin
The steps:
- Lift one leg up, bring your foot forward, and tap the object in front of you.
- Then, bring that foot back to where it started.
- Next, switch to the other leg and tap.
- Alternate between your right and left legs, shifting back and forth.
- Your goal is to do this for 10 repetitions on each leg without holding on.
How it works:
Whenever you tap, you have to lift one leg up and reach it out in front of you. Doing this requires you to stand on one leg while moving a weight (namely: your other leg), which is something many people, especially upon getting older, are hesitant to do. If you’re unable to stand on one leg, let alone move your center of gravity (per the counterbalance of the other leg) while doing so, you may end up shuffling and walking with your feet sliding across the ground—something you really want to avoid.
For more on all of this plus a visual demonstration, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Fall Special ← this is about not falling, or, failing that, minimizing injury if you do
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Art of Being Unflappable (Tricks For Daily Life)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Art of Being Unflappable
From Stoicism to CBT, thinkers through the ages have sought the unflappable life.
Today, in true 10almonds fashion, we’re going to distil it down to some concentrated essentials that we can all apply in our daily lives:
Most Common/Impactful Cognitive Distortions To Catch (And Thus Avoid)
These are like the rhetorical fallacies with which you might be familiar (ad hominem, no true Scotsman, begging the question, tu quoque, straw man, etc), but are about what goes on between your own ears, pertaining to your own life.
If we learn about them and how to recognize them, however, we can catch them before they sabotage us, and remain “unflappable” in situations that could otherwise turn disastrous.
Let’s take a look at a few:
Catastrophizing / Crystal Ball
- Distortion: not just blowing something out of proportion, but taking an idea and running with it to its worst possible conclusion. For example, we cook one meal that’s a “miss” and conclude we are a terrible cook, and in fact for this reason a terrible housewife/mother/friend/etc, and for this reason everyone will probably abandon us and would be right to do so
- Reality: by tomorrow, you’ll probably be the only one who even remembers it happened
Mind Reading
- Distortion: attributing motivations that may or may not be there, and making assumptions about other people’s thoughts/feelings. An example is the joke about two partners’ diary entries; one is long and full of feelings about how the other is surely dissatisfied in their marriage, has been acting “off” with them all day, is closed and distant, probably wants to divorce, may be having an affair and is wondering which way to jump, and/or is just wondering how to break the news—the other partner’s diary entry is short, and reads “motorcycle won’t start; can’t figure out why”
- Reality: sometimes, asking open questions is better than guessing, and much better than assuming!
All-or-Nothing Thinking / Disqualifying the Positive / Magnifying the Negative
- Distortion: having a negative bias that not only finds a cloud in every silver lining, but stretches it out so that it’s all that we can see. In a relationship, this might mean that one argument makes us feel like our relationship is nothing but strife. In life in general, it may lead us to feel like we are “naturally unlucky”.
- Reality: those negative things wouldn’t even register as negative to us if there weren’t a commensurate positive we’ve experienced to hold them in contrast against. So, find and remember that positive too.
For brevity, we put a spotlight on (and in some cases, clumped together) the ones we think have the most bang-for-buck to know about, but there are many more.
So for the curious, here’s some further reading:
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Body on Fire – by Dr. Monica Aggarwal and Dr. Jyothi Rao
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are times when you do really need a doctor, not a dietician. But there are also times when a doctor will prescribe something for the symptom, leaving the underlying issue untouched. If only there were a way to have the best of both worlds!
That’s where Drs. Rao and Aggarwal come in. They’re both medical doctors… with a keen interest in nutrition and healthy lifestyle changes to make us less sick such that we have less need to go to the doctor at all.
Best of all, they understand—while some things are true for everyone—there’s not a one-size-fits all diet or exercise regime or even sleep setup.
So instead, they take us hand-in-hand (chapter by chapter!) through the various parts of our life (including our diet) that might need tweaking. Each of these changes, if taken up, promise a net improvement that becomes synergistic with the other changes. There’s a degree of biofeedback involved, and listening to your body, to be sure of what’s really best for you, not what merely should be best for you on paper.
The writing style is accessible while science-heavy. They don’t assume prior knowledge, and/but they sure deliver a lot. The book is more text than images, but there are plenty of medical diagrams, explanations, charts, and the like. You will feed like a medical student! And it’s very much worth studying.
Bottom line: highly recommendable even if you don’t have inflammation issues, and worth its weight in gold if you do.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Outlive – by Dr. Peter Attia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We know, we know; this diet, that exercise, don’t smoke or drink, get decent sleep”—a lot of books don’t go beyond this level of advice!
What Dr. Attia offers is a multi-vector approach that covers the above and a lot more.
Themes of the book include:
- The above-mentioned things, of course
- Rethinking medicine for the age of chronic disease
- The pros and cons of…
- caloric restriction
- dietary restriction
- intermittent fasting
- Pre-emptive interventions for…
- specific common cause-of-death conditions
- specific common age-related degenerative conditions
- The oft-forgotten extra pillar of longevity: mental health
The last one in the list there is covered mostly in the last chapter of the book, but it’s there as a matter of importance, not as an afterthought. As Dr. Attia puts it, not only are you less likely to take care of your physical health if you are (for example) depressed, but also… “Longevity is meaningless if your life sucks!”
So, it’s important to do things that promote and maintain good physical and mental health.
Bottom line: if you’re interested in happy, healthy, longevity, this is a book for you.
Click here to check out Dr. Attia’s “Outlive” on Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
6 Worst Foods That Cause Dementia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How many do you consume?
The hit list
Dr. Li bids us avoid:
High carb, low fiber foods: consuming a diet high in carbohydrates, particularly refined carbs like cakes, white bread, pizza, and sugary syrups, can significantly harm brain health. Over time, imbalanced (i.e. not balanced with fiber) carbohydrate consumption leads to the growth of visceral fat (not the same as subcutaneous fat, which is the squishy bits just under your skin; visceral fat is further underneath, around your viscera), , which triggers systemic inflammation and oxidative stress. These processes disrupt communication between brain cells, impair memory, and increase the risk of diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. High carb diets can also contribute to metabolic syndrome—a cluster of conditions, including diabetes, obesity and high blood pressure—that damage blood vessels, leading to strokes and vascular dementia.
Trans fats: these are region-bound, as they’re banned in some places and not others—check your local regulations. Found in processed foods such as fried items, baked goods, packaged snacks, and margarine, trans fats are created through hydrogenation, which makes fats more stable at room temperature. These artificial fats raise bad cholesterol, lower good cholesterol, and promote atherosclerosis. This damages the brain by reducing oxygen supply, triggering chronic inflammation, and increasing the risk of Alzheimer’s and dementia.
Sodas: regular consumption of sodas, whether sugary or artificially sweetened, is harmful to brain health. A single can of soda contains around 9 teaspoons of sugar, which overwhelms metabolism, contributes to insulin resistance, and leads to inflammation. These effects damage blood vessels and brain tissue, disrupt neuron function, and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes and dementia. Furthermore, insulin resistance caused by excessive sugar intake can impair neuronal survival, activate immune responses, and exacerbate cognitive decline. As for the artificial sweeteners, the mechanism of harm depends on the sweetener (and some can also mess up insulin response, for reasons that are not entirely clear yet, but they measurably do), but even picking the healthiest artificial sweetener, training your palate to enjoy hyper-sweetened things will tend to lead to more sugar-laden food choices in other parts of one’s diet.
Processed foods: arguably a broad category that encompasses some of the above, but it’s important to consider it separately for catch-all purposes: these convenience foods, laden with artificial preservatives, colors, and sweeteners, harm brain health through chronic inflammation and usually a lack of essential nutrients. Processed foods are also a significant source of microplastics, which have been found to accumulate in the arteries, contributing to plaque build-up, atherosclerosis, and reduced blood flow to the brain. This combination of inflammation and oxidative stress from microplastics damages brain cells, paving the way for cognitive decline and dementia.
Seafood with high mercury levels: large fish such as tuna, swordfish, sharks, and tilefish accumulate high amounts of mercury, a potent neurotoxin. Fish that are larger, older, and/or higher up the food chain will have the most mercury (and other cumulative contaminants, for that matter, but we’re considering mercury here). Mercury disrupts essential brain chemicals like dopamine and serotonin, triggering oxidative stress and damaging brain cells. Chronic exposure to mercury leads to inflammation and neuroinflammation, both of which increase the risk of Alzheimer’s and dementia.
Alcohol: contrary to popular belief, any amount of alcohol is detrimental to brain health. While red wine is often promoted for its health benefits, the purported positive effects come from polyphenols, not the alcohol itself, and (for example) resveratrol from red wine cannot be delivered in meaningful doses without drinking an impossibly large quantity. Alcohol is a neurotoxin that can damage or kill brain cells, impair neuronal communication, and lead to cognitive decline. Excessive drinking results in hangover symptoms like headaches and brain fog, which are indicators of its harmful impact on the brain. Chronic alcohol consumption exacerbates neuron death, increases inflammation, and raises the risk of dementia.
As for what to eat instead?
Dr. Li recommends including foods such as:
- foods rich in omega-3s that aren’t mercury-laden fish, e.g. flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and hemp seeds, as they reduce inflammation, protect blood vessel linings, and prevent vascular dementia.
- berries, and in particular he recommends organic strawberries, which are rich in ellagic acid and anthocyanins, which improve memory, reduce depressive symptoms, and enhance cognitive function.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: