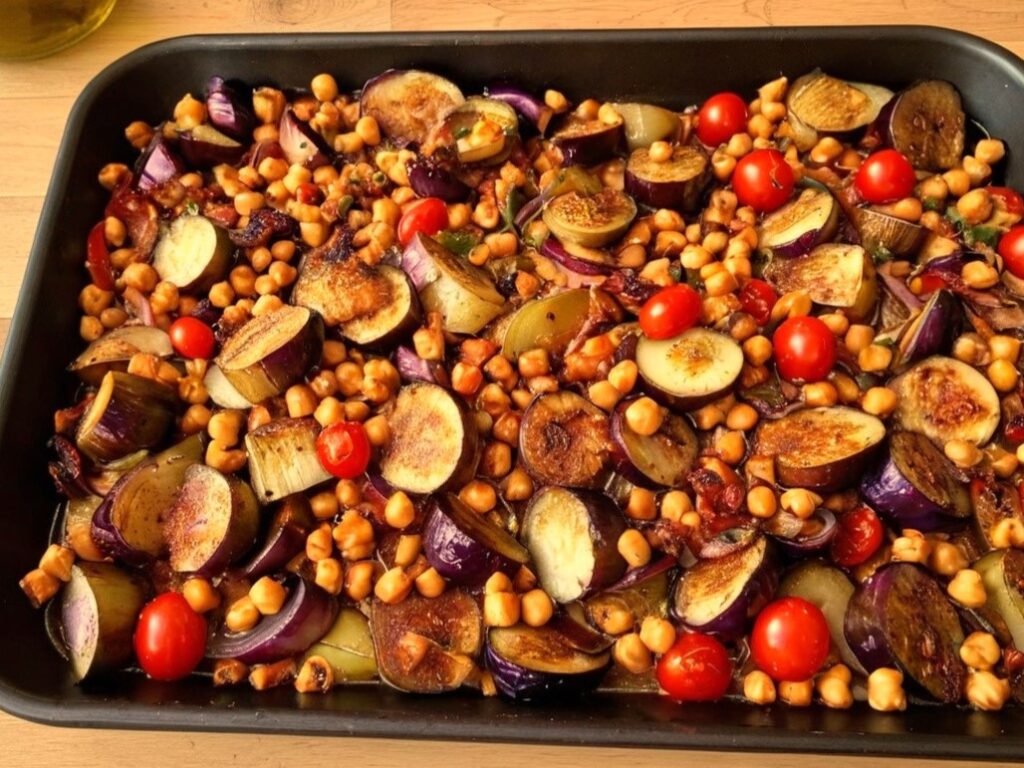
Entertaining Harissa Traybake
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
No, it’s not entertaining in the sense that it will tell you jokes or perhaps dance for you, but rather: it can be easily prepared in advance, kept in the fridge for up to 3 days, and reheated when needed as part of a spread when entertaining, leaving you more time to spend with your houseguests.
Aside from its convenience, it is of course nutritious and delicious:
You will need
- 14 oz cherry tomatoes
- 2 cans chickpeas, drained and rinsed (or 2 cups cooked chickpeas, drained and rinsed)
- 2 eggplants, cut into ¾” cubes
- 1 red onion, roughly chopped
- 1 bulb garlic
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp harissa paste
- 1 tbsp ras el-hanout
- 1 tsp MSG or 2 tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃
2) Mix the onion, eggplant, and garlic (whole cloves; just peel them and put them in) with the olive oil in a mixing bowl, ensuring everything is coated evenly.
3) Add in 1 tbsp of the harissa paste, 1 tbsp of the ras-el hanout, and half of the MSG/salt, and again mix thoroughly to coat evenly.
4) Bake in the oven, in a walled tray, for about 30 minutes, giving things a stir/jiggle halfway through to ensure they cook evenly.
5) Add the cherry tomatoes to the tray, and return to the oven for another 10 minutes.
6) Mix the chickpeas with the other 1 tbsp of the harissa paste, the other 1 tbsp of the ras-el hanout, and the other half of the MSG/salt, and add to the tray, returning it to the oven for a final 10 minutes.
7) Serve hot, or set aside for later, refrigerating once cool enough to do so. When you do serve, we recommend serving with a yogurt, cucumber, and mint dip, and perhaps flatbreads (you can use our Healthy Homemade Flatbreads recipe):

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
7 Healthy Gut Habits For Women Over 40 – by Lara West
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
With regard to the titular 7 healthy gut habits for women over 40, a chapter is devoted to each one of those habits, and she goes into quite some detail in each category, more than you might expect.
As for the 7 things, we’ll not keep them a mystery; they are:
- Intermittent fasting
- Prebiotics & probiotics
- Mindful eating
- Understanding ingredients
- Movement
- Sleep
- Stress management
Of course, all of these things are good regardless of one’s age or gender, but West is writing with women over 40 in mind, and as such, she will focus on things that are especially relevant to those of us who are indeed women over 40.
You may be wondering: what if I’m a long way over 40, and menopause is a distant memory? In that case, 90% of this will still be relevant to you; the only parts that won’t be, are those that pertain specifically to the menopausal transitional phase itself, rather than the post-menopause state.
You may also be wondering: what if I’m a man, and menopause is just not in the cards for me? In that case, maybe about 70% of this will still be relevant to you, because of the broad applicability of most of the advice. That said, if it’s just for yourself, you’d probably do better with a book of which 100% is relevant to you, rather than this one.
The style is conversational pop-science, with personal anecdotes mixed in with references to science. It’s definitely on the light/easy-reading end of books that we’ve reviewed on the topic.
Bottom line: if you’re a woman over 40 who would like to improve your gut health, this book was written for you.
Click here to check out 7 Healthy Gut Habits For Women Over 40, and rediscover vitality!
Share This Post
-
The Link Between Introversion & Sensory Processing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve talked before about how to beat loneliness and isolation, and how that’s important for all of us, including those of us on the less social end of the scale.
However, while we all need at least the option of social contact in order to be at our best, there’s a large portion of the population who also need to be able to retreat to somewhere quiet to recover from too much social goings-on.
Clinically speaking, this sometimes gets called introversion, or at least a negative score for extroversion on the “Big Five Inventory”, the only personality-typing system that actually gets used in science. Today we’re going to be focusing on a term that typically gets applied to those generally considered introverts:
The “highly sensitive person”
This makes it sound like a very rare snowflake condition, when in fact the diagnostic criteria yield a population bell curve of 30:40:30, whereupon 30% are in the band of “high sensitivity”, 40% “normal sensitivity” and the remaining 30% “low sensitivity”.
You may note that “high” and “low” together outnumber “normal”, but statistics is like that. It is interesting to note, though, that this statistical spread renders it not a disorder, so much as simply a description.
You can read more about it here:
Sensory-processing sensitivity and its relation to introversion and emotionality
What it means in practical terms
Such a person will generally seek solitude more frequently during the day than others will, and it’s not because of misanthropy (at least, statistically speaking it’s not; can’t speak for individuals!), but rather, it’s about needing downtime after what has felt like too much sensory processing resulting:
If this need for solitude is not met (sometimes it’s simply not practicable), then it can lead to overwhelm.
Sidenote about overwhelm: pick your battles! No, pick fewer than that. Put some back. That’s still too many 😜
Back to seriousness: if you’re the sort of person to walk into a room and immediately do the Sherlock Holmes thing of noticing everything about everyone, who is doing what, what has changed about the room since last time you were there, etc… Then that’s great; it’s a sign of a sharp mind, but it’s also a lot of information to process and you’re probably going to need a little decompression afterwards:
This is the biological equivalent of needing to let an overworked computer or phone cool down after excessive high-intensity use of its CPU.
The same goes if you’re the sort of person who goes into “performance mode” when in company, is “the life and soul of the party” etc, and/or perhaps “the elegant hostess”, but needs to then collapse afterwards because it’s more of a role you play than your natural inclination.
Take care of your battery
To continue the technological metaphor from earlier, if you repeatedly overuse a device without allowing it cooldown periods, it will break down (and if it’s a certain generation of iPhone, it might explode).
Similarly, if you repeatedly overuse your own highly sensitive senses (such as being often in social environment where there’s a lot going on) without allowing yourself adequate cooldown periods, you will break down (or indeed, explode: not literally, but some people are prone to emotional outbursts after bottling things up).
None of this is good for the health, not in the short term and not in the long term, either:
With that in mind, take care to take care of yourself, meeting your actual needs instead of just those that get socially assumed.
Want to take the test?
Here’s a two-minute test (results available immediately right there on-screen; no need to give your email or anything) 😎
Want to know more?
We reviewed this book about playing to one’s strengths in the context of sensitivity, a while back, and highly recommend it:
Sensitive – by Jenn Granneman and Andre Sólo
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Menopause, & When Not To Let Your Guard Down
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Jessica Shepherd, a physician Fellow of the American College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, CEO at Sanctum Medical & Wellness, and CMO at Hers.
She’s most well-known for her expertise in the field of the menopause. So, what does she want us to know?
Untreated menopause is more serious than most people think
Beyond the famous hot flashes, there’s also the increased osteoporosis risk, which is more well-known at least amongst the health-conscious, but oft-neglected is the increased cardiovascular disease risk:
What Menopause Does To The Heart
…and, which a lot of Dr. Shepherd’s work focuses on, it also increases dementia risk; she cites that 60–80% of dementia cases are women, and it’s also established that it progresses more quickly in women than men too, and this is associated with lower estrogen levels (not a problem for men, because testosterone does it for them) which had previously been a protective factor, but in untreated menopause, was no longer there to help:
Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear
Treated menopause is safer than many people think
The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) study, conducted in the 90s and published in 2002, linked HRT to breast cancer, causing fear, but it turned out that this was quite bad science in several ways and the reporting was even worse (even the flawed data did not really support the conclusion, much less the headlines); it was since broadly refuted (and in fact, it can be a protective factor, depending on the HRT regimen), but fearmongering headlines made it to mainstream news, whereas “oopsies, never mind, we take that back” didn’t.
The short version of the current state of the science is: breast cancer risk varies depending on age, HRT type, and dosage; some kinds of HRT can increase the risk marginally in those older than 60, but absolute risk is low compared to placebo, and taking estrogen alone can reduce risk at any age in the event of not having a uterus (almost always because of having had a hysterectomy; as a quirk, it is possible to be born without, though).
It’s worth noting that even in the cases where HRT marginally increased the risk of breast cancer, it significantly decreased the risk of cancers in total, as well fractures and all-cause-mortality compared to the placebo group.
In other words, it might be worth having a 0.12% risk of breast cancer, to avoid the >30% risk of osteoporosis, which can ultimately be just as fatal (without even looking at the other things the HRT is protective against).
However! In the case of those who already have (or have had) breast cancer, increasing estrogen levels can indeed make that worse/return, and it becomes more complicated in cases where you haven’t had it, but there is a family history of it, or you otherwise know you have the gene for it.
You can read more about HRT and breast cancer risk (increases and decreases) here:
…and about the same with regard to HMT, here:
The Hormone Therapy That Reduces Breast Cancer Risk & More
Lifestyle matters, and continues to matter
Menopause often receives the following attention from people:
- Perimenopause: “Is this menopause?”
- Menopause: “Ok, choices to make about HRT or not, plus I should watch out for osteoporosis”
- Postmenopause: “Yay, that’s behind me now, back to the new normal”
The reality, Dr. Shepherd advises, is that “postmenopause” is a misnomer because if it’s not being treated, then the changes are continuing to occur in your body.
This is a simple factor of physiology; your body is always rebuilding itself, will never stop until you die, and in untreated menopause+postmenopause, it’s now doing it without much estrogen.
So, you can’t let your guard down!
Thus, she recommends: focus on maintaining muscle mass, bone health, and cardiovascular health. If you focus on those things, the rest (including your brain, which is highly dependent on cardiovascular health) will mostly take care of itself.
Because falls and fractures, particularly hip fractures, drastically reduce quality and length of life in older adults, it is vital to avoid those, and try to be sufficiently robust so that if you do go A over T, you won’t injure yourself too badly, because your bones are strong. As a bonus, the same things (especially that muscle mass we talked about) will help you avoid falling in the first place, by improving stability.
See also: Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
And about falls specifically: Fall Special: Be Robust, Mobile, & Balanced!
Want to know more from Dr. Shepherd?
You might like this book of hers that we reviewed not long back:
Generation M – by Dr. Jessica Shepherd
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
7 Principles of Becoming a Leader – by Riku Vuorenmaa
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We urge you to overlook the cliché cover art (we don’t know what they were thinking, going for the headless suited torso) because…
This one could be the best investment you make in your career this year! You may be wondering what the titular 7 principles are. We won’t keep you guessing; they are:
- Professional development: personal excellence, productivity, and time management
- Leadership development: mindset and essential leadership skills
- Personal development: your motivation, character, and confidence as a leader
- Career management: plan your career, get promoted and paid well
- Social skills & networking: work and connect with the right people
- Business- & company-understanding: the big picture
- Commitment: make the decision and commit to becoming a great leader
A lot of leadership books repeat the same old fluff that we’ve all read many times before… padded with a lot of lengthy personal anecdotes and generally editorializing fluff. Not so here!
While yes, this book does also cover some foundational things first, it’d be remiss not to. It also covers a whole (much deeper) range of related skills, with down-to-earth, brass tacks advice on putting them into practice.
This is the kind of book you will want to set as a recurring reminder in your phone, to re-read once a year, or whatever schedule seems sensible to you.
There aren’t many books we’d put in that category!
Pick Up Your Copy of the “7 Principles of Becoming a Leader” on Amazon Today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Stop Negative Thinking – by Daniel Paul
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Just think positive thoughts” is all well and good, but it doesn’t get much mileage in the real world, does it?
What Daniel Paul offers is a lot better than that. Taking a CBT approach, he recommends tips and tricks, gives explanations and exercises, and in short, puts tools in the reader’s toolbox.
But it doesn’t stop at just stopping negative thinking. Rather, it takes a holistic approach to also improve your general life…
- Bookending your day with a good start and finish
- Scheduling a time for any negative thinking that does need to occur (again with the useful realism!)
- Inviting the reader to take on small challenges, of the kind that’ll have knock-on effects that add and multiply and compound as we go
The format is very easy-reading, and we love that there are clear section headings and chapter summaries, too.
Bottom line: definitely a book with the potential to improve your life from day one, and that’ll keep you coming back to it as a cheatsheet and references source.
Get your copy of “How to Stop Negative Thinking” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Seasonal Allergies Mean For Your Heart
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most people associate seasonal allergies with itchy eyes and stuffy noses, but the effects can go a lot deeper.
This is because allergic reactions don’t just affect the respiratory system; they trigger chronic inflammation throughout the body, and in fact:
❝Allergic disease is a systemic and inflammatory condition❞
~ Dr. Rauno Joks, whose work we will cite in a moment
The important thing to understand in terms of heart health, is that chronic* systemic inflammation can contribute to coronary artery disease, where plaque buildup in arteries (bearing in mind, arterial plaque is in large part made of dead immune cells) raises the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
*Yes, a season once or twice per year counts as “chronic”.
A large (n=603,140) study found that allergic rhinitis (hay fever) increased the odds of coronary heart disease by 25% and heart attacks by 20%. Asthma, especially during flare-ups, posed an even greater risk:
Beyond biology
The effects aren’t just biological; allergies can limit physical activity, leading to a sedentary lifestyle that harms heart health.
In other words: if you’re not going outdoors because there’s pollen, and you’re not exercising because you’re exhausted, then the rest of your health is going to take a nose-dive (so to speak) too.
So, one more reason to take it seriously and not just dismiss it as “it’s just allergies, I’ll survive”.
Practical takeaways
Some things we can all do:
- Monitor your risk factors; i.e. keep on top of your heart health metrics, especially blood pressure and cholesterol, as well as any known genetic predisposition to cardiovascular disease.
- Watch out for alternative causes: symptoms like fatigue or shortness of breath may not always be allergies; they could signal asthma, reflux (for example if wheezing), or even heart disease. An allergist is a good first port-of-call, though.
- Be cautious with medications: some decongestants / allergy meds / asthma meds can raise blood pressure and/or interfere with other medications. Your pharmacist is the best person to speak to about this; they know this kind of thing much better than doctors, as a rule. And whenever you get a new medication, it is good practice to make a habit of always reading the information leaflet that comes with it, and/or look it up on a reputable website such as Drugs.com or the the BNF, to learn about what it is, how it works, what the risks are, what its contraindications are, etc.
- Don’t ignore warning signs: lightheadedness or chest pain could indicate a heart issue and should be addressed immediately. It’s better to be wrong and temporarily embarrassed, than wrong and permanently dead. Besides, even if it’s not a heart issue, it may be something else that would benefit from attention, so taking it seriously is always a good idea.
Want to know more?
Check out:
- What Your Mucus Says About Your Health
- Antihistamines’ Generation Gap
- Oh, Honey: The Bee’s Knees? ← what science has to say about “honey will inoculate you against allergies”
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: