Detox: What’s Real, What’s Not, What’s Useful, What’s Dangerous?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Detox: What’s Real, What’s Not, What’s Useful, What’s Dangerous?
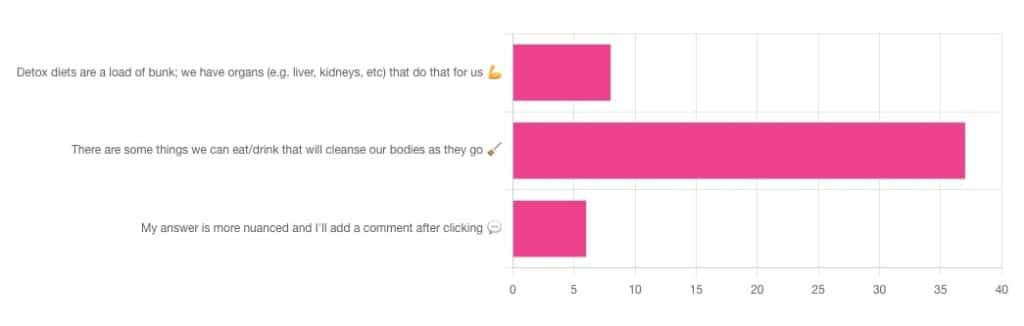
Out of the subscribers who engaged in the poll, it looks like we have a lot of confidence in at least some detox approaches being useful!
Celery juice is most people’s go-to, and indeed it was the only one to get mentioned in the comments added. So let’s take a look at that first…
Celery juice
Celery juice is enjoyed by many people, with many health benefits in mind, including to:
- reduce inflammation
- lower blood pressure
- heal the liver
- fight cancer
- reduce bloating
- support the digestive system
- increase energy
- support weight loss
- promote good mental health
An impressive list! With such an impressive list, we would hope for an impressive weight of evidence, so regular readers might be wondering why those bullet-pointed items aren’t all shiny hyperlinks to studies backing those claims. The reason is…
There aren’t any high-quality studies that back any of those claims.
We found one case study (so, a study with a sample size of one; not amazing) that observed a blood pressure change in an elderly man after drinking celery juice.
Rather than trawl up half of PubMed to show the lacklustre results in a way more befitting of Research Review Monday, though, here’s a nice compact article detailing the litany of disappointment that is science’s observations regards celery juice:
Why Are People Juicing Their Celery? – by Allison Webster, PhD, RD
A key take-away is: juicing destroys the fiber that is celery’s biggest benefit, and its phytochemicals are largely unproven to be of use.
If you enjoy celery, great! It (when not juiced) is a great source of fiber and water. If you juice it, it’s a great source of water.
Activated Charcoal
Unlike a lot of greenery—whose “cleansing” benefits mostly come from fiber and disappear when juiced—activated charcoal has a very different way of operating.
Activated charcoal is negatively charged on a molecular level*, and that—along with its porous nature—traps toxins. It really is a superpowered detox that actually works very well indeed.
But…
It works very well indeed. It will draw out toxins so well, that it’s commonly used to treat poisonings. “Wait”, we hear you say, “why was that a but”?
It doesn’t know what a toxin is. It just draws out all of the things. You took medicine recently? Not any more you didn’t. You didn’t even take that medication orally, you took it some other way? Activated charcoal does not care:
- The effect of activated charcoal on drug exposure following intravenous administration: A meta-analysis
- Activated charcoal for acute overdose: a reappraisal
Does this mean that activated charcoal can be used to “undo” a night of heavy drinking?
Sadly not. That’s one of the few things it just doesn’t work for. It won’t work for alcohol, salts, or metals:
The Use of Activated Charcoal to Treat Intoxications
*Fun chemistry mnemonic about ions:
Cations are pussitive
Anions (by process of elimination) are negative
Onions taste good in salad (remember also: Cole’s Law)
Bottom line on detox foods/drinks:
- Fiber is great; juicing removes fiber. Eat your greens (don’t drink them)!
- Activated charcoal is the heavy artillery of detoxing
- Sometimes it will remove things you didn’t want removed, though
- It also won’t help against alcohol, sadly
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Intermittent Fasting, Intermittently?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Have you come across any research on alternate-day intermittent fasting—specifically switching between one day of 16:8 fasting and the next day of regular eating patterns? I’m curious if there are any benefits or drawbacks to this alternating approach, or if the benefits mainly come from consistent intermittent fasting?❞
Short and unhelpful answer: no
Longer and hopefully more helpful answer:
As you probably know, usually people going for approaches based on the above terms either
- practise 16:8 fasting (fast for 16 hours each day, eat during an 8-hour window) or
- practise alternate-day fasting (fast for 24 hours, eat whenever for 24 hours, repeat)
…which latter scored the best results in this large meta-analysis of studies:
There is also the (popular) less extreme version of alternate-day fasting, sometimes called “eat stop eat”, which is not a very helpful description because that describes almost any kind of eating/fasting, but it usually refers to “once per week, take a day off from eating”.
You can read more about each of these (and some other variants), here:
Intermittent Fasting: What’s The Truth?
What you are describing (doing 16:8 fasting on alternate days, eating whenever on the other days) is essentially: intermittent fasting, just with one 16-hour fast per 48 hours instead of per the usual 24 hours.
See also: International consensus on fasting terminology ← the section on the terms “STF & PF” covers why this gets nudged back under the regular IF umbrella
Good news: this means there is a lot of literature into the acute (i.e., occurring the same day, not long-term)* benefits of 16:8 IF, and that means that you will be getting those benefits, every second day.
You remember that meta-analysis we posted above? While it isn’t mentioned in the conclusion (which only praised complete alternate-day fasting producing the best outcomes overall), sifting through the results data discovers that time-restricted eating (which is what you are doing, by these classifications) was the only fasting method to significantly reduce fasting blood glucose levels.
(However, no significant differences were observed between any IF form and the reference (continuous energy restriction, CER, i.e. calorie-controlled) diets in fasting insulin and HbA1c levels)
*This is still good news in the long-term though, because getting those benefits every second day is better than getting those benefits on no days, and this will have a long-term impact on your healthy longevity, just like how it is better to exercise every second day than it is to exercise no days, or better to abstain from alcohol every second day than it is to abstain on no days, etc.
In short, by doing IF every second day, you are still giving your organs a break sometimes, and that’s good.
All the same, if it would be convenient and practical for you, we would encourage you to consider either the complete alternate-day fasting (which, according to a lot of data, gives the best results overall),or time-restricted eating (TRE) every day (which, according to a lot of data, gives the best fasting blood sugar levels).
You could also improve the TRE days by shifting to 20:4 (i.e., 20 hours fasting and 4 hours eating), this giving your organs a longer break on those days.
Want to learn more?
For a much more comprehensive discussion of the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches to intermitted fasting, check out:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Ovarian cancer is hard to detect. Focusing on these 4 symptoms can help with diagnosis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ovarian cancers are often found when they are already advanced and hard to treat.
Researchers have long believed this was because women first experienced symptoms when ovarian cancer was already well-established. Symptoms can also be hard to identify as they’re vague and similar to other conditions.
But a new study shows promising signs ovarian cancer can be detected in its early stages. The study targeted women with four specific symptoms – bloating, abdominal pain, needing to pee frequently, and feeling full quickly – and put them on a fast track to see a specialist.
As a result, even the most aggressive forms of ovarian cancer could be detected in their early stages.
So what did the study find? And what could it mean for detecting – and treating – ovarian cancer more quickly?
Ground Picture/Shutterstock Why is ovarian cancer hard to detect early?
Ovarian cancer cannot be detected via cervical cancer screening (which used to be called a pap smear) and pelvic exams aren’t useful as a screening test.
Current Australian guidelines recommend women get tested for ovarian cancer if they have symptoms for more than a month. But many of the symptoms – such as tiredness, constipation and changes in menstruation – are vague and overlap with other common illnesses.
This makes early detection a challenge. But it is crucial – a woman’s chances of surviving ovarian cancer are associated with how advanced the cancer is when she is diagnosed.
If the cancer is still confined to the original site with no spread, the five-year survival rate is 92%. But over half of women diagnosed with ovarian cancer first present when the cancer has already metastatised, meaning it has spread to other parts of the body.
If the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, the survival rate is reduced to 72%. If the cancer has already metastasised and spread to distant sites at the time of diagnosis, the rate is only 31%.
There are mixed findings on whether detecting ovarian cancer earlier leads to better survival rates. For example, a trial in the UK that screened more than 200,000 women failed to reduce deaths.
That study screened the general public, rather than relying on self-reported symptoms. The new study suggests asking women to look for specific symptoms can lead to earlier diagnosis, meaning treatment can start more quickly.
What did the new study look at?
Between June 2015 and July 2022, the researchers recruited 2,596 women aged between 16 and 90 from 24 hospitals across the UK.
They were asked to monitor for these four symptoms:
- persistent abdominal distension (women often refer to this as bloating)
- feeling full shortly after starting to eat and/or loss of appetite
- pelvic or abdominal pain (which can feel like indigestion)
- needing to urinate urgently or more often.
Women who reported at least one of four symptoms persistently or frequently were put on a fast-track pathway. That means they were sent to see a gynaecologist within two weeks. The fast track pathway has been used in the UK since 2011, but is not specifically part of Australia’s guidelines.
Some 1,741 participants were put on this fast track. First, they did a blood test that measured the cancer antigen 125 (CA125). If a woman’s CA125 level was abnormal, she was sent to do a internal vaginal ultrasound.
What did they find?
The study indicates this process is better at detecting ovarian cancer than general screening of people who don’t have symptoms. Some 12% of women on the fast-track pathway were diagnosed with some kind of ovarian cancer.
A total of 6.8% of fast-tracked patients were diagnosed with high-grade serous ovarian cancer. It is the most aggressive form of cancer and responsible for 90% of ovarian cancer deaths.
Out of those women with the most aggressive form, one in four were diagnosed when the cancer was still in its early stages. That is important because it allowed treatment of the most lethal cancer before it had spread significantly through the body.
There were some promising signs in treating those with this aggressive form. The majority (95%) had surgery and three quarters (77%) had chemotherapy. Complete cytoreduction – meaning all of the cancer appears to have been removed – was achieved in six women out of ten (61%).
It’s a promising sign that there may be ways to “catch” and target ovarian cancer before it is well-established in the body.
What does this mean for detection?
The study’s findings suggest this method of early testing and referral for the symptoms leads to earlier detection of ovarian cancer. This may also improve outcomes, although the study did not track survival rates.
It also points to the importance of public awareness about symptoms.
Clinicians should be able to recognise all of the ways ovarian cancer can present, including vague symptoms like general fatigue.
But empowering members of the general public to recognise a narrower set of four symptoms can help trigger testing, detection and treatment of ovarian cancer earlier than we thought.
This could also save GPs advising every woman who has general tiredness or constipation to undergo an ovarian cancer test, making testing and treatment more targeted and efficient.
Many women remain unaware of the symptoms of ovarian cancer. This study shows recognising them may help early detection and treatment.
Jenny Doust, Clinical Professorial Research Fellow, Australian Women and Girls’ Health Research Centre, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Tuna vs Catfish – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing tuna to catfish, we picked the tuna.
Why?
Today in “that which is more expensive and/or harder to get is not necessarily healthier”…
Looking at their macros, tuna has more protein and less fat (and overall, less saturated fat, and also less cholesterol).
In the category of vitamins, both are good but tuna distinguishes itself: tuna has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, and D, while catfish has more of vitamins B5, B9, B12, E, and K. They are both approximately equal in choline, and as an extra note in tuna’s favor (already winning 6:5), tuna is a very good source of vitamin D, while catfish barely contains any. All in all: a moderate, but convincing, win for tuna.
When it comes to minerals, things are clearer still: tuna has more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while catfish has more calcium, manganese, and zinc. Oh, and catfish is also higher in one other mineral: sodium, which most people in industrialized countries need less of, on average. So, a 6:3 win for tuna, before we even take into account the sodium content (which makes the win for tuna even stronger).
In short: tuna wins the day in every category!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught (It Makes Quite A Difference)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Peach vs Papaya – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing peach to papaya, we picked the peach.
Why?
It was close!
In terms of macros, there’s not much between them; they are close to identical on protein, carbs, and fiber. Technically peach has slightly more protein (+0.4g/100g) and papaya has slightly more carbs and fiber (+1.28g/100g carbs, +0.2g/100g fiber), but since the differences are so tiny, we’re calling this section a tie—bearing in mind, these numbers are based on averages, which means that when they’re very close, they’re meaningless—one could easily, for example, pick up a peach that has more fiber than a papaya, because that 0.2g/100g is well within the margin of variation. So, as we say: a tie.
When it comes to vitamins, things are also close; peaches have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, and E, while papaya has more of vitamins A, B6, B9, and C. This is a 4:4 tie, but since the most notable margin of difference is vitamin C (of which papayas have 9x more) while the others are much closer, we’ll call this a tie-breaker win for papaya.
The category of minerals sets things apart more: peaches have more copper, iron, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while papaya has more calcium, magnesium, and selenium. That’s already a 6:3 win for peaches, before we take into account that the numbers for papaya’s calcium and selenium are tiny, so adding this to the already 6:3 win for peaches makes for a clear and easy win for peaches in this category.
Adding up the sections is 1W/1D/1L for both fruits, but looking at the win/loss for each, it’s clear which won/lost on a tiebreaker, and which won/lost by a large margin, so peaches get the victory here.
Of course, enjoy either or both, though! And see below for a bonus feature of peaches:
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← peaches are high on this list! They kill cancer cells while sparing healthy ones 🙂
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cavolo Nero & Sweet Potato Hash
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
🎶 Sweet potato hash? It’s a seasonal smash… Catches on in a flash… Let’s do the hash 🎶
You will need
- 6 oz cavolo nero, tough stems removed, chopped
- 1 large sweet potato, diced
- 1 large red onion, finely chopped
- 1 parsnip, grated
- 1 small red pepper, chopped
- 4 oz baby portobello mushrooms, chopped
- ½ cup fresh or thawed peas
- ¼ bulb garlic, thinly sliced
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp dried rosemary
- 1 tsp dried thyme (dried for convenience; fresh is also fine if you have it)
- 1 tsp red chili flakes (dried for convenience; fresh is also fine if you have it)
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 425℉ / 220℃.
2) Toss the diced sweet potato in 1 tbsp olive oil, as well as the nutritional yeast, ground turmeric, black pepper, and MSG/salt, ensuring an even distribution. Roast in the oven on a lined baking tray, for 30 minutes, turning at least once to get all sides of the potato. When it is done, remove from the oven and set aside.
3) Heat a little oil in a sauté pan or large skillet (either is fine; we’re not adding liquids today), and fry the onion, parsnip, and pepper until softened, which should take about 5 minutes (this is one reason why we grated the parsnip; the other is for the variation in texture).
4) Add the garlic, mushrooms, herbs, and chili flakes, and cook for a further 1 minute, while stirring.
5) Add the cavolo nero and peas, stir until the cavolo nero begins to wilt, and then…
6) Add the roasted sweet potato; cook for about 5 more minutes, pressing down with the spatula here and there to mash the ingredients together.
7) Turn the hash over when it begins to brown on the bottom, to lightly brown the other side too.
8) Serve hot.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Which Bell Peppers To Pick?
- Ergothioneine: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Rosehip’s Benefits, Inside & Out
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s In The Hips
Rosehip (often also written: “rose hip”, “rosehips”, or “rose hips”, but we’ll use the singular compound here to cover its use as a supplement) is often found as an extra ingredient in various supplements, and also various herbal teas. But what is it and what does it actually do?
What it is: it’s the fruiting body that appears on rose plants underneath where the petals appear. They are seasonal.
As for what it does, read on…
Anti-inflammatory
Rosehip is widely sought for (and has been well-studied for) its anti-inflammatory powers.
Because osteoarthritis is one of the most common inflammatory chronic diseases around, a lot of the studies are about OA, but the mechanism of action is well-established as being antioxidant and anti-inflammatory in general:
❝Potent antioxidant radical scavenging effects are well documented for numerous rose hip constituents besides Vitamin C.
Furthermore, anti-inflammatory activities include the reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, reduction of NF-kB signaling, inhibition of pro-inflammatory enzymes, including COX1/2, 5-LOX and iNOS, reduction of C-reactive protein levels, reduction of chemotaxis and chemoluminescence of PMNs, and an inhibition of pro-inflammatory metalloproteases.❞
Note that while rosehip significantly reduces inflammation, it doesn’t affect the range of movement in OA—further making clear its mechanism of action:
Read: Rosa canina fruit (rosehip) for osteoarthritis: a cochrane review
Anti-aging
This is partly about its antioxidant effect, but when it comes to skin, also partly its high vitamin C content. In this 8-week study, for example, taking 3mg/day resulted in significant reductions of many measures of skin aging:
Heart healthy
The dose required to achieve this benefit is much higher, but nonetheless its effectiveness is clear, for example:
❝Daily consumption of 40 g of rose hip powder for 6 weeks can significantly reduce cardiovascular risk in obese people through lowering of systolic blood pressure and plasma cholesterol levels. ❞
~ Dr. Mona Landin-Olsson et al.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: