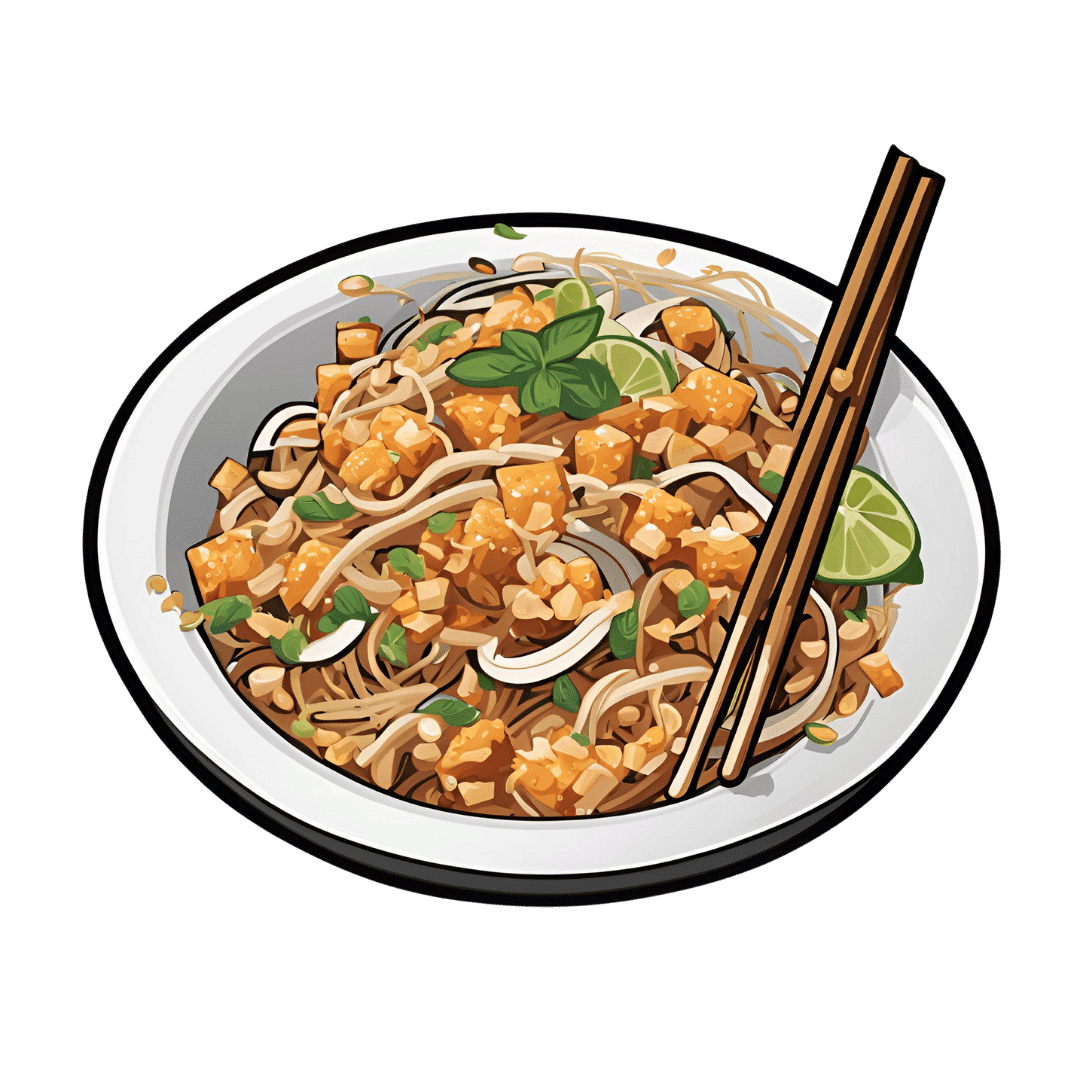
Crispy Tofu Pad Thai
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Easy to make, delicious to enjoy, and packed with phytonutrients, this dish is a great one to add to your repertoire:
You will need
- 10 oz ready-to-wok rice noodles, or 6 oz dry
- 5 oz silken tofu
- 5 oz firm or extra firm tofu, cut into small cubes
- 1 oz arrowroot (or cornstarch if you don’t have arrowroot)
- 4 scallions, sliced
- ¼ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 1″ piece fresh ginger, grated
- 1 red chili, chopped (multiply per your heat preferences)
- 1 red bell pepper, deseeded and thinly sliced
- 4 oz bok choi, thinly sliced
- 4 oz mung bean sprouts
- 1 tbsp tamari (or other, but tamari is traditional) soy sauce
- 1 tbsp sweet chili sauce
- Juice of ½ lime
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Avocado oil, or your preferred oil for stir-frying
- To serve: lime wedges
- Optional garnish: crushed roasted peanuts (if allergic, substitute sesame seeds; peanuts are simply traditional, that’s all)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Scramble the silken tofu. For guidance and also additional seasoning pointers, see our Tasty Tofu Scramble recipe, but omit the thyme.
2) Cook the noodles if necessary (i.e. if they are the dry type and need boiling, as opposed to “ready-to-wok” noodles that don’t), drain, and set aside.
4) Prepare the tofu cubes: if the tofu cubes are dry to the touch, toss them gently in a little oil to coat. If they’re wet to the touch, no need. Dust the tofu cubes with the arrowroot and MSG/salt; you can do this in a bowl, tossing gently to distribute the coating evenly.
4) Heat some oil in a wok over a high heat, and fry the tofu on each side until golden and crispy all over, and set aside.
5) Stir-fry the scallions, garlic, ginger, chili, and bell pepper for about 2 minutes.
6) Add the bean sprouts and bok choi, and keep stir-frying for another 2 minutes.
7) Add everything that’s not already in the pan except the lime wedges and peanuts (i.e., add the things you set aside, plus the remaining as-yet-untouched ingredients) and stir-fry for a further 2 minutes.
8) Serve hot, garnished with the crushed peanuts if using, and with the lime wedges on the side:
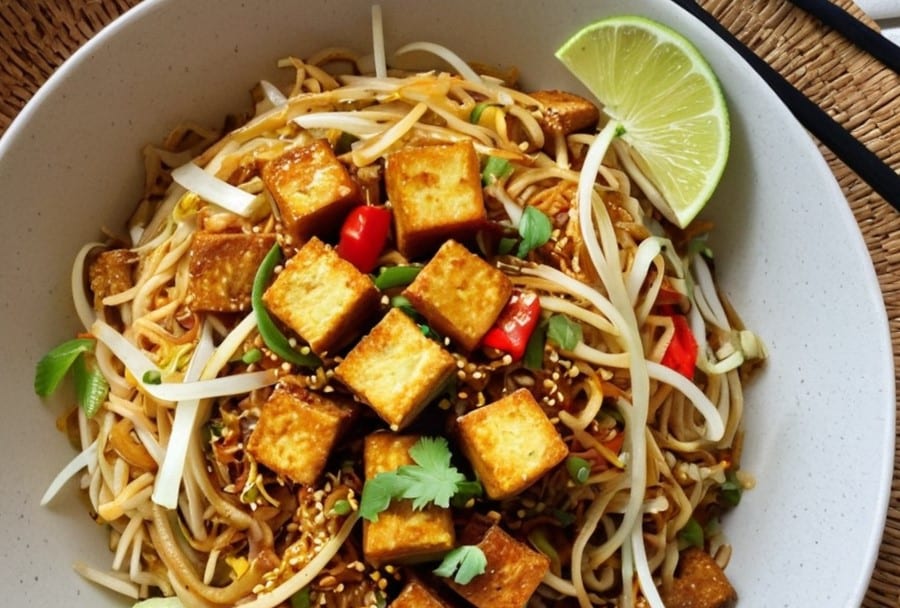

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc
- Which Bell Peppers To Pick? A Spectrum Of Specialties
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healthy Longevity As A Lifestyle Choice
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
7 Keys To Healthy Longevity
This is Dr. Luigi Fontana. He’s a research professor of Geriatrics & Nutritional Science, and co-director of the Longevity Research Program at Washington University in St. Louis.
What does he want us to know?
He has a many-fold approach to healthy longevity, most of which may not be news to you, but you might want to prioritize some things:
Consider caloric restriction with optimal nutrition (CRON)
This is about reducing the metabolic load on your body, which frees up bodily resources for keeping yourself young.
Keeping your body young and healthy is your body’s favorite thing to do, but it can’t do that if it never gets a chance because of all the urgent metabolic tasks you’re giving it.
If CRON isn’t your thing (isn’t practicable for you, causes undue suffering, etc) then intermittent fasting is a great CR mimetic, and he recommends that too. See also:
- Is Cutting Calories The Key To Healthy Long Life?
- Fasting Without Crashing? We Sort The Science From The Hype
Keep your waistline small
Whichever approach you prefer to use to look after your metabolic health, keeping your waistline down is much more important for health than BMI.
Specifically, he recommends keeping it:
- under 31.5” for women
- under 37” for men
The disparity here is because of hormonal differences that influence both metabolism and fat distribution.
Exercise as part of your lifestyle
For Dr. Fontana, he loves mountain-biking (this writer could never!) and weight-lifting (also not my thing). But what’s key is not the specifics, but what’s going on:
- Some kind of frequent movement
- Some kind of high-intensity interval training
- Some kind of resistance training
Frequent movement because our bodies are evolved to be moving more often than not:
The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, & Move More
High-Intensity Interval Training because unlike most forms of exercise (which slow metabolism afterwards to compensate), it boosts metabolism for up to 2 hours after training:
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Resistance training because strength (of muscles and bones) matters too:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
Writer’s examples:
So while I don’t care for mountain-biking or weight-lifting, what I do is:
1) movement: walk (briskly!) everywhere and also use a standing desk
2) HIIT: 2-minute bursts of hindu squats and/or exercise bike sprints
3) resistance: pilates and other calisthenicsModeration is not key
Dr. Fontana advises that we do not smoke, and that we do not drink alcohol, for example. He also notes that just as the only healthy amount of alcohol is zero, less ultra-processed food is always better than more.
Maybe you don’t want to abstain completely, but mindful wilful consumption of something unhealthy is preferable to believing “moderate consumption is good for the health” and an unhealthy habit develops!
Greens and beans
Shocking absolutely nobody, Dr. Fontana advocates for (what has been the most evidence-based gold standard of healthy-aging diets for quite some years now) the Mediterranean diet.
See also: Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet ← this is about tweaking the Mediterranean diet per personal area of focus, e.g. anti-inflammatory bonus, best for gut, heart healthiest, and most neuroprotective.
Take it easy
Dr. Fontana advises us (again, with a wealth of evidence) Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction, and to get good sleep.
Not shocked?
To quote the good doctor,
❝There are no shortcuts. No magic pills or expensive procedures can replace the beneficial effects of a healthy diet, exercise, mindfulness, or a regenerating night’s sleep.❞
Always a good reminder!
Want to know more?
You might enjoy his book “The Path to Longevity: How to Reach 100 with the Health and Stamina of a 40-Year-Old”, which we reviewed previously
You might also like this video of his, about changing the conversation from “chronic disease” to “chronic health”:
Want to watch it, but not right now? Bookmark it for later
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Connection Cure – by Julia Hotz
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may recognize some of the things in the subtitle as being notable elements of the Blue Zones supercentenarians’ lifestyles, but this book looks at numerous quite diverse countries, and people from many walks of life.
What they have in common—and this is mostly a very person-centered book, relying a lot on case studies, with additional references coming from wider sociological data—is social prescribing.
What is social prescribing? That’s what the author (a journalist by general profession) answers comprehensively here, and it’s about looking at the ways medical problems can often have nonmedical solutions. It doesn’t necessarily mean that walking will cure your cancer or art will cure your diabetes, but it does mean that very often a key part of an unhealthy lifestyle is fundamentally something that can be fixed by one or more of: movement, nature, art, service, and belonging.
She looks at social prescribing in its birthplace (the UK, where cheap solutions that are nevertheless evidence-based are very much prioritized), in big countries like Canada and Australia, in aging countries like Singapore and South Korea, and yes, also in the #1 country of pill prescribing, the US.
The structure of the book is interesting, we first have 5 person-centered chapters addressing each of the social prescribing aspects and how they helped in two example case studies for each one, then 5 country-by-country epidemiological chapters looking at the big picture, then 5 person-centered chapters again, this time looking at personalizing social prescribing for oneself (this section of the book being headed “Social Prescribing For You And Me”), looking at what is going on in one’s life and health, which of the 5 elements might be missing, and what tangible goal-oriented benefits can—according to the evidence—be obtained by tending to what one actually needs in terms of social prescribing.
The style is narrative and journalistic, with very little hard science, but very little that’s wishy-washy either. It is, in short, a pleasant and informative read that helps the reader really understand social prescribing, the better to implement it in our own lives.
Bottom line: if you like having extra nonmedical approaches to avoid or alleviate medical problems, then this book will really help you achieve that.
Click here to check out The Connection Cure, and get social prescribing!
Share This Post
-
Reverse Inflammation Naturally – by Dr. Michelle Honda
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is in some ways not as marketable as some; it doesn’t have lots of colorful healthy food on the cover; it doesn’t even have a “woman laughing alone with salad” (you know the stock photo trope), let alone someone looking glamorous in a labcoat with a stethoscope draped over their shoulder despite listening to hearts not being a regular part of their job as an immunologist or such.
What it does have, instead, is a lot of very useful information, and much more than you’ll usually find in a book for laypeople.
For example, you probably know that for fighting inflammation, a green salad is better than a cheeseburger, say, and a black coffee is better than a glass of wine.
But do you know about the roles, for good or ill, of prostaglandins and linoleic fats vs dietary fats? How about delta-6-desaturase? Neu5Gc and arachidonic acid?
Dr. Honda demystifies all of these and more, as well as talking about the impacts of very many foods and related habits on various different inflammation-based disease. And of course, almost all disease involves some kind of inflammation (making fighting inflammation one of the best things you can do for your overall disease-avoidance strategy!), but she singles out some of the most relevant, as per the list on the front cover.
She also talks a lot of “pharmacy in your kitchen”, in other words, what herbs, spices, and plant extracts we can enjoy for (evidence-based!) benefits on top of our default healthy diet free (or at least mostly free, for surely none of us are perfect) from inflammatory agents.
Not content with merely giving a huge amount of information, she also gives recipes and a meal plan, but honestly, it’s the informational chapters that are the real value of the book.
Bottom line: if you’d like to reduce your body’s inflammation levels (and/or perhaps those of a loved one for whom you cook), then this book will be an invaluable resource.
Click here to check out Reverse Inflammation Naturally, and reverse inflammation naturally!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
As the U.S. Struggles With a Stillbirth Crisis, Australia Offers a Model for How to Do Better
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ProPublica is a Pulitzer Prize-winning investigative newsroom. Sign up for The Big Story newsletter to receive stories like this one in your inbox.
Series: Stillbirths:When Babies Die Before Taking Their First Breath
The U.S. has not prioritized stillbirth prevention, and American parents are losing babies even as other countries make larger strides to reduce deaths late in pregnancy.
The stillbirth of her daughter in 1999 cleaved Kristina Keneally’s life into a before and an after. It later became a catalyst for transforming how an entire country approaches stillbirths.
In a world where preventing stillbirths is typically far down the list of health care priorities, Australia — where Keneally was elected as a senator — has emerged as a global leader in the effort to lower the number of babies that die before taking their first breaths. Stillbirth prevention is embedded in the nation’s health care system, supported by its doctors, midwives and nurses, and touted by its politicians.
In 2017, funding from the Australian government established a groundbreaking center for research into stillbirths. The next year, its Senate established a committee on stillbirth research and education. By 2020, the country had adopted a national stillbirth plan, which combines the efforts of health care providers and researchers, bereaved families and advocacy groups, and lawmakers and government officials, all in the name of reducing stillbirths and supporting families. As part of that plan, researchers and advocates teamed up to launch a public awareness campaign. All told, the government has invested more than $40 million.
Meanwhile, the United States, which has a far larger population, has no national stillbirth plan, no public awareness campaign and no government-funded stillbirth research center. Indeed, the U.S. has long lagged behind Australia and other wealthy countries in a crucial measure: how fast the stillbirth rate drops each year.
According to the latest UNICEF report, the U.S. was worse than 151 countries in reducing its stillbirth rate between 2000 and 2021, cutting it by just 0.9%. That figure lands the U.S. in the company of South Sudan in Africa and doing slightly better than Turkmenistan in central Asia. During that period, Australia’s reduction rate was more than double that.
Definitions of stillbirth vary by country, and though both Australia and the U.S. mark stillbirths as the death of a fetus at 20 weeks or more of pregnancy, to fairly compare countries globally, international standards call for the use of the World Health Organization definition that defines stillbirth as a loss after 28 weeks. That puts the U.S. stillbirth rate in 2021 at 2.7 per 1,000 total births, compared with 2.4 in Australia the same year.
Every year in the United States, more than 20,000 pregnancies end in a stillbirth. Each day, roughly 60 babies are stillborn. Australia experiences six stillbirths a day.
Over the past two years, ProPublica has revealed systemic failures at the federal and local levels, including not prioritizing research, awareness and data collection, conducting too few autopsies after stillbirths and doing little to combat stark racial disparities. And while efforts are starting to surface in the U.S. — including two stillbirth-prevention bills that are pending in Congress — they lack the scope and urgency seen in Australia.
“If you ask which parts of the work in Australia can be done in or should be done in the U.S., the answer is all of it,” said Susannah Hopkins Leisher, a stillbirth parent, epidemiologist and assistant professor in the stillbirth research program at the University of Utah Health. “There’s no physical reason why we cannot do exactly what Australia has done.”
Australia’s goal, which has been complicated by the pandemic, is to, by 2025, reduce the country’s rate of stillbirths after 28 weeks by 20% from its 2020 rate. The national plan laid out the target, and it is up to each jurisdiction to determine how to implement it based on their local needs.
The most significant development came in 2019, when the Stillbirth Centre of Research Excellence — the headquarters for Australia’s stillbirth-prevention efforts — launched the core of its strategy, a checklist of five evidence-based priorities known as the Safer Baby Bundle. They include supporting pregnant patients to stop smoking; regular monitoring for signs that the fetus is not growing as expected, which is known as fetal growth restriction; explaining the importance of acting quickly if fetal movement changes or decreases; advising pregnant patients to go to sleep on their side after 28 weeks; and encouraging patients to talk to their doctors about when to deliver because in some cases that may be before their due date.
Officials estimate that at least half of all births in the country are covered by maternity services that have adopted the bundle, which focuses on preventing stillbirths after 28 weeks.
“These are babies whose lives you would expect to save because they would survive if they were born alive,” said Dr. David Ellwood, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Griffith University, director of maternal-fetal medicine at Gold Coast University Hospital and a co-director of the Stillbirth Centre of Research Excellence.
Australia wasn’t always a leader in stillbirth prevention.
In 2000, when the stillbirth rate in the U.S. was 3.3 per 1,000 total births, Australia’s was 3.7. A group of doctors, midwives and parents recognized the need to do more and began working on improving their data classification and collection to better understand the problem areas. By 2014, Australia published its first in-depth national report on stillbirth. Two years later, the medical journal The Lancet published the second report in a landmark series on stillbirths, and Australian researchers applied for the first grant from the government to create the stillbirth research center.
But full federal buy-in remained elusive.
As parent advocates, researchers, doctors and midwives worked to gain national support, they didn’t yet know they would find a champion in Keneally.
Keneally’s improbable journey began when she was born in Nevada to an American father and Australian mother. She grew up in Ohio, graduating from the University of Dayton before meeting the man who would become her husband and moving to Australia.
When she learned that her daughter, who she named Caroline, would be stillborn, she remembers thinking, “I’m smart. I’m educated. How did I let this happen? And why did nobody tell me this was a possible outcome?”
A few years later, in 2003, Keneally decided to enter politics. She was elected to the lower house of state parliament in New South Wales, of which Sydney is the capital. In Australia, newly elected members are expected to give a “first speech.” She was able to get through just one sentence about Caroline before starting to tear up.
As a legislator, Keneally didn’t think of tackling stillbirth as part of her job. There wasn’t any public discourse about preventing stillbirths or supporting families who’d had one. When Caroline was born still, all Keneally got was a book titled “When a Baby Dies.”
In 2009, Keneally became New South Wales’ first woman premier, a role similar to that of an American governor. Another woman who had suffered her own stillbirth and was starting a stillbirth foundation learned of Keneally’s experience. She wrote to Keneally and asked the premier to be the foundation’s patron.
What’s the point of being the first female premier, Keneally thought, if I can’t support this group?
Like the U.S., Australia had previously launched an awareness campaign that contributed to a staggering reduction in sudden infant death syndrome, or SIDS. But there was no similar push for stillbirths.
“If we can figure out ways to reduce SIDS,” Keneally said, “surely it’s not beyond us to figure out ways to reduce stillbirth.”
She lost her seat after two years and took a break from politics, only to return six years later. In 2018, she was selected to serve as a senator at Australia’s federal level.
Keneally saw this as her second chance to fight for stillbirth prevention. In the short period between her election and her inaugural speech, she had put everything in place for a Senate inquiry into stillbirth.
In her address, Keneally declared stillbirth a national public health crisis. This time, she spoke at length about Caroline.
“When it comes to stillbirth prevention,” she said, “there are things that we know that we’re not telling parents, and there are things we don’t know, but we could, if we changed how we collected data and how we funded research.”
The day of her speech, March 27, 2018, she and her fellow senators established the Select Committee on Stillbirth Research and Education.
Things moved quickly over the next nine months. Keneally and other lawmakers traveled the country holding hearings, listening to testimony from grieving parents and writing up their findings in a report released that December.
“The culture of silence around stillbirth means that parents and families who experience it are less likely to be prepared to deal with the personal, social and financial consequences,” the report said. “This failure to regard stillbirth as a public health issue also has significant consequences for the level of funding available for research and education, and for public awareness of the social and economic costs to the community as a whole.”
It would be easy to swap the U.S. for Australia in many places throughout the report. Women of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander backgrounds experienced double the rate of stillbirth of other Australian women; Black women in America are more than twice as likely as white women to have a stillbirth. Both countries faced a lack of coordinated research and corresponding funding, low autopsy rates following a stillbirth and poor public awareness of the problem.
The day after the report’s release, the Australian government announced that it would develop a national plan and pledged $7.2 million in funding for prevention. Nearly half was to go to education and awareness programs for women and their health care providers.
In the following months, government officials rolled out the Safer Baby Bundle and pledged another $26 million to support parents’ mental health after a loss.
Many in Australia see Keneally’s first speech as senator, in 2018, as the turning point for the country’s fight for stillbirth prevention. Her words forced the federal government to acknowledge the stillbirth crisis and launch the national action plan with bipartisan support.
Australia’s assistant minister for health and aged care, Ged Kearney, cited Keneally’s speech in an email to ProPublica where she noted that Australia has become a world leader in stillbirth awareness, prevention and supporting families after a loss.
“Kristina highlighted the power of women telling their story for positive change,” Kearney said, adding, “As a Labor Senator Kristina Keneally bravely shared her deeply personal story of her daughter Caroline who was stillborn in 1999. Like so many mothers, she helped pave the way for creating a more compassionate and inclusive society.”
Keneally, who is now CEO of Sydney Children’s Hospitals Foundation, said the number of stillbirths a day in Australia spurred the movement for change.
“Six babies a day,” Keneally said. “Once you hear that fact, you can’t unhear it.”
Australia’s leading stillbirth experts watched closely as the country moved closer to a unified effort. This was the moment for which they had been waiting.
“We had all the information needed, but that’s really what made it happen.” said Vicki Flenady, a perinatal epidemiologist, co-director of the Stillbirth Centre of Research Excellence based at the Mater Research Institute at the University of Queensland, and a lead author on The Lancet’s stillbirth series. “I don’t think there’s a person who could dispute that.”
Flenady and her co-director Ellwood had spent more than two decades focused on stillbirths. After establishing the center in 2017, they were now able to expand their team. As part of their work with the International Stillbirth Alliance, they reached out to other countries with a track record of innovation and evidence-based research: the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Ireland. They modeled the Safer Baby Bundle after a similar one in the U.K., though they added some elements.
In 2019, the state of Victoria, home to Melbourne, was the first to implement the Safer Baby Bundle. But 10 months into the program, the effort had to be paused for several months because of the pandemic, which forced other states to cancel their launches altogether.
“COVID was a major disruption. We stopped and started,” Flenady said.
Still, between 2019 and 2021, participating hospitals across Victoria were able to reduce their stillbirth rate by 21%. That improvement has yet to be seen at the national level.
A number of areas are still working on implementing the bundle. Westmead Hospital, one of Australia’s largest hospitals, planned to wrap that phase up last month. Like many hospitals, Westmead prominently displays the bundle’s key messages in the colorful posters and flyers hanging in patient rooms and in the hallways. They include easy-to-understand slogans such as, “Big or small. Your baby’s growth matters,” and, “Sleep on your side when baby’s inside.”
As patients at Westmead wait for their names to be called, a TV in the waiting room plays a video on stillbirth prevention, highlighting the importance of fetal movement. If a patient is concerned their baby’s movements have slowed down, they are instructed to come in to be seen within two hours. The patient’s chart gets a colorful sticker with a 16-point checklist of stillbirth risk factors.
Susan Heath, a senior clinical midwife at Westmead, came up with the idea for the stickers. Her office is tucked inside the hospital’s maternity wing, down a maze of hallways. As she makes the familiar walk to her desk, with her faded hospital badge bouncing against her navy blue scrubs, it’s clear she is a woman on a mission. The bundle gives doctors and midwives structure and uniform guidance, she said, and takes stillbirth out of the shadows. She reminds her staff of how making the practices a routine part of their job has the power to change their patients’ lives.
“You’re trying,” she said, “to help them prevent having the worst day of their life.”
Christine Andrews, a senior researcher at the Stillbirth Centre who is leading an evaluation of the program’s effectiveness, said the national stillbirth rate beyond 28 weeks has continued to slowly improve.
“It is going to take a while until we see the stillbirth rate across the whole entire country go down,” Andrews said. “We are anticipating that we’re going to start to see a shift in that rate soon.”
As officials wait to receive and standardize the data from hospitals and states, they are encouraged by a number of indicators.
For example, several states are reporting increases in the detection of babies that aren’t growing as they should, a major factor in many late-gestation stillbirths. Many also have seen an increase in the number of pregnant patients who stopped smoking. Health care providers also are more consistently offering post-stillbirth investigations, such as autopsies.
In addition to the Safer Baby Bundle, the national plan also calls for raising awareness and reducing racial disparities. The improvements it recommends for bereavement care are already gaining global attention.
To fulfill those directives, Australia has launched a “Still Six Lives” public awareness campaign, has implemented a national stillbirth clinical care standard and has spent two years developing a culturally inclusive version of the Safer Baby Bundle for First Nations, migrant and refugee communities. Those resources, which were recently released, incorporated cultural traditions and used terms like Stronger Bubba Born for the bundle and “sorry business babies,” which is how some Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander women refer to stillbirth. There are also audio versions for those who can’t or prefer not to read the information.
In May, nearly 50 people from the state of Queensland met in a large hotel conference room. Midwives, doctors and nurses sat at round tables with government officials, hospital administrators and maternal and infant health advocates. Some even wore their bright blue Safer Baby T-shirts.
One by one, they discussed their experiences implementing the Safer Baby Bundle. One midwifery group was able to get more than a third of its patients to stop smoking between their first visit and giving birth.
Officials from a hospital in one of the fastest-growing areas in the state discussed how they carefully monitored for fetal growth restriction.
And staff from another hospital, which serves many low-income and immigrant patients, described how 97% of pregnant patients who said their baby’s movements had decreased were seen for additional monitoring within two hours of voicing their concern.
As the midwives, nurses and doctors ticked off the progress they were seeing, they also discussed the fear of unintended consequences: higher rates of premature births or increased admissions to neonatal intensive care units. But neither, they said, has materialized.
“The bundle isn’t causing any harm and may be improving other outcomes, like reducing early-term birth,” Flenady said. “I think it really shows a lot of positive impact.”
As far behind as the U.S. is in prioritizing stillbirth prevention, there is still hope.
Dr. Bob Silver, who co-authored a study that estimated that nearly 1 in 4 stillbirths are potentially preventable, has looked to the international community as a model. Now, he and Leisher — the University of Utah epidemiologist and stillbirth parent — are working to create one of the first stillbirth research and prevention centers in the U.S. in partnership with stillbirth leaders from Australia and other countries. They hope to launch next year.
“There’s no question that Australia has done a better job than we have,” said Silver, who is also chair of the University of Utah Health obstetrics and gynecology department. “Part of it is just highlighting it and paying attention to it.”
It’s hard to know what parts of Australia’s strategy are making a difference — the bundle as a whole, just certain elements of it, the increased stillbirth awareness across the country, or some combination of those things. Not every component has been proven to decrease stillbirth.
The lack of U.S. research on the issue has made some cautious to adopt the bundle, Silver said, but it is clear the U.S. can and should do more.
There comes a point when an issue is so critical, Silver said, that people have to do the best they can with the information that they have. The U.S. has done that with other problems, such as maternal mortality, he said, though many of the tactics used to combat that problem have not been proven scientifically.
“But we’ve decided this problem is so bad, we’re going to try the things that we think are most likely to be helpful,” Silver said.
After more than 30 years of working on stillbirth prevention, Silver said the U.S. may be at a turning point. Parents’ voices are getting louder and starting to reach lawmakers. More doctors are affirming that stillbirths are not inevitable. And pressure is mounting on federal institutions to do more.
Of the two stillbirth prevention bills in Congress, one already sailed through the Senate. The second bill, the Stillbirth Health Improvement and Education for Autumn Act, includes features that also appeared in Australia’s plan, such as improving data, increasing awareness and providing support for autopsies.
And after many years, the National Institutes of Health has turned its focus back to stillbirths. In March, it released a report with a series of recommendations to reduce the nation’s stillbirth rate that mirror ProPublica’s reporting about some of the causes of the crisis. Since then, it has launched additional groups to begin to tackle three critical angles: prevention, data and bereavement. Silver co-chairs the prevention group.
In November, more than 100 doctors, parents and advocates gathered for a symposium in New York City to discuss everything from improving bereavement care in the U.S to tackling racial disparities in stillbirth. In 2022, after taking a page out of the U.K.’s book, the city’s Mount Sinai Hospital opened the first Rainbow Clinic in the U.S., which employs specific protocols to care for people who have had a stillbirth.
But given the financial resources in the U.S. and the academic capacity at American universities and research institutions, Leisher and others said federal and state governments aren’t doing nearly enough.
“The U.S. is not pulling its weight in relation either to our burden or to the resources that we have at our disposal,” she said. “We’ve got a lot of babies dying, and we’ve got a really bad imbalance of who those babies are as well. And yet we look at a country with a much smaller number of stillbirths who is leading the world.”
“We can do more. Much more. We’re just not,” she added. “It’s unacceptable.”
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Imposter Syndrome (and why almost everyone has it)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Imposter Syndrome (and why almost everyone has it)
Imposter syndrome is the pervasive idea that we’re not actually good enough, people think we are better than we are, and at any moment we’re going to get found out and disappoint everyone.
Beyond the workplace
Imposter syndrome is most associated with professionals. It can range from a medical professional who feels like they’ve been projecting an image of confidence too much, to a writer or musician who is sure that their next piece will never live up to the acclaim of previous pieces and everyone will suddenly realize they don’t know what they’re doing, to a middle-manager who feels like nobody above or below them realizes how little they know how to do.
But! Less talked-about (but no less prevalent) is imposter syndrome in other areas of life. New parents tend to feel this strongly, as can the “elders” of a family that everyone looks to for advice and strength and support. Perhaps worst is when the person most responsible for the finances of a household feels like everyone just trusts them to keep everything running smoothly, and maybe they shouldn’t because it could all come crashing down at any moment and everyone will see them for the hopeless shambles of a human being that they really are.
Feelings are not facts
And yet (while everyone makes mistakes sometimes) the reality is that we’re all doing our best. Given that imposter syndrome affects up to 82% of people, let’s remember to have some perspective. Everyone feels like they’re winging it sometimes. Everyone feels the pressure.
Well, perhaps not everyone. There’s that other 18%. Some people are sure they’re the best thing ever. Then again, there’s probably some in that 18% that actually feel worse than the 82%—they just couldn’t admit it, even in an anonymized study.
But one thing’s for sure: it’s very, very common. Especially in high-performing women, by the way, and people of color. In other words, people who typically “have to do twice as much to get recognized as half as good”.
That said, the flipside of this is that people who are not in any of those categories may feel “everything is in my favor, so I really have no excuse to not achieve the most”, and can sometimes take very extreme actions to try to avoid perceived failure, and it can be their family that pays the price.
Things to remember
If you find imposter syndrome nagging at you, remember these things:
- There are people far less competent than you, doing the same thing
- Nobody knows how to do everything themselves, especially at first
- If you don’t know how to do something, you can usually find out
- There is always someone to ask for help, or at least advice, or at least support
At the end of the day, we evolved to eat fruit and enjoy the sun. None of us are fully equipped for all the challenges of the modern world, but if we do our reasonable best, and look after each other (and that means that you too, dear reader, deserve looking after as well), we can all do ok.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healthy Butternut Macaroni Cheese
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A comfort food classic, healthy and plant-based, without skimping on the comfort.
You will need
- ½ butternut squash, peeled and cut into small pieces (if buying ready-chopped, this should be about 1 lb)
- 1 onion, chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 12 oz (or thereabouts) wholegrain macaroni, or similar pasta shape (even penne works fine—which is good, as it’s often easier to buy wholegrain penne than wholegrain macaroni) (substitute with a gluten-free pasta such as buckwheat pasta, if avoiding gluten)
- 6 oz (or thereabouts) cashews, soaked in hot water for at least 15 minutes (but longer is better)
- ½ cup milk (your preference what kind; we recommend hazelnut for its mellow nutty flavor)
- 3 tbsp nutritional yeast
- Juice of ½ lemon
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Optional: smoked paprika, to serve
Note: if you are allergic to nuts, please accept our apologies that there’s no substitution available in this one. Simply put, removing the cashews would mean changing most of the rest of the recipe to compensate, so there’s no easy “or substitute with…” that we can mention. We’ll have to find/develop a good healthy plant-based no-nuts recipe for you at a later date.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Combine the butternut squash, onion, and garlic with the olive oil, in a large roasting tin, tossing thoroughly to ensure an even coat of oil. Roast them for about 25 minutes until soft.
3) Cook the macaroni while you wait (this should take about 10 minutes or so in salted water), drain, and rinse thoroughly in cold water, before setting aside. This cooling increases the pasta’s resistant starch content (that’s good, for your gut and for your blood sugars, and thus also for your heart and brain), and it will maintain this benefit even when we reheat it later.
4) Drain the cashews, and tip them into a high-speed blender with the milk, and process until smooth. Add the roasted vegetables and the remaining ingredients apart from the pasta, and continue to process until again smooth. You can add a little more milk if you need to, but go easy with it.
5) Heat the sauce (that you just made in the food processor) gently in a saucepan, and refresh the pasta by pouring a kettle of boiling water through it in a colander.
6) Optional: combine the pasta and sauce in an ovenproof dish or cast iron pan, and give it a few minutes under the hottest grill (or browning iron, if you have such) your oven can muster. Alternatively, use a culinary blowtorch, if you have one.
7) Serve; and if you didn’t do the optional step above, this means combining the pasta and sauce. You can also dust the top with some extra seasonings if you like. Smoked paprika works well for this.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Butternut Squash vs Pumpkin – Which is Healthier?
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: