Anti-Cholesterol Cardamom & Pistachio Porridge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This tasty breakfast’s beta-glucan content binds to cholesterol and carries it out of the body; there are lots of other nutritional benefits too!
You will need
- 1 cup coconut milk
- ⅓ cup oats
- 4 tbsp crushed pistachios
- 6 cardamom pods, crushed
- 1 tsp rose water or 4 drops edible rose essential oil
- Optional sweetener: drizzle of honey or maple syrup
- Optional garnishes: rose petals, chopped nuts, dried fruit
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat the coconut milk, adding the oats and crushed cardamom pods. Simmer for 5–10 minutes depending on how cooked you want the oats to be.
2) Stir in the crushed pistachio nuts, as well as the rose water.
3) Serve in a bowl, adding any optional toppings:
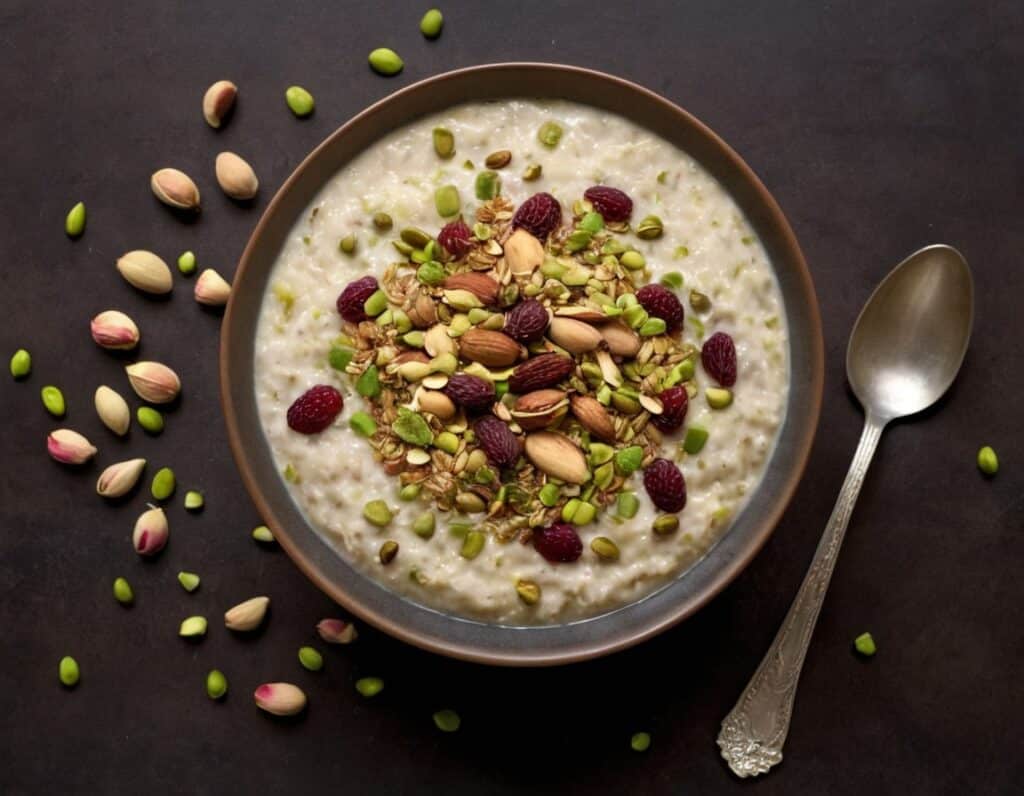

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health? ← it’s beta-glucan, which is fund abundantly in oats
- Pistachios vs Pecans – Which is Healthier? ← have a guess
- Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy? ← coconut can!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Undo The Sun’s Damage To Your Skin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s often said that our skin is our largest organ. Our brain or liver are the largest solid organs by mass (which one comes out on top will vary from person to person), our gut is the longest, and our lungs are the largest by surface area. But our skin is large, noticeable, and has a big impact on the rest of our health.
The sun is one of the main damaging factors for our skin; assorted toxins are also a major threat for many people, and once the skin barrier gets broken, it’s a field-day for bacteria.
So, what can we do about it?
Tretinoin: the skin’s rejuvenator
Tretinoin is also called retinoic acid, not to be mistaken for retinol, although they are both retinoids. Tretinoin is much stronger.
As for what it’s stronger at:
It’s usually prescribed for the treatment of sun-damage, acne, and wrinkles. Paradoxically, it works by inflaming the skin (and then making it better, and having done so, keeping it better).
In few words: it encourages your skin to speed up its life cycle, which means that cells die and are replaced sooner, which means the average age of skin cells will be considerably younger at any given time.
This is the same principle as we see at work when it comes to cellular apoptosis and autophagy in general, and specifically the same idea as we discussed when talking about senolytics, compounds that kill aging cells:
Fisetin: The Anti-Aging Assassin
About that paradoxical inflammation…
❝The topical use of tretinoin as an antiacne agent began almost a half century ago. Since that time it has been successfully used to treat comedonal and inflammatory acne.
Over the intervening years, the beneficial effects of tretinoin have grown from an understanding of its potent cornedolytie-related properties to an evolving appreciation of its antiinflammatory actions.
…
The topical use of clindamycin and tretinoin as a combination treatment modality that includes antibacterial, comedolytic, and antiinflammatoiy properties has proven to be a very effective therapy for treating the various stages of acne
…
It is now becoming increasingly clear that there may be good reasons for these observations.❞
~ Drs. Schmidt & Gans, lightly edited here for brevity
Read in full: Tretinoin: A Review of Its Anti-inflammatory Properties in the Treatment of Acne
Against damage by the sun
The older we get, the more likely sun damage is a problem than acne. And in the case of tretinoin,
❝In several well-controlled clinical trials, the proportion of patients showing improvement was significantly higher with 0.01 or 0.05% tretinoin cream than with placebo for criteria such as global assessment, fine and coarse wrinkling, pigmentation and roughness.
Improvements in the overall severity of photodamage were also significantly greater with tretinoin than with placebo.
…
Several placebo-controlled clinical studies have demonstrated that topical tretinoin has significant efficacy in the treatment of photodamaged skin. Improvements in subjective global assessment scores were recorded in:
49–100% of patients using once-daily 0.01% tretinoin,
68–100% of patients using 0.05% tretinoin, and
0–44% of patients using placebo.❞
~ Drs. Wagstaff & Noble
…which is quite compelling.
Read in full: Tretinoin: A Review of its Pharmacological Properties and Clinical Efficacy in the Topical Treatment of Photodamaged Skin
This is very well-established by now; here’s an old paper from when the mechanism of action was unknown (here in the current day, 17 mechanisms of action have been identified; beyond the scope of this article as we only have so much room, but it’s nice to see science building on science):
❝Tretinoin cream has been used extensively to reverse the changes of photoaging. It is the first topical therapy to undergo controlled clinical testing and proved to be efficacious. These results have been substantiated with photography, histopathologie examination, and skin surface replicas.
…
Tretinoin cream has an excellent safety record; a local cutaneous hypervitaminosis A reaction is the only common problem.❞
~ Dr. Goldfarb et al.
Read in full: Topical tretinoin therapy: Its use in photoaged skin
Is it safe?
For most people, when used as directed*, yes. However, it’s likely to irritate your skin at first, and that’s normal. If this persists more than a few weeks, or seems unduly severe, then you might want to stop and talk to your doctor again.
*See also: Scarring following inappropriate use of 0.05% tretinoin gel
(in the case of a young woman who used it 4x daily instead of 1x daily)
Want to try some?
Tretinoin is prescription-only, so speak with your doctor/pharmacist about that. Alternatively, retinal (not retinol) is the strongest natural alternative that works on the same principles; here’s an example product on Amazon 😎
Take care!
Share This Post
-
What Your Hands Can Tell You About Your Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Siobhan Deshauer tells us what our hands say about our health—she’s not practicing palmistry though; she’s a rheumatologist, and everything here is about clinical signs of health/disease.
The signs include…
“Spider fingers” (which your writer here has; I always look like I’m ready to cast a spell of some kind), and that’s really the medical name, or arachnodactyly for those who like to get Greek about it. It’s about elongated digits. Elongated other bones too, typically, but the hands are where it’s most noticeable.
The tests:
- Make a fist with your thumb inside (the way you were told never to punch); does your thumb poke out the side notably past the edge of your hand, unassisted (i.e., don’t poke it, just let it rest where it goes to naturally)?
- Take hold of one of your wrists with the fingers of the other hand, wrapping them around. If they reach, that’s normal; if there’s a notable overlap, we’re in Spidey-territory now.
If both of those are positive results for you, Dr. Deshauer recommends getting a genetic test to see if you have Marfan syndrome, because…
Arachnodactyly often comes from a genetic condition called Marfan syndrome, and as well as the elongated digits of arachnodactyly, Marfan syndrome affects the elastic fibers of the body, and comes with the trade-off of an increased risk of assorted kinds of sudden death (if something goes “ping” where it shouldn’t, like the heart or lungs).
But it can also come from Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome!
EDS is characterized by hypermobility of joints, meaning that they are easily flexed past the normal human limit, and/but also easily dislocated.
The tests:
- Put your hand flat on a surface, and using your other hand, see how far back your fingers will bend (without discomfort, please); do they go further than 90°?
- Can you touch your thumb to your wrist* (on the same side?)
*She says “wrist”; for this arachnodactylic writer here it’s halfway down my forearm, but you get the idea
For many people this is a mere quirk and inconvenience, for others it can be more serious and a cause of eventual chronic pain, and for a few, it can be very serious and come with cardiovascular problems (similar to the Marfan syndrome issues above). This latter is usually diagnosed early in life, though, such as when a child comes in with an aneurysm, or there’s a family history of it. Another thing to watch out for!
Check out the video for more information on these, as well as what our fingerprints can mean, indicators of diabetes (specifically, a test for diabetic cheiroarthropathy that you can do at home, like the tests above), carpal tunnel syndrome, Raynaud phenomenon, and more!
She covers 10 main medical conditions in total:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to read more?
- We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of ← because collagen comes up a lot in the video
- How To Really Look After Your Joints
Take care!
Share This Post
-
It Didn’t Start with You – by Mark Wolynn
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There is a trend in psychology to “blame the parents” for “childhood trauma” that can result in problems later in life. Sometimes fairly, sometimes not. This book’s mostly not about that.
It does touch on our own childhood trauma, if applicable. But mostly, it’s about epigenetic trauma inheritance. In other words, not just trauma that’s passed on in terms of “the cycle of abuse”, but trauma that’s passed on in terms of “this generation experienced trauma x, developed trauma response y, encoded it epigenetically, and passed it on to their offspring”.
So, how does one heal from a trauma one never directly experienced, and just inherited the response to it? That’s what most of this book is about, after establishing how epigenetic trauma inheritance works.
The author, a therapist, provides practical advice for how to do the things that can be done to rewrite the epigenetic code we inherited. Better late than never!
Bottom line: it is well-established that trauma is inheritable. But unlike one’s eye color or the ability to smell asparagus metabolites in urine, we can rewrite epigenetic things, to a degree. This book explains how.
Click here to check out It Didn’t Start With You, and put things to rest!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What are heart rate zones, and how can you incorporate them into your exercise routine?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you spend a lot of time exploring fitness content online, you might have come across the concept of heart rate zones. Heart rate zone training has become more popular in recent years partly because of the boom in wearable technology which, among other functions, allows people to easily track their heart rates.
Heart rate zones reflect different levels of intensity during aerobic exercise. They’re most often based on a percentage of your maximum heart rate, which is the highest number of beats your heart can achieve per minute.
But what are the different heart rate zones, and how can you use these zones to optimise your workout?
The three-zone model
While there are several models used to describe heart rate zones, the most common model in the scientific literature is the three-zone model, where the zones may be categorised as follows:
- zone 1: 55%–82% of maximum heart rate
- zone 2: 82%–87% of maximum heart rate
- zone 3: 87%–97% of maximum heart rate.
If you’re not sure what your maximum heart rate is, it can be calculated using this equation: 208 – (0.7 × age in years). For example, I’m 32 years old. 208 – (0.7 x 32) = 185.6, so my predicted maximum heart rate is around 186 beats per minute.
There are also other models used to describe heart rate zones, such as the five-zone model (as its name implies, this one has five distinct zones). These models largely describe the same thing and can mostly be used interchangeably.
What do the different zones involve?
The three zones are based around a person’s lactate threshold, which describes the point at which exercise intensity moves from being predominantly aerobic, to predominantly anaerobic.
Aerobic exercise uses oxygen to help our muscles keep going, ensuring we can continue for a long time without fatiguing. Anaerobic exercise, however, uses stored energy to fuel exercise. Anaerobic exercise also accrues metabolic byproducts (such as lactate) that increase fatigue, meaning we can only produce energy anaerobically for a short time.
On average your lactate threshold tends to sit around 85% of your maximum heart rate, although this varies from person to person, and can be higher in athletes.
Wearable technology has taken off in recent years. Ketut Subiyanto/Pexels In the three-zone model, each zone loosely describes one of three types of training.
Zone 1 represents high-volume, low-intensity exercise, usually performed for long periods and at an easy pace, well below lactate threshold. Examples include jogging or cycling at a gentle pace.
Zone 2 is threshold training, also known as tempo training, a moderate intensity training method performed for moderate durations, at (or around) lactate threshold. This could be running, rowing or cycling at a speed where it’s difficult to speak full sentences.
Zone 3 mostly describes methods of high-intensity interval training, which are performed for shorter durations and at intensities above lactate threshold. For example, any circuit style workout that has you exercising hard for 30 seconds then resting for 30 seconds would be zone 3.
Striking a balance
To maximise endurance performance, you need to strike a balance between doing enough training to elicit positive changes, while avoiding over-training, injury and burnout.
While zone 3 is thought to produce the largest improvements in maximal oxygen uptake – one of the best predictors of endurance performance and overall health – it’s also the most tiring. This means you can only perform so much of it before it becomes too much.
Training in different heart rate zones improves slightly different physiological qualities, and so by spending time in each zone, you ensure a variety of benefits for performance and health.
So how much time should you spend in each zone?
Most elite endurance athletes, including runners, rowers, and even cross-country skiers, tend to spend most of their training (around 80%) in zone 1, with the rest split between zones 2 and 3.
Because elite endurance athletes train a lot, most of it needs to be in zone 1, otherwise they risk injury and burnout. For example, some runners accumulate more than 250 kilometres per week, which would be impossible to recover from if it was all performed in zone 2 or 3.
Of course, most people are not professional athletes. The World Health Organization recommends adults aim for 150–300 minutes of moderate intensity exercise per week, or 75–150 minutes of vigorous exercise per week.
If you look at this in the context of heart rate zones, you could consider zone 1 training as moderate intensity, and zones 2 and 3 as vigorous. Then, you can use heart rate zones to make sure you’re exercising to meet these guidelines.
What if I don’t have a heart rate monitor?
If you don’t have access to a heart rate tracker, that doesn’t mean you can’t use heart rate zones to guide your training.
The three heart rate zones discussed in this article can also be prescribed based on feel using a simple 10-point scale, where 0 indicates no effort, and 10 indicates the maximum amount of effort you can produce.
With this system, zone 1 aligns with a 4 or less out of 10, zone 2 with 4.5 to 6.5 out of 10, and zone 3 as a 7 or higher out of 10.
Heart rate zones are not a perfect measure of exercise intensity, but can be a useful tool. And if you don’t want to worry about heart rate zones at all, that’s also fine. The most important thing is to simply get moving.
Hunter Bennett, Lecturer in Exercise Science, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fasting Cancer – by Dr. Valter Longo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Dr. Longo’s “The Longevity Diet”, and whereas that one was about eating, this one is (superficially, at least) about not eating. Nor is this any kind of dissonance, because, in fact, it’s important to do both!
That said, he discusses not just fasting per se, but also the use of a personalized fast-mimicking diet, to accomplish the same goal of not overloading the metabolism—as overloading the metabolism results in metabolic disease, and cancer is, ultimately, a metabolic disease of immune dysfunction with genetic disorder*—which makes for quite a deadly trifecta.
*not in the sense of “hereditary”, though certainly genes can influence cancer risk, but rather, in the sense of “your gene-copying process becomes disordered”.
The first three chapters (after the introduction, which we’ll comment on shortly) are devoted to explaining the principles at hand:
- Fasting cancer while feeding patients
- Genes, aging, and cancer
- Fasting, nutrition, and physical activity in cancer prevention
In those chapters, he details a lot of the science for exactly how and why it is possible to “feed the patient and starve the cancer” at the same time.
After that, the rest of the book—another nine chapters, not counting appendices etc—are given over to fasting and nutrition in the context of nine main types of cancer, one chapter per type. These are not hyperspecific, though, and are rather categorizations, such as “blood cancers”, and “gynecological cancers” and so forth. It’s comprehensive, and while it could be argued that it may mean chapters feel irrelevant to some people (à la “I have never smoked and have no pressing concern about my lung cancer risk” etc), the reality is that it’s good to know how to avoid them all, because if nothing else, it’d be super embarrassing to get a cancer you “thought you couldn’t get”. So, it’s honestly worth the time to read each chapter.
In the category of criticism, he did open the introduction with a handful of anecdotes to defend the consumption of (well-established group 1 carcinogens) red meat and alcohol as “secondary concerns that might not be such a big deal”, even discussing how surprised his colleagues in the field are that he has this view. Suffice it to say, it’s contrary to the overwhelming body of evidence, and reads suspiciously like a man who simply doesn’t want to give up his steak and wine despite his own longevity diet forswearing them.
The style is self-indulgently autobiographical and very complimentary, and (in this reviewer’s opinion) it can be tedious to wade through that to get to the science, but at the end of the day, his self-accolades might be needless fluff, but they don’t actually remove anything from the science in question.
Bottom line: as you can see, there are good and bad things to say about this book, but the information contained in the good makes it well worth reading through the stylistically questionable to get it.
Click here to check out Fasting Cancer, and starve cancer cells while nourishing your healthy ones!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Death by Food Pyramid – by Denise Minger
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one is less about “here’s the perfect way of eating” or even “these specific foods are ontologically evil”, but more about teaching science literacy.
The author explores various health trends from the 70s until time of writing (the book was published in 2014), what rationales originally prompted them, and what social phenomena either helped them to persist, or caused them to get dropped quite quickly.
Of course, even in the case of fads that are societally dropped quite quickly, on an individual level there will always be someone just learning about it for the first time, reading some older material, and thinking “that sounds like just the miracle life-changer I need!”
What she teaches the reader to do is largely what we do a lot of here at 10almonds—examine the claims, go to the actual source material (studies! Not just books about studies!), and see whether the study conclusions actually support the claim, to start with, and then further examine to see if there’s some way (or sometimes, a plurality of ways) in which the study itself is methodologically flawed.
Which does happen sometimes, do actually watch out for that!
The style is quite personal and entertaining for the most part, and yet even moving sometimes (the title is not hyperbole; deaths will be discussed). As one might expect of a book teaching science literacy, it’s very easy to read, with copious footnotes (well, actually they are at the back of the book doubling up as a bibliography, but they are linked-to throughout) for those who wish to delve deeper—something the author, of course, encourages.
Bottom line: if you’d like to be able to sort the real science from the hype yourself, then this book can set you on the right track!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: