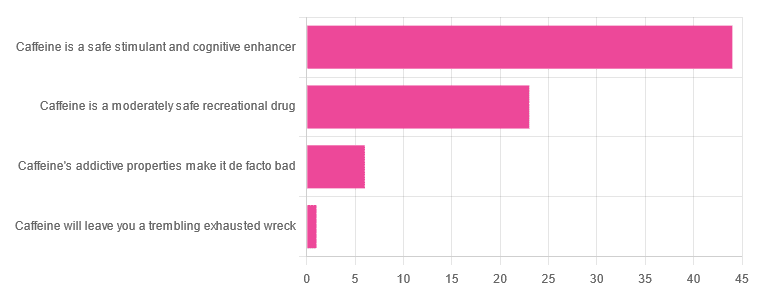
Celery vs Rhubarb – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing celery to rhubarb, we picked the rhubarb.
Why?
In terms of macros, rhubarb has more carbs and fiber, the ratio of which give it the lower glycemic index, though both are low glycemic index foods. This means this category is a very marginal win for rhubarb.
When it comes to vitamins, rhubarb has more vitamin C, while celery has more of vitamins A, B5, B6, and B9. A win for celery, this time.
In the category of minerals, rhubarb has more calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, and selenium, while celery has more copper and phosphorus. This one’s a win for rhubarb.
Let’s give a quick nod also to polyphenols; rhubarb has more by overall quantity, and more in terms of “more useful to humans” too, being rich in an assortment of flavanols while celery must make do with some furanocoumarins.
In short, enjoy either or both, but nutritional density is a great reason to get some rhubarb in!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What is a virtual emergency department? And when should you ‘visit’ one?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For many Australians the emergency department (ED) is the physical and emblematic front door to accessing urgent health-care services.
But health-care services are evolving rapidly to meet the population’s changing needs. In recent years, we’ve seen growing use of telephone, video, and online health services, including the national healthdirect helpline, 13YARN (a crisis support service for First Nations people), state-funded lines like 13 HEALTH, and bulk-billed telehealth services, which have helped millions of Australians to access health care on demand and from home.
The ED is similarly expanding into new telehealth models to improve access to emergency medical care. Virtual EDs allow people to access the expertise of a hospital ED through their phone, computer or tablet.
All Australian states and the Northern Territory have some form of virtual ED at least in development, although not all of these services are available to the general public at this stage.
So what is a virtual ED, and when is it appropriate to consider using one?
Shutterstock/Nils Versemann How does a virtual ED work?
A virtual ED is set up to mirror the way you would enter the physical ED front door. First you provide some basic information to administration staff, then you are triaged by a nurse (this means they categorise the level of urgency of your case), then you see the ED doctor. Generally, this all takes place in a single video call.
In some instances, virtual ED clinicians may consult with other specialists such as neurologists, cardiologists or trauma experts to make clinical decisions.
A virtual ED is not suitable for managing medical emergencies which would require immediate resuscitation, or potentially serious chest pains, difficulty breathing or severe injuries.
A virtual ED is best suited to conditions that require immediate attention but are not life-threatening. These could include wounds, sprains, respiratory illnesses, allergic reactions, rashes, bites, pain, infections, minor burns, children with fevers, gastroenteritis, vertigo, high blood pressure, and many more.
People with these sorts of conditions and concerns may not be able to get in to see a GP straight away and may feel they need emergency advice, care or treatment.
When attending the ED, they can be subject to long wait times and delayed specialist attention because more serious cases are naturally prioritised. Attending a virtual ED may mean they’re seen by a doctor more quickly, and can begin any relevant treatment sooner.
From the perspective of the health-care system, virtual EDs are about redirecting unnecessary presentations away from physical EDs, helping them be ready to respond to emergencies. The virtual ED will not hesitate in directing callers to come into the physical ED if staff believe it is an emergency.
The doctor in the virtual ED may also direct the patient to a GP or other health professional, for example if their condition can’t be assessed visually, or if they need physical treatment.
The results so far
Virtual EDs have developed significantly over the past three years, predominantly driven by the COVID pandemic. We are now starting to slowly see assessments of these services.
A recent evaluation my colleagues and I did of Queensland’s Metro North Virtual ED found roughly 30% of calls were directed to the physical ED. This suggests 70% of the time, cases could be managed effectively by the virtual ED.
Preliminary data from a Victorian virtual ED indicates it curbed a similar rate of avoidable ED presentations – 72% of patients were successfully managed by the virtual ED alone. A study on the cost-effectiveness of another Victorian virtual ED suggested it has the potential to generate savings in health-care costs if it prevents physical ED visits.
Only 1.2% of people assessed in Queensland’s Metro North Virtual ED required unexpected hospital admission within 48 hours of being “discharged” from the virtual ED. None of these cases were life-threatening. This indicates the virtual ED is very safe.
The service experienced an average growth rate of 65% each month over a two-year evaluation period, highlighting increasing demand and confidence in the service. Surveys suggested clinicians also view the virtual ED positively.
The right advice could tell you whether you need to visit hospital in person or not. 1st footage/Shutterstock What now?
We need further research into patient outcomes and satisfaction, as well as the demographics of those using virtual EDs, and how these measures compare to the physical ED across different triage categories.
There are also challenges associated with virtual EDs, including around technology (connection and skills among patients and health professionals), training (for health professionals) and the importance of maintaining security and privacy.
Nonetheless, these services have the potential to reduce congestion in physical EDs, and offer greater convenience for patients.
Eligibility differs between different programs, so if you want to use a virtual ED, you may need to check you are eligible in your jurisdiction. Most virtual EDs can be accessed online, and some have direct phone numbers.
Jaimon Kelly, Senior Research Fellow in Telehealth delivered health services, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
7 Steps to Get Off Sugar and Carbohydrates – by Susan Neal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We will not keep the steps a mystery; abbreviated, they are:
- decide to really do this thing
- get knowledge and support
- clean out that pantry/fridge/etc and put those things behind you
- buy in healthy foods while starving your candida
- plan for an official start date, so that everything is ready
- change the way you eat (prep methods, timings, etc)
- keep on finding small ways to improve, without turning back
Particularly important amongst those are starving the candida (the fungus in your gut that is responsible for a lot of carb cravings, especially sugar and alcohol—which latter can be broken down easily into sugar), and changing the “how” of eating as well as the “what”; those are both things that are often overlooked in a lot of guides, but this one delivers well.
Walking the reader by the hand through things like that is probably the book’s greatest strength.
In the category of subjective criticism, the author does go off-piste a little at the end, to take a moment while she has our attention to talk about other things.
For example, you may not need “Appendix 7: How to Become A Christian and Disciple of Jesus Christ”.
Of course if that calls to you, then by all means, follow your heart, but it certainly isn’t a necessary step of quitting sugar. Nevertheless, the diversion doesn’t detract from the good dietary change advice that she has just spent a book delivering.
Bottom line: there’s no deep science here, but there’s a lot of very good, very practical advice, that’s consistent with good science.
Click here to check out 7 Steps to Get Off Sugar, and watch your health improve!
Share This Post
-
The Good Skin Solution – by Shann Jones
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Not everyone knows that eczema is not just a skin condition; it’s an autoimmune condition. And thus to heal one’s skin, the gut is a good place to start.
This is not your average gut health book though, because it is focused on optimizing things for one’s skin… Although the author herself learned about this while helping her husband to battle an MRSA infection. In other words, a multi-fronted battle for sure.
The advices in this book are good for, as the subtitle promises, an assortment of other skin conditions too, including psoriasis, rosacea, and acne. She covers the usual bases, and recommends probiotics, of which she’s particularly keen to praise kefir, while advising against the use of antibiotics unless absolutely necessary—something we’ve talked about from time to time at 10almonds, too.
Not content to merely cover those things, she also talks allergies, and walking the fine line between avoiding triggers and developing hypersensitivity by treating to live in a perfectly clean bubble.
Ultimately, she offers “7 daily habits”, 3 of which involve goat’s milk kefir, that’s how keen on it she is. So if you’re vegan, probably this book isn’t as good value, however much it discusses the health woes that can be caused and/or exacerbated by drinking cow’s milk.
The style is very light and personable, which makes for easy reading, more like one friend talking to another, than a scientific textbook.
Bottom line: if you’d like healthier skin, are interested in dietary tweaks and homemade soaps, and have no aversion to goat’s milk and/or kefir, then this book is full of fascinating pointers.
Click here to check out The Good Skin Solution, and who knows, maybe you’ll find it’s the G.O.A.T!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
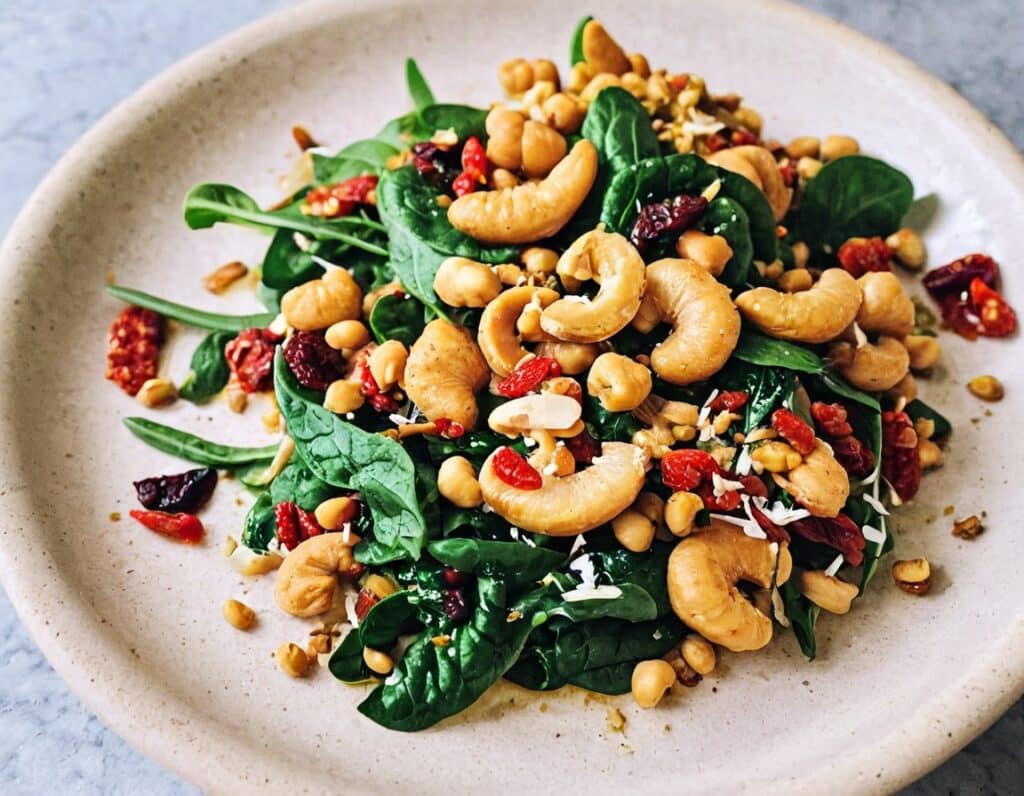
Protein Immune Support Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How to get enough protein from a salad, without adding meat? Cashews and chickpeas have you more than covered! Along with the leafy greens and an impressive array of minor ingredients full of healthy phytochemicals, this one’s good for your muscles, bones, skin, immune health, and more.
You will need
- 1½ cups raw cashews (if allergic, omit; the chickpeas and coconut will still carry the dish for protein and healthy fats)
- 2 cans (2x 14oz) chickpeas, drained
- 1½ lbs baby spinach leaves
- 2 large onions, finely chopped
- 3 oz goji berries
- ½ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 2 tbsp dessicated coconut
- 1 tbsp dried cumin
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp chili flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil, for cooking
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat a little oil in a pan; add the onions and cook for about 3 minutes.
2) Add the garlic and cook for a further 2 minutes.
3) Add the spinach, and cook until it wilts.
4) Add the remaining ingredients except the coconut, and cook for another three minutes.
5) Heat another pan (dry); add the coconut and toast for 1–2 minutes, until lightly golden. Add it to the main pan.
6) Serve hot as a main, or an attention-grabbing side:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- What Matters Most For Your Heart?
- Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are Electrolyte Supplements Worth It?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When To Take Electrolytes (And When We Shouldn’t!)
Any sports nutrition outlet will sell electrolyte supplements. Sometimes in the form of sports drinks that claim to be more hydrating than water, or tablets that can be dissolved in water to make the same. How do they work, and should we be drinking them?
What are electrolytes?
They’re called “electrolytes” because they are ionized particles (so, they have a positive or negative electrical charge, depending on which kind of ion they are) that are usually combined in the form of salts.
The “first halves” of the salts include:
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Magnesium
The “second halves” of the salts include:
- Chloride
- Phosphate
- Bicarbonate
- Nitrate
It doesn’t matter too much which way they’re combined, provided we get what we need. Specifically, the body needs them in a careful balance. Too much or too little, and bad things will start happening to us.
If we live in a temperate climate with a moderate lifestyle and a balanced diet, and have healthy working kidneys, usually our kidneys will keep them all in balance.
Why might we need to supplement?
Firstly, of course, you might have a dietary deficiency. Magnesium deficiency in particular is very common in North America, as people simply do not eat as much greenery as they ideally would.
But, also, you might sweat out your electrolytes, in which case, you will need to replace them.
In particular, endurance training and High Intensity Interval Training are likely to prompt this.
However… Are you in a rush? Because if not, you might just want to recover more slowly:
❝Vigorous exercise and warm/hot temperatures induce sweat production, which loses both water and electrolytes. Both water and sodium need to be replaced to re-establish “normal” total body water (euhydration).
This replacement can be by normal eating and drinking practices if there is no urgency for recovery.
But if rapid recovery (<24 h) is desired or severe hypohydration (>5% body mass) is encountered, aggressive drinking of fluids and consuming electrolytes should be encouraged to facilitate recovery❞
Source: Fluid and electrolyte needs for training, competition, and recovery
Should we just supplement anyway, as a “catch-all” to be sure?
Probably not. In particular, it is easy to get too much sodium in one’s diet, let alone by supplementation.And, oversupplementation of calcium is very common, and causes its own health problems. See:
To look directly to the science on this one, we see a general consensus amongst research reviews: “this is complicated and can go either way depending on what else people are doing”:
- Trace minerals intake: risks and benefits for cardiovascular health
- Electrolyte minerals intake and cardiovascular health
Well, that’s not helpful. Any clearer pointers?
Yes! Researchers Latzka and Mountain put together a very practical list of tips. Rather, they didn’t put it as a list, but the following bullet points are information extracted directly from their abstract, though we’ve also linked the full article below:
- It is recommended that individuals begin exercise when adequately hydrated.
- This can be facilitated by drinking 400 mL to 600 mL of fluid 2 hours before beginning exercise and drinking sufficient fluid during exercise to prevent dehydration from exceeding 2% body weight.
- A practical recommendation is to drink small amounts of fluid (150-300 mL) every 15 to 20 minutes of exercise, varying the volume depending on sweating rate.
- During exercise lasting less than 90 minutes, water alone is sufficient for fluid replacement
- During prolonged exercise lasting longer than 90 minutes, commercially available carbohydrate electrolyte beverages should be considered to provide an exogenous carbohydrate source to sustain carbohydrate oxidation and endurance performance.
- Electrolyte supplementation is generally not necessary because dietary intake is adequate to offset electrolytes lost in sweat and urine; however, during initial days of hot-weather training or when meals are not calorically adequate, supplemental salt intake may be indicated to sustain sodium balance.
Source: Water and electrolyte requirements for exercise
Bonus tip:
We’ve talked before about the specific age-related benefits of creatine supplementation, but if you’re doing endurance training or HIIT, you might also want to consider a creatine-electrolyte combination sports drink (even if you make it yourself):
Where can I get electrolyte supplements?
They’re easy to find in any sports nutrition store, or you can buy them online; here’s an example product on Amazon for your convenience
You can also opt for natural and/or homemade electrolyte drinks:
Healthline | 8 Healthy Drinks Rich in Electrolytes
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Two Sides Of Caffeine
We asked you for your health-related opinions on caffeine itself, not necessarily the coffee, tea, energy drinks, etc that might contain it.
We have, by the way previously written about the health effects of coffee and tea specifically:
As for our question about caffeine itself, though, we got the above-depicted, below-described, set of results:
- About 59% said “caffeine is a safe stimulant and cognitive enhancer”
- About 31% said “caffeine is a moderately safe recreational drug”
- About 8% said “caffeine’s addictive properties make it de facto bad”
- One (1) person said “caffeine will leave you a trembling exhausted wreck”
But what does the science say?
Caffeine is addictive: True or False?
True, though one will find occasional academics quibbling the definition. Most of the studies into the mechanisms of caffeine addiction have been conducted on rats, but human studies exist too and caffeine is generally considered addictive for humans, for example:
See also:
Notwithstanding its addictive status, caffeine is otherwise safe: True or False?
True-ish, for most people. Some people with heart conditions or a hypersensitivity to caffeine may find it is not safe for them at all, and for the rest of us, the dose makes the poison. For example:
❝Can too much caffeine kill you? Although quite rare, caffeine can be fatal in cases of overdose; such circumstances are generally not applicable to healthy individuals who typically consume caffeine via beverages such as tea or coffee.❞
this paper, by the way, also includes a good example of academics quibbling the definition of addiction!
Caffeine is a cognitive enhancer: True or False?
True, but only in the case of occasional use. If you are using it all the time, your physiology will normalize it and you will require caffeine in order to function at your normal level. To attain higher than that, once addicted to caffeine, would now require something else.
Read more: Caffeine: benefits and drawbacks for technical performance
Caffeine will leave you a trembling exhausted wreck: True or False?
True or False depending on usage:
- The famously moderate 3–5 cups per day will not, for most people, cause any such problems.
- Using/abusing it to make up for lost sleep (or some other source of fatigue, such as physical exhaustion from exertion), however, is much more likely to run into problems.
In the latter case, caffeine really is the “payday loan” of energy! It’ll give you an adrenal boost now (in return, you must suffer the adrenal dumping later, along with lost energy expended in the adrenaline surge), and also, the tiredness that you thought was gone, was just caffeine’s adenosine-blocking activities temporarily preventing you from being able to perceive the tiredness. So you’ll have to pay that back later, with interest, because of the extra time/exertion too.
Want to make caffeine a little more gentle on your system?
Taking l-theanine alongside caffeine can ameliorate some of caffeine’s less wonderful effects—and as a bonus, l-theanine has some nifty benefits of its own, too:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: