Can Home Tests Replace Check-Ups?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I recently hit 65 and try to get regular check-ups, but do you think home testing can be as reliable as a doctor visit? I try to keep as informed as I can and am a big believer in taking responsibility for my own health if I can, but I don’t want to miss something important either. Best as a supplemental thing, perhaps?❞
Depends what’s being tested! And your level of technical knowledge, though there’s always something to be said for ongoing learning.
- If you’re talking blood tests, urine tests, etc per at-home test kits that get sent off to a lab, then provided they’re well-sourced (and executed correctly by you), they should be as accurate as what a doctor will give, since they are basically doing the same thing (taking a sample and sending it off to a lab).
- If you’re talking about checking for lumps etc, then a dual approach is best: check yourself at home as often as you feel is reasonable (with once per month being advised at a minimum, especially if you’re aware of an extra risk factor for you) and check-ups with the doctor per their recommendations.
- If you’re talking about general vitals (blood pressure, heart rate, heart rate variability, VO₂ max, etc), then provided you have a reliable way of testing them, then doing them very frequently at home, to get the best “big picture” view. In contrast, getting them done once a year at your doctor’s could result in a misleading result, if you just ate something different that day or had a stressful morning, for example.
Enjoy
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Be Your Own Therapist – by Owen O’Kane
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Finding the right therapist can be hard. Sometimes, even just accessing a therapist, any therapist, can be hard, if circumstances are adverse. Sometimes we’d like therapy, but want to feel “better prepared for it” before we do.
Owen O’Kane, a highly qualified and well-respected psychotherapist, wants to put some tools in our hands. The premise of this book is that “in 10 minutes a day” one can give oneself an amount of therapy that will be beneficial.
Naturally, in 10 minutes a day, this isn’t going to be the kind of therapy that will work through major traumas, so what can it do?
Those 10 minutes are spread into three sessions:
- 4 minutes in the morning
- 3 minutes in the afternoon
- 3 minutes in the evening
The idea is:
- To do a quick mental health “check-in” before the day gets started, ascertain what one needs in that context, and make a simple plan to get/have it.
- To keep one’s mental health on track by taking a little pause to reassess and adjust if necessary
- To reflect on the day, amplify the positive, and let go of the negative to what extent is practical, in order to rest well ready for the next day
Where O’Kane excels is in explaining how to do those things in a way that is neither overly simplistic and wishy-washy, nor so arcane and convoluted as to create more work and render the day more difficult.
In short, this book is a great prelude to (or adjunct to) formal therapy, and for those for whom therapy isn’t accessible and/or desired, a great way to keep oneself on a mentally healthy track.
Share This Post
-
Are Electrolyte Supplements Worth It?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When To Take Electrolytes (And When We Shouldn’t!)
Any sports nutrition outlet will sell electrolyte supplements. Sometimes in the form of sports drinks that claim to be more hydrating than water, or tablets that can be dissolved in water to make the same. How do they work, and should we be drinking them?
What are electrolytes?
They’re called “electrolytes” because they are ionized particles (so, they have a positive or negative electrical charge, depending on which kind of ion they are) that are usually combined in the form of salts.
The “first halves” of the salts include:
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Magnesium
The “second halves” of the salts include:
- Chloride
- Phosphate
- Bicarbonate
- Nitrate
It doesn’t matter too much which way they’re combined, provided we get what we need. Specifically, the body needs them in a careful balance. Too much or too little, and bad things will start happening to us.
If we live in a temperate climate with a moderate lifestyle and a balanced diet, and have healthy working kidneys, usually our kidneys will keep them all in balance.
Why might we need to supplement?
Firstly, of course, you might have a dietary deficiency. Magnesium deficiency in particular is very common in North America, as people simply do not eat as much greenery as they ideally would.
But, also, you might sweat out your electrolytes, in which case, you will need to replace them.
In particular, endurance training and High Intensity Interval Training are likely to prompt this.
However… Are you in a rush? Because if not, you might just want to recover more slowly:
❝Vigorous exercise and warm/hot temperatures induce sweat production, which loses both water and electrolytes. Both water and sodium need to be replaced to re-establish “normal” total body water (euhydration).
This replacement can be by normal eating and drinking practices if there is no urgency for recovery.
But if rapid recovery (<24 h) is desired or severe hypohydration (>5% body mass) is encountered, aggressive drinking of fluids and consuming electrolytes should be encouraged to facilitate recovery❞
Source: Fluid and electrolyte needs for training, competition, and recovery
Should we just supplement anyway, as a “catch-all” to be sure?
Probably not. In particular, it is easy to get too much sodium in one’s diet, let alone by supplementation.And, oversupplementation of calcium is very common, and causes its own health problems. See:
To look directly to the science on this one, we see a general consensus amongst research reviews: “this is complicated and can go either way depending on what else people are doing”:
- Trace minerals intake: risks and benefits for cardiovascular health
- Electrolyte minerals intake and cardiovascular health
Well, that’s not helpful. Any clearer pointers?
Yes! Researchers Latzka and Mountain put together a very practical list of tips. Rather, they didn’t put it as a list, but the following bullet points are information extracted directly from their abstract, though we’ve also linked the full article below:
- It is recommended that individuals begin exercise when adequately hydrated.
- This can be facilitated by drinking 400 mL to 600 mL of fluid 2 hours before beginning exercise and drinking sufficient fluid during exercise to prevent dehydration from exceeding 2% body weight.
- A practical recommendation is to drink small amounts of fluid (150-300 mL) every 15 to 20 minutes of exercise, varying the volume depending on sweating rate.
- During exercise lasting less than 90 minutes, water alone is sufficient for fluid replacement
- During prolonged exercise lasting longer than 90 minutes, commercially available carbohydrate electrolyte beverages should be considered to provide an exogenous carbohydrate source to sustain carbohydrate oxidation and endurance performance.
- Electrolyte supplementation is generally not necessary because dietary intake is adequate to offset electrolytes lost in sweat and urine; however, during initial days of hot-weather training or when meals are not calorically adequate, supplemental salt intake may be indicated to sustain sodium balance.
Source: Water and electrolyte requirements for exercise
Bonus tip:
We’ve talked before about the specific age-related benefits of creatine supplementation, but if you’re doing endurance training or HIIT, you might also want to consider a creatine-electrolyte combination sports drink (even if you make it yourself):
Where can I get electrolyte supplements?
They’re easy to find in any sports nutrition store, or you can buy them online; here’s an example product on Amazon for your convenience
You can also opt for natural and/or homemade electrolyte drinks:
Healthline | 8 Healthy Drinks Rich in Electrolytes
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
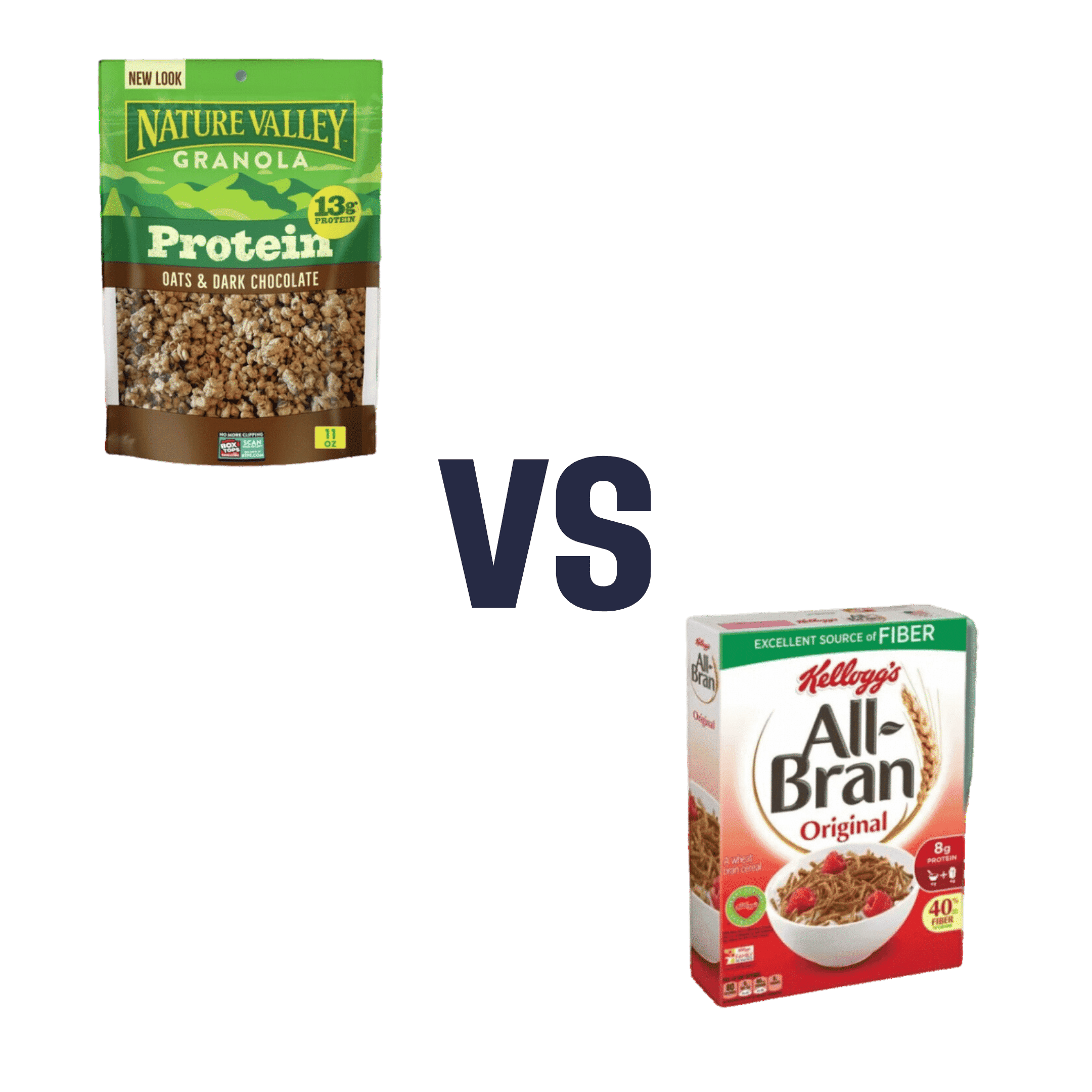
Nature Valley Protein Granola vs Kellog’s All-Bran – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Nature Valley Protein Granola to Kellog’s All-Bran, we picked the All-Bran.
Why?
While the Protein Granola indeed contains more protein (13g/cup, compared to 5g/cup), it also contains three times as much sugar (18g/cup, compared to 9g/cup) and only ⅓ as much fiber (4g/cup, compared to 12g/cup)
Given that fiber is what helps our bodies to absorb sugar more gently (resulting in fewer spikes), this is extremely important, especially since 18g of sugar in one cup of Protein Granola is already most of the recommended daily allowance, all at once!
For reference: the AHA recommends no more than 25g added sugar for women, or 32g for men
Hence, we went for the option with 3x as much fiber and ⅓ of the sugar, the All-Bran.
For more about keeping blood sugars stable, see:
10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Applesauce vs Cranberry Sauce – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing applesauce to cranberry sauce, we picked the applesauce.
Why?
It mostly comes down to the fact that apples are sweeter than cranberries:
In terms of macros, they are both equal on fiber (both languishing at a paltry 1.1g/100g), and/but cranberry sauce has 4x the carbs, of which, more than 3x the sugar. Simply, cranberry sauce recipes invariably have a lot of added sugar, while applesauce recipes don’t need that. So this is a huge relative win for applesauce (we say “relative” because it’s still not great, but cranberry sauce is far worse).
In the category of vitamins, applesauce has more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, B9, and C, while cranberry sauce has more of vitamins E, K, and choline. A more moderate win for applesauce this time.
When it comes to minerals, applesauce has more calcium, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium, while cranberry sauce has more iron, manganese, and selenium. Another moderate win for applesauce.
Since we’ve discussed relative amounts rather than actual quantities, it’s worth noting that neither sauce is a good source of vitamins or minerals, and neither are close to just eating the actual fruits. Just, cranberry sauce is the relatively more barren of the two.
While cranberries famously have some UTI-fighting properties, you cannot usefully gain this benefit from a sauce that (with its very high sugar content and minimal fiber) actively feeds the very C. albicans you are likely trying to kill.
All in all, a pitiful show of nutritional inadequacy from these two products today, but one is relatively less bad than the other, and that’s the applesauce.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Mattress Is Best, By Science?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Foundations of Good Sleep
You probably know the importance of good sleep for good health. If not, here’s a quick refresher:
- Why You Probably Need More Sleep
- How Sleep-Deprived Are You, Really?
- The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
You should also definitely check out this quite famous book on the topic:
Why We Sleep – by Dr Matthew Walker
What helps, to get that good sleep
We’ve covered this a little before too, for example:
- Safe Effective Sleep Aids For Seniors
- Sleep Better With Better Air
- How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
How to level-up from there
One of the biggest barriers to good sleep for many people is obstructive sleep apea:
Healthier, Natural Sleep Without Obstruction!
We covered (in the above article) a whole lot of ways of mitigating/managing obstructive sleep apnea. One of the things we mentioned as beneficial was avoiding sleeping on one’s back, and this is something Mayo Clinic’s Dr. Somers agreed with:
Back Sleeping, And Sleeping Differently After 50
“But side-sleeping is uncomfortable”
If this is you, then chances are you have the wrong mattress.
If your mattress is too firm, you can get around it by using this “five pillow” method:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
If your mattress is too soft, then sorry, you really just have to throw that thing out and start again.
The Goldilocks mattress
While different people will have different subjective preferences, the science is quite clear on what is actually best for people’s spines. As this review of 39 qualified scholarly articles concluded:
❝Results of this systematic review show that a medium-firm mattress promotes comfort, sleep quality and rachis alignment❞
~ Dr. Gianfilippo Caggiari et al.
Read in full: What type of mattress should be chosen to avoid back pain and improve sleep quality? Review of the literature
Note: to achieve “medium-firm” that remains “medium firm” has generally been assumed to require a memory-foam mattress.
How memory-foam works: memory-foam is a moderately thermosoftening material, designed to slightly soften at the touch of human body temperature, and be firmer at room temperature. This will result in it molding itself to the form of a human body, providing what amounts to personalized support for your personal shape and size, meaning your spine can stay exactly as it’s supposed to when you’re sleeping on your side, instead of (for example) your hips being wider meaning that your lumbar vertebrae are raised higher than your thoracic vertebrae, giving you the equivalent of a special nocturnal scoliosis.
It will, therefore, stop working if
- the ambient temperature is comparable to human body temperature (as happens in some places sometimes, and increasingly often these days)
- you die, and thus lose your body temperature (but in that case, your spinal alignment will be the least of your concerns)
Here’s a good explanation of the mechanics of memory foam from the Sleep Foundation:
Sleep Foundation | What is Memory Foam?
An alternative to memory foam?
If you don’t like memory foam (one criticism is that it doesn’t allow good ventilation underneath the body), there is an alterative, the grid mattress.
It’s very much “the new kid on the block” and the science is young for this, but for example this recent (April 2024) study that concluded:
❝The grid mattress is a simple, noninvasive, and nonpharmacological intervention that improved adults sleep quality and health. Controlled trials are encouraged to examine the effects of this mattress in a variety of populations and environments.❞
~ Dr. Heather Hausenblas et al.
Read in full: Effectiveness of a grid mattress on adults’ sleep quality and health: A quasi-experimental intervention study
However, that was a small (n=39) uncontrolled (i.e. there was no control group) study, and the conflict of interest statement is, well, interesting:
❝Heather A. Hausenblas, Stephanie L. Hooper, Martin Barragan, and Tarah Lynch declare no conflict of interest. Michael Breus served as a former consultant for Purple, LLC.❞
~ Ibid.
…which is a fabulous way of distracting from the mention in the “Acknowledgements” section to follow, that…
❝Purple, LLC, provided financial support for the study❞
~ Ibid.
Purple is the company that invented the mattress being tested. So while this doesn’t mean the study is necessarily dishonest and/or corrupt, it does at the very least raise a red flag for a potential instance of publication bias (because Purple may have funded multiple studies and then pulled funding of the ones that weren’t going their way).
If you are interested in Purple’s mattress and how it works, you can check it out here ← this is a link for your interest and information; not an advertisement or an endorsement. We look forward to seeing more science for this though, and echo their own call for randomized controlled trials!
Summary
Sleep is important, and while it’s a popular myth that we need less as we get older, the truth is that we merely get less on average, while still needing the same amount.
A medium-firm memory-foam mattress is a very good, well-evidenced way to support that (both figuratively and literally!).
A grid mattress is an interesting innovation, and/but we’d like to see more science for it.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How old’s too old to be a doctor? Why GPs and surgeons over 70 may need a health check to practise
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A growing number of complaints against older doctors has prompted the Medical Board of Australia to announce today that it’s reviewing how doctors aged 70 or older are regulated. Two new options are on the table.
The first would require doctors over 70 to undergo a detailed health assessment to determine their current and future “fitness to practise” in their particular area of medicine.
The second would require only general health checks for doctors over 70.
A third option acknowledges existing rules requiring doctors to maintain their health and competence. As part of their professional code of conduct, doctors must seek independent medical and psychological care to prevent harming themselves and their patients. So, this third option would maintain the status quo.
PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock Haven’t we moved on from set retirement ages?
It might be surprising that stricter oversight of older doctors’ performance is proposed now. Critics of mandatory retirement ages in other fields – for judges, for instance – have long questioned whether these rules are “still valid in a modern society”.
However, unlike judges, doctors are already required to renew their registration annually to practise. This allows the Medical Board of Australia not only to access sound data about the prevalence and activity of older practitioners, but to assess their eligibility regularly and to conduct performance assessments if and when they are needed.
What has prompted these proposals?
This latest proposal identifies several emerging concerns about older doctors. These are grounded in external research about the effect of age on doctors’ competence as well as the regulator’s internal data showing surges of complaints about older doctors in recent years.
Studies of medical competence in ageing doctors show variable results. However, the Medical Board of Australia’s consultation document emphasises studies of neurocognitive loss. It explains how physical and cognitive impairment can lead to poor record-keeping, improper prescribing, as well as disruptive behaviour.
The other issue is the number of patient complaints against older doctors. These “notifications” have surged in recent years, as have the number of disciplinary actions against older doctors.
In 2022–2023, the Medical Board of Australia took disciplinary action against older doctors about 1.7 times more often than for doctors under 70.
In 2023, notifications against doctors over 70 were 81% higher than for the under 70s. In that year, patients sent 485 notifications to the Medical Board of Australia about older doctors – up from 189 in 2015.
While older doctors make up only about 5.3% of the doctor workforce in Australia (less than 1% over 80), this only makes the high numbers of complaints more starkly disproportionate.
It’s for these reasons that the Medical Board of Australia has determined it should take further regulatory action to safeguard the health of patients.
So what distinguishes the two new proposed options?
The “fitness to practise” assessment option would entail a rigorous assessment of doctors over 70 based on their specialisation. It would be required every three years after the age of 70 and every year after 80.
Surgeons, for example, would be assessed by an independent occupational physician for dexterity, sight and the ability to give clinical instructions.
Importantly, the results of these assessments would usually be confidential between the assessor and the doctor. Only doctors who were found to pose a substantial risk to the public, which was not being managed, would be obliged to report their health condition to the Medical Board of Australia.
The second option would be a more general health check not linked to the doctor’s specific role. It would occur at the same intervals as the “fitness to practise” assessment. However, its purpose would be merely to promote good health-care decision-making among health practitioners. There would be no general obligation on a doctor to report the results to the Medical Board of Australia.
In practice, both of these proposals appear to allow doctors to manage their own general health confidentially.
Older surgeons could be independently assessed for dexterity, sight and the ability to give clinical instructions. worradirek/Shutterstock The law tends to prioritise patient safety
All state versions of the legal regime regulating doctors, known as the National Accreditation and Registration Scheme, include a “paramountcy” provision. That provision basically says patient safety is paramount and trumps all other considerations.
As with legal regimes regulating childcare, health practitioner regulation prioritises the health and safety of the person receiving the care over the rights of the licensed professional.
Complicating this further, is the fact that a longstanding principle of health practitioner regulation has been that doctors should not be “punished” for errors in practice.
All of this means that reforms of this nature can be difficult to introduce and that the balance between patient safety and professional entitlements must be handled with care.
Could these proposals amount to age discrimination?
It is premature to analyse the legal implications of these proposals. So it’s difficult to say how these proposals interact with Commonwealth age- and other anti-discrimination laws.
For instance, one complication is that the federal age discrimination statute includes an exemption to allow “qualifying bodies” such as the Medical Board of Australia to discriminate against older professionals who are “unable to carry out the inherent requirements of the profession, trade or occupation because of his or her age”.
In broader terms, a licence to practise medicine is often compared to a licence to drive or pilot an aircraft. Despite claims of discrimination, New South Wales law requires older drivers to undergo a medical assessment every year; and similar requirements affect older pilots and air traffic controllers.
Where to from here?
When changes are proposed to health practitioner regulation, there is typically much media attention followed by a consultation and behind-the-scenes negotiation process. This issue is no different.
How will doctors respond to the proposed changes? It’s too soon to say. If the proposals are implemented, it’s possible some older doctors might retire rather than undergo these mandatory health assessments. Some may argue that encouraging more older doctors to retire is precisely the point of these proposals. However, others have suggested this would only exacerbate shortages in the health-care workforce.
The proposals are open for public comment until October 4.
Christopher Rudge, Law lecturer, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: