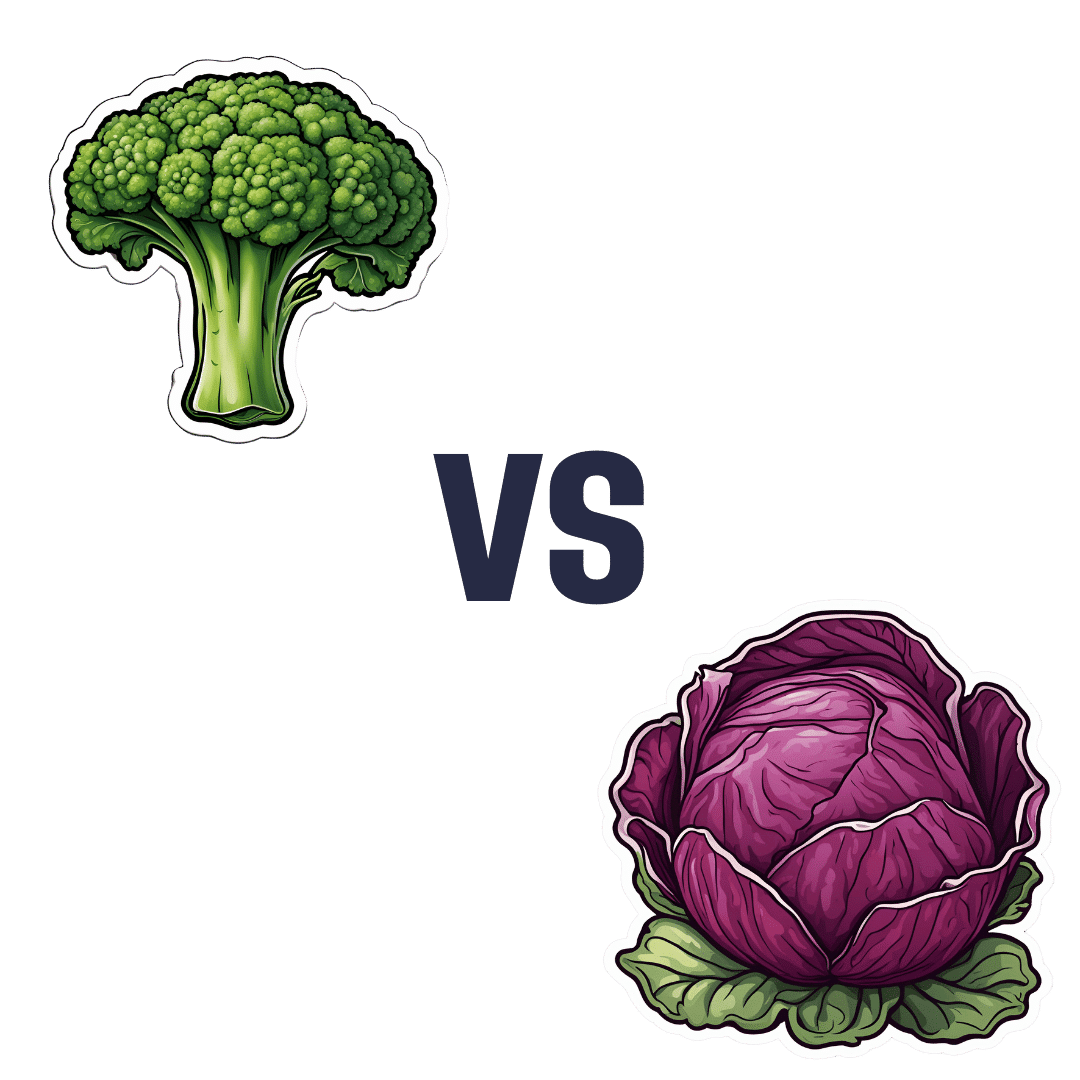
Broccoli vs Red Cabbage – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing broccoli to red cabbage, we picked the broccoli.
Why?
Both are certainly great! Which is usual for any Brassica oleracea cultivar (as both of these vegetables are). But there is a clear winner:
In terms of macros, broccoli has more fiber and protein, while red cabbage has more carbs. Now, nobody is getting metabolic disease from eating cabbage, but by the numbers, this is a simple win for broccoli, especially on account of the fiber.
In the category of vitamins, broccoli has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, C, E, K, and choline, while red cabbage has more of vitamins A and B6. Another win for broccoli.
When it comes to minerals, it’s a similar story: broccoli has more copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while red cabbage has more iron and manganese. They’re equal in calcium, by the way. Broccoli wins again.
Looking at polyphenols, both cultivars have plenty, but broccoli has more in total, as well as more variety, so yet another win for broccoli here.
Now, standing next to broccoli has made red cabbage look bad, but we want to assure you that red cabbage is itself a nutritional powerhouse—broccoli is just even more so.
So of course, by all means do enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
21 Most Beneficial Polyphenols & What Foods Have Them
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Welcoming the Unwelcome – by Pema Chödrön
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a lot in life that we don’t get to choose. Some things we have zero control over, like the weather. Others, we can only influence, like our health. Still yet others might give us an illusion of control, only to snatch it away, like a financial reversal or a bereavement.
How, then, to suffer those “slings and arrows of outrageous fortune” and come through the other side with an even mind and a whole heart?
Author Pema Chödrön has a guidebook for us.
Quick note: this book does not require the reader to have any particular religious faith to enjoy its benefits, but the author is a nun. As such, the way she describes things is generally within the frame of her religion. So that’s a thing to be aware of in case it might bother you. That said…
The largest part of her approach is one that psychology might describe as rational emotive behavioral therapy.
As such, we are encouraged to indeed “meet with triumph and disaster, and treat those two imposters just the same”, and more importantly, she lays out the tools for us to do so.
Does this mean not caring? No! Quite the opposite. It is expected, and even encouraged, that we might care very much. But: this book looks at how to care and remain compassionate, to others and to ourselves.
For Chödrön, welcoming the unwelcome is about de-toothing hardship by accepting it as a part of the complex tapestry of life, rather than something to be endured.
Bottom line: this book can greatly increase the reader’s ability to “go placidly amid the noise and haste” and bring peace to an often hectic world—starting with our own.
Share This Post
-
Wouldn’t It Be Nice To Have Regenerative Superpowers?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Best-Laid Schemes of Mice and Medical Researchers…
This is Dr. Ellen Heber-Katz. She’s an internationally-renowned immunologist and regeneration biologist, but her perhaps greatest discovery was accidental.
Unlike in Robert Burns’ famous poem, this one has a happy ending!
But it did involve the best-laid schemes of mice and medical researchers, and how they did indeed “gang gagly“ (or in the English translation, “go awry”).
How it started…
Back in 1995, she was conducting autoimmune research, and doing a mouse study. Her post-doc assistant was assigned to punch holes in the ears of mice that had received an experimental treatment, to distinguish them from the control group.
However, when the mice were later checked, none of them had holes (nor even any indication there ever had been holes punched)—the experiment was ruined, though the post-doc swore she did her job correctly.
So, they had to start from scratch in the new year, but again, a second batch of mice repeated the trick. No holes, no wounds, no scarring, not disruption to their fur, no damage to the cartilage that had been punched through.
In a turn of events worthy of a superhero origin story, they discovered that their laboratory-made autoimmune disease had accidentally given the mice super-healing powers of regeneration.
In the animal kingdom, this is akin to a salamander growing a new tail, but it’s not something usually found in mammals.
Read: A New Murine Model for Mammalian Wound Repair and Regeneration
How it’s going…
Dr. Heber-Katz and colleagues took another 20 years of work to isolate hypoxia-inducible factor-1a (HIF-1a) as a critical molecule that, if blocked, would eliminate the regenerative response.
Further, a drug (which they went on to patent), 1,4-dihydrophenonthrolin-4-one-3-carboxylic acid (1,4-DPCA), chemically induced this regenerative power:
See: Drug-induced regeneration in adult mice
Another 5 years later, they found that this same drug can be used to stimulate the regrowth of bones, too:
And now…
The research is continuing. Here’s the latest, a little over a month ago:
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition: an organizing principle of mammalian regeneration
Regrowing nerves has also been added into the list of things the drug can do.
What about humans?
Superpowered mice are all very well and good, but when can we expect this in humans?
The next step is testing the drug in larger animals, which she hopes to do next year, followed eventually by studies in humans.
Read the latest:
Regrowing nerves and healing without scars? A scientist’s career-long quest comes closer to fruition
Very promising!
Share This Post
-
Going for a bushwalk? 3 handy foods to have in your backpack (including muesli bars)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This time of year, many of us love to get out and spend time in nature. This may include hiking through Australia’s many beautiful national parks.
Walking in nature is a wonderful activity, supporting both physical and mental health. But there can be risks and it’s important to be prepared.
You may have read the news about hiker, Hadi Nazari, who was recently found alive after spending 13 days lost in Kosciuszko National Park.
He reportedly survived for almost two weeks in the Snowy Mountains region of New South Wales by drinking fresh water from creeks, and eating foraged berries and two muesli bars.
So next time you’re heading out for a day of hiking, what foods should you pack?
Here are my three top foods to carry on a bushwalk that are dense in nutrients and energy, lightweight and available from the local grocery store.
Leah-Anne Thompson/Shutterstock 1. Muesli bars
Nazari reportedly ate two muesli bars he found in a mountain hut. Whoever left the muesli bars there made a great choice.
Muesli bars come individually wrapped, which helps them last longer and makes them easy to transport.
They are also a good source of energy. Muesli bars typically contain about 1,500–1,900 kilojoules per 100 grams. The average energy content for a 35g bar is about 614kJ.
This may be a fraction of what you’d usually need in a day. However, the energy from muesli bars is released at a slow to moderate pace, which will help keep you going for longer.
Muesli bars are also packed with nutrients. They contain all three macronutrients (carbohydrate, protein and fat) that our body needs to function. They’re a good source of carbohydrates, in particular, which are a key energy source. An average Australian muesli bar contains 14g of whole grains, which provide carbohydrates and dietary fibre for long-lasting energy.
Muesli bars that contain nuts are typically higher in fat (19.9g per 100g) and protein (9.4g per 100g) than those without.
Fat and protein are helpful for slowing down the release of energy from foods and the protein will help keep you feeling full for longer.
There are many different types of muesli bars to choose from. I recommend looking for those with whole grains, higher dietary fibre and higher protein content.
2. Nuts
Nuts are nature’s savoury snack and are also a great source of energy. Cashews, pistachios and peanuts contain about 2,300-2,400kJ per 100g while Brazil nuts, pecans and macadamias contain about 2,700-3,000kJ per 100g. So a 30g serving of nuts will provide about 700-900kJ depending on the type of nut.
Just like muesli bars, the energy from nuts is released slowly. So even a relatively small quantity will keep you powering on.
Nuts are also full of nutrients, such as protein, fat and fibre, which will help to stave off hunger and keep you moving for longer.
When choosing which nuts to pack, almost any type of nut is going to be great.
Peanuts are often the best value for money, or go for something like walnuts that are high in omega-3 fatty acids, or a nut mix.
Whichever nut you choose, go for the unsalted natural or roasted varieties. Salted nuts will make you thirsty.
Nut bars are also a great option and have the added benefit of coming in pre-packed serves (although nuts can also be easily packed into re-usable containers).
If you’re allergic to nuts, roasted chickpeas are another option. Just try to avoid those with added salt.
Nuts are nature’s savoury snack and are also a great source of energy. Eakrat/Shutterstock 3. Dried fruit
If nuts are nature’s savoury snack, fruit is nature’s candy. Fresh fruits (such as grapes, frozen in advance) are wonderfully refreshing and perfect as an everyday snack, although can add a bit of weight to your hiking pack.
So if you’re looking to reduce the weight you’re carrying, go for dried fruit. It’s lighter and will withstand various conditions better than fresh fruit, so is less likely to spoil or bruise on the journey.
There are lots of varieties of dried fruits, such as sultanas, dried mango, dried apricots and dried apple slices.
These are good sources of sugar for energy, fibre for fullness and healthy digestion, and contain lots of vitamins and minerals. So choose one (or a combination) that works for you.
Don’t forget water
Next time you head out hiking for the day, you’re all set with these easily available, lightweight, energy- and nutrient-dense snacks.
This is not the time to be overly concerned about limiting your sugar or fat intake. Hiking, particularly in rough terrain, places demands on your body and energy needs. For instance, an adult hiking in rough terrain can burn upwards of about 2,000kJ per hour.
And of course, don’t forget to take plenty of water.
Having access to even limited food, and plenty of fresh water, will not only make your hike more pleasurable, it can save your life.
Margaret Murray, Senior Lecturer, Nutrition, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
5 Self-Care Trends That Are Actually Ruining Your Mental Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ok, some of these are trends; some are more perennial to human nature. For example, while asceticism is not a new idea, the “dopamine detox” is, and “bed rotting” is not a trend that this writer has seen recommended anywhere, but on the other hand, there are medieval illustrations of it—there was no Netflix in sight in the medieval illustrations, but perhaps a label diagnosing it as “melancholy”, for example.
So without further ado, here are five things to not do…
Don’t fall into these traps
The 5 things to watch out for are:
- Toxic positivity: constantly promoting positivity regardless of the reality of a situation can shame or invalidate genuine emotions, preventing people from processing their real feelings and leading to negative mental health outcomes—especially if it involves a “head in sand” approach to external problems as well as internal ones (because then those problems will never actually get dealt with).
- Self-indulgence: excessive focus on personal desires can make you more self-centered, less disciplined, and ultimately dissatisfied, which hinders personal growth and mental wellness.
- Bed rotting: spending prolonged time in bed for relaxation or entertainment can decrease motivation, productivity, and lead to (or worsen) depression rather than promoting genuine rest and rejuvenation.
- Dopamine detox: abstaining from pleasurable activities to “reset” the brain simply does not work and can lead to loneliness, boredom, and worsen mental health, especially when done excessively.
- Over-reliance on self-help: consuming too much self-help content or relying on material possessions for well-being can lead to information overload, unrealistic expectations, and the constant need for self-fixing, rather than fostering self-acceptance and authentic growth. Useful self-help can be like taking your car in for maintenance—counterproductive self-help is more like having your car always in for maintenance and never actually on the road.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read, and yes these are pretty much one-for-one with the 5 items above, doing a deeper dive into each in turn,
- How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
- Self-Care That’s Not Just Self-Indulgence
- The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
- The Dopamine Myth
- Behavioral Activation Against Depression & Anxiety
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sizing Aside: Are You Wearing The Right Bra For Your Breast Shape?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s well-known that most women wear incorrectly-fitting bras. Even with careful measurements, buying “off-the-rack” can be a challenge, because the sizing system only takes two measurements, when there are actually many more things to consider. Today’s video demystifies a lot of what else is going on!
For example…
Some of the different breast shapes/arrangements to consider:
- Wide-set breasts: likely to find there’s a bit of a gap between your breasts and the inside (nearest to your sternum) parts of the cups—while spilling out a little at the outside edges. The solution? Bras that offer side-support, to keep things pointing more forwards. Central-closing bras can also help gather things together, and a balconette bra can redistribute things more evenly. Any of these options will be a lot more comfortable.
- Small breasts: bralettes are your friend, keeping things comfortable while not wearing more bra than necessary to do the job (of course going braless is also an option, but we’re talking bra-fitting here, not bra-flinging-off never to be seen again)
- Deflated breasts: often the case for someone who used to have larger breasts, but they lost size for hormonal reasons rather than for weight loss reasons. This often occurs a little while after childbirth, and also happens a lot in menopause. The bra recommendation for this? A push-up plunge bra with ¾ coverage not only provides cleavage if that’s wanted, but also, will keep things much more snug and thus more evenly-distributed. If ever you’ve found yourself needing to adjust yourself every now and gain while out, this will fix that and keep you comfortable for much longer.
There’s more, along with a visual guide, so do check it out:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Further reading
While we haven’t written about this specifically (maybe we’ll do a “Life Hacks” edition one of these days), we have written about…
Keeping Abreast Of Your Cancer Risk
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Come As You Are – by Dr. Emily Nagoski
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve all heard the jokes, things like: Q: “Why is the clitoris like Antarctica?” A: “Most men know it’s there; most don’t give a damn”
But… How much do people, in general, really know about the anatomy and physiology of sexual function? Usually very little, but often without knowing how little we know.
This book looks to change that. Geared to a female audience, but almost everyone will gain useful knowledge from this.
The writing style is very easy-to-read, and there are “tl;dr” summaries for those who prefer to skim for relevant information in this rather sizeable (400 pages) tome.
Yes, that’s “what most people don’t know”. Four. Hundred. Pages.
We recommend reading it. You can thank us later!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: