Life After Death? (Your Life; A Loved One’s Death)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Show Must Go On
We’ve previously written about the topics of death and dying. It’s not cheery, but it is important to tackle.
Sooner is better than later, in the case of:
Preparations For Managing Your Own Mortality
And for those who are left behind, of course it is hardest of all:
What Grief Does To Your Body (And How To Manage It)
But what about what comes next? For those who are left behind, that is.
Life goes on
In cases when the death is that of a close loved one, the early days after death can seem like a surreal blur. How can the world go ticking on as normal when [loved one] is dead?
But incontrovertibly, it does, so we can only ask again: how?
And, we get to choose that, to a degree. The above-linked article about grief gives a “101” rundown, but it’s (by necessity, for space) a scant preparation for one of the biggest challenges in life that most of us will ever face.
For many people, processing grief involves a kind of “saying goodbye”. For others, it doesn’t, as in the following cases of grieving the loss of one’s child—something no parent should ever have to face, but it happens:
Dr. Ken Druck | The Love That Never Dies
(with warning, the above article is a little heavy)
In short: for those who choose not to “say goodbye” in the case of the death of a loved one, it’s more often not a case of cold neglect, but rather the opposite—a holding on. Not in the “denial” sense of holding on, but rather in the sense of “I am not letting go of this feeling of love, no matter how much it might hurt to hold onto; it’s all I have”.
What about widows, and love after death?
Note: we’ll use the feminine “widow” here as a) it’s the most common and b) most scientific literature focuses on widows, but there is no reason why most of the same things won’t also apply to widowers.
We say “most”, as society does tend to treat widows and widowers differently, having different expectations about a respectful mourning period, one’s comportment during same, and so on.
As an aside: most scientific literature also assumes heterosexuality, which is again statistically reasonable, and for the mostpart the main difference is any extra challenges presented by non-recognition of marriages, and/or homophobic in-laws. But otherwise, grief is grief, and as the saying goes, love is love.
One last specificity before we get into the meat of this: we are generally assuming marriages to be monogamous here. Polyamorous arrangements will likely sidestep most of these issues completely, but again, they’re not the norm.
Firstly, there’s a big difference between remarrying (or similar) after being widowed, and remarrying (or similar) after a divorce, and that largely lies in the difference of how they begin. A divorce is (however stressful it may often be) more often seen as a transition into a new period of freedom, whereas bereavement is almost always felt as a terrible loss.
The science, by the way, shows the stats for this; people are less likely to remarry, and slower to remarry if they do, in instances of bereavement rather than divorce, for example:
Timing of Remarriage Among Divorced and Widowed Parents
Love after death: the options
For widows, then, there seem to be multiple options:
- Hold on to the feelings for one’s deceased partner; never remarry
- Grieve, move on, find new love, relegating the old to history
- Try to balance the two (this is tricky but can be done*)
*Why is balancing the two tricky, and how can it be done?
It’s tricky because ultimately there are three people’s wishes at hand:
- The deceased (“they would want me to be happy” vs “I feel I would be betraying them”—which two feelings can also absolutely come together, by the way)
- Yourself (whether you actually want to get a new partner, or just remain single—this is your 100% your choice either way, and your decision should be made consciously)
- The new love (how comfortable are they with your continued feelings for your late love, really?)
And obviously only two of the above can be polled for opinions, and the latter one might say what they think we want to hear, only to secretly and/or later resent it.
One piece of solid advice for the happily married: talk with your partner now about how you each would feel about the other potentially remarrying in the event of your death. Do they have your pre-emptive blessing to do whatever, do you ask a respectable mourning period first (how long?), would the thought just plain make you jealous? Be honest, and bid your partner be honest too.
One piece of solid advice for everyone: make sure you, and your partner(s), as applicable, have a good emotional safety net, if you can. Close friends or family members that you genuinely completely trust to be there through thick and thin, to hold your/their hand through the emotional wreck that will likely follow.
Because, while depression and social loneliness are expected and looked out for, it’s emotional loneliness that actually hits the hardest, for most people:
Longitudinal Examination of Emotional Functioning in Older Adults After Spousal Bereavement
…which means that having even just one close friend or family member with whom one can be at one’s absolute worst, express emotions without censure, not have to put on the socially expected appearance of emotional stability… Having that one person (ideally more, but having at least one is critical) can make a huge difference.
But what if a person has nobody?
That’s definitely a hard place to be, but here’s a good starting point:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Apples vs Figs – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apples to figs, we picked the figs.
Why?
These two fruits are both known for being quite rich in sugar (but also rich in fiber, which offsets it metabolically), and indeed their macros are quite similar. That said, figs have slightly more protein, fiber, and carbs. Both are considered low glycemic index foods. We can consider this category a tie, or perhaps a nominal win for apples, whose glycemic index is the lower of the two. But since figs’ GI is also low, it’s really not a deciding factor.
In terms of vitamins, apples have more of vitamins C and E, while figs have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, and choline, with noteworthy margins of difference. A clear for figs here.
When it comes to minerals, apples are not higher in any minerals, while figs are several times higher in calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. An overwhelming win for figs.
Of course, enjoy either or both, but if you want nutritional density, apples simply cannot compete with figs.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
HRT: Bioidentical vs Animal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
HRT: A Tale Of Two Approaches
In yesterday’s newsletter, we asked you for your assessment of menopausal hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
- A little over a third said “It can be medically beneficial, but has some minor drawbacks”
- A little under a third said “It helps, but at the cost of increased cancer risk; not worth it”
- Almost as many said “It’s a wondrous cure-all that makes you happier, healthier, and smell nice too”
- Four said “It is a dangerous scam and a sham; “au naturel” is the way to go”
So what does the science say?
Which HRT?
One subscriber who voted for “It’s a wondrous cure-all that makes you healthier, happier, and smell nice too” wrote to add:
❝My answer is based on biodentical hormone replacement therapy. Your survey did not specify.❞
And that’s an important distinction! We did indeed mean bioidentical HRT, because, being completely honest here, this European writer had no idea that Premarin etc were still in such wide circulation in the US.
So to quickly clear up any confusion:
- Bioidentical hormones: these are (as the name suggests) identical on a molecular level to the kind produced by humans.
- Conjugated Equine Estrogens: such as Premarin, come from animals. Indeed, the name “Premarin” comes from “pregnant mare urine”, the substance used to make it.
There are also hormone analogs, such as medroxyprogesterone acetate, which is a progestin and not the same thing as progesterone. Hormone analogs such as the aforementioned MPA are again, a predominantly-American thing—though they did test it first in third-world countries, after testing it on animals and finding it gave them various kinds of cancer (breast, cervical, ovarian, uterine).
A quick jumping-off point if you’re interested in that:
Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate and the risk of breast and gynecologic cancer
this is about its use as a contraceptive (so, much lower doses needed), but it is the same thing sometimes given in the US as part of menopausal HRT. You will note that the date on that research is 1996; DMPA is not exactly cutting-edge and was first widely used in the 1950s.
Similarly, CEEs (like Premarin) have been used since the 1930s, while estradiol (bioidentical estrogen) has been in use since the 1970s.
In short: we recommend being wary of those older kinds and mostly won’t be talking about them here.
Bioidentical hormones are safer: True or False?
True! This is an open-and-shut case:
❝Physiological data and clinical outcomes demonstrate that bioidentical hormones are associated with lower risks, including the risk of breast cancer and cardiovascular disease, and are more efficacious than their synthetic and animal-derived counterparts.
Until evidence is found to the contrary, bioidentical hormones remain the preferred method of HRT. ❞
Further research since that review has further backed up its findings.
Source: Are Bioidentical Hormones Safer or More Efficacious than Other Commonly Used Versions in HRT?
So simply, if you’re going on HRT (estrogen and/or progesterone), you might want to check it’s the bioidentical kind.
HRT can increase the risk of breast cancer: True or False?
Contingently True, but for most people, there is no significant increase in risk.
First: again, we’re talking bioidentical hormones, and in this case, estradiol. Older animal-derived attempts had much higher risks with much lesser efficaciousness.
There have been so many studies on this (alas, none that have been publicised enough to undo the bad PR in the wake of old-fashioned HRT from before the 70s), but here’s a systematic review that highlights some very important things:
❝Estradiol-only therapy carries no risk for breast cancer, while the breast cancer risk varies according to the type of progestogen.
Estradiol therapy combined with medroxyprogesterone, norethisterone and levonorgestrel related to an increased risk of breast cancer, estradiol therapy combined with dydrogesterone and progesterone carries no risk❞
In fewer words:
- Estradiol by itself: no increased risk of breast cancer
- Estradiol with MDPA or other progestogens that aren’t really progesterone: increased risk of breast cancer
- Estradiol with actual progesterone: back to no increased risk of breast cancer
So again, you might want to make sure you are getting actual bioidentical hormones, and not something else!
However! If you are aware that you already have an increased risk of breast cancer (e.g. family history, you’ve had it before, you know you have certain genes for it, etc), then you should certainly discuss that with your doctor, because your personal circumstances may be different:
❝Tailored HRT may be used without strong evidence of a deleterious effect after ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, most other gynecological cancers, bowel cancer, melanoma, a family history of breast cancer, benign breast disease, in carriers of BRACA mutations, after breast cancer if adjuvant therapy is not being used, past thromboembolism, varicose veins, fibroids and past endometriosis.
Relative contraindications are existing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease and breast cancer being treated with adjuvant therapies❞
Source: HRT in difficult circumstances: are there any absolute contraindications?
HRT makes you happier, healthier, and smell nice too: True or False?
Contingently True, assuming you do want its effects, which generally means the restoration of much of the youthful vitality you enjoyed pre-menopause.
The “and smell nice too” was partly rhetorical, but also partly literal: our scent is largely informed by our hormones, and higher estrogen results in a sweeter scent; lower estrogen results in a more bitter scent. Not generally considered an important health matter, but it’s a thing, so hey.
More often, people take menopausal HRT for more energy, stronger bones (reduced osteoporosis risk), healthier heart (reduced CVD risk), improved sexual health, better mood, healthier skin and hair, and general avoidance of menopause symptoms:
Read more: Skin, hair and beyond: the impact of menopause
We’d need another whole main feature to discuss all the benefits properly; today we’re just mythbusting.
HRT does have some drawbacks: True or False?
True, and/but how serious they are (beyond the aforementioned consideration in the case of an already-increased risk of breast cancer) is a matter of opinion.
For example, it is common to get a reprise of monthly cramps and/or mood swings, depending on how one is taking the HRT and other factors (e.g. your own personal physiology and genetic predispositions). For most people, these will even out over time.
It’s also even common to get a reprise of (much slighter than before) monthly bleeding, unless you have for example had a hysterectomy (no uterus = no bleeding). Again, this will usually settle down in a matter of months.
If you experience anything more alarming than that, then indeed check with your doctor.
HRT is a dangerous scam and sham: True or False?
False, simply. As described above, for most people they’re quite safe. Again, talking bioidentical hormones.
The other kind are in the most neutral sense a sham (i.e. they are literally sham hormones), though they’re not without their merits and for many people they may be better than nothing.
As for being a scam, biodentical hormones are widely prescribed in the many countries that have universal healthcare and/or a single-payer healthcare system, where there would be no profit motive (and considerable cost) in doing so.
They’re prescribed because they are effective and thus reduce healthcare spending in other areas (such as treating osteoporosis or CVD after the fact) and improve Health Related Quality of Life, and by extension, health-adjusted life-years, which is one of the top-used metrics for such systems.
See for example:
Our apologies, gentlemen
We wanted to also talk about testosterone therapy for the andropause, but we’ve run out of room today (because of covering the important distinction of bioidentical vs old-fashioned HRT)!
To make it up to you, we’ll do a full main feature on it (it’s an interesting topic) in the near future, so watch this space
Ladies, we’ll also at some point cover the pros and cons of different means of administration, e.g. pills, transdermal gel, injections, patches, pessaries, etc—which often have big differences.
That’ll be in a while though, because we try to vary our topics, so we can’t talk about menopausal HRT all the time, fascinating and important a topic it is.
Meanwhile… take care, all!
Share This Post
-
Healthiest-Three-Nut Butter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re often telling you to “diversify your nuts”, so here’s a great way to get in three at once with no added sugar, palm oil, or preservatives, and only the salt you choose to put in. We’ve picked three of the healthiest nuts around, but if you happen to be allergic, don’t worry, we’ve got you covered too.
You will need
- 1 cup almonds (if allergic, substitute a seed, e.g. chia, and make it ½ cup)
- 1 cup walnuts (if allergic, substitute a seed, e.g. pumpkin, and make it ½ cup)
- 1 cup pistachios (if allergic, substitute a seed, e.g. poppy, and make it ½ cup)
- 1 tbsp almond oil (if allergic, substitute extra virgin olive oil) (if you prefer sweet nut butter, substitute 1 tbsp maple syrup; the role here is to emulsify the nuts, and this will do the same job)
- Optional: ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1a) If using nuts, heat your oven to 350℉ / 180℃. Place the nuts on a baking tray lined with baking paper, and bake/roast for about 10 minutes, but keep an eye on it to ensure the nuts don’t burn, and jiggle them if necessary to ensure they toast evenly. Once done, allow to cool.
1b) If using seeds, you can either omit that step, or do the same for 5 minutes if you want to, but really it’s not necessary.
2) Blend all ingredients (nuts/seeds, oil, MSG/salt) in a high-speed blender. Note: this will take about 10 minutes in total, and we recommend you do it in 30-second bursts so as to not overheat the motor. You also may need to periodically scrape the mixture down the side of the blender, to ensure a smooth consistency.
3) Transfer to a clean jar, and enjoy at your leisure:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Sesame Seeds vs Poppy Seeds – Which is Healthier?
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Darwin’s Bed Rest: Worthwhile Idea?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I recall that Charles Darwin (of Evolution fame) used to spend a day a month in bed in order to maintain his physical and psychological equilibrium. Do you see merit in the idea?❞
Well, it certainly sounds wonderful! Granted, it may depend on what you do in bed :p
Descartes did a lot of his work from bed (and also a surprising amount of it while hiding in an oven, but that’s another story), which was probably not so good for the health.
As for Darwin, his health was terrible in quite a lot of ways, so he may not be a great model.
However! Certainly taking a break is well-established as an important and healthful practice:
How To Rest More Efficiently (Yes, Really)
❝I don’t like to admit it but I am getting old. Recently, I had my first “fall” (ominous word!) I was walking across some wet decking and, before I knew what had happened, my feet were shooting forwards, and I crashed to the ground. Luckily I wasn’t seriously damaged. But I was wondering whether you can give us some advice about how best to fall. Maybe there are some good videos on the subject? I would like to be able to practice falling so that it doesn’t come as such a shock when it happens!❞
This writer has totally done the same! You might like our recent main feature on the topic:
…if you’ll pardon the pun
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Old Is Too Old For HRT?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝I think you guys do a great job. Wondering if I can suggest a topic? Older women who were not offered hormone replacement therepy because of a long term study that was misread. Now, we need science to tell us if we are too old to benefit from begininng to take HRT. Not sure how old your readers are on average but it would be a great topic for older woman. Thanks❞
Thank you for the kind words, and the topic suggestion!
About the menopause and older age thereafter
We’ve talked a bit before about the menopause, for example:
What You Should Have Been Told About The Menopause Beforehand
And we’ve even discussed the unfortunate social phenomenon of post-menopausal women thinking “well, that’s over and done with now, time to forget about that”, because spoiler, it will never be over and done with—your body is always changing every day, and will continue to do so until you no longer have a body to change.
This means, therefore, that since changes are going to happen no matter what, the onus is on us to make the changes as positive (rather than negative) as possible:
Menopause, & When Not To Let Your Guard Down
About cancer risk
It sounds like you know this one, but for any who were unaware: indeed, there was an incredibly overblown and misrepresented study, and even that was about older forms of HRT (being conjugated equine estrogens, instead of bioidentical estradiol):
As for those who have previously had breast cancer or similar, there is also:
The Hormone Therapy That Reduces Breast Cancer Risk & More
Is it too late?
Fortunately, there is a quick and easy test to know whether you are too old to benefit:
First, find your pulse, by touching the first two fingers of one hand, against the wrist of the other. If you’re unfamiliar with where to find the pulse at the wrist, here’s a quick explainer.
Or if you prefer a video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Did you find it?
Good; in that case, it’s not too late!
Scientists have tackled this question, looking at women of various ages, and finding that when comparing age groups taking HRT, disease risk changes do not generally vary much by age i.e., someone at 80 gets the same relative benefit from HRT as someone at 50, with no extra risks from the HRT. For example, if taking HRT at 50 reduces a risk by n% compared to an otherwise similar 50-year-old not on HRT, then doing so at 80 reduces the same risk by approximately the same percentage, compared to an otherwise similar 80-year-old not on HRT.
There are a couple of exceptions, such as in the case of already having advanced atherosclerotic lesions (in which specific case HRT could increase inflammation; not something it usually does), or in the case of using conjugated equine estrogens instead of modern bioidentical estradiol (as we talked about before).
Thus, for the most part, HRT is considered safe and effective regardless of age:
How old is too old for hormone therapy?
👆 that’s from 2015 though, so how about a new study, from 2024?
❝Compared with never use or discontinuation of menopausal hormone therapy after age 65 years, the use of estrogen monotherapy beyond age 65 years was associated with significant risk reductions in mortality (19% or adjusted hazards ratio, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.79-0.82), breast cancer (16%), lung cancer (13%), colorectal cancer (12%), congestive heart failure (CHF) (5%), venous thromboembolism (3%), atrial fibrillation (4%), acute myocardial infarction (11%), and dementia (2%).❞
❝Among senior Medicare women, the implications of menopausal hormone therapy use beyond age 65 years vary by types, routes, and strengths. In general, risk reductions appear to be greater with low rather than medium or high doses, vaginal or transdermal rather than oral preparations, and with estradiol rather than conjugated estrogen.❞
Read in full: Use of menopausal hormone therapy beyond age 65 years and its effects on women’s health outcomes by types, routes, and doses
As for more immediately-enjoyable benefits (improved mood, healthier skin, better sexual function, etc), yes, those also are benefits that people enjoy at least into their eighth decade:
See: Use of hormone therapy in Swedish women aged 80 years or older
What about…
Statistically speaking, most people who take HRT have a great time with it and consider it life-changing in a good way. However, nothing is perfect; sometimes going on HRT can have a shaky start, and for those people, there may be some things that need addressing. So for that, check out:
HRT Side Effects & Troubleshooting
And also, while estrogen monotherapy is very common, it is absolutely worthwhile to consider also taking progesterone alongside it:
Progesterone Menopausal HRT: When, Why, And How To Benefit
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ricezempic: is there any evidence this TikTok trend will help you lose weight?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you spend any time looking at diet and lifestyle content on social media, you may well have encountered a variety of weight loss “hacks”.
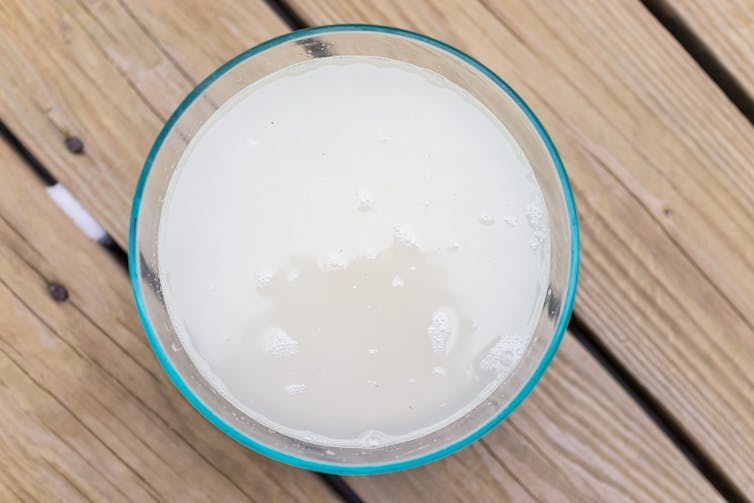
One of the more recent trends is a home-made drink called ricezempic, made by soaking uncooked rice and then straining it to drink the leftover starchy water. Sounds delicious, right?
Its proponents claim it leads to weight loss by making you feel fuller for longer and suppressing your appetite, working in a similar way to the sought-after drug Ozempic – hence the name.
So does this drink actually mimic the weight loss effects of Ozempic? Spoiler alert – probably not. But let’s look at what the evidence tells us.
New Africa/Shutterstock How do you make ricezempic?
While the recipe can vary slightly depending on who you ask, the most common steps to make ricezempic are:
- soak half a cup of white rice (unrinsed) in one cup of warm or hot water up to overnight
- drain the rice mixture into a fresh glass using a strainer
- discard the rice (but keep the starchy water)
- add the juice of half a lime or lemon to the starchy water and drink.
TikTokers advise that best results will happen if you drink this concoction once a day, first thing in the morning, before eating.
The idea is that the longer you consume ricezempic for, the more weight you’ll lose. Some claim introducing the drink into your diet can lead to a weight loss of up to 27 kilograms in two months.
Resistant starch
Those touting ricezempic argue it leads to weight loss because of the resistant starch rice contains. Resistant starch is a type of dietary fibre (also classified as a prebiotic). There’s no strong evidence it makes you feel fuller for longer, but it does have proven health benefits.
Studies have shown consuming resistant starch may help regulate blood sugar, aid weight loss and improve gut health.
Research has also shown eating resistant starch reduces the risk of obesity, diabetes, heart disease and other chronic diseases.
Ricezempic is made by soaking rice in water. Kristi Blokhin/Shutterstock Resistant starch is found in many foods. These include beans, lentils, wholegrains (oats, barley, and rice – particularly brown rice), bananas (especially when they’re under-ripe or green), potatoes, and nuts and seeds (particularly chia seeds, flaxseeds and almonds).
Half a cup of uncooked white rice (as per the ricezempic recipe) contains around 0.6 grams of resistant starch. For optimal health benefits, a daily intake of 15–20 grams of resistant starch is recommended. Although there is no concrete evidence on the amount of resistant starch that leaches from rice into water, it’s likely to be significantly less than 0.6 grams as the whole rice grain is not being consumed.
Ricezempic vs Ozempic
Ozempic was originally developed to help people with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels but is now commonly used for weight loss.
Ozempic, along with similar medications such as Wegovy and Trulicity, is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. These drugs mimic the GLP-1 hormone the body naturally produces. By doing so, they slow down the digestive process, which helps people feel fuller for longer, and curbs their appetite.
While the resistant starch in rice could induce some similar benefits to Ozempic (such as feeling full and therefore reducing energy intake), no scientific studies have trialled ricezempic using the recipes promoted on social media.
Ozempic has a long half-life, remaining active in the body for about seven days. In contrast, consuming one cup of rice provides a feeling of fullness for only a few hours. And simply soaking rice in water and drinking the starchy water will not provide the same level of satiety as eating the rice itself.
Other ways to get resistant starch in your diet
There are several ways to consume more resistant starch while also gaining additional nutrients and vitamins compared to what you get from ricezempic.
1. Cooked and cooled rice
Letting cooked rice cool over time increases its resistant starch content. Reheating the rice does not significantly reduce the amount of resistant starch that forms during cooling. Brown rice is preferable to white rice due to its higher fibre content and additional micronutrients such as phosphorus and magnesium.
2. More legumes
These are high in resistant starch and have been shown to promote weight management when eaten regularly. Why not try a recipe that has pinto beans, chickpeas, black beans or peas for dinner tonight?
3. Cooked and cooled potatoes
Cooking potatoes and allowing them to cool for at least a few hours increases their resistant starch content. Fully cooled potatoes are a rich source of resistant starch and also provide essential nutrients like potassium and vitamin C. Making a potato salad as a side dish is a great way to get these benefits.
In a nutshell
Although many people on social media have reported benefits, there’s no scientific evidence drinking rice water or “ricezempic” is effective for weight loss. You probably won’t see any significant changes in your weight by drinking ricezempic and making no other adjustments to your diet or lifestyle.
While the drink may provide a small amount of resistant starch residue from the rice, and some hydration from the water, consuming foods that contain resistant starch in their full form would offer significantly more nutritional benefits.
More broadly, be wary of the weight loss hacks you see on social media. Achieving lasting weight loss boils down to gradually adopting healthy eating habits and regular exercise, ensuring these changes become lifelong habits.
Emily Burch, Accredited Practising Dietitian and Lecturer, Southern Cross University and Lauren Ball, Professor of Community Health and Wellbeing, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: