Fall Special
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some fall-themed advice…
It is now, nominally at least, fall. We’re going to talk about the other kind of “fall” though, the kind that results in broken hips and more.
If you’re thinking “not me; that happens to older more infirm people”, rest assured, it can and statistically probably will happen to you at some point. So, how to play the odds?
First, be robust!
We may not be able to make ourselves like children who bounce easily, but we also don’t have to crumble into dust at the slightest knock, either. There are two important ways we can start to make ourselves robust from the inside out, and they are simple: diet and exercise.
- Diet: The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
- Exercise: Osteoporosis Exercises
“But I don’t have osteoporosis”—great! But osteoporosis is preceded by osteopenia, which is generally asymptomatic at first, and also if we’re not very careful about it, we will lose about 1% bone density per year from the age of about 35 onwards, with that rate of loss climbing sharply from the age of 50 onwards, and even more steeply in cases of untreated menopause.
So in other words, don’t take your bone strength for granted; there’s a first time for everything, and you don’t want to find out the hard (and yet, dare we say it, brittle) way.
Second, be dynamic!
Be able to fall and get up safely. If your later life is going to be a triathlon of things you need to train for now, then being able to fall and get up safely should be at the top of the list.
Being able to “deep squat” will help you a lot here, in being able to get up with minimal (or no) use of your hands. We shared a great instructional video about this last week.
It also means that the more your lower body can still take your weight while your torso is closer to the ground (without your legs buckling and collapsing, for instance), the softer and gentler you’ll hit the floor if you do fall, because the final “drop” will be from a lower height.
If at all possible, consider taking some classes of a martial art that involves safely falling—aikido is typically the softest and gentlest and is famously great for people of all ages, but judo or jujitsu will suffice if aikido isn’t available where you are. You don’t have to get a black belt (unless you want to), and any decent instructor will be happy to guide you through the basics of safely falling and then send you on your merry way, if that’s all you wanted.
The benefits of this are twofold:
- Obviously, if you fall, you will have better technique and thus be less likely to incur injury
- As you are falling, you will be less afraid, and thus less likely to tense up mid-fall (tensing up will exacerbate any falling injury)
Click here to find an aikido teacher near you (you can search by country, state, and city)
Third, be balanced!
Spending even just a few minutes each day working on your balance can go a long way.
Standing on one leg (and then the other) is a very good obvious starting point. Please, do so safely. The shower is not the best place to take up this practice, for instance. A nice safe grassy area is great. Your carpeted living room or bedroom is next-best.
Another great approach is the practice of bāguàzhǎng circle-walking.
Bāguà is tai chi’s lesser-known cousin, and those arts are two of the three main schools of wǔdāngquán. But, fear not, you don’t have to don orange robes and live atop the Wudang mountains to get what you need in this case.
To give a text-based summary: bāguàzhǎng circle-walking involves walking in a small circle, with a low center of gravity, moving one’s weight very purposefully from one leg to the other, keeping complete stability the whole time that one is (often!) on one leg.
Once you get good at this, you’ll see that this is essentially a super-enhanced version of the “standing on one leg” exercise, because it’s about keeping balance while on one leg, and/but while moving also.
Naturally, if you do get good at this, you’ll be very unlikely to fall in the first place.
Here’s a visual primer. This video will show the basic footwork, and the video that follows it (it’ll prompt you if you want to watch it) shows how to bring it up to a standard walking speed, without losing fluidity of movement:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Food Fix – by Dr. Mark Hyman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
On a simplistic level, “eat more plants, but ideally not monocrops, and definitely fewer animals” is respectable, ecologically-aware advice that is also consistent with good health. But it is a simplification, and perhaps an oversimplification.
Is there space on a healthy, ecologically sound plate for animal products? Yes, argues Dr. Mark Hyman. It’s a small space, but it’s there.
For example, some kinds of fish are both healthier and more sustainable as a food source than others, same goes for some kinds of dairy products. Poultry, too, can be farmed sustainably in a way that promotes a small self-contained ecosystem—and in terms of health, consumption of poultry appears to be health-neutral at worst.
As this book explores:
- Oftentimes, food choices look like: healthy/sustainable/cheap (choose one).
- Dr. Hyman shows how in fact, we can have it more like: healthy/sustainable/cheap (choose two).
- He argues that if more people “vote with their fork”, production will continue to adjust accordingly, and we’ll get: healthy/sustainable/cheap (all three).
To this end, while some parts of the book can feel like they are purely academic (pertaining less to what we can do as individuals, and more on what governments, farming companies, etc can do), it’s good to know what issues we might also take to the ballot box, if we’re able.
The big picture aside, the book remains very strong even just from an individual health perspective, though.
Bottom line: if you have an interest in preserving your own health, and possibly humanity itself, this is an excellent book.
Share This Post
-
Getting COMFY – by Jordan Gross
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s easy to see how good “morning people” seem to have it; it’s harder, it seems, to become one.
And, if we’re forced by circumstance to be the morning person we’re not? We all-too-easily find ourselves greeting each coming day without the joy that, in an ideal world, we might.
So, is it possible to learn this power? Jordan Gross has it mapped out for it us…
The “COMFY” of the title is indeed an acronym, and it stands for:
- Calm
- Openness
- Movement
- Funny
- You
There’s a chapter explaining each in detail, and they’re bookended with other chapters explaining more about the whys and the hows.
As you might expect, the key to a good morning starts the night before, but there’s also a formula to follow. Of course, you can change it up, mix and match if you like… but this book provides a base framework to build from, which is something that can make a huge difference!
Bottom line: it’s a highly enjoyable book to read, and also provides genuine powerful help to bring us the brighter happier mornings we deserve—the set-up to the perfect day!
Click here to check out “Getting COMFY” and perk up your mornings—you deserve it!
Share This Post
-
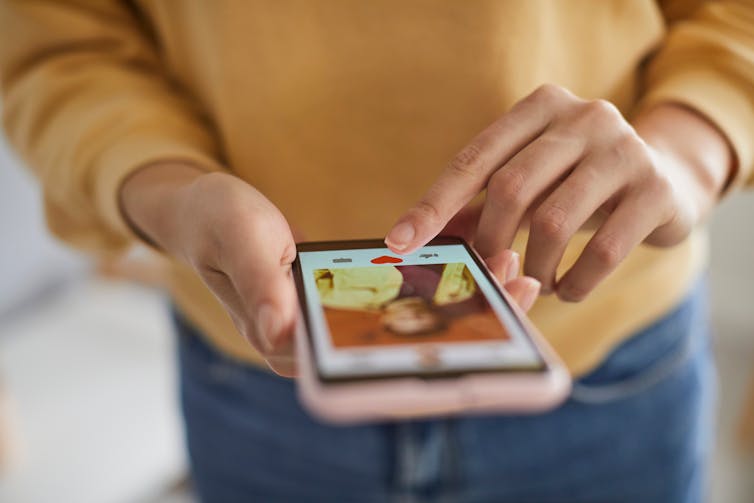
Dating apps could have negative effects on body image and mental health, our research shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Around 350 million people globally use dating apps, and they amass an estimated annual revenue of more than US$5 billion. In Australia, 49% of adults report using at least one online dating app or website, with a further 27% having done so in the past.
But while dating apps have helped many people find romantic partners, they’re not all good news.
In a recent review, my colleagues and I found using dating apps may be linked to poorer body image, mental health and wellbeing.
Dikushin Dmitry/Shutterstock We collated the evidence
Our study was a systematic review, where we collated the results of 45 studies that looked at dating app use and how this was linked to body image, mental health or wellbeing.
Body image refers to the perceptions or feelings a person has towards their own appearance, often relating to body size, shape and attractiveness.
Most of the studies we included were published in 2020 onwards. The majority were carried out in Western countries (such as the United States, the United Kingdom and Australia). Just under half of studies included participants of all genders. Interestingly, 44% of studies observed men exclusively, while only 7% included just women.
Of the 45 studies, 29 looked at the impact of dating apps on mental health and wellbeing and 22 considered the impact on body image (some looked at both). Some studies examined differences between users and non-users of dating apps, while others looked at whether intensity of dating app use (how often they’re used, how many apps are used, and so on) makes a difference.
More than 85% of studies (19 of 22) looking at body image found significant negative relationships between dating app use and body image. Just under half of studies (14 of 29) observed negative relationships with mental health and wellbeing.
The studies noted links with problems including body dissatisfaction, disordered eating, depression, anxiety and low self-esteem.
Dating apps are becoming increasingly common. But could their use harm mental health? Rachata Teyparsit/Shutterstock It’s important to note our research has a few limitations. For example, almost all studies included in the review were cross-sectional – studies that analyse data at a particular point in time.
This means researchers were unable to discern whether dating apps actually cause body image, mental health and wellbeing concerns over time, or whether there is simply a correlation. They can’t rule out that in some cases the relationship may go the other way, meaning poor mental health or body image increases a person’s likelihood of using dating apps.
Also, the studies included in the review were mostly conducted in Western regions with predominantly white participants, limiting our ability to generalise the findings to all populations.
Why are dating apps linked to poor body image and mental health?
Despite these limitations, there are plausible reasons to expect there may be a link between dating apps and poorer body image, mental health and wellbeing.
Like a lot of social media, dating apps are overwhelmingly image-centric, meaning they have an emphasis on pictures or videos. Dating app users are initially exposed primarily to photos when browsing, with information such as interests or hobbies accessible only after manually clicking through to profiles.
Because of this, users often evaluate profiles based primarily on the photos attached. Even when a user does click through to another person’s profile, whether or not they “like” someone may still often be determined primarily on the basis of physical appearance.
This emphasis on visual content on dating apps can, in turn, cause users to view their appearance as more important than who they are as a person. This process is called self-objectification.
People who experience self-objectification are more likely to scrutinise their appearance, potentially leading to body dissatisfaction, body shame, or other issues pertaining to body image.
Dating apps are overwhelmingly image-centric. Studio Romantic/Shutterstock There could be several reasons why mental health and wellbeing may be impacted by dating apps, many of which may centre around rejection.
Rejection can come in many forms on dating apps. It can be implied, such as having a lack of matches, or it can be explicit, such as discrimination or abuse. Users who encounter rejection frequently on dating apps may be more likely to experience poorer self-esteem, depressive symptoms or anxiety.
And if rejection is perceived to be based on appearance, this could lead again to body image concerns.
What’s more, the convenience and game-like nature of dating apps may lead people who could benefit from taking a break to keep swiping.
What can app developers do? What can you do?
Developers of dating apps should be seeking ways to protect users against these possible harms. This could, for example, include reducing the prominence of photos on user profiles, and increasing the moderation of discrimination and abuse on their platforms.
The Australian government has developed a code of conduct – to be enforced from April 1 this year – to help moderate and reduce discrimination and abuse on online dating platforms. This is a positive step.
Despite the possible negatives, research has also found dating apps can help build confidence and help users meet new people.
If you use dating apps, my colleagues and I recommend choosing profile images you feel display your personality or interests, or photos with friends, rather than semi-clothed images and selfies. Engage in positive conversations with other users, and block and report anyone who is abusive or discriminatory.
It’s also sensible to take breaks from the apps, particularly if you’re feeling overwhelmed or dejected.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14. The Butterfly Foundation provides support for eating disorders and body image issues, and can be reached on 1800 334 673.
Zac Bowman, PhD Candidate, College of Education, Psychology & Social Work, Flinders University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Stevia vs Acesulfame Potassium – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing stevia to acesulfame potassium, we picked the stevia.
Why?
You may be wondering: is acesulfame potassium a good source of potassium?
And the answer is: no, it is not. Obviously, it does contain potassium, but let’s do some math here:
- Acesulfame potassium is 200x sweeter than sugar
- Therefore replacing a 15g teaspoon of sugar = 75mg acesulfame potassium
- Acesulfame potassium’s full name is “potassium 6-methyl-2,2-dioxo-2H-1,2λ6,3-oxathiazin-4-olate”
- That’s just one potassium atom in there with a lot of other stuff
- Acesulfame potassium has a molar mass of 201.042 g/mol
- Potassium itself has a molar mass of 39.098 g/mol
- Therefore acesulfame potassium is 100(39.098/201.042) = 19.45% potassium by mass
- So that 75mg of acesulfame potassium contains just under 15mg of potassium, which is less than 0.5% of your recommended daily amount of potassium. Please consider eating a fruit instead.
So, that’s that, and the rest of the nutritional values of both sweeteners are just a lot of zeros.
What puts stevia ahead? Simply, based on studies available so far, moderate consumption of stevia improves gut microdiversity, whereas acesulfame potassium harms gut microdiversity:
- The Effects of Stevia Consumption on Gut Bacteria: Friend or Foe?
- The Artificial Sweetener Acesulfame Potassium Affects the Gut Microbiome
Want to give stevia a try?
Here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sciatica Exercises & Home Treatment – by Dr. George Best
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Best is a doctor of chiropractic, but his work here is compelling. He starts by giving an overview of the relevant anatomy, and then the assorted possible causes of sciatica, before moving on to the treatments.
As is generally the case for chiropractic, nothing here will be “cured”, but it will give methods for ongoing management to keep you pain-free—which in the case of sciatica, is usually the single biggest thing that most people suffering from it most dearly want.
We get to read a lot about self-massage and exercises, of the (very well-evidenced; about the most well-evidenced thing there is for back pain) McKenzie technique exercises, as well as assorted acupressure-based techniques that are less well-evidenced but have good anecdotal support.
He also writes about preventing sciatica—which if you already have it, that doesn’t mean it’s too late; it just means, in that case do these things (along with the aforementioned exercises) to gradually reverse the harm done and get back to where you were pre-sciatica.
Lastly, he does also speak on when signs might point to your problems being beyond the scope of this book, and seeking professional examination if you haven’t already.
The style throughout is straight to the point, informative, and instructional. There is zero fluff or padding, and no sensationalization. There are diagrams and illustrative photos where appropriate.
Bottom line: if you have, or fear the threat of, sciatica, then this is an excellent book to have and use its exercises.
Click here to check out Sciatica Exercises & Home Treatment, and live pain-free!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Chromium Picolinate For Blood Sugar Control & Weight Loss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, a quick disambiguation:
- chromium found in food, trivalent chromium of various kinds, is safe (in the quantities usually consumed) and is sometimes considered an essential mineral, sometimes considered unnecessary but beneficial. It’s hard to know for sure, since it’s in a lot of foods (naturally, like many trace elements)
- chromium found in pollution, hexavalent chromium (so: twice as many cationic bonds, if this writer’s chemistry serves her correctly) is poisonous.
We’re going to be writing about the food kind, which is also possible to take as a supplement.
In this case, supplementing vs getting from food is quite a big difference, by the way, since (unlike for a lot of things, which are often the other way around) the bioavailability of chromium from food is very low (around 2.5%), whereas chromium picolinate, one of the most commonly-used supplement forms, boasts higher bioavailability.
Does it work for blood sugars?
Yes, it does! At least, it does in the case of people with type 2 diabetes. Rather than bombard you with many individual studies, here’s a systematic review and meta-analysis of 22 criteria-meeting randomized clinical trials that found:
❝The available evidence suggests favourable effects of chromium supplementation on glycaemic control in patients with diabetes.
Chromium monosupplement may additionally improve triglycerides and HDL-C levels.❞
Type 1 diabetes does not have anything like the same weight of evidence, and indeed,
we couldn’t find a single human study. It was beneficial for mice with artificially-induced T1D, thoughwait no, we have an update! We found literally a single human study:Chromium picolinate supplementation for diabetes mellitus
Literally, as in: it’s a case study of one person, and the results were a modest reduction in Hb A1c levels after 3 months of 600μg daily; the researchers concluded that ❝chromium picolinate continues to fall squarely within the scope of “alternative medicine,” with both unproven benefits and unknown risks❞.
As for people without diabetes, it may reduce the risk of diabetes:
Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Is Lower in US Adults Taking Chromium-Containing Supplements
However! This was an observational study, and correlation ≠ causation.
Furthermore, they said:
❝Over one-half the adult US population consumes nutritional supplements, and over one-quarter consumes supplemental chromium. The odds of having T2D were lower in those who, in the previous 30 d, had consumed supplements containing chromium❞
That “over one-quarter consumes supplemental chromium” brought our attention to the fact that this is not talking about specifically chromium “monosupplements” (definitely not quarter of the adult population take those), but rather, “multivitamin and mineral” supplements that also contain a tiny amount (often under 50μg) of chromium.
In other words, this ruins the data and honestly the benefit could have been from anything in the “multivitamin and mineral” supplement, or indeed, could just be “the kind of person who takes supplements is the kind of person who lives a lifestyle that is less conducive to becoming diabetic”.
Does it work for weight loss?
We’re running out of space here, so we’ll be brief:
No.
There are many papers that have concluded this, but here are two:
Chromium picolinate supplementation for overweight or obese adults
and
Is it safe?
Science’s current best answer is “we don’t know; it hasn’t been tested enough; we haven’t even established the tolerable upper limit, which is usually step 1 of establishing safety”.
Nor is there an estimated average requirement (if indeed there even is a requirement, which question is also not as yet answered conclusively by science), and science falls back to “here’s an average of what people consume in their diet, so that’s probably safe, we guess”.
(that average was reckoned as 25μg/day for young women and 25μg/day for young men, by the way; older ages not as yet reckoned)
You can read about this sorry state of affairs here.
Want to try some?
Notwithstanding the above lack of data for safety, it does have benefits for blood sugars, so if that’s a gamble you’re willing to make, then here’s an example product on Amazon.
Note: the dosage per capsule there (800μg) is half of the low end of the dose that was implicated in the serious kidney condition caused in this case study (1200–2400μg), so if you are going to try it, we strongly recommend not taking more than one per day.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: