Bath vs Shower – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing bathing to showering, we picked the shower.
Why?
For the basic task of getting your body clean, the shower is better as it is an entirely one-way process. Clean water hits your body, dirty water leaves it, and no dirt is making its way back.
Baths do not have this advantage, and if you enter a bath dirty, you will then be sitting in dirty water. You will leave it a lot cleaner than you entered it (because a lot of the dirt stayed in the bathwater to be drained away after the bath), but not as clean as if you had showered.
One could argue soap or equivalent will prevent the dirt re-sticking, and that’s true, but it’s true for soap in the shower too, so it doesn’t offset anything.
Additionally, being immersed in water for more than 15 minutes can start to have a (paradoxically) dehydrating effect on the skin; this happens not only because of losing skin oils to the water, but also because of osmosis, the resultant mild edema, the body’s homeostatic response to the mild edema, then getting out the bath and drying, leaving one with the response having now just caused dehydrated skin.
Baths do have some health advantages! And these come primarily from the mental health benefits of relaxation in warm water and/or generally pampering oneself. Additionally, some bath oils or bath salts can be beneficial in a way that couldn’t be administered the same way in the shower.
Best of both worlds?
In some parts of the world (Thailand and Turkey come to mind; doubtlessly there are many others) there are traditions of first taking a shower to get clean, and then taking a bath for the rest of the bathing experience. As a bonus, the bathing experience is then all the more pleasant for the water remaining just as clean as it was to start with.
However, if you do have to pick one (and for the purpose of our “This or That” exercise, we do), then it’s the shower, hands-down.
Want to read more?
You might want to also take into account how it’s still possible to have too much of a good thing:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cynthia’s Thoughts on Intermittent Fasting
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Myth of Breakfast and Snacking
Here at 10almonds we love addressing misconceptions in the health world.
When it comes to eating habits and fasting, we’ve written our own pieces on how to break your fast (otherwise known as break-fast, or breakfast), alongside a general breakdown of intermittent fasting, and a much-requested piece on fasting specifically for women.
Cynthia Thurlow, though, instead of just writing a few articles, has dedicated the majority of her working years to intermittent fasting and, in her TEDx talk (below), makes a strong argument challenging the long-held belief that breakfast is the most important meal of the day.
Cynthia Thurlow’s Two Main Points
Thurlow argues that it’s not what you eat but when you eat that has a more profound impact on health and aging. And she argues this is crucial regardless of your age.
Complementing her views on fasting are her views on snacking; she argues that snacking all day long is outdated advice and can overtax the digestive system, leading to various health issues.
Practical Tips for Starting Intermittent Fasting
To begin intermittent fasting, Thurlow suggests starting with a 12-13 hour fasting window and gradually increasing it to 16 hours.
In terms of food choice, she recommends eating whole, unprocessed foods during eating periods as well as staying well-hydrated with water, coffee, or tea.
But you won’t see results immediately; Thurlow advises giving the strategy a solid 30 days to see results and consulting a healthcare provider if there are any existing health conditions.
You can dive deeper and join the 15 million other people who have listened to her thoughts on fasting by watching her TEDx talk below:
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Share This Post
-
Butter vs Ghee – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing butter to ghee, we picked the butter.
Why?
Assuming a comparable source for each—e.g. butter from grass-fed cows, or ghee made from butter from grass-fed cows—both have a mostly comparable nutritional profile.
Note: the above is not a safe assumption to make in the US, unless you’re paying attention. Grass-fed cows are not the norm in the US, so it’s something that has to be checked for. On the other hand, ghee is usually imported, and grass-fed cows are the norm in most of the rest of the world, including the countries that export ghee the most. So if “buying blind”, ghee will be the safer bet. However, checking labels can overcome this.
Many of the Internet-popular health claims for ghee are exaggerated. For example, yes it contains butyrate… But at 1% or less. You’d be better off getting your butyrate from fibrous fruit and vegetables. Yes it contains medium-chain triglycerides (that’s also good), but in trace amounts. It even has conjugated linoleic acid, but you guessed it, the dose is insignificant.
Meanwhile, both butter and ghee contain heart-unhealthy animal-based saturated fats (which are usually worse for the health than some, but not all, of their plant-based equivalents). However…
- A tablespoon of butter contains about 7 grams of saturated fat
- A tablespoon of ghee contains about 9 grams of saturated fat
So, in this case, “ghee is basically butter, but purer” becomes a bad thing (and the deciding factor between the two).
There is one reason to choose butter over ghee, but it’s not health-related—it simply has a higher smoke point, as is often the case for fats that have been more processed compared to fats that have been less processed.
In short: either can be used in moderation, but even 2 tbsp of butter are taking an average person (because it depends on your metabolism, so we’ll say average) to the daily limit for saturated fats already, so we recommend to go easy even on that.
Want to know more?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
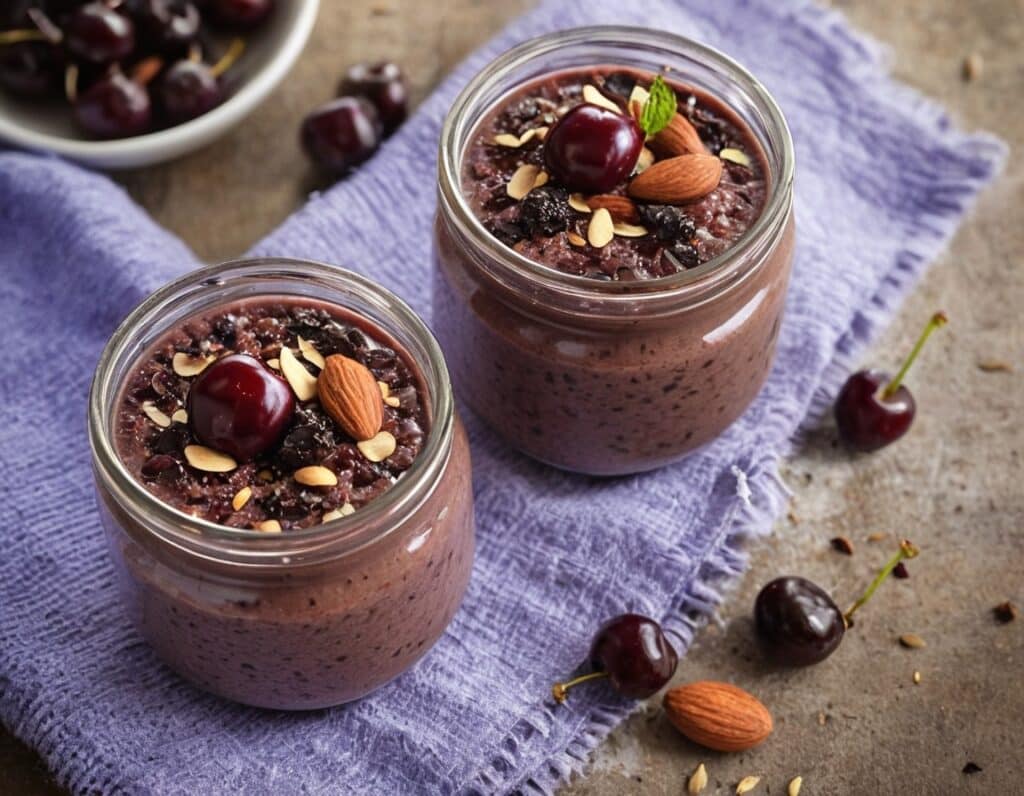
Black Forest Chia Pudding
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This pudding tastes so decadent, it’s hard to believe it’s so healthy, but it is! Not only is it delicious, it’s also packed with nutrients including protein, carbohydrates, healthy fats (including omega-3s), fiber, vitamins, minerals, and assorted antioxidant polyphenols. Perfect dessert or breakfast!
You will need
- 1½ cups pitted fresh or thawed-from-frozen cherries
- ½ cup mashed banana
- 3 tbsp unsweetened cocoa powder
- 2 tbsp chia seeds, ground
- Optional: 2 pitted dates, soaked in hot water for 10 minutes and then drained (include these if you prefer a sweeter pudding)
- Garnish: a few almonds, and/or berries, and/or cherries and/or cacao nibs
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the ingredients except for the chia seeds and the garnish, with ½ cup of water, until completely smooth
2) Divide into two small bowls or glass jars
3) Add 1 tbsp ground chia seeds to each, and stir until evenly distributed
4) Add the garnish and refrigerate overnight or at least for some hours. There’s plenty of wiggle-room here, so make it at your convenience and serve at your leisure.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Cherries’ Very Healthy Wealth Of Benefits!
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Heart Rate Zones, Oxalates, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I think the heart may be an issue for lots of us. I know it is for me due to AFib. When I’m in my training zone like on a treadmill, I’m usually around 110 to 120. But there are occasionally times when I’m at 140 or 150. How dangerous is that? If I use that formula of 180 minus age, thats 103. I get nothing from that. My resting heart rate is in the 50 to 60 range.❞
First, for safety, let us draw attention to our medical disclaimer at the bottom of each email, and also specifically note that we are not cardiologists here, let alone your cardiologist. There’s a lot we can’t know or advise about. However, as general rules of thumb:
For people without serious health conditions, it is considered good and healthful for one’s heart rate to double (from its resting rate) during exercise, with even more than 2.5x resting rate being nothing more than a good cardio workout.
As for “180 minus age” (presuming you mean: to calculate the safe maximum heart rate), more common (and used by the American Heart Association) is 220 minus age. In your case, that’d give 143.
Having atrial fibrillation may change this however, and we can’t offer medical advice.
We can point to this AHA “AFib Resources For Patients and Professionals”, including this handy FAQ sheet which says:
“Am I able to exercise?” / “Yes, as long as you’re cleared by your doctor, you can perform normal activities of daily living that you can tolerate” (accompanied by a little graphic of a person using an exercise bike)
You personally probably know this already, of course, but it’s quite an extensive collection of resources, so we thought we’d include it.
It’s certainly a good idea for everyone to be aware of their healthy heart rate ranges, regardless of having a known heart condition or not, though!
American Heart Association: Target Heart Rates Chart
❝I would like to see some articles on osteoporosis❞
You might enjoy this mythbusting main feature we did a few weeks ago!
The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
❝Interesting, but… Did you know spinach is high in oxylates? Some people are sensitive and can cause increased inflammation, joint pain or even kidney stones. Moderation is key. My sister and I like to eat healthy but found out by experience that too much spinach salad caused us joint and other aches.❞
It’s certainly good to be mindful of such things! For most people, a daily serving of spinach shouldn’t cause ill effects, and certainly there are other greens to eat.
We wondered whether there was a way to reduce the oxalate content, and we found:
How to Reduce Oxalic Acid in Spinach: Neutralizing Oxalates
…which led us this product on Amazon:
Nephure Oxalate Reducing Enzyme, Low Oxalate Diet Support
We wondered what “nephure” was, and whether it could be trusted, and came across this “Supplement Police” article about it:
Nephure Review – Oxalate Reducing Enzyme Powder Health Benefits?
…which honestly, seems to have been written as a paid advertisement. But! It did reference a study, which we were able to look up, and find:
In vitro and in vivo safety evaluation of Nephure™
…which seems to indicate that it was safe (for rats) in all the ways that they checked. They did not, however, check whether it actually reduced oxalate content in spinach or any other food.
The authors did declare a conflict of interest, in that they had a financial relationship with the sponsor of the study, Captozyme Inc.
All in all, it may be better to just have kale instead of spinach:
- 20 Foods High in Oxalates to Limit if You Have Kidney Stones
- The Kidney Dietician: The Best Low Oxalate Greens
We turn the tables and ask you a question!
We’ll then talk about this tomorrow:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Your Simplest Life – by Lisa Turner
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We probably know how to declutter, and perhaps even do a “unnecessary financial expenditures” audit. So, what does this offer beyond that?
A large portion of this book focuses on keeping our general life in a state of “flow”, and strategies include:
- How to make sure you’re doing the right part of the 80:20 split on a daily basis
- Knowing when to switch tasks, and when not to
- Knowing how to plan time for tasks
- No more reckless optimism, but also without falling foul of Parkinson’s Law (i.e. work expands to fill the time allotted to it)
- Decluttering your head, too!
When it comes to managing life responsibilities in general, Turner is very attuned to generational differences… Including the different challenges faced by each generation, what’s more often expected of us, what we’re used to, and how we probably initially learned to do it (or not).
To this end, a lot of strategies are tailored with variations for each age group. Not often does an author take the time to address each part of their readership like that, and it’s really helpful that she does!
All in all, a great book for simplifying your daily life.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
No-Exercise Exercise!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do you love to go to the gym?
If so, today’s article might not be for you so much. Or maybe it will, because let’s face it, exercise is fun!
At least… It can be, and should be 😎
So without further ado, here’s a slew of no-exercise exercise ideas; we’re willing to bet that somewhere in the list there’s at least some you haven’t tried before, and probably some you haven’t done in a while but might enjoy making a reprise!
Walking
No surprises here: walking is great. Hopefully you have some green spaces near you, but if you don’t, [almost] any walking is better than no walking. So unless there’s some sort of environmental disaster going on outside, lace up and get stepping.
If you struggle to “walk for walking’s sake” give yourself a little mission. Walk to the shop to buy one item. Walk to the park and find a flower to photograph. Walk to the library and take out a book. Whatever works for you!
See also: The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, And Move More
Take the stairs
This one doesn’t need many words, just: make it a habit.
Treat the elevators as though they aren’t there!
See also: How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Dance
Dance is amazing! Any kind of dance, whatever suits your tastes. This writer loves salsa and tango, but no matter whether for you it’s zouk or zumba, breakdancing or line dancing, whatever gets you moving is going to be great for you.
If you don’t know how, online tutorials abound, and best of all is to attend local classes if you can, because they’re always a fun social experience too.
Make music
Not something often thought of as an exercise, but it is! Most instruments require that we be standing or siting with good posture, focusing intently on our movements, and often as not, breathing very mindfully too. And yes, it’s great for the brain as well!
Check out: This Is Your Brain on Music: The Science of a Human Obsession – by Dr. Daniel Levitin
Take a stand
If you spend a lot of time at a desk, please consider investing in a standing desk; they can be truly life-changing. Not only is it so much better for your back, hips, neck, and internal organs, but also it burns hundreds more calories than sitting, due to the no-exercise exercise that is keeping your body constantly stabilized while on your feet.
(or, if you’re like this writer: on your foot. I do have two feet, I just spend an inordinate amount of time at my desk standing on one leg at a time; I’m a bit of a flamingo like that)
See also: Deskbound: Standing Up to a Sitting World – by Kelly Starrett and Glen Cordoza
Sit, but…
Sit in a sitting squat! Sometimes called a Slav squat, or an Asian squat, or a resting squat, or various other names:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Alternatively, sitting in seiza (the traditional Japanese sitting position) is also excellent, but watch out! While it’s great once your body is accustomed to it, if you haven’t previously sat this way much, you may cut off your own circulation, hurt your knees, and (temporarily) lose feeling in your feet. So if you don’t already sit in seiza often, gradually work up the time period you spend sitting in seiza, so that your vasculature can adapt and improve, which honestly, is a very good thing for your legs and feet to have.
Breathe
Perhaps the absolute most “no-exercise exercise” there is. And yes, of course you are (hopefully) breathing all the time, but how you are breathing matters a lot:
The Inside Job Of Fixing Our Breathing: Exercises That Can Fix Sinus Problems (And More)
Clean
This doesn’t have to mean scrubbing floors like a sailor—even merely giving your house the Marie Kondo treatment counts, because while you’re distracted with all the objects, you’re going to be going back and forth, getting up and down, etc, clocking up lots of exercise that you barely even notice!
PS, check out: The Life-Changing Manga Of Tidying Up – by Marie Kondo
Garden
As with the above, it’s lots of activity that doesn’t necessarily feel like it (assuming you’re doing more pruning and weeding etc, and less digging ditches etc), and as a bonus, there are a stack of mental health benefits to being in a green natural environment and interacting with soil:
Read more: The Antidepressant In Your Garden
Climb
Depending on where you live, this might mean an indoor climbing wall, but give it a go! They have color-coded climbs from beginner to advanced, so don’t worry about being out of your depth.
And the best thing is, the beginner climbs will be as much a workout to a beginner as the advanced climbs will be to an advanced climber, because at the end of the day, you’re still clinging on for dear life, no matter whether it’s a sizeable handhold not far from the ground, or the impression of a fingernail crack in an overhang 100ft in the air.
Video games (but…)
Less in the category of Stardew Valley, and more in the category of Wii Fit.
So, dust off that old controller (or treat yourself to one if you didn’t have one already), and get doing a hundred sports and other physical activities in the comfort of your living room, with a surprisingly addictive gaming system!
Sex!
You probably don’t need instructions here, and if you do, well honestly, we’re running out of space today. But the answer to “does xyz count?” is “did it get your heart racing?” because if so, it counts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: