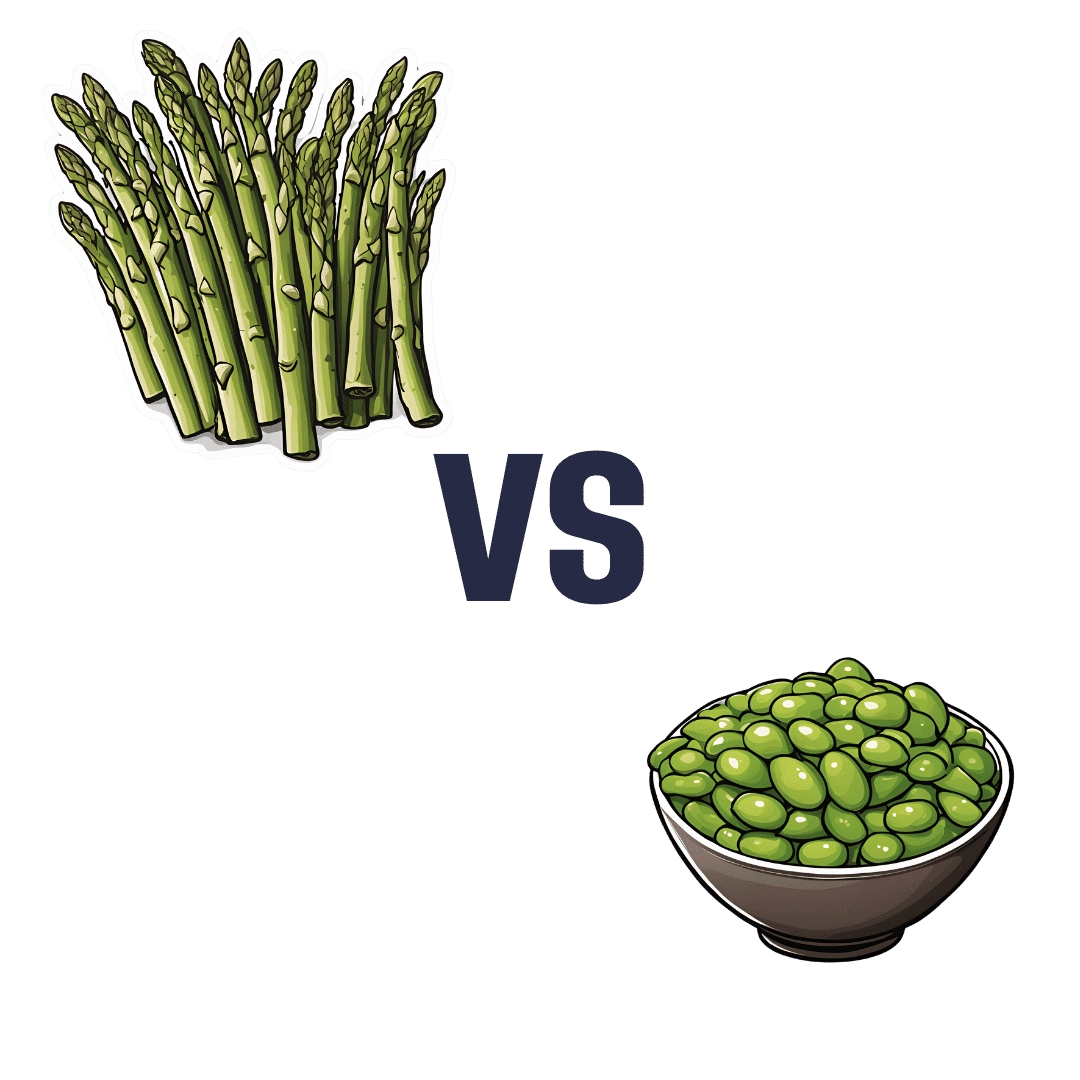
Asparagus vs Edamame – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing asparagus to edamame, we picked the edamame.
Why?
Perhaps it’s a little unfair comparing a legume to a vegetable that’s not leguminous (given legumes’ high protein content), but these two vegetables often serve a similar culinary role, and there is more to nutrition than protein. That said…
In terms of macros, edamame has a lot more protein and fiber; it also has more carbs, but the ratio is such that edamame still has the lower glycemic index. Thus, the macros category is a win for edamame in all relevant aspects.
When it comes to vitamins, things are a little closer; asparagus has more of vitamins A, B3, and C, while edamame has more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, and B9. All in all, a moderate win for edamame, unless we want to consider the much higher vitamin C content of asparagus as particularly more relevant.
In the category of minerals, asparagus boasts only more selenium (and more sodium, not that that’s a good thing for most people in industrialized countries), while edamame has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. An easy win for edamame.
In short, enjoy both (unless you have a soy allergy, because edamame is young soy beans), but edamame is the more nutritionally dense by far.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Darwin’s Bed Rest: Worthwhile Idea?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I recall that Charles Darwin (of Evolution fame) used to spend a day a month in bed in order to maintain his physical and psychological equilibrium. Do you see merit in the idea?❞
Well, it certainly sounds wonderful! Granted, it may depend on what you do in bed :p
Descartes did a lot of his work from bed (and also a surprising amount of it while hiding in an oven, but that’s another story), which was probably not so good for the health.
As for Darwin, his health was terrible in quite a lot of ways, so he may not be a great model.
However! Certainly taking a break is well-established as an important and healthful practice:
How To Rest More Efficiently (Yes, Really)
❝I don’t like to admit it but I am getting old. Recently, I had my first “fall” (ominous word!) I was walking across some wet decking and, before I knew what had happened, my feet were shooting forwards, and I crashed to the ground. Luckily I wasn’t seriously damaged. But I was wondering whether you can give us some advice about how best to fall. Maybe there are some good videos on the subject? I would like to be able to practice falling so that it doesn’t come as such a shock when it happens!❞
This writer has totally done the same! You might like our recent main feature on the topic:
…if you’ll pardon the pun
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Brain Maker – by Dr. David Perlmutter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Regular 10almonds readers probably know about the gut-brain connection already, so what’s new here?
Dr. David Perlmutter takes us on a tour of gut and brain health, specifically, the neuroprotective effect of healthy gut microbiota.
This seems unlikely! After all, vagus nerve or no, the gut microbiota are confined to the gut, and the brain is kept behind the blood-brain barrier. So how does one thing protect the other?
Dr. Perlmutter presents the relevant science, and the honest answer is, we’re not 100% sure how this happens! We do know part of it: that bad gut microbiota can result in a “leaky gut”, and that may in turn lead to such a thing as a “leaky brain”, where the blood-brain barrier has been compromised and some bad things can get in with the blood.
When it comes to gut-brain health…
Not only is the correlation very strong, but also, in tests where someone’s gut microbiota underwent a radical change, e.g. due to…
- antibiotics (bad)
- fasting (good)
- or a change in diet (either way)
…their brain health changed accordingly—something we can’t easily check outside of a lab, but was pretty clear in those tests.
We’re also treated to an exposé on the links between gut health, brain health, inflammation, and dementia… Which links are extensive.
In closing, we’ll mention that throughout this book we’re also given many tips and advices to improve our gut/brain health, reverse damage done already, and set ourselves up well for the future.
Click here to check out “Brain Maker” on Amazon and take care of this important part of your health!
Share This Post
-
7 Healthy Gut Habits For Women Over 40 – by Lara West
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
With regard to the titular 7 healthy gut habits for women over 40, a chapter is devoted to each one of those habits, and she goes into quite some detail in each category, more than you might expect.
As for the 7 things, we’ll not keep them a mystery; they are:
- Intermittent fasting
- Prebiotics & probiotics
- Mindful eating
- Understanding ingredients
- Movement
- Sleep
- Stress management
Of course, all of these things are good regardless of one’s age or gender, but West is writing with women over 40 in mind, and as such, she will focus on things that are especially relevant to those of us who are indeed women over 40.
You may be wondering: what if I’m a long way over 40, and menopause is a distant memory? In that case, 90% of this will still be relevant to you; the only parts that won’t be, are those that pertain specifically to the menopausal transitional phase itself, rather than the post-menopause state.
You may also be wondering: what if I’m a man, and menopause is just not in the cards for me? In that case, maybe about 70% of this will still be relevant to you, because of the broad applicability of most of the advice. That said, if it’s just for yourself, you’d probably do better with a book of which 100% is relevant to you, rather than this one.
The style is conversational pop-science, with personal anecdotes mixed in with references to science. It’s definitely on the light/easy-reading end of books that we’ve reviewed on the topic.
Bottom line: if you’re a woman over 40 who would like to improve your gut health, this book was written for you.
Click here to check out 7 Healthy Gut Habits For Women Over 40, and rediscover vitality!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Triphala Against Cognitive Decline, Obesity, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Triphala is not just one thing, it is a combination of three plants being used together as one medicine:
- Alma (Emblica officinalis)
- Bibhitaki (Terminalia bellirica)
- Haritaki (Terminalia chebula)
…generally prepared in a 1:1:1 ratio.
This is a traditional preparation from ayurveda, and has enjoyed thousands of years of use in India. In and of itself, ayurveda is classified as a pseudoscience (literally: it doesn’t adhere to scientific method; instead, it merely makes suppositions that seem reasonable and acts on them), but that doesn’t mean it doesn’t still have a lot to offer—because, simply put, a lot of ayurvedic medicines work (and a lot don’t).
So, ayurveda’s unintended job has often been finding things for modern science to test.
For more on ayurveda: Ayurveda’s Contributions To Science (Without Being Itself Rooted in Scientific Method)
So, under the scrutiny of modern science, how does triphala stand up?
Against cognitive decline
It has most recently come to attention because one of its ingredients, the T. chebula, has been highlighted as effective against mild cognitive impairment (MCI) by several mechanisms of action, via its…
❝171 chemical constituents and 11 active constituents targeting MCI, such as flavonoids, which can alleviate MCI, primarily through its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties. T. Chebula shows potential as a natural medicine for the treatment and prevention of MCI.❞
Read in full: The potential of Terminalia chebula in alleviating mild cognitive impairment: a review
The review was quite groundbreaking, to the extent that it got a pop-science article written about it:
We’d like to talk about those 11 active constituents in particular, but we don’t have room for all of them, so we’ll mention that one of them is quercetin, which we’ve written about before:
Fight Inflammation & Protect Your Brain, With Quercetin
For gut health
It’s also been found to improve gut health by increasing transit time, that is to say, how slowly things move through your gut. Counterintuitively, this reduces constipation (without being a laxative), by giving your gut more time to absorb everything it needs to, and more time for your gut bacteria to break down the things we can’t otherwise digest:
For weight management
Triphala can also aid with weight reduction, particularly in the belly area, by modulating our insulin responses to improve insulin sensitivity:
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
With all this bird flu around, how safe are eggs, chicken or milk?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Enzo Palombo, Swinburne University of Technology
Recent outbreaks of bird flu – in US dairy herds, poultry farms in Australia and elsewhere, and isolated cases in humans – have raised the issue of food safety.
So can the virus transfer from infected farm animals to contaminate milk, meat or eggs? How likely is this?
And what do we need to think about to minimise our risk when shopping for or preparing food?
AS Foodstudio/Shutterstock How safe is milk?
Bird flu (or avian influenza) is a bird disease caused by specific types of influenza virus. But the virus can also infect cows. In the US, for instance, to date more than 80 dairy herds in at least nine states have been infected with the H5N1 version of the virus.
Investigations are under way to confirm how this happened. But we do know infected birds can shed the virus in their saliva, nasal secretions and faeces. So bird flu can potentially contaminate animal-derived food products during processing and manufacturing.
Indeed, fragments of bird flu genetic material (RNA) were found in cow’s milk from the dairy herds associated with infected US farmers.
However, the spread of bird flu among cattle, and possibly to humans, is likely to have been caused through contact with contaminated milking equipment, not the milk itself.
The test used to detect the virus in milk – which uses similar PCR technology to lab-based COVID tests – is also highly sensitive. This means it can detect very low levels of the bird flu RNA. But the test does not distinguish between live or inactivated virus, just that the RNA is present. So from this test alone, we cannot tell if the virus found in milk is infectious (and capable of infecting humans).
It’s best to stick with pasteurised milk. Amnixia/Shutterstock Does that mean milk is safe to drink and won’t transmit bird flu? Yes and no.
In Australia, where bird flu has not been reported in dairy cattle, the answer is yes. It is safe to drink milk and milk products made from Australian milk.
In the US, the answer depends on whether the milk is pasteurised. We know pasteurisation is a common and reliable method of destroying concerning microbes, including influenza virus. Like most viruses, influenza virus (including bird flu virus) is inactivated by heat.
Although there is little direct research on whether pasteurisation inactivates H5N1 in milk, we can extrapolate from what we know about heat inactivation of H5N1 in chicken and eggs.
So we can be confident there is no risk of bird flu transmission via pasteurised milk or milk products.
However, it’s another matter for unpasteurised or “raw” US milk or milk products. A recent study showed mice fed raw milk contaminated with bird flu developed signs of illness. So to be on the safe side, it would be advisable to avoid raw milk products.
How about chicken?
Bird flu has caused sporadic outbreaks in wild birds and domestic poultry worldwide, including in Australia. In recent weeks, there have been three reported outbreaks in Victorian poultry farms (two with H7N3 bird flu, one with H7N9). There has been one reported outbreak in Western Australia (H9N2).
The strains of bird flu identified in the Victorian and Western Australia outbreaks can cause human infection, although these are rare and typically result from close contact with infected live birds or contaminated environments.
Therefore, the chance of bird flu transmission in chicken meat is remote.
Nonetheless, it is timely to remind people to handle chicken meat with caution as many dangerous pathogens, such as Salmonella and Campylobacter, can be found on chicken carcasses.
Always handle chicken meat carefully when shopping, transporting it home and storing it in the kitchen. For instance, make sure no meat juices cross-contaminate other items, consider using a cool bag when transporting meat, and refrigerate or freeze the meat within two hours.
Avoid washing your chicken before cooking to prevent the spread of disease-causing microbes around the kitchen.
Finally, cook chicken thoroughly as viruses (including bird flu) cannot survive cooking temperatures.
Are eggs safe?
The recent Australian outbreaks have occurred in egg-laying or mixed poultry flocks, so concerns have been raised about bird flu transmission via contaminated chicken eggs.
Can flu viruses contaminate chicken eggs and potentially spread bird flu? It appears so. A report from 2007 said it was feasible for influenza viruses to enter through the eggshell. This is because influenza virus particles are smaller (100 nanometres) than the pores in eggshells (at least 200 nm).
So viruses could enter eggs and be protected from cleaning procedures designed to remove microbes from the egg surface.
Therefore, like the advice about milk and meat, cooking eggs is best.
The US Food and Drug Administration recommends cooking poultry, eggs and other animal products to the proper temperature and preventing cross-contamination between raw and cooked food.
In a nutshell
If you consume pasteurised milk products and thoroughly cook your chicken and eggs, there is nothing to worry about as bird flu is inactivated by heat.
The real fear is that the virus will evolve into highly pathogenic versions that can be transmitted from human to human.
That scenario is much more frightening than any potential spread though food.
Enzo Palombo, Professor of Microbiology, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Stop Checking Your Likes – by Susie Moore
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You might think this one’s advice is summed up sufficiently by the title, that there’s no need for a book! But…
There’s a lot more to this than “stop comparing the worst out-takes of your life to someone else’s highlight reel”, and there’s a lot more to this than “just unplug”.
Instead, Susie Moore discusses the serious underlying real emotional considerations of the need for approval (and even just acceptance) by our community, as well the fear of missing out.
It’s not just about how social media is designed to hijack various parts of our brain, or how The Alogorithm™ is out to personally drag your soul through Hell for a few more clicks; it’s also about the human element that would exist even without that. Who remembers MySpace? No algorithm in those days, but oh the drama potential for those “top 8 friends” places. And if you think that kind of problem is just for young people 20 years ago, you have mercifully missed the drama that older generations can get into on Facebook.
Along with the litany of evil, though, Moore also gives practical advice on how to overcome those things, how to “see the world through comedy-colored glasses”, how to ask “what’s missing, really?”, and how to make your social media experience work for you, rather than it merely using you as fuel. ← link is to our own related article!
Bottom line: if social media sucks a lot of your time, there may be more to it than just “social media sucks in general”, and there are ways to meet your emotional needs without playing by corporations’ rules to do so.
Click here to check out Stop Checking Your Likes, and breathe easy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: