Avoiding Anemia (More Than Just “Get More Iron”)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Iron Dilemma: Factors To Consider
Anemia affects around 10% of American seniors, and that number jumps to 34–39% if there’s a comorbidity such as diabetes, hypertension, or hypercholesterolemia, which in turn climbs with increasing age or with other chronic conditions:
So, what can we do about it?
Get iron yes, but how?
We’d be remiss not to say: yes, do of course make sure you get plenty of iron.
Most people know that red meats, which are terrible for the heart and for cancer risk, are good sources of iron.
Well, good insofar as they provide plenty of it! They’re bad for other reasons.
❝Studies consistently show that consumption of red meat has been contributory to a multitude of chronic conditions such as diabetes, CVD, and malignancies.
There are various emerging reasons that strengthen this link-from the basic constituents of red meat like the heme iron component, the metabolic reactions that take place after consumption, and finally to the methods used to cook it.
The causative links show that even occasional use raises the risk of T2DM.❞
Source: Red Meat Consumption (Heme Iron Intake) and Risk for Diabetes and Comorbidities?
To heme or not to heme
Did you catch that in the middle there, about the heme iron component?
Dietary iron is broadly divided into two kinds: heme, and non-heme.
- Heme iron comes from animals
- Non-heme iron comes from plants
Bad news for vegans: non-heme iron is not so easily absorbed as heme iron.
This means that if you’re just eating plants, the RDA may be significantly lowballing the amount actually required. As a rule, about 1.8x more iron may be needed for vegans, to compensate for it being less easily absorbed.
Why this happens: it’s because of the phytic acid / phytate in the plants that contain the iron, blocking its absorption.
Good news for vegans: however, taking iron with vitamin C increases its absorption rate by about 5x better absorption, and several other side-along nutrients do similarly, including allium (from garlic), carotenoids (from many colorful plants), and fermented foods.
Why this happens: it’s because they bind with similar sites as phytic acid, without causing the same effect. To make a metaphor: these foods steal phytic acid’s parking space, so phytic acid can’t do its iron-blocking thing.
By happy coincidence, today’s featured recipe has all of these things in, by the way (vitamin C, allium, carotenoids, and fermented foods), and the star ingredient (fava beans) is a rich source of iron.
What are good sources of iron, then?
In the category of plants:
- Beans (pick your favorites / eat a variety)
- Lentils (pick your favorites / eat a variety)
- Greens (especially dark leafy greens)
- Apricots (you can get these dried, for convenience!)
- Dark chocolate (5mg per 1oz square!)*
*Ok, technically dark chocolate is not a plant; cacao is a plant; dark chocolate is usually plant-based, though, as there is no reason to add milk.
In the category of dairy products:
That’s not a publication error; dairy products are just not great for iron. Cheeses are more nutrient-dense than milk, and have less than 0.5mg per oz, in other words, the top dairy product has around 10x less iron than dark chocolate, which came in 5th place and let’s face it, we were doing broad categories there. If we listed all the beans, lentils, greens, etc it’d be a much longer list.
Eggs, which are sometimes considered under the category of dairy by virtue of not being an animal (yet!) but an animal product, have around 1mg per egg, by the way, so considering eggs are nearer 2oz, that’s not much better than the cheese.
“But what about if…”
The above is good science and general good advice for most people. That said, some people may have conditions that preclude the foods we recommended, or have other considerations, and so things may be different. Anemia can sometimes be caused by things that can’t be fixed by diet (beyond the scope of today’s article; another time, perhaps), but for example, if you have leukemia then definitely discuss things with your doctors first. Other illnesses, and some medications, can also have troublesome effects that can contribute to anemia. Again, we can offer very good general information here, but we don’t know your medical history, and our standard legal/medical disclaimer applies as always.
See also: Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Women Rowing North – by Dr. Mary Pipher
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ageism is rife, as is misogyny. And those can be internalized too, and compounded as they intersect.
Clinical psychologist Dr. Mary Pipher, herself 75, writes for us a guidebook of, as the subtitle goes, “navigating life’s currents and flourishing as we age”.
The book does assume, by the way, that the reader is…
- a woman, and
- getting old (if not already old)
However, the lessons the book imparts are vital for women of any age, and valuable as a matter of insight and perspective for any reader.
Dr. Pipher takes us on a tour of aging as a woman, and what parts of it we can make our own, do things our way, and take what joy we can from it.
Nor is the book given to “toxic positivity” though—it also deals with themes of hardship, frustration, and loss.
When it comes to those elements, the book is… honest, human, and raw. But also, an exhortation to hope, beauty, and a carpe diem attitude.
Bottom line: this book is highly recommendable to anyone of any age; life is precious and can be short. And be we blessed with many long years, this book serves as a guide to making each one of them count.
Click here to check out Women Rowing North—it really is worth it
Share This Post
-
Pistachios vs Brazil Nuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pistachios to Brazil nuts, we picked the pistachios.
Why?
In terms of macros, pistachios have more protein, carbs, and fiber, while Brazil nuts have more fat. The fats are mostly healthy, although it is worth noting that Brazil nuts have not only more total saturated fat, but also more saturated fat proportionally to total fats. All in all, Brazil nuts’ macro balance isn’t bad, but we say pistachios have it better.
When it comes to vitamins, pistachios have a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and C, while Brazil nuts have more vitamin E. An easy win for pistachios here.
In the category of minerals, it gets interesting: pistachios have more iron and potassium, while Brazil nuts have more calcium, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. Sounds great, but… About that selenium:
- A cup of cashews contains 38% of the RDA of selenium. This will go towards helping your hair be luscious and shiny (also important for energy conversion).
- A cup of Brazil nuts contains 10,456% of the RDA of selenium. This is way past the point of selenium toxicity, and your (luscious, shiny) hair will fall out.
For this reason, it’s recommended to eat no more than 3–4 Brazil nuts per day.
We consider that a point against Brazil nuts.
Adding up the sections gives us an overall win for pistachios. Of course, enjoy Brazil nuts too if you will, but in careful moderation please!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Does PRP Work For Hair Loss?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Ankit Gupta takes us through the details of this hair loss remedy for androgenic alopecia.
The bald truth
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) is a controversial treatment for androgenic hair loss.
What it involves: blood is drawn and separated using a centrifuge. PRP—including growth proteins and hormones—is extracted from the blood; about 30 ml of blood is needed to produce 5 ml of PRP. This is then injected directly into the scalp. As this can be painful, local anaesthetic is sometimes used first. This usually involves monthly sessions for the first 3 months, then booster sessions every 3–6 months thereafter.
Does it work? Research is young; so far 60% of trials have found it worked; 40% found it didn’t. When it works, effectiveness (in terms of hair restoration) is considered to be between 25–43%. Results are inconsistent and seem to vary from person to person.
In short, this doctor’s recommendation is to consider it after already having tried standard treatments such as finasteride and/or minoxidil, as they are more likely to work and don’t involve such exciting procedures as injecting your own blood extracts back into your head.
For more on all of this, plus links to the 13 papers cited, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Hair-Loss Remedies, By Science
- Hair Growth: Caffeine and Minoxidil Strategies
- Gentler Hair Health Options
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
When Bad Joints Stop You From Exercising (5 Things To Change)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The first trick to exercising with bad joints is to have better joints.
Now, this doesn’t necessarily mean you can take a supplement and magically your joint problems will be cured, but there are adjustable lifestyle factors that can and will make things relatively better or worse.
We say “and will”, because you don’t get a choice in that part. Everything we do, every little choice in our day, makes our health a little better or a little worse in some aspect(s). But we do get a choice between “relatively better” and “relatively worse”.
With that in mind, do check out:
- Avoiding/Managing Osteoarthritis
- Avoiding/Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
- How To Really Look After Your Joints
Ok, you have bad joints though; what next?
Let’s assume you’re doing your best with the above, and/or have simply decided not to, which is your call. You know your circumstances best. Either way, your joints are still not in sufficiently good condition to be able to exercise the way you’d like.
First, the obvious: enjoy low-impact exercises
For example:
- Swimming
- Yoga (much more appropriate here than the commonly-paired “and tai chi”)*
- Isometric exercises (i.e. exercise without movement, e.g. squeezing things, or stationary stability exercises)
*This is not to say that tai chi is bad. But if your problem is specifically your knees, there are many movements in most forms of tai chi that require putting the majority of one’s weight on one bent leg, which means the knee of that leg is going to suffer. If your knees are fine, then this won’t be an issue and it will simply continue strengthening your knees without discomfort. But they have to be fine first.
See also: Exercising With Osteoporosis
Second: support your joints through a full range of motion
If you have bad joints, you probably know that there’s an unfortunate paradox whereby you get to choose between:
- Exercise, and inflame your joints
- Rest, and your joints seize up
This is the way to get around that damaging dilemma.
Moving your joints through a full range of motion regularly is critical for their maintenance, so do that in a way that isn’t straining them:
If it’s your shoulders, for example, you can do (slow, gentle!) backstroke or front-crawl or butterfly motions while standing in the comfort of your living room.
If it’s your knees, then supported squats can do you a world of good. That means, squat in front of a table or other stable object, with your fingertips (or as much of your hands as you need) on it, to take a portion of your weight (it can be a large portion; that’s fine too!) while you go through the full range of motion of the squat. Repeat.
And so forth for other joints.
See also: The Most Underrated Hip Mobility Exercise (Not Stretching)
Third: work up slowly, and stop early
You can do exercises that involve impact, and if you live a fairly normal life, you’ll probably have to (walking is an impact exercise). You can also enjoy cycling (low-impact, but not so low-impact as we discussed in the last section) and work up to running if you want to.
However…
While building up your joints’ mobility and strength, it is generally a good idea to stop before you think you need to.
This means that it’s important to do those exercises in a way that you can stop early. For example, an exercise bike or a treadmill can be a lot of use here, so that you don’t find you need to stop for the day while miles from your house.
If you get such a device, it doesn’t even have to be fancy and/or expensive. This writer got herself an inexpensive exercise bike like this one, and it’s perfectly adequate.
Fourth: prioritize recovery, even if it doesn’t feel like you need it
Everyone should do this anyway, but if your joints are bad, it goes double:
Overdone It? How To Speed Up Recovery After Exercise (According To Actual Science)
Fifth: get professional help
Physiotherapists are great for this. Find one, and take their advice for your specific body and your specific circumstances and goals.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I’ve recovered from a cold but I still have a hoarse voice. What should I do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cold, flu, COVID and RSV have been circulating across Australia this winter. Many of us have caught and recovered from one of these common upper respiratory tract infections.
But for some people their impact is ongoing. Even if your throat isn’t sore anymore, your voice may still be hoarse or croaky.
So what happens to the voice when we get a virus? And what happens after?
Here’s what you should know if your voice is still hoarse for days – or even weeks – after your other symptoms have resolved.
Why does my voice get croaky during a cold?
A healthy voice is normally clear and strong. It’s powered by the lungs, which push air past the vocal cords to make them vibrate. These vibrations are amplified in the throat and mouth, creating the voice we hear.
The vocal cords are two elastic muscles situated in your throat, around the level of your laryngeal prominence, or Adam’s apple. (Although everyone has one, it tends to be more pronounced in males.) The vocal cords are small and delicate – around the size of your fingernail. Any small change in their structure will affect how the voice sounds.
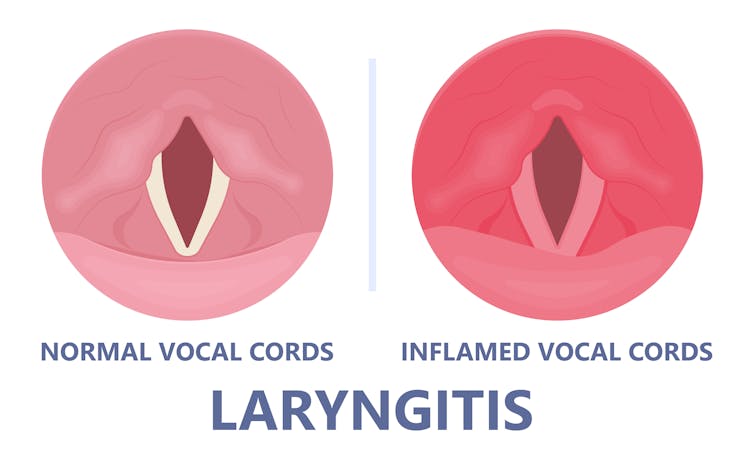
When the vocal cords become inflamed – known as laryngitis – your voice will sound different. Laryngitis is a common part of upper respiratory tract infections, but can also be caused through misuse.
Viruses such as the common cold can inflame the vocal cords. Pepermpron/Shutterstock Catching a virus triggers the body’s defence mechanisms. White blood cells are recruited to kill the virus and heal the tissues in the vocal cords. They become inflamed, but also stiffer. It’s harder for them to vibrate, so the voice comes out hoarse and croaky.
In some instances, you may find it hard to speak in a loud voice or have a reduced pitch range, meaning you can’t go as high or loud as normal. You may even “lose” your voice altogether.
Coughing can also make things worse. It is the body’s way of trying to clear the airways of irritation, including your own mucus dripping onto your throat (post-nasal drip). But coughing slams the vocal cords together with force.
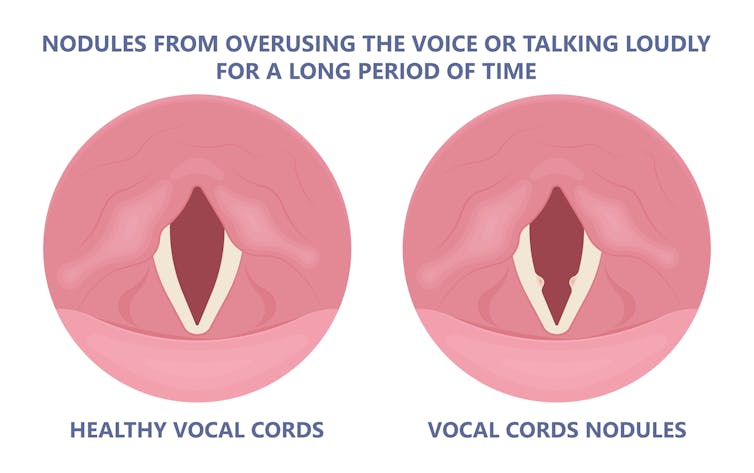
Chronic coughing can lead to persistent inflammation and even thicken the vocal cords. This thickening is the body trying to protect itself, similar to developing a callus when a pair of new shoes rubs.
Thickening on your vocal cords can lead to physical changes in the vocal cords – such as developing a growth or “nodule” – and further deterioration of your voice quality.
Coughing and exertion can cause inflamed vocal cords to thicken and develop nodules. Pepermpron/Shutterstock How can you care for your voice during infection?
People who use their voices a lot professionally – such as teachers, call centre workers and singers – are often desperate to resume their vocal activities. They are more at risk of forcing their voice before it’s ready.
The good news is most viral infections resolve themselves. Your voice is usually restored within five to ten days of recovering from a cold.
Occasionally, your pharmacist or doctor may prescribe cough suppressants to limit additional damage to the vocal cords (among other reasons) or mucolytics, which break down mucus. But the most effective treatments for viral upper respiratory tract infections are hydration and rest.
Drink plenty of water, avoid alcohol and exposure to cigarette smoke. Inhaling steam by making yourself a cup of hot water will also help clear blocked noses and hydrate your vocal cords.
Rest your voice by talking as little as possible. If you do need to talk, don’t whisper – this strains the muscles.
Instead, consider using “confidential voice”. This is a soft voice – not a whisper – that gently vibrates your vocal cords but puts less strain on your voice than normal speech. Think of the voice you use when communicating with someone close by.
During the first five to ten days of your infection, it is important not to push through. Exerting the voice by talking a lot or loudly will only exacerbate the situation. Once you’ve recovered from your cold, you can speak as you would normally.
What should you do if your voice is still hoarse after recovery?
If your voice hasn’t returned to normal after two to three weeks, you should seek medical attention from your doctor, who may refer you to an ear nose and throat specialist.
If you’ve developed a nodule, the specialist would likely refer you to a speech pathologist who will show you how to take care of your voice. Many nodules can be treated with voice therapy and don’t require surgery.
You may have also developed a habit of straining your vocal cords, if you forced yourself to speak or sing while they were inflamed. This can be a reason why some people continue to have a hoarse voice even when they’ve recovered from the cold.
In those cases, a speech pathologist may play a valuable role. They may teach you to exercises that make voicing more efficient. For example, lip trills (blowing raspberries) are a fun and easy way you can learn to relax the voice. This can help break the habit of straining your voice you may have developed during infection.
Yeptain Leung, Postdoctoral Research and Lecturer of Speech Pathology, School of Health Sciences, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Sweet Truth About Glycine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Make Your Collagen Work Better
This is Dr. James Nicolantonio. He’s a doctor of pharmacy, and a research scientist. He has a passion for evidence-based nutrition, and has written numerous books on the subject.
Controversy! Dr. DiNicolatonio’s work has included cardiovascular research, in which field he has made the case for increasing (rather than decreasing) the recommended amount of salt in our diet. This, of course, goes very much against the popular status quo.
We haven’t reviewed that research so we won’t comment on it here, but we thought it worth a mention as a point of interest. We’ll investigate his claims in that regard another time, though!
Today, however, we’ll be looking at his incisive, yet not controversial, work pertaining to collagen and glycine.
A quick recap on collagen
We’ve written about collagen before, and its importance for maintaining… Well, pretty much most of our body, really, buta deficiency in collagen can particularly weaken bones and joints.
On a more surface level, collagen’s also important for healthy elastic skin, and many people take it for that reason alone,
Since collagen is found only in animals, even collagen supplements are animal-based (often marine collagen or bovine collagen). However, if we don’t want to consume those, we can (like most animals) synthesize it ourselves from the relevant amino acids, which we can get from plants (and also laboratories, in some cases).
You can read our previous article about this, here:
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
What does he want us to know about collagen?
We’ll save time and space here: first, he’d like us to know the same as what we said in our article above
However, there is also more:
Let’s assume that your body has collagen to process. You either consumed it, or your body has synthesized it. We’ll skip describing the many steps of collagen synthesis, fascinating as that is, and get to the point:
When our body weaves together collagen fibrils out of the (triple-helical) collagen molecules…
- the cross-linking of the collagen requires lysyl oxidase
- the lysyl oxidase (which we make inside us) deanimates some other amino acids yielding aldehydes that allow the stable cross-links important for the high tensile strength of collagen, but to do that, it requires copper
- in order to use the copper it needs to be in its reduced cuprous form and that requires vitamin C
- but moving it around the body requires vitamin A
So in other words: if you are taking (or synthesizing) collagen, you also need copper and vitamins A and C.
However! Just to make things harder, if you take copper and vitamin C together, it’ll reduce the copper too soon in the wrong place.
Dr. DiNicolantonio therefore advises taking vitamin C after copper, with a 75 minutes gap between them.
What does he want us to know about glycine?
Glycine is one of the amino acids that makes up collagen. Specifically, it makes up every third amino acid in collagen, and even more specifically, it’s also the rate-limiting factor in the formation of glutathione, which is a potent endogenous (i.e., we make it inside us) antioxidant that works hard to fight inflammation inside the body.
What this means: if your joints are prone to inflammation, being glycine-deficient means a double-whammy of woe.
As well as being one of the amino acids most key to collagen production, glycine has another collagen-related role:
First, the problem: as we age, glycated collagen accumulates in the skin and cartilage (that’s bad; there is supposed to be collagen there, but not glycated).
More on glycation and what it is and why it is so bad:
Are You Eating Advanced Glycation End-Products? The Trouble Of The AGEs
Now, the solution: glycine suppresses advanced glycation end products, including the glycation of collagen.
See for example:
With these three important functions of glycine in mind…
Dr. DiNicolantonio therefore advises getting glycine at a dose of 100mg/kg/day. So, if you’re the same size as this rather medium-sized writer, that means 7.2g/day.
Where can I get it?
Glycine is found in many foods, including gelatin for those who eat that, eggs for the vegetarians, and spinach for vegans.
However, if you’d like to simply take it as a supplement, here’s an example product on Amazon
(the above product is not clear whether it’s animal-derived or not, so if that’s important to you, shop around. This writer got some locally that is certified vegan, but is in Europe rather than N. America, which won’t help most of our subscribers)
Note: pure glycine is a white crystalline powder that has the same sweetness as glucose. Indeed, that is how it got its name, from the Greek “γλυκύς”, pronounced /ɡly.kýs/, meaning “sweet”. Yes, same etymology as glucose.
So don’t worry that you’ve been conned if you order it and think “this is sugar!”; it just looks and tastes the same.
That does mean you should buy from a reputable source though, as a con would be very easy!
this does also mean that if you like a little sugar/sweetener in your tea or coffee, glycine can be used as a healthy substitute.
If you don’t like sweet tastes, then, condolences. This writer pours two espresso coffees (love this decaffeinated coffee that actually tastes good), puts the glycine in the first, and then uses the second to get rid of the sweet taste of the first. So that’s one way to do it.
Enjoy (if you can!)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: