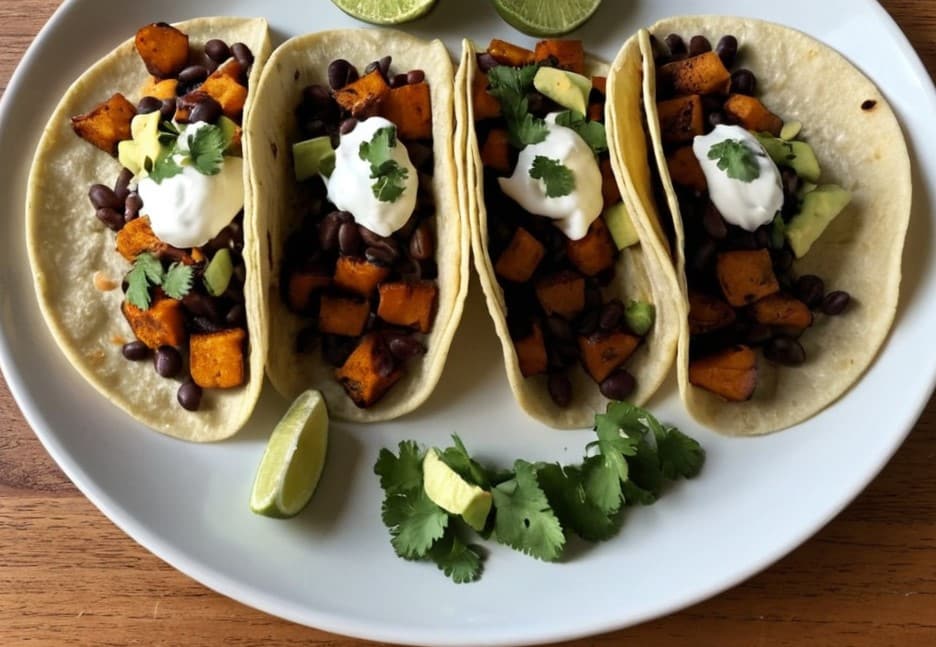
Without Medicare Part B’s Shield, Patient’s Family Owes $81,000 for a Single Air-Ambulance Flight
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Without Medicare Part B’s Shield, Patient’s Family Owes $81,000 for a Single Air-Ambulance Flight
Debra Prichard was a retired factory worker who was careful with her money, including what she spent on medical care, said her daughter, Alicia Wieberg. “She was the kind of person who didn’t go to the doctor for anything.”
That ended last year, when the rural Tennessee resident suffered a devastating stroke and several aneurysms. She twice was rushed from her local hospital to Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, 79 miles away, where she was treated by brain specialists. She died Oct. 31 at age 70.
One of Prichard’s trips to the Nashville hospital was via helicopter ambulance. Wieberg said she had heard such flights could be pricey, but she didn’t realize how extraordinary the charge would be — or how her mother’s skimping on Medicare coverage could leave the family on the hook.
Then the bill came.
The Patient: Debra Prichard, who had Medicare Part A insurance before she died.
Medical Service: An air-ambulance flight to Vanderbilt University Medical Center.
Service Provider: Med-Trans Corp., a medical transportation service that is part of Global Medical Response, an industry giant backed by private equity investors. The larger company operates in all 50 states and says it has a total of 498 helicopters and airplanes.
Total Bill: $81,739.40, none of which was covered by insurance.
What Gives: Sky-high bills from air-ambulance providers have sparked complaints and federal action in recent years.
For patients with private insurance coverage, the No Surprises Act, which went into effect in 2022, bars air-ambulance companies from billing people more than they would pay if the service were considered “in-network” with their health insurers. For patients with public coverage, such as Medicare or Medicaid, the government sets payment rates at much lower levels than the companies charge.
But Prichard had opted out of the portion of Medicare that covers ambulance services.
That meant when the bill arrived less than two weeks after her death, her estate was expected to pay the full air-ambulance fee of nearly $82,000. The main assets are 12 acres of land and her home in Decherd, Tennessee, where she lived for 48 years and raised two children. The bill for a single helicopter ride could eat up roughly a third of the estate’s value, said Wieberg, who is executor.
The family’s predicament stems from the complicated nature of Medicare coverage.
Prichard was enrolled only in Medicare Part A, which is free to most Americans 65 or older. That section of the federal insurance program covers inpatient care, and it paid most of her hospital bills, her daughter said.
But Prichard declined other Medicare coverage, including Part B, which handles such things as doctor visits, outpatient treatment, and ambulance rides. Her daughter suspects she skipped that coverage to avoid the premiums most recipients pay, which currently are about $175 a month.
Loren Adler, a health economist for the Brookings Institution who studies ambulance bills, estimated the maximum charge that Medicare would have allowed for Prichard’s flight would have been less than $10,000 if she’d signed up for Part B. The patient’s share of that would have been less than $2,000. Her estate might have owed nothing if she’d also purchased supplemental “Medigap” coverage, as many Medicare members do to cover things like coinsurance, he said.
Nicole Michel, a spokesperson for Global Medical Response, the ambulance provider, agreed with Adler’s estimate that Medicare would have limited the charge for the flight to less than $10,000. But she said the federal program’s payment rates don’t cover the cost of providing air-ambulance services.
“Our patient advocacy team is actively engaged with Ms. Wieberg’s attorney to determine if there was any other applicable medical coverage on the date of service that we could bill to,” Michel wrote in an email to KFF Health News. “If not, we are fully committed to working with Ms. Wieberg, as we do with all our patients, to find an equitable solution.”
The Resolution: In mid-February, Wieberg said the company had not offered to reduce the bill.
Wieberg said she and the attorney handling her mother’s estate both contacted the company, seeking a reduction in the bill. She said she also contacted Medicare officials, filled out a form on the No Surprises Act website, and filed a complaint with Tennessee regulators who oversee ambulance services. She said she was notified Feb. 12 that the company filed a legal claim against the estate for the entire amount.
Wieberg said other health care providers, including ground ambulance services and the Vanderbilt hospital, wound up waiving several thousand dollars in unpaid fees for services they provided to Prichard that are normally covered by Medicare Part B.
But as it stands, Prichard’s estate owes about $81,740 to the air-ambulance company.
More from Bill of the Month
- The Colonoscopies Were Free. But the ‘Surgical Trays’ Came With $600 Price Tags. Jan 25, 2024
- When a Quick Telehealth Visit Yields Multiple Surprises Beyond a Big Bill Dec 19, 2023
- Out for Blood? For Routine Lab Work, the Hospital Billed Her $2,400 Nov 21, 2023
The Takeaway: People who are eligible for Medicare are encouraged to sign up for Part B, unless they have private health insurance through an employer or spouse.
“If someone with Medicare finds that they are having difficulty paying the Medicare Part B premiums, there are resources available to help compare Medicare coverage choices and learn about options to help pay for Medicare costs,” Meena Seshamani, director of the federal Center for Medicare, said in an email to KFF Health News.
She noted that every state offers free counseling to help people navigate Medicare.
In Tennessee, that counseling is offered by the State Health Insurance Assistance Program. Its director, Lori Galbreath, told KFF Health News she wishes more seniors would discuss their health coverage options with trained counselors like hers.
“Every Medicare recipient’s experience is different,” she said. “We can look at their different situations and give them an unbiased view of what their next best steps could be.”
Counselors advise that many people with modest incomes enroll in a Medicare Savings Program, which can cover their Part B premiums. In 2023, Tennessee residents could qualify for such assistance if they made less than $1,660 monthly as a single person or $2,239 as a married couple. Many people also could obtain help with other out-of-pocket expenses, such as copays for medical services.
Wieberg, who lives in Missouri, has been preparing the family home for sale.
She said the struggle over her mother’s air-ambulance bill makes her wonder why Medicare is split into pieces, with free coverage for inpatient care under Part A, but premiums for coverage of other crucial services under Part B.
“Anybody past the age of 70 is likely going to need both,” she said. “And so why make it a decision of what you can afford or not afford, or what you think you’re going to use or not use?”
Bill of the Month is a crowdsourced investigation by KFF Health News and NPR that dissects and explains medical bills. Do you have an interesting medical bill you want to share with us? Tell us about it!
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healing Spices – by Dr. Bharat Aggarwal & Debora Yost
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is exactly what the subtitle promises it to be, and more. It’s actually herbs and spices, but definitely mostly spices, and includes the kinds found in even the smallest supermarket, to some you might not have heard of, and might need to order online.
We are treated to an explanation of the health-giving properties of each (and any potential contraindications), as well as the culinary properties, many tables of what goes with what and how and why, and even recipes to use them in. For the more adventurous, there’s even advice on how to grow, prepare, and store each of them.
An extra benefit is that everything is cross-linked such that you can look things up by spice or by health condition or by flavor profile, and find what you need and what’ll go with it.
The style is simple and informational, clearly laid-out in encyclopedic form.
Bottom line: this book should be in your kitchen (or related nearby kitchen-book-place).
Click here to check out Healing Spices, and advance your culinary repertoire!
Share This Post
-
Sweet Potato & Black Bean Tacos
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fiber, protein, and polyphenols! What more could one ask for? Well, great taste and warm healthy goodness, which these deliver:
You will need
For the sweet potatoes:
- 2 medium sweet potatoes, cubed (we recommend leaving the skin on, but you can peel them if you really want to)
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tsp garlic powder
- 2 tsp smoked paprika
- 1 tsp chili powder
- 1 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
For the black beans:
- 2 cans black beans, drained and rinsed (or 2 cups black beans that you cooked yourself)
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced
- 1 fresh jalapeño finely chopped (or ¼ cup jalapeños from a jar, finely chopped) ← adjust quantities per your preference and per the quality of the pepper(s) you’re using; we can’t judge that from here without tasting them, so we give a good basic starting suggestion.
- 2 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
For serving:
- 8 small corn tortillas, or your preference if substituting
- 1 avocado, pitted, peeled, cubed, and tossed in lime juice ← we’re mentioning this here because you want to do this as soon as you cut it, to avoid oxidation
- Any other salad you’d like to include; fresh parsley is also a good option when it comes to greenery, or cilantro if you don’t have the soap gene
- Tomato salsa (quantity and spice level per your preference)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400°F / 200°C.
2) Toss the sweet potato cubes in a large bowl with the rest of the ingredients from the sweet potato section above, ensuring they are evenly coated.
3) Bake them in the oven, on a baking tray lined with baking paper, for about 30 minutes or until tender inside and crispy at the edges. Turn them over halfway through.
4) While that’s happening, mix the black beans in a bowl with the other ingredients from the black bean section above, and heat them gently. You could do this in a saucepan, but honestly, while it’s not glamorous, the microwave is actually better for this. Note: many people find the microwave cooks food unevenly, but there are two reasons for this and they’re both easily fixable:
- instead of using high power for x minutes, use medium power for 2x minutes; this will produce better results
- instead of putting the food just in a bowl, jug, or similar, use a wide bowl or similar container, and then inside that, place a small empty microwave-safe glass jar or similar upturned in the middle, and then add the food around it, so that the food is arranged in a donut shape rather than a wide cylinder shape. This means there is no “middle bit” to go underheated while the edges are heated excessively; instead, it will heat through evenly.
If you really don’t want to do that though, use a saucepan on a very low heat, add a small amount of liquid (or tomato salsa), and stir constantly.
5) Heat the tortillas in a dry skillet for about 30 seconds each on each side, when ready to serve.
6) Assemble the tacos; you can do this how you like but a good order of operations is: tortilla, leafy salad (if using), potato, beans, non-leafy salad including avocado, salsa or other topping per your preference.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- White Potato vs Sweet Potato – Which is Healthier?
- Kidney Beans or Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
- Coconut vs Avocado – Which is Healthier?
- Glutathione: More Than An Antioxidant
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we hit 4/5 today!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Research Review: Collagen
For something that’s a very popular supplement, not many people understand what collagen is, where it comes from, or what it does.
In a nutshell:
Collagen is a kind of protein. Our bodies make it naturally, and we can also get more in our diet and/or take extra as a supplement.
Our bodies use collagen in connective tissue, skin, tendon, bone, and cartilage. It has many functions, but a broad description would be “holding things together”.
As we get older, our bodies produce less collagen. Signs of this include wrinkles, loss of skin hydration, and joint pain.
Quick test: pinch the skin on the middle of the back of one of your hands, and then watch what happens when you get low. How quickly and easily did your skin returns to its original shape?
If it was pretty much instantanous and flawless, congratulations, you have plenty of collagen (and also elastin). If you didn’t, you are probably low on both!
(they are quite similar proteins and are made from the same base “stuff”, so if you’re low on one, you’ll usually be low on both)
Quick note: A lot of research out there has been funded by beauty companies, so we had our work cut out for us today, and have highlighted where any research may be biased.
More than skin deep
While marketing for collagen is almost exclusively aimed at “reduce wrinkles and other signs of aging”, it does a lot more than that.
You remember we mentioned that many things from the bones outward are held together by collagen? We weren’t kidding…
Read: Osteoporosis, like skin ageing, is caused by collagen loss which is reversible
Taking extra collagen isn’t the only way
We can’t (yet!) completely halt the age-related loss of collagen, but we can slow it, with our lifestyle choices:
- Don’t smoke tobacco
- Drink only in moderation (or not at all)
- Avoid foods with added sugar, and high-processed foods in general
- Wear sunscreen when appropriate
Can I get collagen from food?
Yep! Just as collagen holds our bodies together, it holds the bodies of other animals together. And, just like collagen is found in most parts of our body but most plentifully in our skin and bones, that’s what to eat to get collagen from other animals, e.g:
- Chicken skin
- Fish skin
- Bone broth ← health benefits and recipes at this link!
What about vegans?
Yes, vegans are also held together by collagen! We do not, however, recommend eating their skin or boiling their bones into broth. Ethical considerations aside, cannibalism can give you CJD!
More seriously, if you’re vegan, you can’t get collagen from a plant-based diet, but you can get the stuff your body uses to make collagen. Basically, you want to make sure you get plenty of:
- Protein (beans, pulses, nuts, etc are all fine; it’s hard to go wrong with this)
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- and Zinc
Just be sure to continue to remember to avoid highly-processed foods. So:
- Soy mince/chunks whose ingredients list reads: “soya”? Yes!
- The Incredible Burger or Linda McCartney’s Sausages? Sadly less healthy
Read: Advanced Glycation End Products in Foods and a Practical Guide to Their Reduction in the Diet
Meat-eaters might want to read that one too. By far the worst offenders for AGEs (Advanced Glycation End Products, which can not only cause collagen to stiffen, but also inactivate proteins responsible for collagen repair, along with doing much more serious damage to your body’s natural functions) include:
- Hot dogs
- Bacon
- Fried/roasted/grilled meats
Is it worth it as a supplement?
That depends on you, your age, and your lifestyle, but it’s generally considered safe*
*if you have a seafood allergy, be careful though, as many supplements are from fish or shellfish—you will need to find one that’s free from your allergen
Also, all collagen is animal-derived. So if you’re a vegan, decide for yourself whether this constitutes medicine and if so, whether that makes it ethically permissible to you.
With that out of the way:
What the science says on collagen supplementation
Collagen for skin
Read: Effects of collagen supplementation on skin aging (systematic review and meta-analysis)
The short version is that they selected 19 studies with over a thousand participants in total, and they found:
In the meta-analysis, a grouped analysis of studies showed favorable results of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation compared with placebo in terms of skin hydration, elasticity, and wrinkles.
The findings of improved hydration and elasticity were also confirmed in the subgroup meta-analysis.
Based on results, ingestion of hydrolyzed collagen for 90 days is effective in reducing skin aging, as it reduces wrinkles and improves skin elasticity and hydration.
Caveat: while that systematic review had no conflicts of interests, at least some of the 19 studies will have been funded by beauty companies. Here are two, so that you know what that looks like:
Funded by Quiris to investigate their own supplement, Elasten®:
A Collagen Supplement Improves Skin Hydration, Elasticity, Roughness, and Density
Funded by BioCell to investigate their own supplement, BioCell Collagen:
The Effects of Skin Aging Associated with the Use of BioCell Collagen
A note on funding bias: to be clear, the issue is not that the researchers might be corrupt (though that could happen).
The issue is more that sometimes companies will hire ten labs to do ten research studies… and then pull funding from ones whose results aren’t going the way they’d like.
So the “best” (for them) study is the one that gets published.
Here’s another systematic review—like the one at the top of this section—that found the same, with doses ranging from 2.5g–15g per day for 8 weeks or longer:
Read: Oral Collagen Supplementation: A Systematic Review of Dermatological Applications
Again, some of those studies will have been funded by beauty companies. The general weight of evidence does seem clear and favorable, though.
Collagen for bones
Here, we encountered a lot less in the way of potential bias, because this is simply marketed a lot less. Despite being arguably far more important!
We found a high quality multi-vector randomized controlled study with a sample size of 131 postmenopausal women. They had these women take 5g collagen supplement (or placebo), and studied the results over the course of a year.
They found:
- The intake of the supplement increased bone mineral density (BMD)
- Supplementation was also associated with a favorable shift in bone markers, indicating:
- increased bone formation
- reduced bone degradation
Read: Specific Collagen Peptides Improve Bone Mineral Density and Bone Markers in Postmenopausal Wome
A follow-up study with 31 of these women found that taking 5 grams of collagen daily for a total of 4 years was associated with a progressive increase in BMD.
You might be wondering if collagen also helps against osteoarthritis.
The answer is: yes, it does (at least, it significantly reduces the symptoms)
Read: Effect of collagen supplementation on osteoarthritis symptoms
In summary:
- You need collagen for health skin, bones, joints, and more
- Your body makes collagen from your food
- You can help it by getting plenty of protein, vitamins, and minerals
- You can also help it by not doing the usual Bad Things™ (smoking, drinking, eating processed foods, especially processed meats)
- You can also eat collagen directly in the form of other animals’ skin and bones
- You can also buy collagen supplements (but watch out for allergens)
Want to try collagen supplementation?
We don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience…
Check it out: Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides (the same as in most of the above studies), 90 days supply at 5g/day
We selected this one because it’s the same kind used in many of the studies, and it doesn’t contain any known allergens.
It’s bovine collagen, meaning it’s from cows, so it’s not vegan, and also some subscribers may want to abstain for religious reasons. We respect that, and/but make our recommendations based solely on the science of health and productivity.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Ginkgo Biloba, For Memory And, Uh, What Else Again?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ginkgo biloba, for memory and, uh, what else again?
Ginkgo biloba extract has enjoyed use for thousands of years for an assortment of uses, and has made its way from Traditional Chinese Medicine, to the world supplement market at large. See:
Ginkgo biloba: A Treasure of Functional Phytochemicals with Multimedicinal Applications
But what does the science say about the specific claims?
Antioxidant & anti-inflammatory
We’re going to lump these two qualities together for examination, since one invariably leads to the other.
A quick note: things that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, often also help guard against cancer and aging. However, in this case, there are few good studies pertaining to anti-aging, and none that we could find pertaining to anti-cancer potential.
So, does it have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, first?
Yes, it has potent antioxidants that do fight inflammation; this is clear, from an abundance of in vitro and in vivo studies, including with human patients:
- Properties of Ginkgo biloba L.: incl. Antioxidant Characterization
- Anti-inflammatory effects of Ginkgo biloba extract against hippocampal neuronal injury
- Gingko biloba-derived lactone prevents osteoarthritis by activating anti-inflammatory signaling pathway
- The anti-inflammatory properties of Ginkgo biloba for the treatment of pulmonary diseases
In short: it helps, and there’s plenty of science for it.
What about anti-aging effects?
For this, there is science, but a lot of the science is not great. As one team of researchers concluded while doing a research review of their own:
❝Based on the reviewed information regarding EGb’s effects in vitro and in vivo, most have reported very positive outcomes with strong statistical analyses, indicating that EGb must have some sort of beneficial effect.
However, information from the reported clinical trials involving EGb are hardly conclusive since many do not include information such as the participant’s age and physical condition, drug doses administered, duration of drug administered as well as suitable control groups for comparison.
We therefore call on clinicians and clinician-scientists to establish a set of standard and reliable standard operating procedure for future clinical studies to properly evaluate EGb’s effects in the healthy and diseased person since it is highly possible it possesses beneficial effects.❞
Translation from sciencese: “These results are great, but come on, please, we are begging you to use more robust methodology”
If you’d like to read the review in question, here it is:
Advances in the Studies of Ginkgo Biloba Leaves Extract on Aging-Related Diseases
Does it have cognitive enhancement effects?
The claims here are generally that it helps:
- improve memory
- improve focus
- reduce cognitive decline
- reduce anxiety and depression
Let’s break these down:
Does it improve memory and cognition?
Ginkgo biloba was quite popular for memory 20+ years ago, and perhaps had an uptick in popularity in the wake of the 1999 movie “Analyze This” in which the protagonist psychiatrist mentions taking ginkgo biloba, because “it helps my memory, and I forget what else”.
Here are a couple of studies from not long after that:
- A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of Ginkgo biloba in cognitively intact older adults: neuropsychological findings
- Effects of Ginkgo biloba on mental functioning in healthy volunteers
In short:
- in the first study, it helped in standardized tests of memory and cognition (quite convincing)
- In the second study, it helped in subjective self-reports of mental wellness (also placebo-controlled)
On the other hand, here’s a more recent research review ten years later, that provides measures of memory, executive function and attention in 1132, 534 and 910 participants, respectively. That’s quite a few times more than the individual studies we cited above, by the way. They concluded:
❝We report that G. biloba had no ascertainable positive effects on a range of targeted cognitive functions in healthy individuals❞
Read: Is Ginkgo biloba a cognitive enhancer in healthy individuals? A meta-analysis
Our (10almonds) conclusion: we can’t say either way, on this one.
Does it have neuroprotective effects (i.e., against cognitive decline)?
Yes—probably by the same mechanism will discuss shortly.
- Ginkgo Biloba for Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Treatment effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on symptoms of dementia: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Can it help against depression and anxiety?
Yes—but probably indirectly by the mechanism we’ll get to in a moment:
- Role of Ginkgo biloba extract as an adjunctive treatment of elderly patients with depression
- Ginkgo biloba in generalized anxiety disorder and adjustment disorder with anxious mood
Likely this helps by improving blood flow, as illustrated better per:
Efficacy of ginkgo biloba extract as augmentation of venlafaxine in treating post-stroke depression
Which means…
Bonus: improved blood flow
This mechanism may support the other beneficial effects.
See: Ginkgo biloba extract improves coronary blood flow in healthy elderly adults
Is it safe?
Ginkgo biloba extract* is generally recognized as safe.
- However, as it improves blood flow, please don’t take it if you have a bleeding disorder.
- Additionally, it may interact badly with SSRIs, so you might want to avoid it if you’re taking such (despite it having been tested and found beneficial as an adjuvant to citalopram, an SSRI, in one of the studies above).
- No list of possible contraindications can be exhaustive, so please consult your own doctor/pharmacist before taking something new.
*Extract, specifically. The seeds and leaves of this plant are poisonous. Sometimes “all natural” is not better.
Where can I get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else), but here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Circadian Rhythm: Far More Than Most People Know
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Circadian Rhythm: Far More Than Most People Know
This is Dr. Satchidananda (Satchin) Panda, the scientist behind the discovery of the blue-light sensing cell type in the retina, and the many things it affects. But, he’s discovered more…
First, what you probably know (with a little more science)
Dr. Panda discovered that melanopsin, a photopigment, is “the primary candidate for photoreceptor-mediated entrainment”.
To put that in lay terms, it’s the brain’s go-to for knowing approximately what time of day or night it is, according to how much light there is (or isn’t), and how long it has (or hasn’t) been there.
But… the brain’s “go-to” isn’t the only method. By creating mice without melanopsin, he was able to find that they still keep a circadian rhythm, even in complete darkness:
Melanopsin (Opn4) Requirement for Normal Light-Induced Circadian Phase Shifting
In other words, it was a helpful, but not completely necessary, means of keeping a circadian rhythm.
So… What else is going on?
Dr. Panda and his team did a lot of science that is well beyond the scope of this main feature, but to give you an idea:
- With jargon: it explored the mechanisms and transcription translation negative feedback loops that regulate chronobiological processes, such as a histone lysine demathlyase 1a (JARID1a) that enhances Clock-Bmal1 transcription, and then used assorted genomic techniques to develop a model for how JARID1a works to moderate the level of Per transcription by regulating the transition between its repression and activation, and discovered that this heavily centered on hepatic gluconeogenesis and glucose homeostasis, facilitated by the protein cryptochrome regulating the fasting signal that occurs when glucagon binds to a G-protein coupled receptor, triggering CREB activation.
- Without jargon: a special protein tells our body how to respond to eating/fasting at different times of day—and conversely, certain physiological responses triggered by eating/fasting help us know what time of day it is.
- Simplest: our body keeps on its best cycle if we eat at the same time every day
This is important, because our circadian rhythm matters for a lot more than sleeping/waking! Take hormones, for example:
- Obvious hormones: testosterone and estrogen peak in the mornings around 9am, progesterone peaks between 10pm and 2am
- Forgotten hormones: cortisol peaks in the morning around 8:30am, melatonin peaks between 10pm and 2am
- More hormones: ghrelin (hunger hormone) peaks around 10am, leptin (satiety hormone) peaks 20 minutes after eating a certain amount of satiety-triggering food (protein does this most quickly), insulin is heavily tied to carbohydrate intake, but will still peak and trough according to when the body expects food.
What does this mean for us in practical terms?
For a start, it means that intermittent fasting can help guard against metabolic and related diseases (including inflammation, and thus also cancer, diabetes, arthritis, and more) a lot more if we practice it with our circadian rhythm in mind.
So that “8-hour window” for eating, that many intermittent fasting practitioners adhere to, is going to do much, much better if it’s 10am to 6pm, rather than, say, 4pm to midnight.
Additionally, Dr. Panda and his team found that a 12-hour eating window wasn’t sufficient to help significantly.
Some other take-aways:
- For reasons beyond the scope of this article, it’s good to exercise a) early b) before eating, so getting in some exercise between 8.30am and 10am is ideal
- It also means it’s beneficial to “front-load” eating, so a large breakfast at 10am, and smaller meals/snacks afterwards, is best.
- It also means that getting sunlight (even if cloud-covered) around 8.30am helps guard against metabolic disorders a lot, since the light remains the body’s go-to way of knowing the time.
- We realize that sunlight is not available at 8.30am at all latitudes at all times of year. Artificial is next-best.
- It also means sexual desire will typically peak in men in the mornings (per testosterone) and women in the evenings (per progesterone), but this is just an interesting bit of trivia, and not so relevant to metabolic health
What to do next…
Want to stabilize your own circadian rhythm in the best way, and also help Dr. Panda with his research?
His team’s (free!) app, “My Circadian Clock”, can help you track and organize all of the body’s measurable-by-you circadian events, and, if you give permission, will contribute to what will be the largest-yet human study into the topics covered today, to refine the conclusions and learn more about what works best.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
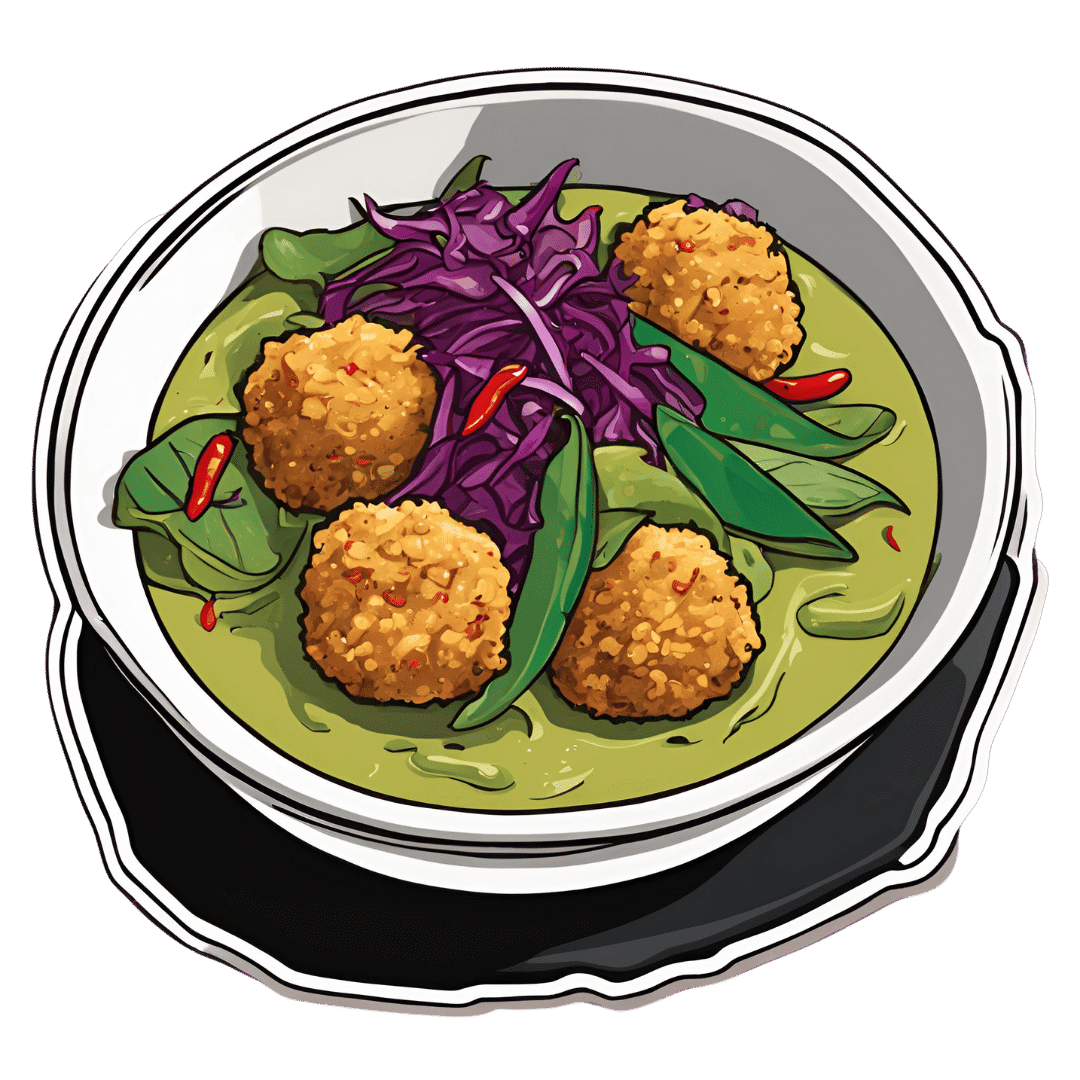
Thai Green Curry With Crispy Tofu Balls
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Diversity is key here, with a wide range of mostly plants, offering an even wider range of phytochemical benefits:
You will need
- 7 oz firm tofu
- 1 oz cashew nuts (don’t soak them)
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp turmeric
- 4 scallions, sliced
- 7 oz mangetout
- 7 oz fermented red cabbage (i.e., from a jar)
- 1 cup coconut milk
- Juice of ½ lime
- 2 tsp light soy sauce
- 1 handful fresh cilantro, or if you have the “cilantro tastes like soap” gene, then parsley
- 1 handful fresh basil
- 1 green chili, chopped (multiply per heat preference)
- 1″ piece fresh ginger, roughly chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic, crushed
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Avocado oil for frying
- Recommended, to serve: lime wedges
- Recommended, to serve: your carbohydrate of choice, such as soba noodles or perhaps our Tasty Versatile Rice.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat the oven to 350℉ / 180℃, and bake the cashews on a baking tray for about 8 minutes until lightly toasted. Remove from the oven and allow to cool a little.
2) Combine the nuts, tofu, nutritional yeast, turmeric, and scallions in a food processor, and process until the ingredients begin to clump together. Shape into about 20 small balls.
3) Heat some oil in a skillet and fry the tofu balls, jiggling frequently to get all sides; it should take about 5 minutes to see them lightly browned. Set aside.
4) Combine the coconut milk, lime juice, soy sauce, cilantro/parsley, basil, scallions, green chili, ginger, garlic, and MSG/salt in a high-speed blender, and blend until a smooth liquid.
5) Transfer the liquid to a saucepan, and bring to the boil. Reduce the heat, add the mangetout, and simmer for about 5 minutes to reduce slightly. Stir in the red chili flakes and black pepper.
6) Serve with your preferred carbohydrate, adding the fermented red cabbage and the crispy tofu balls you set aside, along with any garnish you might like to add.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
- Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- What’s Your Plant Diversity Score? ← a score of 8.25 for this dish, not counting whatever carbs you might add. Remember, herbs/spices* count for ¼ of a point each!
*but not MSG or salt, as while they may in culinary terms get lumped in with spices, they are of course not plants. Nor is nutritional yeast (nor any other yeast, for that matter). However, mushrooms (not seen in this recipe, though to be honest they would be a respectable addition) would get included for a whole point per mushroom type, since while they are not technically plants but fungi, the nutritional profile is plantlike.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: