The Sun Exposure Dilemma
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Sun Exposure Dilemma
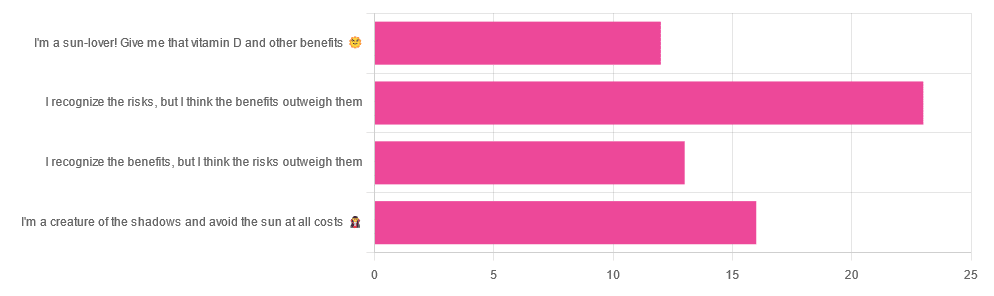
Yesterday, we asked you about your policy on sun exposure, and got the above-pictured, below-described, set of answers:
- A little over a third of respondents chose “I recognize the risks, but I think the benefits outweigh them”
- A quarter of respondents chose “I am a creature of the shadows and I avoid the sun at all costs”
- A little over a fifth of respondents chose “I recognize the benefits, but I think the risks outweigh them”
- A little under a fifth of respondents chose “I’m a sun-lover! Give me that vitamin D and other benefits!”
All in all, this is perhaps the most even spread of answers we’ve had for Friday mythbuster polls—though the sample size was smaller than it often is.
Of those who added comments, common themes were to mention your local climate, and the importance of sunscreen and/or taking vitamin D supplements.
One subscriber mentioned having lupus and living in Florida, which is a particularly unfortunate combination:
Lupus Foundation | Lupus & UV exposure: What you need to know
Another subscriber wrote:
❝Use a very good sunscreen with a high SPF all the time. Reapply after swimming or as needed! I also wear polarized sunglasses anytime I’m outside.❞
…which are important things to note too, and a lot of people forget!
See also: Who Screens The Sunscreens? (on fearing chemical dangers, vs the protection given)
But, onto today’s science for the topic at hand…
We need to get plenty of sun to get plenty of vitamin D: True or False?
True or False, depending on so many factors—to the point that many people get it wildly wrong in either direction.
Whether we are getting enough vitamin D depends on many circumstances, including:
- The climate (and depending on latitude, time of year) where we live
- Our genes, and especially (but not only) our skintone
- The clothes we wear (or don’t)
- Our diet (and not just “how much vitamin D do we consume”)
- Chronic diseases that affect vitamin D metabolism and/or requirements and/or sensitivity to the sun
For a rundown on these factors and more, check out:
Should I be getting my vitamin D levels checked?
Notably, on the topic of whether you should stay in the sun for longer to get more vitamin D…
❝The body can only produce a certain amount of vitamin D at the time, so staying in the sun any longer than needed (which could be just a few minutes, in a sunny climate) is not going to help increase your vitamin D levels, while it will increase your risk of skin cancer.❞
In contrast, she does also note:
❝During winter, catching enough sun can be difficult, especially if you spend your days confined indoors. Typically, the required exposure increases to two to three hours per week in winter. This is because sunlight exposure can only help produce vitamin D if the UVB rays reach us at the correct angle. So in winter we should regularly spend time outside in the middle of the day to get our dose of vitamin D.❞
See also: Vitamin D & Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
We can skip the sun and get our vitamin D from diet/supplements: True or False?
True! However, vitamin D is not the only health benefit of sun exposure.
Not only is sunlight-induced serotonin production important for many things ranging from mood to circadian rhythm (which in turn affects many other aspects of health), but also…
While too much sun can cause skin cancer, too little sun could cause other kinds of cancer:
Benefits of Sunlight: A Bright Spot for Human Health
Additionally, according to new research, the circadian rhythm benefits we mentioned above may also have an impact on type 2 diabetes:
Can catching some rays help you fight off type 2 diabetes?
Which way to jump?
A lot of it depends on who you are, ranging from the factors we mentioned earlier, to even such things as “having many moles” or “having blonde hair”.
This latter item, blonde hair, is a dual thing: it’s a matter of genetic factors that align with being prone to being more sensitive to the sun, as well as being a lesser physical barrier to the sun’s rays than dark hair (that can block some UV rays).
So for example, if two people have comparably gray hair now, but one of them used to have dark hair and the other blonde, there will still be a difference in how they suffer damage, or don’t—and yes, even if their skin is visually of the same approximate skintone.
You probably already know for yourself whether you are more likely to burn or tan in the sun, and the former group are less resistant to the sun’s damage… But the latter group are more likely to spend longer in the sun, and accumulate more damage that way.
If you’d like a very comprehensive downloadable, here are the guidelines issued by the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence:
NICE Guidelines | Sunlight exposure: risks and benefits
…and skip to “At risk groups”, if you don’t want to read the whole thing; “Skin type” is also an important subsection, which also uses your hair and eye color as indicators.
Writer’s note: genetics are complicated and not everyone will fall neatly into categories, which is why it’s important to know the individual factors.
For example, I am quite light-skinned with slightly graying dark hair and gray-blue eyes, and/but also have an obscure Sámi gene that means my skin makes vitamin D easily, while simultaneously being unusually resistant to burning (I just tan). Basically: built for the midnight sun of the Arctic circle.
And yet! My hobbies include not getting skin cancer, so I tend to still be quite mindful of UV levels in different weathers and times of day, and make choices (schedule, clothing, sunscreen or not) accordingly.
Bottom line:
That big self-perpetuating nuclear explosion in the sky is responsible for many things, good and bad for our health, so be aware of your own risk factors, especially for vitamin D deficiency, and skin cancer.
- If you have a predisposition to both, that’s unfortunate, but diet and supplementation at least can help with the vitamin D while getting modest amounts of sun at most.
- Remember that you can only make so much vitamin D at once, so sunbathing for health benefits need only take a few minutes
- Remember that sunlight is important for our circadian rhythm, which is important for many things.
- That’s governed by specific photoreceptor cells, though, so we don’t need our skin to be exposed for that; we just need to be able to see sunlight.
- If you’re going to be out in the sun, and not covered up, sunscreen is your friend, and yes, that goes for clear cold days under the winter sun too.
- Most phone weather apps these days have a UV index score as part of the data they give. Get used to checking it as often as you’d check for rain.
Stay safe, both ways around!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What To Leave Off Your Table (To Stay Off This Surgeon’s)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Why we eat too much (and how we can fix that)
This is Dr. Andrew Jenkinson. He’s a Consultant Surgeon specializing in the treatment of obesity, gallstones, hernias, heartburn and abdominal pain. He runs regular clinics in both London and Dubai. What he has to offer us today, though, is insight as to what’s on our table that puts us on his table, and how we can quite easily change that up.
So, why do we eat too much?
First things first: some metabolic calculations. No, we’re not going to require you to grab a calculator here… Your body does it for you!
Our body’s amazing homeostatic system (the system that does its best to keep us in the “Goldilocks Zone” of all our bodily systems; not too hot or too cold, not dehydrated or overhydrated, not hyperglycemic or hypoglycemic, blood pressure not too high or too low, etc, etc) keeps track of our metabolic input and output.
What this means: if we increase or decrease our caloric consumption, our body will do its best to increase or decrease our metabolism accordingly:
- If we don’t give it enough energy, it will try to conserve energy (first by slowing our activities; eventually by shutting down organs in a last-ditch attempt to save the rest of us)
- If we give it too much energy, it will try to burn it off, and what it can’t burn, it will store
In short: if we eat 10% or 20% more or less than usual, our body will try to use 10% to 20% more or less than usual, accordingly.
So… How does this get out of balance?
The problem is in how our system does that, and how we inadvertently trick it, to our detriment.
For a system to function, it needs at its most base level two things—a sensor and a switch:
- A sensor: to know what’s going on
- A switch: to change what it’s doing accordingly
Now, if we eat the way we’re evolved to—as hunter-gatherers, eating mostly fruit and vegetables, supplemented by animal products when we can get them—then our body knows exactly what it’s eating, and how to respond accordingly.
Furthermore, that kind of food takes some eating! Most fruit these days is mostly water and fiber; in those days it often had denser fiber (before agricultural science made things easier to eat), but either way, our body knows when we are eating fruit and how to handle that. Vegetables, similarly. Unprocessed animal products, again, the gut goes “we know what this is” and responds accordingly.
But modern ultra-processed foods with trans-fatty acids, processed sugar and flour?
These foods zip calories straight into our bloodstream like greased lightning. We get them so quickly so easily and in such great caloric density, that our body doesn’t have the chance to count them on the way in!
What this means is: the body has no idea what it’s just consumed or how much or what to do with it, and doesn’t adjust our metabolism accordingly.
Bottom line:
Evolutionarily speaking, your body has no idea what ultra-processed food is. If you skip it and go for whole foods, you can, within the bounds of reason, eat what you like and your body will handle it by adjusting your metabolism accordingly.
Now, advising you “avoid ultra-processed foods and eat whole foods” was probably not a revelation in and of itself.
But: sometimes knowing a little more about the “why” makes the difference when it comes to motivation.
Want to know more about Dr. Jenkinson’s expert insights on this topic?
If you like, you can check out his website here—he has a book too
Why We Eat (Too Much) – Dr. Andrew Jenkinson on the Science of Appetite
Share This Post
-
Why Telomeres Shorten, & What Can Be Done About It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Telomeres are protective caps at the ends of our DNA, similar to the plastic tips on shoelaces (there’s a repeated “junk DNA” string, TTAGGG in humans, kept safe in a sheathe, which made of shelterin, a protein complex).
They prevent our genetic material from becoming damaged or tangled. However, each time a cell divides, telomeres get a little shorter because the copying process isn’t perfect (DNA polymerase can’t replicate everything inside the sheathe, because it is too well-protected).
So, how do we deal with this?
Lacing up for long life
An enzyme called telomerase (discovered as recently as 2009 by Nobel Prize-winning scientists Dr. Elizabeth Blackburn et al.) can rebuild telomeres. It has two main parts: one part1 that makes new DNA and another part2 that acts as a guide. Most cells don’t produce enough telomerase, so telomeres still tend to shrink over time.
1 TERT (Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase), which synthesizes telomeric DNA
2 TERC (Telomerase RNA Component), which serves as a templateWhen telomeres become too short, cells stop dividing. Some cells may enter a damaged state (e.g. senescent “zombie” cells) or die. In some cases, cells bypass this limit by reactivating telomerase, which can lead to cancer.
Studies on mice show that when telomerase is missing, they age more quickly and struggle to repair tissues. When telomerase is restored, aging effects are reversed. Human research also links short telomeres to age-related diseases like immune system decline and organ damage.
Researchers have already found some ways to slow aging by:
- Activating telomerase (e.g. with small molecules like TA-65).
- Gene therapy to transiently express telomerase.
- Stabilizing TERC RNA component to prevent degradation.
However, increasing telomerase too much could raise the risk of cancer. So, it’s a bit of a juggling act yet.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Fisetin: The Anti-Aging Assassin ← kills senescent cells, meaning newer cells are copied rather than older ones, resulting in copied cells with less DNA damage
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Undo It! – by Dr. Dean Ornish & Anne Ornish
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Of course, no lifestyle changes will magically undo Type 1 Diabetes or Cerebral Palsy. But for many chronic diseases, a lot can be done. The question is,how does one book cover them all?
As authors Dr. Dean Ornish and Anne Ornish explain, very many chronic diseases are exacerbated, or outright caused, by the same factors:
- Gene expression
- Inflammation
- Oxidative stress
This goes for chronic disease from heart disease to type 2 diabetes to cancer and many autoimmune diseases.
We cannot change our genes, but we can change our gene expression (the authors explain how). And certainly, we can control inflammation and oxidative stress.
Then first part of the book is given over to dietary considerations. If you’re a regular 10almonds reader, you won’t be too surprised at their recommendations, but you may enjoy the 70 recipes offered.
Attention is also given to exercising in ways optimized to beat chronic disease, and to other lifestyle factors.
Limiting stress is important, but the authors go further when it comes to psychological and sociological factors. Specifically, what matters most to health, when it comes to intimacy and community.
Bottom line: this is a very good guide to a comprehensive lifestyle overhaul, especially if something recently has given you cause to think “oh wow, I should really do more to avoid xyz disease”.
Click here to check out Undo It, and better yet, prevent it in advance!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How Much Does A Vegan Diet Affect Biological Aging?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Slow Your Aging, One Meal At A Time
This one’s a straightforward one today, and the ““life hack” can be summed up:
Enjoy a vegan diet to enjoy younger biological age.
First, what is biological age?
Biological age is not one number, but a collection of numbers, as per different biomarkers of aging, including:
- Visual markers of aging (e.g. wrinkles, graying hair)
- Performative markers of aging (e.g. mobility tests)
- Internal functional markers of aging (e.g. tests for cognitive decline, eyesight, hearing, etc)
- Cellular markers of aging (e.g. telomere length)
We wrote more about this here:
Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
A vegan diet may well impact multiple of those categories of aging, but today we’re highlighting a study (hot off the press; published only a few days ago!) that looks at its effect on that last category: cellular markers of aging.
There’s an interesting paradox here, because this category is:
- the most easily ignorable; because we all feel it if our knees are giving out or our skin is losing elasticity, but who notices if telomeres’ T/S ratio changed by 0.0407? ← the researchers, that’s who, as this difference is very significant
- the most far-reaching in its impact, because cellular aging in turn has an effect on all the other markers of aging
Second, how much difference does it make, and how do we know?
The study was an eight-week interventional identical twin study. This means several things, to start with:
- Eight weeks is a rather short period of time to accumulate cellular aging, let alone for an intervention to accumulate a significant difference in cellular aging—but it did. So, just imagine what difference it might make in a year or ten!
- Doing an interventional study with identical twin pairs already controlled for a lot of factors, that are usually confounding variables in population / cohort / longitudinal / observational studies.
Factors that weren’t controlled for by default by using identical twins, were controlled for in the experiment design. For example, twin pairs were rejected if one or more twin in a given pair already had medical conditions that could affect the outcome:
❝Inclusion criteria involved participants aged ≥18, part of a willing twin pair, with BMI <40, and LDL-C <190 mg/dL. Exclusions included uncontrolled hypertension, metabolic disease, diabetes, cancer, heart/renal/liver disease, pregnancy, lactation, and medication use affecting body weight or energy.
Eligibility was determined via online screening, followed by an orientation meeting and in-person clinic visit. Randomization occurred only after completing baseline visits, dietary recalls, and questionnaires for both twins❞
~ Dr. Varun Dwaraka et al. ← there’s a lot of “et al.” to this one; the paper had 16 collaborating authors!
As to the difference it made over the course of the 8 weeks…
❝Various measures of epigenetic age acceleration (PC GrimAge, PC PhenoAge, DunedinPACE) were assessed, along with system-specific effects (Inflammation, Heart, Hormone, Liver, and Metabolic).
Distinct responses were observed, with the vegan cohort exhibiting significant decreases in overall epigenetic age acceleration, aligning with anti-aging effects of plant-based diets. Diet-specific shifts were noted in the analysis of methylation surrogates, demonstrating the influence of diet on complex trait prediction through DNA methylation markers.❞
~ Ibid.
You can read the whole paper here (it goes into a lot more detail than we have room to here, and also gives infographics, charts, numbers, the works):
Were they just eating more healthily, though?
Well, arguably yes, as the results show, but to be clear:
The omnivorous diet compared to the vegan diet in this study was also controlled; both groups were given a healthy meal plan for their respective diet. So this wasn’t a case of “any omnivorous diet vs healthy vegan diet”, but rather “healthy omnivorous diet vs healthy vegan diet”.
Again, the paper itself has the full details—a short version is that it involved a healthy meal kit delivery service, followed by ongoing dietician involvement in an equal and carefully-controlled fashion.
So, aside from that one group had an omnivorous meal plan and the other vegan, both groups received the same level of “healthy eating” support, guidance, and oversight.
But isn’t [insert your preferred animal product here] healthy?
Quite possibly! For general health, general scientific consensus is that eating at least mostly plants is best, red meat is bad, poultry is neutral in moderation, fish is good in moderation, dairy is good in moderation if fermented, eggs are good in moderation if not fried.
This study looked at the various biomarkers of aging that we listed, and not every possible aspect of health—there’s more science yet to be done, and the researchers themselves are calling for it.
It also bears mentioning that for some (relatively few, but not insignificantly few) people, extant health conditions may make a vegan diet unhealthy or otherwise untenable. Do speak with your own doctor and/or dietician if unsure.
See also: Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy?
We would hypothesize, by the way, that the anti-aging benefits of a vegan diet are probably proportional to abstention from animal products—meaning that even if you simply have some “vegan days”, while still consuming animal products other days, you’ll still get benefit for the days you abstained. That’s just our hypothesis though.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
As Nuns Disappear, Many Catholic Hospitals Look More Like Megacorporations
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ST. LOUIS — Inside the more than 600 Catholic hospitals across the country, not a single nun can be found occupying a chief executive suite, according to the Catholic Health Association.
Nuns founded and led those hospitals in a mission to treat sick and poor people, but some were also shrewd business leaders. Sister Irene Kraus, a former chief executive of Daughters of Charity National Health System, was famous for coining the phrase “no margin, no mission.” It means hospitals must succeed — generating enough revenue to exceed expenses — to fulfill their original mission.
The Catholic Church still governs the care that can be delivered to millions in those hospitals each year, using religious directives to ban abortions and limit contraceptives, in vitro fertilization, and medical aid in dying.
But over time, that focus on margins led the hospitals to transform into behemoths that operate for-profit subsidiaries and pay their executives millions, according to hospital tax filings. These institutions, some of which are for-profit companies, now look more like other megacorporations than like the charities for the destitute of yesteryear.
The absence of nuns in the top roles raises the question, said M. Therese Lysaught, a Catholic moral theologist and professor at Loyola University Chicago: “What does it mean to be a Catholic hospital when the enterprise has been so deeply commodified?”
The St. Louis area serves as the de facto capital of Catholic hospital systems. Three of the largest are headquartered here, along with the Catholic hospital lobbying arm. Catholicism is deeply rooted in the region’s culture. During Pope John Paul II’s only U.S. stop in 1999, he led Mass downtown in a packed stadium of more than 100,000 people.
For a quarter century, Sister Mary Jean Ryan led SSM Health, one of those giant systems centered on St. Louis. Now retired, the 86-year-old said she was one of the last nuns in the nation to lead a Catholic hospital system.
Ryan grew up Catholic in Wisconsin and joined a convent while in nursing school in the 1960s, surprising her family. She admired the nuns she worked alongside and felt they were living out a higher purpose.
“They were very impressive,” she said. “Not that I necessarily liked all of them.”
Indeed, the nuns running hospitals defied the simplistic image often ascribed to them, wrote John Fialka in his book “Sisters: Catholic Nuns and the Making of America.”
“Their contributions to American culture are not small,” he wrote. “Ambitious women who had the skills and the stamina to build and run large institutions found the convent to be the first and, for a long time, the only outlet for their talents.”
This was certainly true for Ryan, who climbed the ranks, working her way from nurse to chief executive of SSM Health, which today has hospitals in Illinois, Missouri, Oklahoma, and Wisconsin.
The system was founded more than a century ago when five German nuns arrived in St. Louis with $5. Smallpox swept through the city and the Sisters of St. Mary walked the streets offering free care to the sick.
Their early foray grew into one of the largest Catholic health systems in the country, with annual revenue exceeding $10 billion, according to its 2023 audited financial report. SSM Health treats patients in 23 hospitals and co-owns a for-profit pharmacy benefit manager, Navitus, that coordinates prescriptions for 14 million people.
But Ryan, like many nuns in leadership roles in recent decades, found herself confronted with an existential crisis. As fewer women became nuns, she had to ensure the system’s future without them.
When Ron Levy, who is Jewish, started at SSM as an administrator, he declined to lead a prayer in a meeting, Ryan recounted in her book, “On Becoming Exceptional.”
“Ron, I’m not asking you to be Catholic,” she recalled telling him. “And I know you’ve only been here two weeks. So, if you’d like to make it three, I suggest you be prepared to pray the next time you’re asked.”
Levy went on to serve SSM for more than 30 years — praying from then on, Ryan wrote.
In Catholic hospitals, meetings are still likely to start with a prayer. Crucifixes often adorn buildings and patient rooms. Mission statements on the walls of SSM facilities remind patients: “We reveal the healing presence of God.”
Above all else, the Catholic faith calls on its hospitals to treat everyone regardless of race, religion, or ability to pay, said Diarmuid Rooney, a vice president of the Catholic Health Association. No nuns run the trade group’s member hospitals, according to the lobbying group. But the mission that compelled the nuns is “what compels us now,” Rooney said. “It’s not just words on a wall.”
The Catholic Health Association urges its hospitals to evaluate themselves every three years on whether they’re living up to Catholic teachings. It created a tool that weighs seven criteria, including how a hospital acts as an extension of the church and cares for poor and marginalized patients.
“We’re not relying on hearsay that the Catholic identity is alive and well in our facilities and hospitals,” Rooney said. “We can actually see on a scale where they are at.”
The association does not share the results with the public.
At SSM Health, “our Catholic identity is deeply and structurally ingrained” even with no nun at the helm, spokesperson Patrick Kampert said. The system reports to two boards. One functions as a typical business board of directors while the other ensures the system abides by the rules of the Catholic Church. The church requires the majority of that nine-member board to be Catholic. Three nuns currently serve on it; one is the chair.
Separately, SSM also is required to file an annual report with the Vatican detailing the ways, Kampert said, “we deepen our Catholic identity and further the healing ministry of Jesus.” SSM declined to provide copies of those reports.
From a business perspective, though, it’s hard to distinguish a Catholic hospital system like SSM from a secular one, said Ruth Hollenbeck, a former Anthem insurance executive who retired in 2018 after negotiating Missouri hospital contracts. In the contracts, she said, the difference amounted to a single paragraph stating that Catholic hospitals wouldn’t do anything contrary to the church’s directives.
To retain tax-exempt status under Internal Revenue Service rules, all nonprofit hospitals must provide a “benefit” to their communities such as free or reduced-price care for patients with low incomes. But the IRS provides a broad definition of what constitutes a community benefit, which gives hospitals wide latitude to justify not needing to pay taxes.
On average, the nation’s nonprofit hospitals reported that 15.5% of their total annual expenses were for community benefits in 2020, the latest figure available from the American Hospital Association.
SSM Health, including all of its subsidiaries, spent proportionately far less than the association’s average for individual hospitals, allocating roughly the same share of its annual expenses to community efforts over three years: 5.1% in 2020, 4.5% in 2021, and 4.9% in 2022, according to a KFF Health News analysis of its most recent publicly available IRS filings and audited financial statements.
A separate analysis from the Lown Institute think tank placed five Catholic systems — including the St. Louis region’s Ascension — on its list of the 10 health systems with the largest “fair share” deficits, which means receiving more in tax breaks than what they spent on the community. And Lown said three St. Louis-area Catholic health systems — Ascension, SSM Health, and Mercy — had fair share deficits of $614 million, $235 million, and $92 million, respectively, in the 2021 fiscal year.
Ascension, Mercy, and SSM disputed Lown’s methodology, arguing it doesn’t take into account the gap between the payments they receive for Medicaid patients and the cost of delivering their care. The IRS filings do.
But, Kampert said, many of the benefits SSM provides aren’t reflected in its IRS filings either. The forms reflect “very simplistic calculations” and do not accurately represent the health system’s true impact on the community, he said.
Today, SSM Health is led by longtime business executive Laura Kaiser. Her compensation in 2022 totaled $8.4 million, including deferred payments, according to its IRS filing. Kampert defended the amount as necessary “to retain and attract the most qualified” candidate.
By contrast, SSM never paid Ryan a salary, giving instead an annual contribution to her convent of less than $2 million a year, according to some tax filings from her long tenure. “I didn’t join the convent to earn money,” Ryan said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Pain-Free Mindset – by Dr. Deepak Ravindran
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First: please ignore the terrible title. This is not the medical equivalent of “think and grow rich”. A better title would have been something like “The Pain-Free Plan”.
Attentive subscribers may notice that this author was our featured expert yesterday, so you can learn about his “seven steps” described in our article there, without us repeating that in our review here.
This book’s greatest strength is also potentially its greatest weakness, depending on the reader: it contains a lot of detailed medical information.
This is good or bad depending on whether you like lots of detailed medical information. Dr. Ravindran doesn’t assume prior knowledge, so everything is explained as we go. However, this means that after his well-referenced clinical explanations, high quality medical diagrams, etc, you may come out of this book feeling like you’ve just done a semester at medical school.
Knowledge is power, though, so understanding the underlying processes of pain and pain management really does help the reader become a more informed expert on your own pain—and options for reducing that pain.
Bottom line: this, disguised by its cover as a “think healing thoughts” book, is actually a science-centric, information-dense, well-sourced, comprehensive guide to pain management from one of the leading lights in the field.
Click here to check out The Pain-Free Mindset, and manage yours more comfortably!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: