The Secret to Mental Health – by George Pransky
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book (and its author) have a sizeable popular following, so it definitely can be said that it has been well-received by many people. The premise in this book is that there is fundamentally nothing wrong with anybody’s brain, and rather everything can be broken down into:
- Mind (the energy and intelligence that animates all life)
- Consciousness (the capacity to be aware of one’s life and experiences)
- Thought (the ability to think, allowing individuals to create their personal experience of reality)
The author explains, over the course of 145 pages, that where anyone with any perceived mental health issue is going wrong is by either lacking self-awareness (Consciousness) or erring by creating an undesirable personal experience of reality (Thought).
In terms of the science of this, frequent references are made to “there is evidence that shows”, “new discoveries about mental health suggest…”, etc, but this claimed evidence is never actually presented, just alluded to. Where many books would have a bibliography, this one has simply a collection of what the author has titled “interesting case studies, conversations, papers, and discussions” (there are no actual case studies or papers; it is just a collection of anecdotes).
The style is… Honestly, in this reviewer’s opinion, barely readable. But, apparently lots of people love it, so your mileage may vary.
We don’t usually delve too far into claimed credentials, but because of the interesting writing style and the bold claims without evidence, we were curious as to where this PhD came from, and apparently it came from a now-shut-down diploma mill that was described by the court as “a complete scam”.
Bottom line: we can’t recommend this one, but we read it so that you don’t have to, and we hope that publishing this review will help reassure you that when we do recommend a book, we mean it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
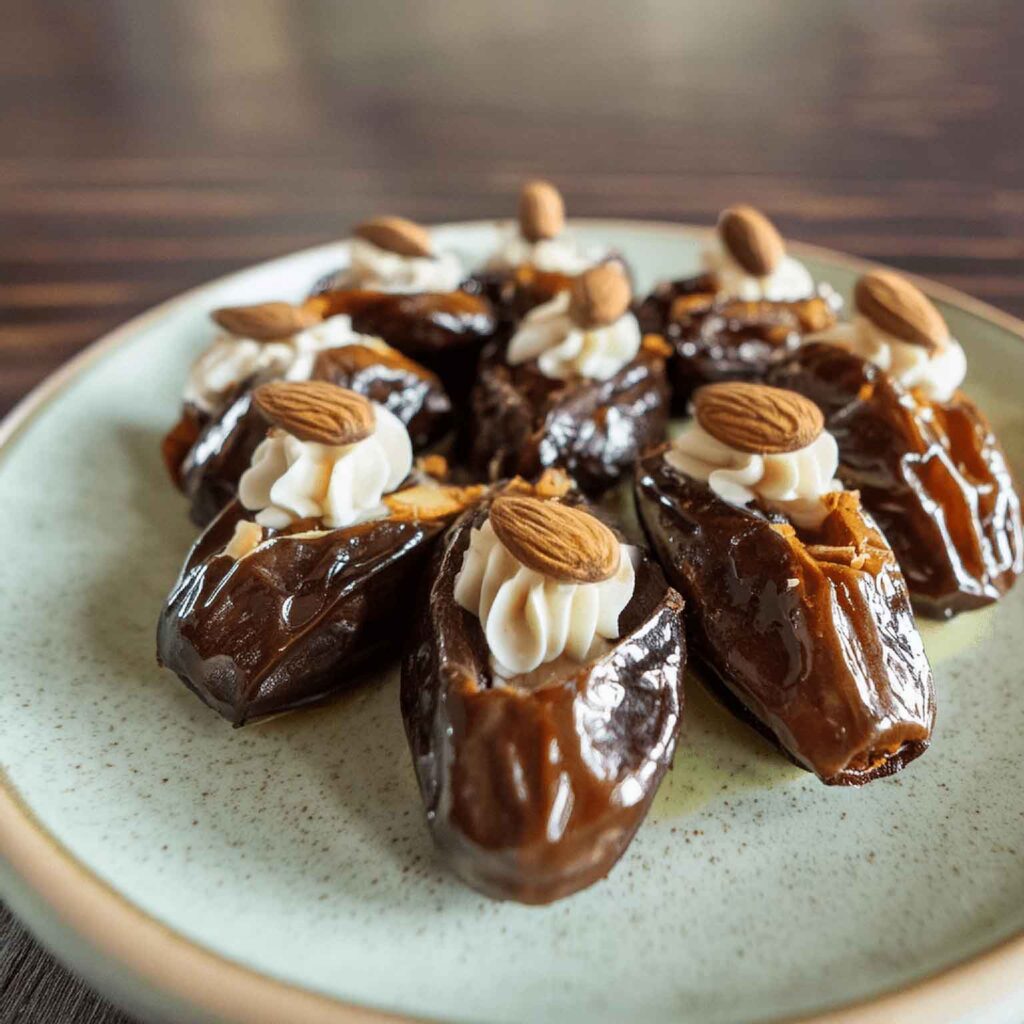
Tiramisu Crunch Bites
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s coffee, it’s creamy, it’s nutty, it’s chocolatey, what’s not to love? It has all the well-loved flavors of tiramisu, but this recipe is a simple one, and it’s essentially stuffed dates in a way you’ve never had them before. They’re delectable, decadent, and decidedly good for your health. These things are little nutrient-bombs that’ll keep you reaching for more.
You will need
- Coffee (we will discuss this)
- 150g (5.5oz) mascarpone (if vegan or lactose-intolerant, can be substituted with vegan varieties, or at a pinch, pressed silken tofu)
- 500g (1lb) dates (Medjool are ideal)
- Twice as many almonds as you have dates
- 50g (2oz) dark chocolate (the darkest, bitterest, you can find)
- Edible flower petals if you can source them (some shops sell dried rose petals for this purpose)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Take the mascarpone and whisk (or blend) it with the coffee. What kind of coffee, you ask? Many will use instant coffee (1tbsp granules mixed with enough boiling water to dissolve it), and that is actually healthiest (counterintuitive but true) but if you care for flavor over health, and have the means to make espresso, make it ristretto (so, stop it halfway through filling up an espresso cup), let it cool, and use that. Absolute bonus for flavor (not for health): if you have the means to make Turkish coffee, use an equivalent amount of that (again, cooled).
You will now have coffee-flavoured mascarpone. It’s great for your gut and full of antioxidant polyphenols. Set it aside for the moment.
2) Take the dark chocolate and melt it. Please don’t microwave it or try to do it in a pan directly over the hob; instead, you will need to use a Bain-Marie. If you don’t have one made-for-purpose, you can place a metal or heatproof glass bowl in a saucepan, with something to stop it from touching the floor of the pan. Then boil water in the pan (without letting the water get into the bowl), and melt the chocolate in the bowl—this will allow you to melt it evenly without burning the chocolate.
You will now have melted dark chocolate. It has its own set of polyphenols, and is great for everything from the brain to the gut microbiome.
3) Cut the dates lengthways on one side and remove the stone. Stuff them carefully with the coffee-flavored mascarpone (you can use a teaspoon, or use a piping kit if you have one). Add a couple of almonds to each one. Place them all on a big plate, and drizzle the melted chocolate over them. Add the petals if you have them.
The dates and almonds deliver extra vitamins and minerals in abundance (not to mention, lots of fiber), and also are an amazing combination even just by themselves. With the mascarpone and chocolate added, this winning on new levels. We’re not done yet, though…
4) Chill them in the fridge for about 30 minutes.
Serve!
Learn more
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Make The Heart-Healthiest Coffee ← this is about cafestol content and why instant is heart-healthiest (alas)
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (Or Is It) ← this is about the health benefits (and some risks, but mostly benefits) of coffee
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts ← almonds are a top-tier choice, but other nuts are good too! This recipe could work well with hazelnuts, for example (we wouldn’t call it “tiramisu crunch bites” in that case, though, since the flavor profile would change)
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same? ← for any worrying “aren’t dates sugary, though?”
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
What Loneliness Does To Your Brain And Body
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Spoiler: it’s nothing good (but it can be addressed!)
Not something to be ignored
Loneliness raises the risk of heart disease by 29% and the risk of stroke by 32%. It also brings about higher susceptibility to illness (flu, COVID, chronic pain, etc), as well as poor sleep quality and cognitive decline, possibly leading to dementia. Not only that, but it also promotes inflammation, and premature death (comparable to smoking).
This is because the lack of meaningful social connections activates the body’s stress response, which in turn increases paranoia, suspicion, and social withdrawal—which makes it harder to seek the social interaction needed to alleviate it.
On a neurological level, cortisol levels become imbalanced, and a faltering dopamine response leads to impulsive behaviors (e.g., drinking, gambling) to try to make up for it. Decreased serotonin, oxytocin, and natural opioids reduce feelings of happiness and negate pain relief.
As for combatting it, the first-line remedy is the obvious one: connecting with others improves emotional and physical wellbeing. However, it is recommended to aim for deep, meaningful connections that make you happy rather than just socializing for its own sake. It’s perfectly possible to be lonely in a crowd, after all.
A second-line remedy is to simply mitigate the harm by means of such things as art therapy and time in nature—they can’t completely replace human connection, but they can at least improve the neurophysiological situation (which in turn, might be enough of a stop-gap solution to enable a return to human connection).
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Which Bell Peppers To Pick?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bell Peppers: A Spectrum Of Specialties
We were going to do this as part of our ongoing “This Or That?” challenge, but as there are four main types all with many different benefits, we thought this bunch of fruits deserved a main feature.
And yes, they’re botanically fruits, even if culinarily used as vegetables—much like tomatoes, famously!
They’re all the same (but also very much not)
A thing to know is that whether bell peppers be green, yellow, orange, or red, they’re all the same plant, Capiscum anuum. All that differs is how early or late they’re harvested.
Notwithstanding the “Capiscum” genus, they don’t contain capsaicin (as is found in hot peppers). Capsaicin’s a wonderful phytochemical:
Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
…but today we’re all about the bell peppers.
So, let’s see how they stack up!
💚 Green for lutein
Lutein is especially important for the eyes and [the rest of the] brain, to the point that there’s now an Alzheimer’s test that measures lutein concentration in the eye:
Green peppers have most of this important carotenoid, though the others all have some too. See also:
💛 Yellow for vitamin C
Yellow peppers are technically highest in vitamin C, but all of them contain far more than the daily dose per fruit already, so if there’s any color of pepper that’s nutritionally the most expendable, it’s yellow, since any other color pepper can take its place.
Watch out, though! Cooking destroys vitamin C, so if you want to get your Cs in, you’re going to want to do it raw.
🧡 Orange for zeaxanthin and cryptoxanthins
Similar in their benefits to lutein, these antioxidant carotenoids are found most generously in orange peppers (20x as much as in yellow, 10x as much as in red, and slightly more than in green).
❤️ Red for vitamins A & B6
Red peppers are richest by far in vitamin A, with one fruit giving the daily dose already. The others have about 10% of that, give or take.
Red peppers also have the most vitamin B6, though the others also have nearly as much.
❤️ Red for lycopene
We must do a main feature for lycopene sometime, as unlike a lot of antioxidant carotenoids, lycopene is found in comparatively very few foods (most famously it’s present in tomatoes).
Red is the only color of pepper to have lycopene.
10almonds tip: to get the most out of your lycopene, cook these ones!
Lycopene becomes 4x more bioavailable when cooked:
Lycopene in tomatoes: chemical and physical properties affected by food processing ← this paper is about tomatoes but lycopene is lycopene and this applies to the lycopene in red peppers, too
And the overall winner is…
You! Because you get to eat all four of them
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Dates vs Banana – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dates to banana, we picked the dates.
Why?
It was close, and bananas do have some strengths too! We pitted these two against each other as they’re both sweet fruits often used as a sweetening and consistency-altering ingredient in desserts and sweet snacks, so if you’re making a choice between them, here are the things to consider:
In terms of macros, dates have more than 3x the fiber, more than 2x the protein, and a little over 3x the carbs. You may be wondering how this adds up in terms of glycemic index: dates have the lower GI. So, we pick dates, here, for that reason and overall nutritional density too.
When it comes to vitamins, bananas have their moment, albeit barely: dates have more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, and K, while bananas have more of vitamins A, B6, C, E, and choline, making for a marginal victory for bananas in this category.
Looking at minerals next, however, it’s quite a different story: dates have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while bananas are not higher in any mineral. No, not even potassium, for which they are famous—dates have nearly 2x more potassium than bananas.
Adding up these sections makes for a clear win for dates in general!
Enjoy either/both, but dates are the more nutritious snack/ingredient.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Collard Greens vs Watercress – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing collard greens to watercress, we picked the collard greens.
Why?
It was close! But…
In terms of macros, collard greens have 8x the fiber, 4x the carbs, and slightly more protein. The fiber-to-carbs ratio also gives collard greens the lower glycemic index, although honestly, nobody is getting metabolic disease from eating watercress. Still, by the numbers it’s a clear win for collard greens, and especially 8x the fiber is not to be undervalued!
When it comes to vitamins, things were much more even; collard greens have more of vitamins A, B3, B9, K, and choline, while watercress has more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, C, and E. They’re tied on vitamin B6, so that makes a 5.5:5.5 tie overall. Looking for a tiebreaker, collard greens’ margins of difference are greater, so we could call this a tie or the narrowest of wins for collard greens ion this category.
In the category of minerals, collard greens have more calcium, copper, iron, manganese, and zinc, while watercress has more copper, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. They’re tied on magnesium. This time the margins of difference are also comparable, so there’s really no tiebreaker available for this one. Thus, an absolute tie on minerals.
Looking at polyphenols, watercress has slightly more, with the main contender being 4mg/100g quercetin.
Adding up the sections results in either a tie or a slight for collard greens based on the tiebreaker in the vitamins category.
We can also put the two clear wins (one for collard greens and one for watercress), and say that in our opinion, collard greens’ 4g/100g fiber beats watercress’s 4mg/100g quercetin.
Quercetin is great and all, but:
- if you buy a quercetin supplement like this one on Amazon it’s 1000mg capsules, so how critical is watercress’s 4mg, really? Yes, getting it from food is better, but it’s not 25,000% better.
- no doctor that we know of is saying “you need more quercetin or you’re going to die”, but they do say “you need more fiber or you’re going to die”
- indeed, the WHO passionately proclaims that 95% of people in the US especially desperately need to eat more fiber, whereas there is no similar giant public health campaign begging people to have 4mg more of quercetin
…so we’ll say that’s another tiebreaker in favor of collard greens.
In short: collard greens scrape a win based on several tiebreakers, but watercress was a very close contender indeed!
Of course, by all means enjoy either or (ideally!) both; diversity is good.
Want to learn more?
You might like:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s the difference between physical and chemical sunscreens? And which one should you choose?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sun exposure can accelerate ageing, cause skin burns, erythema (a skin reaction), skin cancer, melasmas (or sun spots) and other forms of hyperpigmentation – all triggered by solar ultraviolet radiation.
Approximately 80% of skin cancer cases in people engaged in outdoor activities are preventable by decreasing sun exposure. This can be done in lots of ways including wearing protective clothing or sunscreens.
But not all sunscreens work in the same way. You might have heard of “physical” and “chemical” sunscreens. What’s the difference and which one is right for you?
How sunscreens are classified
Sunscreens are grouped by their use of active inorganic and organic ultraviolet (UV) filters. Chemical sunscreens use organic filters such as cinnamates (chemically related to cinnamon oil) and benzophenones. Physical sunscreens (sometimes called mineral sunscreens) use inorganic filters such as titanium and zinc oxide.
These filters prevent the effects of UV radiation on the skin.
Organic UV filters are known as chemical filters because the molecules in them change to stop UV radiation reaching the skin. Inorganic UV filters are known as physical filters, because they work through physical means, such as blocking, scattering and reflection of UV radiation to prevent skin damage.
Nano versus micro
The effectiveness of the filters in physical sunscreen depends on factors including the size of the particle, how it’s mixed into the cream or lotion, the amount used and the refraction index (the speed light travels through a substance) of each filter.
When the particle size in physical sunscreens is large, it causes the light to be scattered and reflected more. That means physical sunscreens can be more obvious on the skin, which can reduce their cosmetic appeal.
Nanoparticulate forms of physical sunscreens (with tiny particles smaller than 100 nanometers) can improve the cosmetic appearance of creams on the skin and UV protection, because the particles in this size range absorb more radiation than they reflect. These are sometimes labelled as “invisible” zinc or mineral formulations and are considered safe.
So how do chemical sunscreens work?
Chemical UV filters work by absorbing high-energy UV rays. This leads to the filter molecules interacting with sunlight and changing chemically.
When molecules return to their ground (or lower energy) state, they release energy as heat, distributed all over the skin. This may lead to uncomfortable reactions for people with skin sensitivity.
Generally, UV filters are meant to stay on the epidermis (the first skin layer) surface to protect it from UV radiation. When they enter into the dermis (the connective tissue layer) and bloodstream, this can lead to skin sensitivity and increase the risk of toxicity. The safety profile of chemical UV filters may depend on whether their small molecular size allows them to penetrate the skin.
Chemical sunscreens, compared to physical ones, cause more adverse reactions in the skin because of chemical changes in their molecules. In addition, some chemical filters, such as dibenzoylmethane tend to break down after UV exposure. These degraded products can no longer protect the skin against UV and, if they penetrate the skin, can cause cell damage.
Due to their stability – that is, how well they retain product integrity and effectiveness when exposed to sunlight – physical sunscreens may be more suitable for children and people with skin allergies.
Although sunscreen filter ingredients can rarely cause true allergic dermatitis, patients with photodermatoses (where the skin reacts to light) and eczema have higher risk and should take care and seek advice.
What to look for
The best way to check if you’ll have a reaction to a physical or chemical sunscreen is to patch test it on a small area of skin.
And the best sunscreen to choose is one that provides broad-spectrum protection, is water and sweat-resistant, has a high sun protection factor (SPF), is easy to apply and has a low allergy risk.
Health authorities recommend sunscreen to prevent sun damage and cancer. Chemical sunscreens have the potential to penetrate the skin and may cause irritation for some people. Physical sunscreens are considered safe and effective and nanoparticulate formulations can increase their appeal and ease of use.
Yousuf Mohammed, Dermatology researcher, The University of Queensland and Khanh Phan, Postdoctoral research associate, Frazer Institute, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: