Soy Beans vs Kidney Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing soy beans to kidney beans, we picked the soy.
Why?
In terms of macros, soy has 2x the protein, while kidney beans have nearly 3x the carbs and very slightly more fiber. Ratio-wise, the “very slightly more fiber” does not offset the “nearly 3x the carbs” when it comes to glycemic index (though both are still good, really, but this is a head-to-head so the comparison is relevant), and 2x the protein is also quite a bonus, so this category’s an easy win for soy.
In the category of vitamins, soy beans have more of vitamins A, B2, B6, C, E, K, and choline, while kidney beans have more of vitamins B3, B5, and B9, thus making for a 7:3 win for soy.
When it comes to minerals, soy beans have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while kidney beans are not higher in any mineral. Another clear win for soy.
Adding up the three strong wins for soy, makes for an overall easy win for soy. Still, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Correct An Upper Spine Hump (Simple Stretch & Exercise)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Generally called a neck hump in this video, it can be in the cervical (neck) vertebrae or it can be in the thoracic (upper back) vertebrae. It’s also known as a dowager’s hump, buffalo hump, or kyphosis.
However, it can be fixed:
What to do
First understand the cause: it generally comes from poor posture, especially from prolonged desk work or phone use.
With that in mind…
- Posture adjustments: lean back in a chair to counter gravity’s pull on your head. Avoid slumping; keep your head aligned with your spine.
- Stretching: lie flat on the floor without pillows to restore spinal alignment. Gradually reduce pillow height during sleep to decrease neck hyperflexion.
- Neck retraction: pull chin straight back while keeping your eyes looking forwards. Hold for 15 seconds, gradually increasing to 60 seconds. Perform 10 repetitions, resting between sets.
- Strengthening: lean forward and pull the chin back against gravity. Hold, or repeat for 10 repetitions. Over time, increase duration to a minute.
For more on all of this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Pains That Good Posture Now Can Help You Avoid Later
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Intuitive Eating Might Not Be What You Think
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In our recent Expert Insights main features, we’ve looked at two fairly opposing schools of thought when it comes to managing what we eat.
First we looked at:
What Flexible Dieting Really Means
…and the notion of doing things imperfectly for greater sustainability, and reducing the cognitive load of dieting by measuring only the things that are necessary.
And then in opposition to that,
What Are The “Bright Lines” Of Bright Line Eating?
…and the notion of doing things perfectly so as to not go astray, and reducing the cognitive load of dieting by having hard-and-fast rules that one does not second-guess or reconsider later when hungry.
Today we’re going to look at Intuitive Eating, and what it does and doesn’t mean.
Intuitive Eating does mean paying attention to hunger signals (each way)
Intuitive Eating means listening to one’s body, and responding to hunger signals, whether those signals are saying “time to eat” or “time to stop”.
A common recommendation is to “check in” with one’s body several times per meal, reflecting on such questions as:
- Do I have hunger pangs? Would I seek food now if I weren’t already at the table?
- If I hadn’t made more food than I’ve already eaten so far, would that have been enough, or would I have to look for something else to eat?
- Am I craving any of the foods that are still before me? Which one(s)?
- How much “room” do I feel I still have, really? Am I still in the comfort zone, and/or am I about to pass into having overeaten?
- Am I eating for pleasure only at this point? (This is not inherently bad, by the way—it’s ok to have a little more just for pleasure! But it is good to note that this is the reason we’re eating, and take it as a cue to slow down and remember to eat mindfully, and enjoy every bite)
- Have I, in fact, passed the point of pleasure, and I’m just eating because it’s in front of me, or so as to “not be wasteful”?
See also: Interoception: Improving Our Awareness Of Body Cues
And for that matter: Mindful Eating: How To Get More Out Of What’s On Your Plate
Intuitive Eating is not “80:20”
When it comes to food, the 80:20 rule is the idea of having 80% of one’s diet healthy, and the other 20% “free”, not necessarily unhealthy, but certainly not moderated either.
Do you know what else the 80:20 food rule is?
A food rule.
Intuitive Eating doesn’t do those.
The problem with food rules is that they can get us into the sorts of problems described in the studies showing how flexible dieting generally works better than rigid dieting.
Suddenly, what should have been our free-eating 20% becomes “wait, is this still 20%, or have I now eaten so much compared to the healthy food, that I’m at 110% for my overall food consumption today?”
Then one gets into “Well, I’ve already failed to do 80:20 today, so I’ll try again tomorrow [and binge meanwhile, since today is already written off]”
See also: Eating Disorders: More Varied (And Prevalent) Than People Think
It’s not “eat anything, anytime”, either
Intuitive Eating is about listening to your body, and your brain is also part of your body.
- If your body is saying “give me sugar”, your brain might add the information “fruit is healthier than candy”.
- If your body is saying “give me fat”, your brain might add the information “nuts are healthier than fried food”
- If your body is saying “give me salt”, your brain might add the information “kimchi is healthier than potato chips”
That doesn’t mean you have to swear off candy, fried food, or potato chips.
But it does mean that you might try satisfying your craving with the healthier option first, giving yourself permission to have the less healthy option afterwards if you still want it (you probably won’t).
See also:
I want to eat healthily. So why do I crave sugar, salt and carbs?
Want to know more about Intuitive Eating?
You might like this book that we reviewed previously:
Intuitive Eating – by Evelyn Tribole and Elyse Resch
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Marrakesh Sorghum Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As the name suggests, it’s a Maghreb dish today! Using sorghum, a naturally gluten-free whole grain with a stack of vitamins and minerals. This salad also comes with fruit and nuts (apricots and almonds; a heavenly combination for both taste and nutrients) as well as greens, herbs, and spices.
Note: to keep things simple today, we’ve listed ras el-hanout as one ingredient. If you’re unfamiliar, it’s a spice blend; you can probably buy a version locally, but you might as well know how to make it yourself—so here’s our recipe for that!
You will need
- 1½ cups sorghum, soaked overnight in water (if you can’t find it locally, you can order it online (here’s an example product on Amazon), or substitute quinoa) and if you have time, soaked overnight and then kept in a jar with just a little moisture for a few days until they begin to sprout—this will be best of all. But if you don’t have time, don’t worry about it; overnight soaking is sufficient already.
- 1 carrot, grated
- ½ cup chopped parsley
- 1 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- ½ tbsp chopped chives
- 2 tbsp ras el-hanout
- 3 cloves garlic, crushed
- 2 tbsp almond butter
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 tsp white miso paste
- ½ cup sliced almonds
- 4 fresh apricots, pitted and cut into wedges
- 1 cup mint leaves, chopped
- To serve: your choice of salad greens; we suggest chopped romaine lettuce and rocket
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the sorghum, which means boiling it for about 45 minutes, or 30 in a pressure cooker. If unsure, err on the side of cooking longer—even up to an hour will be totally fine. You have a lot of wiggle room, and will soon get used to how long it takes with your device/setup. Drain the cooked sorghum, and set it aside to cool. If you’re entertaining, we recommend doing this part the day before and keeping it in the fridge.
2) When it’s cool, add the carrot, the parsley, the chives, the vinegar, and 1 tbsp of the ras el-hanout. Toss gently but thoroughly to combine.
3) Make the dressing, which means putting ¼ cup water into a blender with the other 1 tbsp of the ras el-hanout, the garlic, the almond butter, the lemon juice, and the miso paste. Blend until smooth.
4) Assemble the salad, which means adding the dressing to sorghum-and-ingredients bowl, along with the almonds, apricots, and mint leaves. Toss gently, but sufficiently that everything is coated.
5) Serve on a bed of salad greens.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet ← including an anti-inflammatory version, which is functionally what we’re doing today. As an aside when people hear “Mediterranean” they often think “Italy and Greece”. Which, sure, but N. Africa (and thus Maghreb cuisine) is also very much Mediterranean, and it shows!
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Could ADHD drugs reduce the risk of early death? Unpacking the findings from a new Swedish study
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) can have a considerable impact on the day-to-day functioning and overall wellbeing of people affected. It causes a variety of symptoms including difficulty focusing, impulsivity and hyperactivity.
For many, a diagnosis of ADHD, whether in childhood or adulthood, is life changing. It means finally having an explanation for these challenges, and opens up the opportunity for treatment, including medication.
Although ADHD medications can cause side effects, they generally improve symptoms for people with the disorder, and thereby can significantly boost quality of life.
Now a new study has found being treated for ADHD with medication reduces the risk of early death for people with the disorder. But what can we make of these findings?
A large study from Sweden
The study, published this week in JAMA (the prestigious journal of the American Medical Association), was a large cohort study of 148,578 people diagnosed with ADHD in Sweden. It included both adults and children.
In a cohort study, a group of people who share a common characteristic (in this case a diagnosis of ADHD) are followed over time to see how many develop a particular health outcome of interest (in this case the outcome was death).
For this study the researchers calculated the mortality rate over a two-year follow up period for those whose ADHD was treated with medication (a group of around 84,000 people) alongside those whose ADHD was not treated with medication (around 64,000 people). The team then determined if there were any differences between the two groups.
What did the results show?
The study found people who were diagnosed and treated for ADHD had a 19% reduced risk of death from any cause over the two years they were tracked, compared with those who were diagnosed but not treated.
In understanding this result, it’s important – and interesting – to look at the causes of death. The authors separately analysed deaths due to natural causes (physical medical conditions) and deaths due to unnatural causes (for example, unintentional injuries, suicide, or accidental poisonings).
The key result is that while no significant difference was seen between the two groups when examining natural causes of death, the authors found a significant difference for deaths due to unnatural causes.
So what’s going on?
Previous studies have suggested ADHD is associated with an increased risk of premature death from unnatural causes, such as injury and poisoning.
On a related note, earlier studies have also suggested taking ADHD medicines may reduce premature deaths. So while this is not the first study to suggest this association, the authors note previous studies addressing this link have generated mixed results and have had significant limitations.
In this new study, the authors suggest the reduction in deaths from unnatural causes could be because taking medication alleviates some of the ADHD symptoms responsible for poor outcomes – for example, improving impulse control and decision-making. They note this could reduce fatal accidents.
The authors cite a number of studies that support this hypothesis, including research showing ADHD medications may prevent the onset of mood, anxiety and substance use disorders, and lower the risk of accidents and criminality. All this could reasonably be expected to lower the rate of unnatural deaths.
Strengths and limitations
Scandinavian countries have well-maintained national registries that collect information on various aspects of citizens’ lives, including their health. This allows researchers to conduct excellent population-based studies.
Along with its robust study design and high-quality data, another strength of this study is its size. The large number of participants – almost 150,000 – gives us confidence the findings were not due to chance.
The fact this study examined both children and adults is another strength. Previous research relating to ADHD has often focused primarily on children.
One of the important limitations of this study acknowledged by the authors is that it was observational. Observational studies are where the researchers observe and analyse naturally occurring phenomena without intervening in the lives of the study participants (unlike randomised controlled trials).
The limitation in all observational research is the issue of confounding. This means we cannot be completely sure the differences between the two groups observed were not either partially or entirely due to some other factor apart from taking medication.
Specifically, it’s possible lifestyle factors or other ADHD treatments such as psychological counselling or social support may have influenced the mortality rates in the groups studied.
Another possible limitation is the relatively short follow-up period. What the results would show if participants were followed up for longer is an interesting question, and could be addressed in future research.
What are the implications?
Despite some limitations, this study adds to the evidence that diagnosis and treatment for ADHD can make a profound difference to people’s lives. As well as alleviating symptoms of the disorder, this study supports the idea ADHD medication reduces the risk of premature death.
Ultimately, this highlights the importance of diagnosing ADHD early so the appropriate treatment can be given. It also contributes to the body of evidence indicating the need to improve access to mental health care and support more broadly.
Hassan Vally, Associate Professor, Epidemiology, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
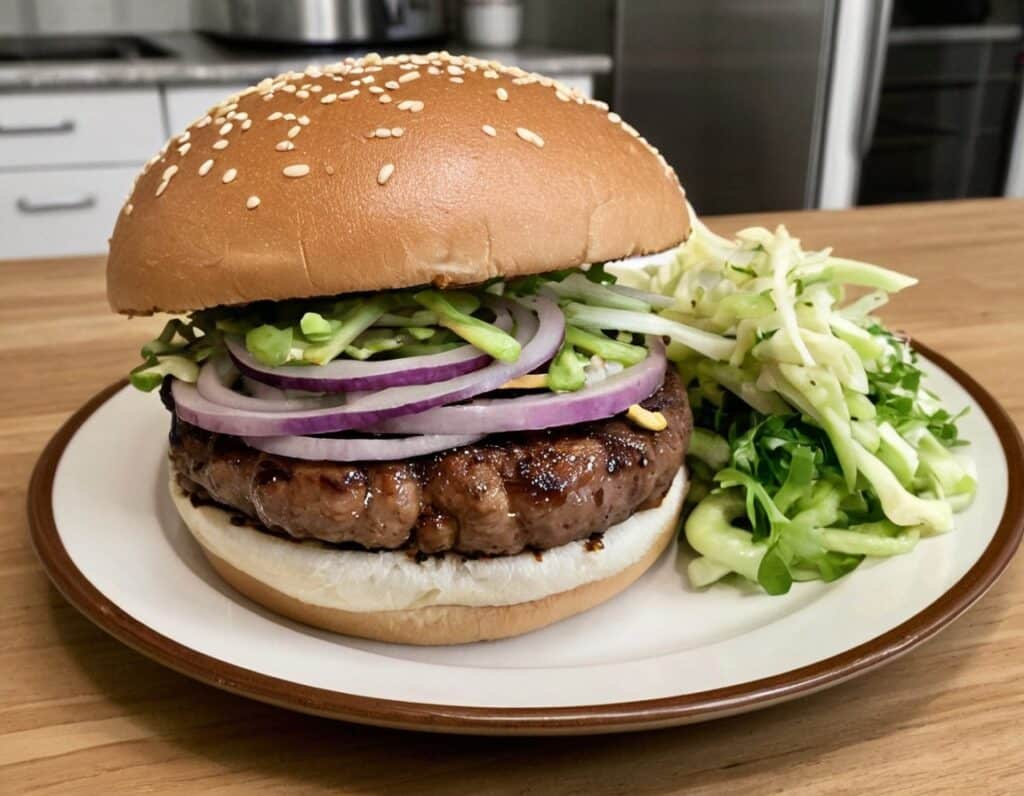
Teriyaki Chickpea Burgers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Burgers are often not considered the healthiest food, but they can be! Ok, so the teriyaki sauce component itself isn’t the healthiest, but the rest of this recipe is, and with all the fiber this contains, it’s a net positive healthwise, even before considering the protein, vitamins, minerals, and assorted phytonutrients.
You will need
- 2 cans chickpeas, drained and rinsed (or 2 cups of chickpeas, cooked drained and rinsed)
- ¼ cup chickpea flour (also called gram flour or garbanzo bean flour)
- ¼ cup teriyaki sauce
- 2 tbsp almond butter (if allergic, substitute with a seed butter if available, or else just omit; do not substitute with actual butter—it will not work)
- ½ bulb garlic, minced
- 1 large chili, minced (your choice what kind, color, or even whether or multiply it)
- 1 large shallot, minced
- 1″ piece of ginger, grated
- 2 tsp teriyaki sauce (we’re listing this separately from the ¼ cup above as that’ll be used differently)
- 1 tsp yeast extract (even if you don’t like it; trust us, it’ll work—this writer doesn’t like it either but uses it regularly in recipes like these)
- 1 tbsp black pepper
- 1 tsp fennel powder
- ½ tsp sweet cinnamon
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil for frying
For serving:
- Burger buns (you can use our Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread recipe)
- Whatever else you want in there; we recommend mung bean sprouts, red onion, and a nice coleslaw
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Roast the chickpeas spaced out on a baking tray (lined with baking paper) for about 15 minutes. Leave the oven on afterwards; we still need it.
3) While that’s happening, heat a little oil in a skillet to a medium heat and fry the shallot, chili, garlic, and ginger, for about 2–3 minutes. You want to release the flavors, but not destroy them.
4) Let them cool, and when the chickpeas are done, let them cool for a few minutes too, before putting them all into a food processor along with the rest of the ingredients from the main section, except the oil and the ¼ cup teriyaki sauce. Process them into a dough.
5) Form the dough into patties; you should have enough dough for 4–6 patties depending on how big you want them.
6) Brush them with the teriyaki sauce; turn them onto a baking tray (lined with baking paper) and brush the other side too. Be generous.
7) Bake them for about 15 minutes, turn them (taking the opportunity to add more teriyaki sauce if it seems to merit it) and bake for another 5–10 minutes.
8) Assemble; we recommend the order: bun, a little coleslaw, burger, red onion, more coleslaw, mung bean sprouts, bun, but follow your heart!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Three Daily Servings of Beans/Legumes?
- Hoisin Sauce vs Teriyaki Sauce – Which is Healthier?
- Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we scored 4/5 today!
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What We Don’t Talk About When We Talk About Fat – by Aubrey Gordon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are books aplenty to encourage and help you to lose weight. This isn’t one of those.
There are also books aplenty to encourage and help you to accept yourself and your body at the weight you are, and forge self-esteem. This isn’t one of those, either—in fact, it starts by assuming you already have that.
There are fair arguments for body neutrality, and fat acceptance. Very worthy also is the constant fight for bodily sovereignty.
These are worthy causes, but they’re for the most-part not what our author concerns herself with here. Instead, she cares for a different and very practical goal: fat justice.
In a world where you may be turned away from medical treatment if you are over a certain size, told to lose half your bodyweight before you can have something you need, she demands better. The battle extends further than healthcare though, and indeed to all areas of life.
Ultimately, she argues, any society that will disregard the needs of the few because they’re a marginal demographic, is a society that will absolutely fail you if you ever differ from the norm in some way.
All in all, an important (and for many, perhaps eye-opening) book to read if you are fat, care about fat people, are a person of any size, or care about people in general.
Pick Up Your Copy of “What We Don’t Talk About When We Talk About Fat”, on Amazon Today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: