Make Your Saliva Better For Your Teeth
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A new study has highlighted the importance of lifestyle factors in shaping the oral microbiome—that is to say, how the things we do affect the bacteria that live in our mouths:
Nepali oral microbiomes reflect a gradient of lifestyles from traditional to industrialized
Neither the study title nor the abstract elucidate how, exactly, one impacts the other, but the study itself does (of course) contain that information; we read it, and the short version is:
In terms of the extremes of “most traditional” to “most industrialized”, foragers have the most diverse oral microbiomes (that’s good), and people with an American industrialized lifestyle had the least diverse oral microbiomes (that’s bad). Between the two extremes, we see the gradient promised by the title.
If you do feel like checking it out, Figure 3 in the paper illustrates this nicely.
Also illustrated in the above-linked Figure 3 is oral microbiome composition. In other words (and to oversimplify it rather), how good or bad our mouth bacteria are for us, independent of diversity (so for example, are there more of this or that kind of bacteria).
Once again, there is a gradient, only this time, the ends of it are even more polarized: foragers have a diverse oral microbiome rich with healthy-for-humans bacteria, while people with an American industrialized lifestyle might not have the diversity, but do have a large number of bad-for-humans bacteria.
While many lifestyle factors are dietary or quasi-dietary, e.g. what kinds of foods people eat, whether they drink alcohol, whether they smoke or use gum, etc, many lifestyle factors were examined, including everything from medications and exercise, to things like kitchen location and what fuel is predominantly used, to education and sexual activity and many other things that we don’t have room for here.
You can see how each lifestyle factor stacked up, in Figure 5.
Why it matters
Our oral microbiome affects many aspects of health, including:
- Locally: caries, periodontal diseases, mucosal diseases, oral cancer, and more
- Systemically: gastrointestinal diseases in general, IBS in particular, nervous system diseases, Alzheimer’s disease, endocrine diseases, all manner of immune/autoimmune diseases, and more
Nor are the effects it has mild; oral microbiome health can be a huge factor, statistically, for many of the above. You can see information and data pertaining to all of the above and more, here:
Oral microbiomes: more and more importance in oral cavity and whole body
What to do about it
Take care of your oral microbiome, to help it to take care of you. As well as the above-mentioned lifestyle factors, it’s worth noting that when it comes to oral hygiene, not all oral hygiene products are created equal:
Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Kinds Help, And Which Kinds Harm?
Additionally, you might want to consider gentler options, but if you do, take care to opt for things that science actually backs., rather than things that merely trended on social media.
This writer (hi, it’s me) is particularly excited about the science and use of the miswak stick, which comes from the Saladora persica tree, and has phytochemical properties that (amongst many other health-giving effects) improve the quality of saliva (i.e., improve its pH and microbiome composition). In essence, your own saliva gets biochemically nudged into being the safest, most effective mouthwash.
There’s a lot of science for the use of S. persica, and we’ve discussed it before in more detail than we have room to rehash today, here:
Less Common Oral Hygiene Options
If you’d like to enjoy these benefits (and also have the equivalent of a toothbrush that you can carry with you at all times and does not require water*), then here’s an example product on Amazon 😎
*don’t worry, it won’t feel like dry-brushing your teeth. Remember what we said about what it does to your saliva. Basically, you chomp it once, and your saliva a) increases and b) becomes biological tooth-cleaning fluid. The stick itself is fibrous, so the end of it frays in a way that makes a natural little brush. Each stick is about 5”×¼” and you can carry it in a little carrying case (you’ll get a couple with each pack of miswak sticks), so you can easily use it in, say, the restroom of a restaurant or before your appointment somewhere, just as easily as you could use a toothpick, but with much better results. You may be wondering how long a stick lasts; well, that depends on how much you use it, but in this writer’s experience, each stick lasts about a month maybe, using it at least 2–3 times per day, probably rather more since I use it after each meal/snack and upon awakening.
(the above may read like an ad, but we promise you it’s not sponsored and this writer’s just enthusiastic, and when you read the science, you will be too)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
10 Ways To Self-Soothe That Don’t Involve Food Or Drink
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If one is accustomed to comfort-eating or drowning one’s sorrows, what are the alternatives that can actually work? Holistic nutritionist Selin Bilgin has a list:
Self-Care That’s Not Self-Sabotage
You might want to make a note of these 10 things, so they can be a sort of “menu” for you when you need them:
- Give your introversion or extroversion what it needs (e.g. alone time to decompress, or social activities)
- Treat your senses: often we don’t actually need food/drink so much as culinary entertainment. So, we can sate this sensory mood in other ways, for example pleasant candles, flowers, and so forth.
- Bathe/shower nicely: it’s cliché but some personal pampering can go a long way
- Beautify yourself: it’s also cliché, but a makeover evening has its place
- Move! Go for a walk, do some yoga, whatever suits you, but move your body.
- Make movie nights luxurious: instead of making it about food/drink, focus on creating an enjoyable atmosphere
- Physically release tension: at 10almonds we recommend progressive relaxation for this!
- Create something: whether it’s art, craft, baking, or something else, creativity feels good
- Tackle things you’ve been procrastinating: this one doesn’t seem like self-soothing from the front end, but from the back end (i.e., having done it), it makes a big difference!
- Journal: expressing your thoughts and feelings can help a lot—really.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
- Rebalancing Dopamine (Without “Dopamine Fasting”)
- Self-Care That’s Not Just Self-Indulgence
Take care!
Share This Post
-
I have a stuffy nose, how can I tell if it’s hay fever, COVID or something else?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hay fever (also called allergic rhinitis) affects 24% of Australians. Symptoms include sneezing, a runny nose (which may feel blocked or stuffy) and itchy eyes. People can also experience an itchy nose, throat or ears.
But COVID is still spreading, and other viruses can cause cold-like symptoms. So how do you know which one you’ve got?
Lysenko Andrii/Shutterstock Remind me, how does hay fever cause symptoms?
Hay fever happens when a person has become “sensitised” to an allergen trigger. This means a person’s body is always primed to react to this trigger.
Triggers can include allergens in the air (such as pollen from trees, grasses and flowers), mould spores, animals or house dust mites which mostly live in people’s mattresses and bedding, and feed on shed skin.
When the body is exposed to the trigger, it produces IgE (immunoglobulin E) antibodies. These cause the release of many of the body’s own chemicals, including histamine, which result in hay fever symptoms.
People who have asthma may find their asthma symptoms (cough, wheeze, tight chest or trouble breathing) worsen when exposed to airborne allergens. Spring and sometimes into summer can be the worst time for people with grass, tree or flower allergies.
However, animal and house dust mite symptoms usually happen year-round.
Ryegrass pollen is a common culprit. bangku ceria/Shutterstock What else might be causing my symptoms?
Hay fever does not cause a fever, sore throat, muscle aches and pains, weakness, loss of taste or smell, nor does it cause you to cough up mucus.
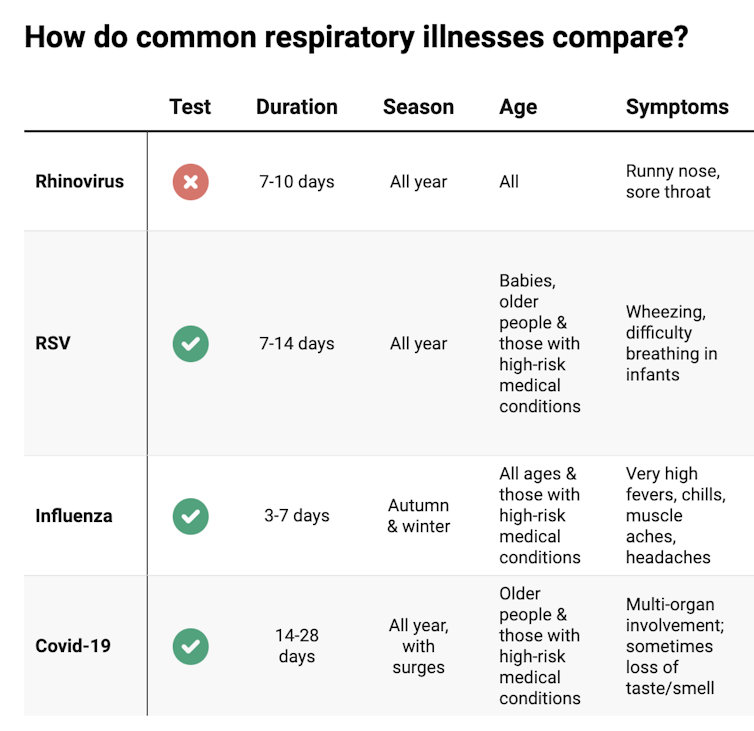
These symptoms are likely to be caused by a virus, such as COVID, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or a “cold” (often caused by rhinoviruses). These conditions can occur all year round, with some overlap of symptoms:
Natasha Yates/The Conversation COVID still surrounds us. RSV and influenza rates appear higher than before the COVID pandemic, but it may be due to more testing.
So if you have a fever, sore throat, muscle aches/pains, weakness, fatigue, or are coughing up mucus, stay home and avoid mixing with others to limit transmission.
People with COVID symptoms can take a rapid antigen test (RAT), ideally when symptoms start, then isolate until symptoms disappear. One negative RAT alone can’t rule out COVID if symptoms are still present, so test again 24–48 hours after your initial test if symptoms persist.
You can now test yourself for COVID, RSV and influenza in a combined RAT. But again, a negative test doesn’t rule out the virus. If your symptoms continue, test again 24–48 hours after the previous test.
If it’s hay fever, how do I treat it?
Treatment involves blocking the body’s histamine release, by taking antihistamine medication which helps reduce the symptoms.
Doctors, nurse practitioners and pharmacists can develop a hay fever care plan. This may include using a nasal spray containing a topical corticosteroid to help reduce the swelling inside the nose, which causes stuffiness or blockage.
Nasal sprays need to delivered using correct technique and used over several weeks to work properly. Often these sprays can also help lessen the itchy eyes of hay fever.
Drying bed linen and pyjamas inside during spring can lessen symptoms, as can putting a smear of Vaseline in the nostrils when going outside. Pollen sticks to the Vaseline, and gently blowing your nose later removes it.
People with asthma should also have an asthma plan, created by their doctor or nurse practitioner, explaining how to adjust their asthma reliever and preventer medications in hay fever seasons or on allergen exposure.
People with asthma also need to be alert for thunderstorms, where pollens can burst into tinier particles, be inhaled deeper in the lungs and cause a severe asthma attack, and even death.
What if it’s COVID, RSV or the flu?
Australians aged 70 and over and others with underlying health conditions who test positive for COVID are eligible for antivirals to reduce their chance of severe illness.
Most other people with COVID, RSV and influenza will recover at home with rest, fluids and paracetamol to relieve symptoms. However some groups are at greater risk of serious illness and may require additional treatment or hospitalisation.
For RSV, this includes premature infants, babies 12 months and younger, children under two who have other medical conditions, adults over 75, people with heart and lung conditions, or health conditions that lessens the immune system response.
For influenza, people at higher risk of severe illness are pregnant women, Aboriginal people, people under five or over 65 years, or people with long-term medical conditions, such as kidney, heart, lung or liver disease, diabetes and decreased immunity.
If you’re concerned about severe symptoms of COVID, RSV or influenza, consult your doctor or call 000 in an emergency.
If your symptoms are mild but persist, and you’re not sure what’s causing them, book an appointment with your doctor or nurse practitioner. Although hay fever season is here, we need to avoid spreading other serious infectious.
For more information, you can call the healthdirect helpline on 1800 022 222 (known as NURSE-ON-CALL in Victoria); use the online Symptom Checker; or visit healthdirect.gov.au or the Australian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy.
Deryn Thompson, Eczema and Allergy Nurse; Lecturer, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Aspirin, CVD Risk, & Potential Counter-Risks
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Aspirin Pros & Cons
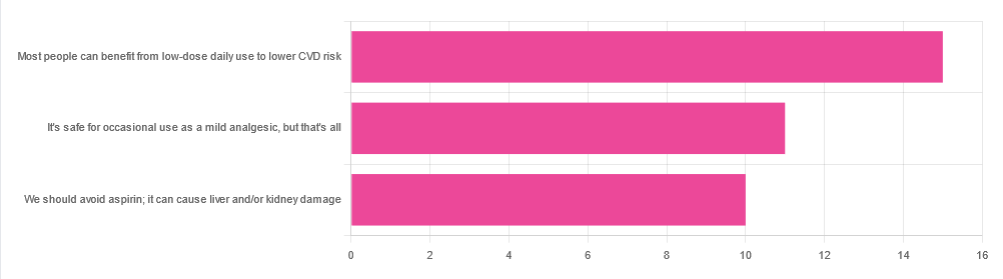
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked your health-related opinion of aspirin, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- About 42% said “Most people can benefit from low-dose daily use to lower CVD risk”
- About 31% said “It’s safe for occasional use as a mild analgesic, but that’s all”
- About 28% said “We should avoid aspirin; it can cause liver and/or kidney damage”
So, what does the science say?
Most people can benefit from low-dose daily aspirin use to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease: True or False?
True or False depending on what we mean by “benefit from”. You see, it works by inhibiting platelet function, which means it simultaneously:
- decreases the risk of atherothrombosis
- increases the risk of bleeding, especially in the gastrointestinal tract
When it comes to balancing these things and deciding whether the benefit merits the risk, you might be asking yourself: “which am I most likely to die from?” and the answer is: neither
While aspirin is associated with a significant improvement in cardiovascular disease outcomes in total, it is not significantly associated with reductions in cardiovascular disease mortality or all-cause mortality.
In other words: speaking in statistical generalizations of course, it may improve your recovery from minor cardiac events but is unlikely to help against fatal ones
The current prevailing professional (amongst cardiologists) consensus is that it may be recommended for secondary prevention of ASCVD (i.e. if you have a history of CVD), but not for primary prevention (i.e. if you have no history of CVD). Note: this means personal history, not family history.
In the words of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology:
❝Low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg orally daily) might be considered for the primary prevention of ASCVD among select adults 40 to 70 years of age who are at higher ASCVD risk but not at increased bleeding risk (S4.6-1–S4.6-8).
Low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg orally daily) should not be administered on a routine basis for the primary prevention of ASCVD among adults >70 years of age (S4.6-9).
Low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg orally daily) should not be administered for the primary prevention of ASCVD among adults of any age who are at increased risk of bleeding (S4.6-10).❞
~ Dr. Donna Arnett et al. (those section references are where you can find this information in the document)
Read in full: Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology
Or if you’d prefer a more pop-science presentation:
Many older adults still use aspirin for CVD prevention, contrary to clinical guidance
Aspirin can cause liver and/or kidney damage: True or False?
True, but that doesn’t mean we must necessarily abstain, so much as exercise caution.
Aspirin is (at recommended doses) not usually hepatotoxic (toxic to the liver), but there is a strong association between aspirin use in children and the development of Reye’s syndrome, a disease involving encephalopathy and a fatty liver. For this reason, most places have an official recommendation that aspirin not be used by children (cut-off age varies from place to place, for example 12 in the US and 16 in the UK, but the key idea is: it’s potentially dangerous for those who are not fully grown).
Aspirin is well-established as nephrotoxic (toxic to the kidneys), however, the toxicity is sufficiently low that this is not expected to be a problem to otherwise healthy adults taking it at no more than the recommended dose.
For numbers, symptoms, and treatment, see this very clear and helpful resource:
An evidence based flowchart to guide the management of acute salicylate (aspirin) overdose
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Why Has Nobody Told Me This Before? – by Dr. Julie Smith
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Superficially, this can be called a “self-help” book, but that undersells it rather. It’s a professionally-written (as in, by a professional psychologist) handbook full of resources. Its goal? Optimizing your mental health to help you stay resilient no matter what life throws your way.
While the marketing of this book is heavily centered around Dr. Smith’s Internet Celebrity™ status, a lot of her motivation for writing it seems to be precisely so that she can delve deeper into the ideas that her social media “bites” don’t allow room for.
Many authors of this genre pad their chapters with examples; there are no lengthy story-telling asides here, and her style doesn’t need them. She knows her field well, and knows well how to communicate the ideas that may benefit the reader.
The main “meat” of the book? Tips, tricks, guides, resources, systems, flowcharts, mental frameworks, and “if all else fails, do this” guidance. The style of the book is clear and simple, with very readable content that she keeps free from jargon without “dumbing down” or patronizing the reader.
All in all, a fine set of tools for anyone’s “getting through life” toolbox.
Get Your Personal Copy Of “Why Has Nobody Told Me This Before?” on Amazon Now!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Green Coffee Bean Extract: Coffee Benefits Without The Coffee?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Coffee is, on balance, very good for the health in moderation. We wrote about it here:
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
Some quick facts before moving on:
- Coffee is the world’s biggest source of antioxidants
- 65% reduced risk of Alzheimer’s for coffee-drinkers
- 67% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes for coffee-drinkers
- 43% reduced risk of liver cancer for coffee-drinkers
- 53% reduced suicide risk for coffee-drinkers
Those are some compelling statistics!
But what about the caffeine content?
Assuming one doesn’t have a caffeine sensitivity, caffeine is also healthy in moderation—but it is easy to accidentally become dependent on it, so it can be good to take a “tolerance break” once in a while, and then reintroduce it with more modest moderation:
Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
We also, for that matter, have discussed its impact on the gut:
Coffee & Your Gut ← surprise, it’s a positive impact
What if I don’t like coffee?
We suspect that, having seen the title of this article, you know what the answer’s going to be here:
Green coffee bean extract is the extract from green (i.e. unroasted) coffee beans. It has one or two advantages over drinking coffee:
- For those who do not like drinking coffee, this supplement sidesteps that neatly
- Roasting coffee beans destroys a lot (sometimes almost all; it depends on the temperature and duration) of their chlorogenic acid, a highly beneficial polyphenol; using unroasted (i.e. green) coffee beans avoids that
See: Role of roasting conditions in the level of chlorogenic acid content in coffee beans
All about GCE and CGA
That’s “green coffee extract” and “chlorogenic acid”, respectively, bearing in mind that the latter is found generously in the former.
As to what it does:
❝CGA is an important and biologically active dietary polyphenol, playing several important and therapeutic roles such as antioxidant activity, antibacterial, hepatoprotective, cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, neuroprotective, anti-obesity, antiviral, anti-microbial, anti-hypertension, free radicals scavenger and a central nervous system (CNS) stimulator. Furthermore, CGA causes hepatoprotective effects.❞
👆 Those are the things we know for sure that it does. And it may do even more things:
❝In addition, it has been found that CGA could modulate lipid metabolism and glucose in both genetically and healthy metabolic related disorders. It is speculated that CGA can perform crucial roles in lipid and glucose metabolism regulation and thus help to treat many disorders such as hepatic steatosis, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity as well.❞
Read in full: Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research
About lipid metabolism…
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly reduces serum total cholesterol levels.
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly reduces serum LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels.
- Increases in HDL (“good” cholesterol) after green coffee bean extract consumption are significant in green coffee bean extract dosages ≥400mg/day.
About blood glucose and insulin…
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly improved fasting blood sugar levels
- Green coffee extract supplementation at ≥400 mg/day significantly lowered postprandial insulin levels (that’s good)
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Banana Bread vs Bagel – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing banana bread to bagel, we picked the bagel.
Why?
Unlike most of the items we compare in this section, which are often “single ingredient” or at least highly standardized, today’s choices are rather dependent on recipe. Certainly, your banana bread and your bagels may not be the same as your neighbor’s. Nevertheless, to compare averages, we’ve gone with the FDA’s Food Central Database for reference values, using the most default average recipes available. Likely you could make either or both of them a little healthier, but as it is, this is how we’ve gone about making it a fair comparison. With that in mind…
In terms of macros, bagels have more than 2x the protein and about 4x the fiber, while banana bread has slightly higher carbs and about 7x more fat. You may be wondering: are the fats healthy? And the answer is, it could be better, could be worse. The FDA recipe went with margarine rather than butter, which lowered the saturated fat to being only ¼ of the total fat (it would have been higher, had they used butter) whereas bagels have no saturated fat at all—which characteristic is quite integral to bagels, unless you make egg bagels, which is rather a different beast. All in all, the macros category is a clear win for bagels, especially when we consider the carb to fiber ratio.
In the category of vitamins, bagels have on average more vitamin B1, B3, B5, and B9, while banana bread has on average more of vitamins A and C. A modest win for bagels.
When it comes to minerals, bagels are the more nutrient dense with more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while banana bread is not higher in any minerals. An obvious and easy win for bagels.
Closing thoughts: while the micronutrient profile quite possibly differs wildly from one baker to another, something that will probably stay more or less the same regardless is the carb to fiber ratio, and protein to fat. As a result, we’d weight the macros category as the more universally relevant. Bagels won in all categories today, as it happened, but it’s fairly safe to say that, on average, a baker who makes bagels and banana bread with the same levels of conscientiousness for health (or lack thereof) will tend to make bagels that are healthier than banana bread, based on the carb to fiber ratio, and the protein to fat ratio.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Wholewheat Bread vs Seeded White – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: